Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Uploaded by
Lalaine RomeroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument8 pages7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru Takishima92% (24)
- UEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Document142 pagesUEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Kim N Lewis100% (3)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFDocument5 pagesDietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFMario The Coach100% (2)
- Columbia Knowledge Management APQC BookDocument77 pagesColumbia Knowledge Management APQC BookRun Ryan Mao100% (2)
- Gastroenteritis+in+children May2014+Document17 pagesGastroenteritis+in+children May2014+Naily HosenNo ratings yet
- ReflujoDocument11 pagesReflujoERICKA PORTOCARRERONo ratings yet
- RubelinDocument7 pagesRubelinPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: Pathophysiology in The UKDocument6 pagesManagement of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: Pathophysiology in The UKMarnia SulfianaNo ratings yet
- CPG Diarrhoea VomitingDocument5 pagesCPG Diarrhoea VomitingLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- PreeclampsiaDocument179 pagesPreeclampsiaJohn Wilbert Birung100% (3)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument179 pagesPre EclampsiaAnton RossiniNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesFact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- Guideline HEGDocument5 pagesGuideline HEGMushlihani HaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case PresentationDocument25 pagesClinical Case Presentationapi-246186340No ratings yet
- Total Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Document38 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2FirnandaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea and Vomiting in ChildrenDocument16 pagesDiarrhoea and Vomiting in ChildrenKenny Josef100% (1)
- Diarroea Nice Guidlines PDFDocument16 pagesDiarroea Nice Guidlines PDFFayzaRayesNo ratings yet
- Nice Diare 2015Document15 pagesNice Diare 2015JovitaNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Document38 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Henry M. BarberenaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain - Royal Children HospitalDocument4 pagesAbdominal Pain - Royal Children HospitalMehrdad IraniNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Fasting GuidelineDocument5 pagesPaediatric Fasting GuidelineluthfianamiftasyafitriNo ratings yet
- Bowel Preparation: Information AboutDocument3 pagesBowel Preparation: Information AboutBobyHarmoyoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum 1Document26 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum 1Jas Castro Jovero100% (3)
- OG 1.3 - Preconception and Prenatal Care Jan 2015Document19 pagesOG 1.3 - Preconception and Prenatal Care Jan 2015kylieverNo ratings yet
- CDC Guidelines DiarrheaDocument4 pagesCDC Guidelines DiarrheaAraz MelkonianNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pracice Guideline For The Treatment of Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis in The Outpatient SettingDocument8 pagesClinical Pracice Guideline For The Treatment of Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis in The Outpatient SettingLaura Anghel-MocanuNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument27 pagesNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis GravidarumxxdrivexxNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Acute GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesPediatric Acute Gastroenteritisjanmichael8No ratings yet
- Pre-Operative Fasting (Report)Document7 pagesPre-Operative Fasting (Report)Carlo Paul Castro SanaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension: DefinitionDocument7 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension: Definitionkristine hinaresNo ratings yet
- DYNAMED Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Aged 1-5 Years - Approach To The PatientDocument17 pagesDYNAMED Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Aged 1-5 Years - Approach To The PatientHugoNo ratings yet
- 1215 LHCC LA - CP.MP.34 Hyperemesis Gravidarum TreatmentDocument9 pages1215 LHCC LA - CP.MP.34 Hyperemesis Gravidarum TreatmentSatriyo Krisna PalgunoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument32 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: by Dr. Abdel Magid M.Ahmed Nov. 2015Document16 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: by Dr. Abdel Magid M.Ahmed Nov. 2015Ibrahim JameelallaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan and RRLDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan and RRLnicoleNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination:: DiarrheaDocument44 pagesBowel Elimination:: DiarrheaBashracel Marie M. SALMORINNo ratings yet
- NICE CG99 Children ConstipationDocument16 pagesNICE CG99 Children Constipationknighting1No ratings yet
- MS 2 P1 Part 1 PDFDocument17 pagesMS 2 P1 Part 1 PDFAngel YN Patricio FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundDocument9 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Backgroundalyssa_flores_3No ratings yet
- Weaningfromparenteral Nutrition: Andrew UklejaDocument26 pagesWeaningfromparenteral Nutrition: Andrew UklejaJosebeth RisquezNo ratings yet
- Liver Problems in Pregnancy - 27 To 40 WeeksDocument9 pagesLiver Problems in Pregnancy - 27 To 40 WeeksJing CruzNo ratings yet
- TPN Question and Answers.2017Document2 pagesTPN Question and Answers.2017M Asif NawazNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Young Children A Synopsis of The American Academy of Pediatrics' Practice Parameter On TheDocument5 pagesManagement of Acute Gastroenteritis in Young Children A Synopsis of The American Academy of Pediatrics' Practice Parameter On TheAbdul Ghaffar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesHypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanMary Grace Belmonte100% (1)
- 1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementDocument52 pages1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementThana Balan100% (1)
- Robinson 2016Document20 pagesRobinson 2016sadiqNo ratings yet
- FNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Document4 pagesFNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Aaron EspirituNo ratings yet
- Oral Health Care For The Pregnant PatientDocument6 pagesOral Health Care For The Pregnant PatientDominique Harz FresnoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Pyloric StenosisDocument15 pagesAlgorithm Pyloric StenosisFetria MelaniNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Dextrose Saline Compared With Normal Saline.13 HegDocument8 pagesDextrose Saline Compared With Normal Saline.13 HegokkynafirianaNo ratings yet
- Plan of Care For:: Nursing Diagnosis: Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesPlan of Care For:: Nursing Diagnosis: Excess Fluid VolumeKenji CadizNo ratings yet
- Piis0002937811009185 PDFDocument24 pagesPiis0002937811009185 PDFLailatuss LelaNo ratings yet
- CBT - Nutrition and Digestive System EditedDocument22 pagesCBT - Nutrition and Digestive System EditedReshma BhogalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document10 pagesDrug Study 2jedialecarceleryahooNo ratings yet
- APH JurnalDocument8 pagesAPH JurnalRegina CaeciliaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis in Children Part II. Prevention and Management 2012Document5 pagesGastroenteritis in Children Part II. Prevention and Management 2012Douglas UmbriaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Pre-Eclampsia On A Repeat Cesarian Section Delivery With Bilateral Tubal LigationDocument17 pagesA Case Study On Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Pre-Eclampsia On A Repeat Cesarian Section Delivery With Bilateral Tubal LigationJennah Ricci Tuazon100% (1)
- Crit Care Nurse 2003 Garrett 31 50Document23 pagesCrit Care Nurse 2003 Garrett 31 50Lalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis: Schistosoma Haematobium Enterobius VermicularisDocument1 pageTrichomonas Vaginalis: Schistosoma Haematobium Enterobius VermicularisLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument1 pageHyperthermiaLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaLeo_Rabacca_3610100% (1)
- How To Perform A Head To Toe AssessmentDocument2 pagesHow To Perform A Head To Toe AssessmentLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Papillary Thyroid CancerDocument7 pagesPapillary Thyroid CancerLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nutri FactsDocument5 pagesNutri FactsLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- ShowPDF Paper - AspxDocument14 pagesShowPDF Paper - AspxShawkat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Epjj)Document59 pagesChapter 10 (Epjj)syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Durastor Tank Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesDurastor Tank Brochure PDFhamadaniNo ratings yet
- Methodology in The New MillenniumDocument15 pagesMethodology in The New Millenniumerzsebetkacso67% (3)
- Project - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideDocument5 pagesProject - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideBeanieNo ratings yet
- Action Plan LIPAWAN ESDocument3 pagesAction Plan LIPAWAN ESJo RieNo ratings yet
- Pensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobDocument340 pagesPensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobLuana LuNo ratings yet
- Last Alaskans Episode GuideDocument1 pageLast Alaskans Episode GuideLisa BarattaNo ratings yet
- The Inner World in The Outer World 565089838Document266 pagesThe Inner World in The Outer World 565089838ramonaNo ratings yet
- SAP Proj Builder Previewer PDFDocument24 pagesSAP Proj Builder Previewer PDFPradeep JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Benefits For Blue Collar Employees - Oishik-1.docx (1) 3Document73 pagesBenefits For Blue Collar Employees - Oishik-1.docx (1) 3Anonymous Fsv7B0No ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Muslim High SchoolDocument12 pagesLived Experiences of Muslim High SchoolJustine ReveloNo ratings yet
- NIV Excerpt PDFDocument57 pagesNIV Excerpt PDFAnonymous tSYkkHToBPNo ratings yet
- Ics Lab Manual PDFDocument46 pagesIcs Lab Manual PDFEyes FlikerNo ratings yet
- Notes On Purposive CommunicationDocument27 pagesNotes On Purposive CommunicationChlea Marie Tañedo AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument17 pagesChap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlrianne Batonghinog100% (1)
- Centers For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesDocument6 pagesCenters For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesabhinavrautNo ratings yet
- Lab Education English Mock Exam - Question Answer BookDocument14 pagesLab Education English Mock Exam - Question Answer BookMichelle ChungNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Definitions PDFDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking Definitions PDFAlpha Niño S SanguenzaNo ratings yet
- Shri Digambar Jain Mandir Shyo Ji Ram Ji: Chowkri ModikhanaDocument3 pagesShri Digambar Jain Mandir Shyo Ji Ram Ji: Chowkri ModikhanaKUNAL GAURAVNo ratings yet
- Short Story ElementsDocument8 pagesShort Story Elementsaaliakhan05No ratings yet
- Design of Sequential Circuits - Example 1.3Document3 pagesDesign of Sequential Circuits - Example 1.3MD Saifuzzaman SohanNo ratings yet
- 3.horor (1970-2012)Document21 pages3.horor (1970-2012)vexa123No ratings yet
- Afghanistan: Health Expenditure ProfileDocument2 pagesAfghanistan: Health Expenditure ProfileJoannaNo ratings yet
- The Tallboy BombDocument28 pagesThe Tallboy BombKIRU SILVIUNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Banana (Musa: Acuminata) and Potato (Solanum Tuberosum) For Increasing The GrowthDocument19 pagesThe Potential of Banana (Musa: Acuminata) and Potato (Solanum Tuberosum) For Increasing The GrowthAlex GarmaNo ratings yet
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Uploaded by
Lalaine RomeroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Diarrhoea +/ Vomiting: Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol Emergency Department
Uploaded by
Lalaine RomeroCopyright:
Available Formats
ChildandAdolescentHealthService PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Backgroundand practicenotes Scope Assessmentand initialintervention Workingdiagnosis andinvestigations Management Patienteducationand dischargeinformation Medications Managementflowchart Associateddocuments Clinicalaudit Definitionofterms
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol EmergencyDepartment
Clinicalprotocolauthorship andapproval References Acknowledgement Disclaimer
Backgroundandpracticenotes
MostchildrenpresentingtotheEmergencyDepartment(ED)withgastroenteritisandnocomorbiditieswillnotrequireany interventionotherthanparentalreassuranceandeducation.Mildcasesofgastroenteritisareusuallyselflimitingandmay cause mild dehydration, which can be treated or prevented by continued feeding and drinking appropriate amounts of fluids. Breastfeeding of affected babies should continue even during oral rehydration1,8,11 as it is thought that this may reduce stool output and shorten duration of diarrhoea.1 Parameters of severity of dehydration vary widely in the literature.6,8,9Forthepurposeofthisclinicalprotocol,thefollowingdiagnosticcriteriaofmildandmoderatedehydrationwill beused.8 Nodehydration Mildtomoderatedehydration (<3%weightloss) Nosigns (38%weightloss) Drymucousmembranes Reducedurineoutput Sunkeneyes Minimalornotears Diminishedskinturgor(pinchtest12secs)
Useoforalrehydrationsolutionistherecommendedfirstlinetherapyfortreatingmildtomoderatedehydrationinchildren with gastroenteritis.2,11 Enteral (oral or nasogastric) rehydration is a much safer means of rehydration compared with intravenous rehydration because it avoids the risks associated with rapid fluid and electrolyte shifts.8 Diarrhoea and vomitingsettlesmorequicklyandappetitereturnsearlierwithuseoforalrehydrationtherapy.8Oralrehydrationtherapy hasbeenshowntobeaseffectiveasintravenoustherapyintreatingmildtomoderatedehydrationinacutegastroenteritis.2 The use of antiemetics for children with gastroenteritis who are vomiting are not routinely indicated, however this issue remains controversial.3,4 Ondansetron has been shown to reduce the frequency of vomiting, improve the success and compliancewithoralrehydrationtherapy2,4,5andreducetheneedforintravenoustherapyinsomecases.2Therehavebeen reports of increased frequency of diarrhoea after its usage, however this is usually transient and well tolerated.2 Some workplacepracticesupportsOndansetronuseinchildrenwithgastroenteritisbutisreservedasasingleoraldoseforthose 9 1,8 withpersistentvomiting. Antidiarrhoealsshouldnotbeusedforacutediarrhoeainchildren. Theydonotreducefluidand 1 electrolyteloss,maydelayexpulsionoforganismsandmaycauseadverseeffects. Featuressuggestiveofadiagnosisotherthangastroenteritisinclude:abdominalpainwithsignificanttenderness,distension, mass or guarding, hepatomegaly, vomiting of blood or bile, bloody diarrhoea, red current jelly stools, pallor, jaundice, 8 systemicallyunwelloutofproportiontothedegreeofdehydration,shockandaneonatewithdiarrhoea. Vomitingalone 8 shouldnotbediagnosedasgastroenteritis. Thefollowingconditionsshouldbeexcludedastheymayhavesimilarfeatures: appendicitis, antibiotic associated diarrhoea, meningitis, haemolytic uraemic syndrome, urinary tract infection and other gastrointestinalsurgicalconditionssuchasintussusceptionandpartialbowelobstruction.
NursePractitionerClinicalProtocol DateIssued:October2011 Diarrhoea+/vomiting DateRevised:January2012 EmergencyDepartment ReviewDate:October2013 PrincessMargaretHospital Authorisedby:PMHEmergencyDepartment Perth,WesternAustralia ReviewTeam:PMHEmergencyDepartment Thisdocumentshouldbereadinconjunctionwithdisclaimerinthisclinicalprotocol
Page1of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Scope NursePractitioner Childrenolderthan12monthsofagewithacute onsetofdiarrhoea+/nausea,vomiting,fever, abdominalpain
Outcomes Identifypatientssuitablefor EmergencyNurse Practitioner(ENP)clinical protocol Identifypatientsnotsuitable Infantslessthan12monthsofage forENPclinicalprotocoland Underlyingsignificantmedicalpathology refertoSeniorMedical eg:previousgastrointestinalsurgery,metabolic Practitioner(SMP) disorders,inflammatoryboweldisease Evidenceoffailuretothrive Childrenpresentingwithhistoryofvomitingbileor However,patientcanbe managedbyENPin blood,redcurrentjellystoolsormalenaorpale, consultationwithSMPif floppyepisodes appropriate Unwelllookingorsepticappearance Evidenceofshockorseveredehydration Cardiovascularinstability Severeabdominalpain Vomitingwithoutdiarrhoea Historyofdiarrhoeaforgreaterthan10days+/ vomitingforgreaterthan7days Outcomes Abnormalprimarysurvey identifiedexitENPclinical protocolandrefertoSMP
MedicalPractitioner+/ NursePractitioner
Assessmentandinitialintervention Primarysurvey Airway Breathing Circulation Disability Exposure Signsandsymptomsofcurrentillness:frequency andnatureofstoolsandvomits Oralintake,volumeandfluidtype Urineoutput,numberofwetnappies Abdominalpain Urinarysymptoms Levelofactivity Riskfactors;recenttravel,knowninfectious contacts,antibioticrelateddiarrhoea Pastmedicalhistory Allergies,immunisationstatus,medications
History
Identifypatientsnotsuitable forENPclinicalprotocoland refertoSMP
Examination
Abnormalexamination Vitalsigns outsidedefinedscoperefer Urinalysisifappropriate(eg:unsettled,poor toSMP feeding,vomitingwithoutdiarrhoea) Generalexamination Abdominalexamination Hydrationstatus;mentalstatus,capillaryrefill time,skinturgor,mucousmembranes,fontanelle, presenceoftears,+/eyessunken Weight(bareif<12monthsofage);comparison withpreillnessandposttreatmentifavailable (goldstandard7)
Page2of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Assessmentandinitialintervention(continued) Painassessment Analgesia Useappropriatepainassessmenttool
Outcomes Determineneedforand typeofanalgesia
Administrationofanalgesiaasrequired Reliefofpain (refertoPainManagementandProcedural SedationENPClinicalProtocol) Notroutinelyindicated
Workingdiagnosisandinvestigations Meetsinclusioncriteria.Historyandexaminationfindingssupportworkingdiagnosisofgastroenteritis. Imaging Pathology Notroutinelyindicated Stoolculturerequiredforthefollowing:8 Bloodinstool Suspectedepidemicforfoodpoisoning Severeorprolongeddiarrhoea(>2weeks) Recentoverseastravel Childresidinginaninstitution Campylobacter,Cryptosporidium,Shigella, Salmonellaandrotavirusarenotifiablediseases12 Bloodtestsarenotroutinelyindicatedbutmaybe clinicallyusefulinthefollowingcircumstances:8 Bloodydiarrhoeaconsiderfullbloodcount (FBC),urea,creatinine Dehydrationwithdoughyfeeltoskinthat mightindicatehypernatraemia Dehydratedchildrenwherehistoryandclinical examinationareinconsistentwithstraight forwarddiarrhoealepisode Anychildreceivingintravenous(IV)rehydration shouldhavescreeningtestspriortotherapy includingFBC,ureaandelectrolytes Appropriatefollowupof stoolcultureorbloodtestsif specimentakenduring presentation Anychildrequiringablood testmustbediscussedwith SMPprior
Page3of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Management Noormilddehydration
ENPwithviewtodischargehome Advisesmallfrequentfluidsandfeeds Continuebreastfeedingifapplicable ProvidefactsheetGastroenteritisHealthFacts Discussrepresentationcriteria Commenceoralfluidtrialusingappropriate departmentaldocumentation Oralfluidtrialshouldconsistoforalrehydration solutionorwater1ml/kgevery5minsandreview in1hour Provideparentalsupportandreassuranceduring thistime ConsideruseofsingleoraldoseofOndansetron forchildrenwithpersistentvomitinganddifficulty toleratingoral/nasogastric(NG)fluidrehydration Improvementinhydrationstatus Preparefordischarge Advisesmallfrequentfluidsandfeeds Continuebreastfeedingifapplicable ProvidefactsheetGastroenteritisHealthFacts Discussrepresentationcriteria Noorpartialimprovement DiscusswithandpatientreviewbySMP ConsiderNGrehydrationat50ml/kgover4hours IVfluidsmaybeconsideredifolderchildandhas difficultytoleratingNGtube Ifrequired0.9%SodiumChlorideand5%Glucose istheIVrehydrationfluidofchoiceinchildren (unlesshypernatraemicorhypovolaemicshock,in whichcaseSodiumChloride0.9%ispreferred) Refertomedicationsectionofthisprotocolfor calculationofIVfluidrequirements AdmittoShortStayUnit Regularreassessmentofhydrationstatusduring thistime,weighpatientpostrehydrationand compareweightwithprehydrationweight Ifconditionimproves,preparefordischargein consultationwithSMP Advisesmallfrequentfluidsandfeeds Continuebreastfeedingifapplicable ProvidefactsheetGastroenteritisHealthFacts Discussrepresentationcriteria Deteriorationincondition RefertoSMP
Outcomes Patientidentifiedassuitable forENPclinicalprotocoland dischargedhome Patientidentifiedassuitable forENPclinicalprotocoland dischargedhome ConsultationwithSMPifno orminimalimprovementor ifconditiondeteriorates
Antiemeticsandantidiarrhoealsarenotroutinelyindicatedforchildrenwithacutediarrhoea+/vomiting.1,8,11
Moderatedehydration
Severedehydration
ExitENPclinicalprotocol andrefertoSMP
Page4of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Management(continued) Recommendationsfor admission Thosechildrenwhoseparentsarenotableto managethechildsconditionathome Childrenathigherriskofbecomingdehydrated maybeobservedforatleast4hourstoensure adequatemaintenanceofhydrationeg:youngage, highfrequencyofwaterystoolsandvomits, childrenwithdisabilityorfeedingissues Childrenwithseveredehydration NoorpartialimprovementwithEDregimen Referralasappropriateto: Interpreter Alliedhealth AboriginalLiaisonOfficer Toleratingoralfluids Improvementinhydration(isnomorethanmildly dehydrated) Nosignsofsepsisorlikelyalternatediagnosis Considertimeofday,distancefrommedicalcare, parentconfidenceandunderstanding Verbalandwritteninstructionsregardingfluid regimen,breastfeeding,diet,medicationuseand infectioncontrolmeasures Identifylikelyprogressionoftheillness,expected outcome,representationcriteriaandreferrals VerbalinstructionsgivenbyENP Simpleanalgesiashorttermifrequired Notroutinelyrequiredunlessspecificconcerns AdviseGPfollowupwithin24hoursifconcerned orotherriskfactorseg:youngerthan12months, significantlosses(waterystools+/vomits) Seekfurthermedicaladviceifnotimproving Verbalandwritteninstructionsasappropriate Nottoleratingoralfluids Significantincreaseinlosses Significantlyreducedurineoutput,increased lethargy,generallymoreunwell Parentalconcern ParenteducationGastroenteritisHealthFacts GPletterifapplicable Medicalcertificate/certificateofattendance Patientmedicalrecord Appropriatefluidorderdocumentation Adequatehydrationstatusachievedpriorto dischargefromED Hydrationstatusmaintainedfollowingdischarge Gradualresolutionofsymptomsandreturntopre illnessbowelhabitswithin710days
Outcomes Appropriatepatient admission
Acutereferral
Patient/parentunderstands referralprocess
Patienteducationanddischargeinformation Dischargecriteria
Outcomes Patientsuitablefor discharge
Treatmentinstructions
Patient/parentunderstands instructionsgiven
Medicationinstructions Followup/referral
Patient/parentunderstands instructionsgiven Patient/parentunderstands followuparrangement
Representationcriteria
Patient/parentunderstands criteriaforrepresentation andisdischargedhome
Documentation
Appropriatedocumentation completed
Expectedoutcome
Page5of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Medications
Oralrehydration solution
Unscheduled
Preparation
Powderfororalliquidinsachets Oralliquid Oralornasogastricuseonly Oralfluidtrial:1ml/kgevery5minsfor1hour8 NGrapidrehydration:50ml/kgover4hours8 Providesfluid,electrolyteandglucosereplacement Welltolerated Moderatedehydrationcorrectionoffluidandelectrolyteloss associatedwithdiarrhoea+/vomiting Childrenwithhistoryofdiabetes,hypertension,renaldisease, phenylketonuria Knownhypersensitivitytoanyingredientinoralrehydration salts Nonereported Replacementsolutionsmaybebettertoleratediffrozenand presentedasaniceblock Nonereported Followadministrationdirectionsprovidedandrefertoproduct information Donotreconstitutewithdiluentsotherthanwater ForfullprescribinginformationrefertoAMHonline
Route/administration Dose Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Indication Contraindications forENPuse
Interactions Paediatric considerations Adverseeffects Patienteducation
Intravenousfluids
Usefullinks
0.9%SodiumChloride with5%Glucose
Unscheduled
Route/administration Dose
Intravenous CalculationofIVfluidrequirements8 100ml/kgper24hoursforfirst10kgofbodyweight Add50ml/kgper24hoursfornext10kgofbodyweight Add20ml/kgper24hoursforremainingkgofbodyweight 8 Estimationofdeficitvolume Thisisbasedontheestimatedpercentageofdehydration %dehydrationxbodyweight(kg)x10 Administerdeficitvolumeover24hoursseenotebelow Note:deficitvolumeistobeaddedtomaintenancerequirement andongoinglossesover24hours;givehalfofthistotalvolumein thefirst8hoursthenrestoverremaining16hours IVrehydrationforchildrenwithmoderatedehydration correctionoffluidandelectrolytelossassociatedwith diarrhoea+/vomiting Childrenwithhypernatraemiaorhypovolaemicshock Childrenwithdiabetes
Indication
Contraindications forENPuse
Page6of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Medications(continued)
Ondansetron
Poisonschedule4
Preparation Route/administration Dose Pharmacology
Wafer4mg,8mg Liquid,each5mlcontains4mgOndansetron Oral/sublingualuse 0.15mg/kg/dosetobegivenasasingledoseonly Centralandperipheral5HT3receptorblockade Precisemodeofactioninthecontrolofnauseaandvomitingis notknown Tablet,waferandoralliquidformulationsarebioequivalent Peakplasmaconcentrationsareachievedinapproximately1.5 hours Volumeofdistributionis1.8L/kg MetabolisedbyP450enzymes Plasmaproteinbindingis7070% Eliminationhalflifeis411hours Persistentnauseaand/orvomitingassociatedwithacute gastroenteritis Childrenwithhistoryofliverimpairment,cardiacdisease(can causeQTprolongation;usuallytransientandclinically insignificant),phenylketonuria(waferscontainaspartame) Childrenyoungerthan2yearsofage Hypersensitivitytootherselective5HT3receptorantagonists Phenytoin,carbamazepine,rifampicin,tramadol Rarebutmayincludeconstipation,headache,dizziness, transientriseinaminotransferases,ECGchanges(rare;is predominantlyassociatedwithintravenousinfusion) SeekadvicefromSMPforuseinchildrenyoungerthan2years ofage Calculateleanbodyweightwherechildisoverweight Ondansetronmaybeusefultoimprovesuccessandcompliance withoralrehydrationtherapy2,4,5 ForfullprescribinginformationrefertoAMHonline
Pharmacokinetics
Indication Contraindicationsfor ENPuse
Interactions Adverseeffects
Paediatric considerations Practicepoints Usefullinks
Page7of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
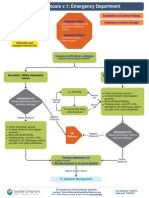
Managementflowchart
Gastroenteritismanagementflowchart
Diarrhoea+/nausea,vomiting,feverand abdominalpain
Yes
Childyoungerthan12months Underlyingrelevantmedicalpathology Systemicallyunwellorevidenceofshock Cardiovascularinstability Septicappearance Bloodinvomitand/orbilestainedvomit Malenaorredcurrentjellystools Hxdiarrhoea>10days+/vomitingfor>7days Vomitingwithoutdiarrhoea
Yes
DiscusswithSMP
No
Workingdiagnosisofgastroenteritis
Yes
No
RefertoSMP
Severedehydration
Yes
RefertoSMP
No Yes
Moderatedehydration
Commenceoralfluidtrial Observechildovernexthour
No
Condition improved
Partialorno improvement
Condition deteriorated
Yes
DiscusswithSMP ConsideradmissionandNG rehydration/ IVrehydration
RefertoSMP
Yes
Noormilddehydration
Yes
Meetsdischargecriteria
Yes
Providedischargeadvice Dischargehome
Page8of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
Associateddocuments GastroenteritisPMHEmergencyDepartmentClinicalPracticeGuideline2010 PainManagementandProceduralSedationENPClinicalProtocol Clinicalaudit Unexpectedrepresentation Definitionofterms ENP ED GP AMH IV NG EmergencyNursePractitioner EmergencyDepartment GeneralPractitioner AustralianMedicinesHandbook Intravenous Nasogastric EmergencyDepartmentInformationSystemandENPclinicallog
Clinicalprotocolauthorshipandapproval Clinicalprotocolauthor JemmaBatesSmith ActingNursePractitioner EmergencyDepartment Datewritten Dateforreview
October2011 October2013
Page9of10
EmergencyDepartment PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren
NursePractitioner ClinicalProtocol Diarrhoea+/vomiting
References
1. AustralianMedicinesHandbook(online).2011Jul.[cited2011Sept6]. Availablefrom: http://www.amh.net.au.pklibresources.health.wa.gov.au/online/view.php?page=chapter12/treatdiarrhoea.t.html#d iarrhoea.t ChowC,LeungA,HonK.Acutegastroenteritis:fromguidelinestoreallife.ClinicalandExperimental Gastroenterology.2010;3:97112. FedorowiczZ,JagannathVA,CarterB.Antiemeticsforreducingvomitingrelatedtoacutegastroenteritisinchildren andadolescents.CochraneDatabaseofSystematicReviews.2011,Issue9.ArtNo:CD005506. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD005506.pub5. FreedmanSB,SteinerMJ,ChanKJ.Oralondansetronadministrationinemergencydepartmentstochildrenwith gastroenteritis:Aneconomicanalysis.PLoSMedicine.2010Oct;7(10):e1000350. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000350. FreedmanSB,AlderM,SeshadriR,PowellE.Oralondansetronforgastroenteritisinapediatricemergency department.TheNewEnglandJournalofMedicine.2006Apr;354(16):16981705. HartlingL,BellemareS,WiebeN,RussellKF,KlassenTP,CraigWR.Oralversusintravenousrehydrationfortreating dehydrationduetogastroenteritisinchildren(Review).CochraneDatabaseofSystematicReviews.2006,Issue3.Art No:CD004390.DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD004390.pub2. MoyerVA,ElliottEJ.Evidencebasedpediatricsandchildhealth[internet].London:BMJPublishingGroup;2004. Chapter37,AcuteGastroenteritis;p37589.[cited2011Sept12].Availablefrom: http://books.google.com.au/books?id=V0axOhNjq_QC&pg=PA381&lpg=PA381&dq=gold+standard+weighing+childre n+with+dehydration&source=bl&ots=GtOVyNiRjv&sig=A CuDWWnPe3ZRD3zOWtSlNvgsB0&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildren,Perth,WesternAustralia.2010.EmergencyDepartmentClinicalPractice Guideline,Gastroenteritis. TheRoyalChildrensHospital,Melbourne,Australia.2009.ClinicalPracticeGuidelines,Gastroenteritis. TheRoyalChildrensHospital,Melbourne,Australia.2004.NursePractitionerClinicalPracticeGuideline,Diarrhoea +/vomiting. TherapeuticGuidelinesonline(eTG).Infectiousdiarrhoea:fluidandelectrolytetherapy(rehydration).2011Feb. [Cited22Aug2011].Availablefrom:http://online.tg.org.au.pklibresources.health.wa.gov.au/ip/ WesternAustralia,DepartmentofHealth.Notifiablediseases.[cited2011Sept12].Availablefrom: http://www.public.health.wa.gov.au/3/284/2/notifiable_communicable_diseases.pm
2. 3.
4.
5. 6.
7.
8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
Acknowledgement
PrincessMargaretHospitalwishestoacknowledgeTheRoyalChildrensHospitalinMelbourne,JoondalupHealthCampus andtheDepartmentofHealth,WesternAustraliafortheirvaluedadviceandsupportwithregardstothecreationofthis clinicalprotocol.
Disclaimer/Statementofintent
ThisclinicalprotocolisintendedforusebyEmergencyNursePractitioners(ENPs)workingintheEmergencyDepartmentat PrincessMargaretHospitalforChildreninthemanagementofchildrenpresentingwithsignsandsymptomssuggestiveof gastroenteritis. Standardsofcarearedeterminedonthebasisofclinicaldataavailableandaresubjecttochangeasscientificknowledge and technology advance and patterns of care evolve. The clinical protocols detail diagnostic criteria and appropriate managementoptions.Departmentalclinicalpracticeguidelinesareavailabletoguidemedicalclinicaldecisionmaking.They formthefoundationfortheENPclinicalprotocolsandensurethatthepracticeoftheENPisconsistent,safeandthatthe boundaries of ENP practice are well defined. It should be noted that clinical protocols provide a framework but do not attempt to take the place of sound clinical judgement. Nurse Practitioners may be responsible for clinical decisions not adequately defined by clinical protocols and under these circumstances collaboration with a Senior Medical Practitioner (SMP)willensurethatdecisionsareappropriate.ASMPwillbetheEDConsultantoraSeniorRegistrardelegatedbytheED Consultant.
NursePractitionerClinicalProtocol DateIssued:October2011 Diarrhoea+/vomiting DateRevised:January2012 EmergencyDepartment ReviewDate:October2013 PrincessMargaretHospital Authorisedby:PMHEmergencyDepartment Perth,WesternAustralia ReviewTeam:PMHEmergencyDepartment Thisdocumentshouldbereadinconjunctionwithdisclaimerinthisclinicalprotocol
Page10of10
You might also like
- 7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument8 pages7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru Takishima92% (24)
- UEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Document142 pagesUEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Kim N Lewis100% (3)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFDocument5 pagesDietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFMario The Coach100% (2)
- Columbia Knowledge Management APQC BookDocument77 pagesColumbia Knowledge Management APQC BookRun Ryan Mao100% (2)
- Gastroenteritis+in+children May2014+Document17 pagesGastroenteritis+in+children May2014+Naily HosenNo ratings yet
- ReflujoDocument11 pagesReflujoERICKA PORTOCARRERONo ratings yet
- RubelinDocument7 pagesRubelinPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: Pathophysiology in The UKDocument6 pagesManagement of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: Pathophysiology in The UKMarnia SulfianaNo ratings yet
- CPG Diarrhoea VomitingDocument5 pagesCPG Diarrhoea VomitingLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- PreeclampsiaDocument179 pagesPreeclampsiaJohn Wilbert Birung100% (3)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument179 pagesPre EclampsiaAnton RossiniNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesFact Sheet Acute Pancreatitis in ChildrenNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- Guideline HEGDocument5 pagesGuideline HEGMushlihani HaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case PresentationDocument25 pagesClinical Case Presentationapi-246186340No ratings yet
- Total Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Document38 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2FirnandaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea and Vomiting in ChildrenDocument16 pagesDiarrhoea and Vomiting in ChildrenKenny Josef100% (1)
- Diarroea Nice Guidlines PDFDocument16 pagesDiarroea Nice Guidlines PDFFayzaRayesNo ratings yet
- Nice Diare 2015Document15 pagesNice Diare 2015JovitaNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Document38 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline-4 - 2Henry M. BarberenaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain - Royal Children HospitalDocument4 pagesAbdominal Pain - Royal Children HospitalMehrdad IraniNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Fasting GuidelineDocument5 pagesPaediatric Fasting GuidelineluthfianamiftasyafitriNo ratings yet
- Bowel Preparation: Information AboutDocument3 pagesBowel Preparation: Information AboutBobyHarmoyoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum 1Document26 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum 1Jas Castro Jovero100% (3)
- OG 1.3 - Preconception and Prenatal Care Jan 2015Document19 pagesOG 1.3 - Preconception and Prenatal Care Jan 2015kylieverNo ratings yet
- CDC Guidelines DiarrheaDocument4 pagesCDC Guidelines DiarrheaAraz MelkonianNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pracice Guideline For The Treatment of Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis in The Outpatient SettingDocument8 pagesClinical Pracice Guideline For The Treatment of Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis in The Outpatient SettingLaura Anghel-MocanuNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument27 pagesNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis GravidarumxxdrivexxNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Acute GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesPediatric Acute Gastroenteritisjanmichael8No ratings yet
- Pre-Operative Fasting (Report)Document7 pagesPre-Operative Fasting (Report)Carlo Paul Castro SanaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension: DefinitionDocument7 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension: Definitionkristine hinaresNo ratings yet
- DYNAMED Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Aged 1-5 Years - Approach To The PatientDocument17 pagesDYNAMED Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Aged 1-5 Years - Approach To The PatientHugoNo ratings yet
- 1215 LHCC LA - CP.MP.34 Hyperemesis Gravidarum TreatmentDocument9 pages1215 LHCC LA - CP.MP.34 Hyperemesis Gravidarum TreatmentSatriyo Krisna PalgunoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument32 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: by Dr. Abdel Magid M.Ahmed Nov. 2015Document16 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: by Dr. Abdel Magid M.Ahmed Nov. 2015Ibrahim JameelallaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan and RRLDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan and RRLnicoleNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination:: DiarrheaDocument44 pagesBowel Elimination:: DiarrheaBashracel Marie M. SALMORINNo ratings yet
- NICE CG99 Children ConstipationDocument16 pagesNICE CG99 Children Constipationknighting1No ratings yet
- MS 2 P1 Part 1 PDFDocument17 pagesMS 2 P1 Part 1 PDFAngel YN Patricio FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundDocument9 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Backgroundalyssa_flores_3No ratings yet
- Weaningfromparenteral Nutrition: Andrew UklejaDocument26 pagesWeaningfromparenteral Nutrition: Andrew UklejaJosebeth RisquezNo ratings yet
- Liver Problems in Pregnancy - 27 To 40 WeeksDocument9 pagesLiver Problems in Pregnancy - 27 To 40 WeeksJing CruzNo ratings yet
- TPN Question and Answers.2017Document2 pagesTPN Question and Answers.2017M Asif NawazNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Young Children A Synopsis of The American Academy of Pediatrics' Practice Parameter On TheDocument5 pagesManagement of Acute Gastroenteritis in Young Children A Synopsis of The American Academy of Pediatrics' Practice Parameter On TheAbdul Ghaffar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesHypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanMary Grace Belmonte100% (1)
- 1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementDocument52 pages1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementThana Balan100% (1)
- Robinson 2016Document20 pagesRobinson 2016sadiqNo ratings yet
- FNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Document4 pagesFNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Aaron EspirituNo ratings yet
- Oral Health Care For The Pregnant PatientDocument6 pagesOral Health Care For The Pregnant PatientDominique Harz FresnoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Pyloric StenosisDocument15 pagesAlgorithm Pyloric StenosisFetria MelaniNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsruthmindosiahaanNo ratings yet
- Dextrose Saline Compared With Normal Saline.13 HegDocument8 pagesDextrose Saline Compared With Normal Saline.13 HegokkynafirianaNo ratings yet
- Plan of Care For:: Nursing Diagnosis: Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesPlan of Care For:: Nursing Diagnosis: Excess Fluid VolumeKenji CadizNo ratings yet
- Piis0002937811009185 PDFDocument24 pagesPiis0002937811009185 PDFLailatuss LelaNo ratings yet
- CBT - Nutrition and Digestive System EditedDocument22 pagesCBT - Nutrition and Digestive System EditedReshma BhogalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document10 pagesDrug Study 2jedialecarceleryahooNo ratings yet
- APH JurnalDocument8 pagesAPH JurnalRegina CaeciliaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis in Children Part II. Prevention and Management 2012Document5 pagesGastroenteritis in Children Part II. Prevention and Management 2012Douglas UmbriaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Pre-Eclampsia On A Repeat Cesarian Section Delivery With Bilateral Tubal LigationDocument17 pagesA Case Study On Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Pre-Eclampsia On A Repeat Cesarian Section Delivery With Bilateral Tubal LigationJennah Ricci Tuazon100% (1)
- Crit Care Nurse 2003 Garrett 31 50Document23 pagesCrit Care Nurse 2003 Garrett 31 50Lalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis: Schistosoma Haematobium Enterobius VermicularisDocument1 pageTrichomonas Vaginalis: Schistosoma Haematobium Enterobius VermicularisLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument1 pageHyperthermiaLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaLeo_Rabacca_3610100% (1)
- How To Perform A Head To Toe AssessmentDocument2 pagesHow To Perform A Head To Toe AssessmentLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Papillary Thyroid CancerDocument7 pagesPapillary Thyroid CancerLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nutri FactsDocument5 pagesNutri FactsLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- ShowPDF Paper - AspxDocument14 pagesShowPDF Paper - AspxShawkat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Epjj)Document59 pagesChapter 10 (Epjj)syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Durastor Tank Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesDurastor Tank Brochure PDFhamadaniNo ratings yet
- Methodology in The New MillenniumDocument15 pagesMethodology in The New Millenniumerzsebetkacso67% (3)
- Project - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideDocument5 pagesProject - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideBeanieNo ratings yet
- Action Plan LIPAWAN ESDocument3 pagesAction Plan LIPAWAN ESJo RieNo ratings yet
- Pensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobDocument340 pagesPensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobLuana LuNo ratings yet
- Last Alaskans Episode GuideDocument1 pageLast Alaskans Episode GuideLisa BarattaNo ratings yet
- The Inner World in The Outer World 565089838Document266 pagesThe Inner World in The Outer World 565089838ramonaNo ratings yet
- SAP Proj Builder Previewer PDFDocument24 pagesSAP Proj Builder Previewer PDFPradeep JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Benefits For Blue Collar Employees - Oishik-1.docx (1) 3Document73 pagesBenefits For Blue Collar Employees - Oishik-1.docx (1) 3Anonymous Fsv7B0No ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Muslim High SchoolDocument12 pagesLived Experiences of Muslim High SchoolJustine ReveloNo ratings yet
- NIV Excerpt PDFDocument57 pagesNIV Excerpt PDFAnonymous tSYkkHToBPNo ratings yet
- Ics Lab Manual PDFDocument46 pagesIcs Lab Manual PDFEyes FlikerNo ratings yet
- Notes On Purposive CommunicationDocument27 pagesNotes On Purposive CommunicationChlea Marie Tañedo AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument17 pagesChap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlrianne Batonghinog100% (1)
- Centers For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesDocument6 pagesCenters For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesabhinavrautNo ratings yet
- Lab Education English Mock Exam - Question Answer BookDocument14 pagesLab Education English Mock Exam - Question Answer BookMichelle ChungNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Definitions PDFDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking Definitions PDFAlpha Niño S SanguenzaNo ratings yet
- Shri Digambar Jain Mandir Shyo Ji Ram Ji: Chowkri ModikhanaDocument3 pagesShri Digambar Jain Mandir Shyo Ji Ram Ji: Chowkri ModikhanaKUNAL GAURAVNo ratings yet
- Short Story ElementsDocument8 pagesShort Story Elementsaaliakhan05No ratings yet
- Design of Sequential Circuits - Example 1.3Document3 pagesDesign of Sequential Circuits - Example 1.3MD Saifuzzaman SohanNo ratings yet
- 3.horor (1970-2012)Document21 pages3.horor (1970-2012)vexa123No ratings yet
- Afghanistan: Health Expenditure ProfileDocument2 pagesAfghanistan: Health Expenditure ProfileJoannaNo ratings yet
- The Tallboy BombDocument28 pagesThe Tallboy BombKIRU SILVIUNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Banana (Musa: Acuminata) and Potato (Solanum Tuberosum) For Increasing The GrowthDocument19 pagesThe Potential of Banana (Musa: Acuminata) and Potato (Solanum Tuberosum) For Increasing The GrowthAlex GarmaNo ratings yet