Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perimetry You Can Trust
Perimetry You Can Trust
Uploaded by
komal4Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Perimetry You Can Trust
Perimetry You Can Trust
Uploaded by
komal4Copyright:
Available Formats
Perimetry you can trust ...
OCTOPUS
G1 Examination program
Phase and Stage concept
Learn more about perimetry - with the Book
"Automated Perimetry" - Visual Field Digest 5th edition
OCTOPUS perimetry is based on features that help save time and gain reliability.
Among these are interstimulus times that adapt to the response times of the patient and
100% fixation control to ensure only stimuli are presented and evaluated that have been
issued to an open eye that looked into the right direction. However, the roots for
OCTOPUS perimetry go much deeper.
G1 Examination program
The program 32 was a standard OCTOPUS set in 1976 out of technical reasons: A test
pattern was to be found that didn’t take longer than 25 minutes including the retest of 10
locations. The calculated 76 locations were distributed in an equidistant pattern grid of
6° resolution. Thus the classical "off axis" central program was created.
In 1987 Professor Flammer et al. introduced the G1 Glaucoma program that’s test
locations have been specially placed to be in sensitive spots and prevent
misinterpretation. This resulted in a program with 59 testlocations in the central 30° with
specialities as:
• More concentrated test locations in the center to find paracentral scotomas
(foveal resolution of 2.8° compared to 4.2° in program 32)
• no test locations on the horizontal and vertical axis except the central point
• to avoid pseudo scotomas caused by correction lens edges the 59 central test
patterns are within 26° and not the traditional 30°
• 14 peripheral test locations with a concentration on the nasal side (to better
detect nasal steps) are added if information outside the central 30° are
requested without prolonging the test duration too much. In this case the
complete G1 has 73 test locations. If only the center 30° are tested this
program is also called G2X as in the OCTOPUS 300series and 1-2-3.
As can be seen, altough G1 comes from Glaucoma, it is just as well suited as a
generally applicable program. This is why it has become the Standard in OCTOPUS
perimetry over 10 years ago
Distribution of test locations in 32 pattern Distribution of test locations in G1 pattern (to 30°)
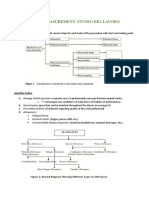
Phase and Stage concept
The examination is not a fixed procedure as would be in example A. It much more
allows to interrupt, adapt or finish the test at predefined break points.
As an example take the G1 program. It consists of 59 locations in the center 30°.
These test locations are split in 4 groups. The first group of locations, considered the
most important concerning the outcome of the examination, is measured first, followed
by group 2, 3 and 4. These groups are named stages) (B).
After each stage the operator can interrupt the exam to continue at a later time or even
save and print the result (D). You still get indices and a result at hand if the patient
should not be able to complete the program, because every complete stage is a
complete set of fully tested thresholds that contribute to the result ) (C).
Phases (E) add additional flexibility in the examination program. If a program consists of
central and peripheral test locations, they are split into different phases. After getting the
result from one phase the doctor can choose whether to a) retest the same area to get
short time fluctuations, b) test peripheral locations to get qualitative information or c)
test the periphery quantitatively.
This proceeding allows to get the necessary amount of information in a way the that can
be well adapted to the patients condition.
Allocation of G1 test locations according to stage inside 30°
You might also like
- Gage R RDocument8 pagesGage R Rshobhit2310No ratings yet
- Fm6 Pipe Network BenchDocument2 pagesFm6 Pipe Network BenchsukidayouNo ratings yet
- Pre ControlDocument9 pagesPre ControlricardoNo ratings yet
- E691 - 99 Standard Practice For Conducting An Interlaboratory Study To Determine The Precision of A Test MethodDocument22 pagesE691 - 99 Standard Practice For Conducting An Interlaboratory Study To Determine The Precision of A Test MethodLupita RamirezNo ratings yet
- The Unturned StoneDocument0 pagesThe Unturned StoneDarkPoolNo ratings yet
- Netra Case Study For EndtermDocument9 pagesNetra Case Study For EndtermGarima GeetikaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PicDocument15 pagesExperiment 1 Picady joffriyNo ratings yet
- P1 Activity SamplingDocument7 pagesP1 Activity SamplingShaz Wa MoAfrikaNo ratings yet
- Advance Metrology (Group 6) Lab Work 4Document9 pagesAdvance Metrology (Group 6) Lab Work 4Rudyee FaiezahNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Traverse by Total Station Instrument Group 4 Ecg422 1a2aDocument20 pagesLab 4 Traverse by Total Station Instrument Group 4 Ecg422 1a2aNoradila RoslanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Work Study and ErgonomicsDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Work Study and ErgonomicsAnkush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Level 1 Running SpeedDocument3 pagesLab 4 Level 1 Running SpeedudinhensembabiNo ratings yet
- DoE To Improve Clinical Processes - 1993Document6 pagesDoE To Improve Clinical Processes - 1993Yogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Rules To Follow in Performing Expt Making Lab Report For BDocument6 pagesRules To Follow in Performing Expt Making Lab Report For BRodgie Christian CruzNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 - Running Speed (Method 2) OEL 1Document3 pagesLAB 2 - Running Speed (Method 2) OEL 1ZULFAQAR BIN MOHAMMAD NIZAMNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument17 pagesLab ManualMuhammad SaifuddinNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument74 pagesSamplingGita MentariNo ratings yet
- Geostatistical Analyst ReportDocument7 pagesGeostatistical Analyst ReportMohd Akmal RazakNo ratings yet
- Estimating Measurement-Uncertainty - in Quantitative Chemical AnalysisDocument18 pagesEstimating Measurement-Uncertainty - in Quantitative Chemical AnalysisMohammad Youssefi100% (2)
- Process Control & Instrumentation Lab BKF 4791 Title of Experiment: Measurement and Control Air Flow System Lecturer's Name Group of Member: Name IDDocument12 pagesProcess Control & Instrumentation Lab BKF 4791 Title of Experiment: Measurement and Control Air Flow System Lecturer's Name Group of Member: Name IDTan Yong ChaiNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Content Uniformity NJPhAST Sep 22 2011Document43 pagesEvaluating Content Uniformity NJPhAST Sep 22 2011marrimanu23No ratings yet
- Safety Mask - Beard - P2Document11 pagesSafety Mask - Beard - P2canakyuzNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Time Series Forecasting Models: An Empirical Study On Performance Estimation MethodsDocument28 pagesEvaluating Time Series Forecasting Models: An Empirical Study On Performance Estimation MethodsmarvinNo ratings yet
- Selecting Particle Count Points For A Continuous FMS System - Manufacturing & Packaging - NG Pharmaceutical Europe - GDS PublishingDocument3 pagesSelecting Particle Count Points For A Continuous FMS System - Manufacturing & Packaging - NG Pharmaceutical Europe - GDS PublishingDavide GrioniNo ratings yet
- Lectuer One-P Gfinal 1mDocument39 pagesLectuer One-P Gfinal 1mahmedNo ratings yet
- Guia GoldmannDocument17 pagesGuia GoldmannMaria Jose Toro RojasNo ratings yet
- Work SamplingDocument25 pagesWork Samplingkunwaraditya100% (1)
- Manual of Modern Physics ExperimentDocument107 pagesManual of Modern Physics ExperimentRishabh SahuNo ratings yet
- Early Postoperative Treatment of Surgical Scars Using A Fractional Carbon Dioxide LaserDocument7 pagesEarly Postoperative Treatment of Surgical Scars Using A Fractional Carbon Dioxide LaserdoctorbanNo ratings yet
- 1010 - Analytical Data - Interpretation and TreatmentDocument16 pages1010 - Analytical Data - Interpretation and TreatmentAnonymous ulcdZToNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 (Air Pressure Process Control)Document16 pagesExp 2 (Air Pressure Process Control)shafiqah wong100% (1)
- A Wal3pracDocument32 pagesA Wal3pracLilo KuleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No 2 How To Determine Repeatability and Reproducibility (R&R)Document74 pagesTutorial No 2 How To Determine Repeatability and Reproducibility (R&R)Aliya JamesNo ratings yet
- EPM - Emergency Planning and Management - 221ECH006Document5 pagesEPM - Emergency Planning and Management - 221ECH006Vis 22777No ratings yet
- Experimental Methods, Instrumentation, and Laboratory PracticeDocument3 pagesExperimental Methods, Instrumentation, and Laboratory PracticeWinnie RomeroNo ratings yet
- No 1 Method ValidationDocument2 pagesNo 1 Method ValidationdanaciortanNo ratings yet
- What Is UltrasoundDocument59 pagesWhat Is UltrasoundKaushik ShahNo ratings yet
- Shams Tuning MethodDocument12 pagesShams Tuning MethodShamsMohdNo ratings yet
- Analisis Waktu Baku Mesin BubutDocument8 pagesAnalisis Waktu Baku Mesin BubutFauziah Amalia DeviNo ratings yet
- CE 111chapgoalswebDocument9 pagesCE 111chapgoalswebHamidNo ratings yet
- GE 10 Course Syllabus WIJ - FIJkDocument2 pagesGE 10 Course Syllabus WIJ - FIJkPatrick Junther SazonNo ratings yet
- Topic4 - POINT OF CARE TESTINGDocument6 pagesTopic4 - POINT OF CARE TESTINGStephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- Cover Page Lab ReportDocument2 pagesCover Page Lab ReportLuqman IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Reporting Practical Work 1.1 Raw DataDocument6 pages1.0 Reporting Practical Work 1.1 Raw DataZafirahAhmadFauziNo ratings yet
- LAB 5 & 6 Finenes Modulus and Particle Size DistributionDocument4 pagesLAB 5 & 6 Finenes Modulus and Particle Size DistributionWHfamily0% (1)
- PDF WEb Version Tholen - MU - Version2Document17 pagesPDF WEb Version Tholen - MU - Version2zhaoyi FangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document12 pagesAssignment 2NURUL IFFAH HIDA BINTI MUHAMAD NAZIR -No ratings yet
- Work Measurement - TIME STUDYDocument10 pagesWork Measurement - TIME STUDYMarcel PretzelNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2015Document19 pagesLab Manual 2015tkjingNo ratings yet
- Environmental Monitoring Risk AssessmentDocument22 pagesEnvironmental Monitoring Risk AssessmentMarcelo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Triaxial - UuDocument11 pagesLab 7 - Triaxial - Uudixn__No ratings yet
- Suplemento 1Document56 pagesSuplemento 1Dessirhe LaraNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ValidationDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical ValidationAnum FaryalNo ratings yet
- End To End TestsDocument19 pagesEnd To End Testsfrancis limaNo ratings yet
- Process Control Laboratory-Student's ManualDocument105 pagesProcess Control Laboratory-Student's ManualAnonymous 8pCXXsNo ratings yet
- Liquid Flow Control LAB 1 - CHE239 - 4D4Document7 pagesLiquid Flow Control LAB 1 - CHE239 - 4D42024568653No ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Survey Sampling For Reseachers and Post GraduatesDocument12 pagesA Practical Approach To Survey Sampling For Reseachers and Post GraduatesHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Triaxial (Uu)Document12 pagesLab 7 - Triaxial (Uu)NurulAdilahNo ratings yet
- Spirometry: Arrazi ClinicsDocument8 pagesSpirometry: Arrazi ClinicsJ Russel DichosoNo ratings yet
- Airborne Particle Monitoring - Satisfying The Changing Demands in Regulations and MethodsDocument17 pagesAirborne Particle Monitoring - Satisfying The Changing Demands in Regulations and MethodsReza-ul JalilNo ratings yet
- Automated Perimeter: - Monica Singh BoptDocument19 pagesAutomated Perimeter: - Monica Singh Boptvincy vargheseNo ratings yet
- Pubmed Thesis Topics in Community MedicineDocument7 pagesPubmed Thesis Topics in Community Medicinefjcz1j5g100% (2)
- 8.OSHA Factsheet JobrelatedDocument2 pages8.OSHA Factsheet JobrelatedsolidrepNo ratings yet
- Preparing For The Regulatory Challenges Wrought by Software As A Medical DeviceDocument12 pagesPreparing For The Regulatory Challenges Wrought by Software As A Medical DeviceCognizantNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 13 MalariaDocument6 pagesParasitology-Lec 13 Malariaapi-3743217No ratings yet
- Anglo Saxon MissionDocument2 pagesAnglo Saxon MissionJoshua J. IsraelNo ratings yet
- Burnished Law Journal: Author: Ashish J Co-Author: Logapriya TDocument11 pagesBurnished Law Journal: Author: Ashish J Co-Author: Logapriya TbhumijaNo ratings yet
- List Obat ApotekDocument5 pagesList Obat ApotekMuhammad RaisNo ratings yet
- Usmle Board Review Step 1Document357 pagesUsmle Board Review Step 1pereje7067% (3)
- CP 1230 1240 Safety Operating InstructionDocument264 pagesCP 1230 1240 Safety Operating InstructionAlejandro Correa BejaranoNo ratings yet
- The Paradox of Prudence Mental Health in The Gilded AgeDocument24 pagesThe Paradox of Prudence Mental Health in The Gilded Agefrancisco pizarroNo ratings yet
- How Patent Law Reform Can Improve Affordability AnDocument5 pagesHow Patent Law Reform Can Improve Affordability AnHopewell MoyoNo ratings yet
- PanelHospitalsMay2024Document3 pagesPanelHospitalsMay2024Sami MughalNo ratings yet
- Division 3: Trauma EmergenciesDocument125 pagesDivision 3: Trauma EmergenciesGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Time For A Paradigm ShiftDocument6 pagesTime For A Paradigm ShiftDavid GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice LLLDocument10 pagesNursing Practice LLLKimberly ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Emergency NursingDocument5 pagesEmergency NursingRoAn DulayNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Vein SamplingDocument8 pagesAdrenal Vein SamplingsirrfsNo ratings yet
- PDF MergeDocument210 pagesPDF MergeAnonymous th8tcpDSNo ratings yet
- The Evils of Big Pharma ExposedDocument5 pagesThe Evils of Big Pharma ExposedAmr Basha100% (1)
- Daftar Harga Obat Pt. Infion 2019 Oral NO Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNA Hna+PpnDocument1 pageDaftar Harga Obat Pt. Infion 2019 Oral NO Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNA Hna+PpnAmaliahNo ratings yet
- Dadi Ma Ke Nuskhe 1Document10 pagesDadi Ma Ke Nuskhe 1Nidhi ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Kangaroo Mother Care On Weight Gain in Low Birth Weight BabiesDocument21 pagesEffect of Kangaroo Mother Care On Weight Gain in Low Birth Weight BabiesTHONDYNALUNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic Management of Ovarian Cyst - A Case RDocument7 pagesHomoeopathic Management of Ovarian Cyst - A Case RB. B.No ratings yet
- Blood Safety IndicatorDocument7 pagesBlood Safety IndicatorCorachea LabNo ratings yet
- Chiral Screening Approach of Atorvastatin Diastereomers by HPLC MethodDocument5 pagesChiral Screening Approach of Atorvastatin Diastereomers by HPLC MethodMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciNo ratings yet
- To Study The Effect of Hypnotics in MiceDocument2 pagesTo Study The Effect of Hypnotics in MiceJaved SaifiNo ratings yet
- Functional Training Plan CDocument11 pagesFunctional Training Plan CbigpetejrNo ratings yet
- See Attachments: Group Fitness Classes TurbokickDocument9 pagesSee Attachments: Group Fitness Classes TurbokickCalhounHonorsCollegeNo ratings yet