Professional Documents
Culture Documents
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
Uploaded by
Eduardo ChaviraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Advanced Electronics 2 - ChassisDocument227 pagesAdvanced Electronics 2 - Chassisaiigee100% (15)
- 2018 03 22 Gethsemane Eng - 2Document2 pages2018 03 22 Gethsemane Eng - 2Jorge Cavalcante67% (3)
- Mercdes w211 NetworkingDocument23 pagesMercdes w211 NetworkingOctavio Ruiz Chavez100% (9)
- Automotive Diagnostic Systems: Understanding OBD-I & OBD-II RevisedFrom EverandAutomotive Diagnostic Systems: Understanding OBD-I & OBD-II RevisedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Networking Mercedes Classe E W211Document31 pagesNetworking Mercedes Classe E W2112hard100% (8)
- CS504 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAIDDocument48 pagesCS504 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAIDHassan Tariq86% (7)
- GM Can CommunicationDocument8 pagesGM Can Communicationcherokewag100% (1)
- Electronic Control Unit ECUDocument17 pagesElectronic Control Unit ECUAhmed Hagag100% (7)
- CAN Bus - How To DiagnoseDocument12 pagesCAN Bus - How To DiagnoseHermawan 0103100% (3)
- Can BusDocument16 pagesCan Bussabtele0% (2)
- CAN BusDocument15 pagesCAN BusKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Controller Area NetworkDocument13 pagesController Area NetworkwakeamiNo ratings yet
- FSHSDHDSFHSDFHSFDSFDocument5 pagesFSHSDHDSFHSDFHSFDSFNiksa MarkovicNo ratings yet
- CAN Bus: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Vehicle Bus Microcontrollers Host Computer Message-Based Protocol MultiplexDocument25 pagesCAN Bus: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Vehicle Bus Microcontrollers Host Computer Message-Based Protocol MultiplexBenjamin HouseNo ratings yet
- CanBus WikipidiaDocument23 pagesCanBus WikipidiaZaw Min NaingNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility & CAN Bus: Todd H. HubingDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic Compatibility & CAN Bus: Todd H. HubingechostarNo ratings yet
- CAN Bus Explained - A Simple Intro (2019)Document13 pagesCAN Bus Explained - A Simple Intro (2019)Hermawan 0103100% (2)
- Automation of Cars Using Embedded Systems: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument9 pagesAutomation of Cars Using Embedded Systems: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringVaka GopiNo ratings yet
- CAN BUS Vs Ethernet Vs FTP PDFDocument5 pagesCAN BUS Vs Ethernet Vs FTP PDFonukvedat7219No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive ElectronicsDocument61 pagesUNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive Electronicsnubla mNo ratings yet
- 07 - F10 Entertainment and CommunicationDocument34 pages07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication81968No ratings yet
- OBD II Network Diagnostics StateDocument18 pagesOBD II Network Diagnostics StateCarlos CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Automation of Cars in Embedded SystemsDocument10 pagesAutomation of Cars in Embedded SystemsVijetha YadlaNo ratings yet
- Embedded System in AutomobilesDocument42 pagesEmbedded System in AutomobilesManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 15AE307J - AEES - Unit 5Document16 pages15AE307J - AEES - Unit 5Nashat MaoudNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Automation of CarDocument9 pagesAutomation of CarLakshmi NarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Design of Automotive Instrument Cluster Based On OSEK StandardDocument5 pagesDesign of Automotive Instrument Cluster Based On OSEK StandardQui PhuNo ratings yet
- Extracting Controller Area Network Data For Reliable Car CommunicationsDocument6 pagesExtracting Controller Area Network Data For Reliable Car CommunicationsRam KasyapNo ratings yet
- Senior Project 2007 Automotive Diagnostic LCD InterfaceDocument44 pagesSenior Project 2007 Automotive Diagnostic LCD InterfacelelNo ratings yet
- AC Delco Bus Diag PDFDocument8 pagesAC Delco Bus Diag PDFschraeubleNo ratings yet
- Black BoxDocument7 pagesBlack Boxlokesh_045No ratings yet
- A GSM Based Vehicle Theft Control SystemDocument115 pagesA GSM Based Vehicle Theft Control SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- 07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication PDFDocument34 pages07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication PDFSalisburNo ratings yet
- Emb System For CArsDocument12 pagesEmb System For CArsvismaywalle1No ratings yet
- MCPDocument148 pagesMCPlink2u_007No ratings yet
- Autoboss V30 CapabilitiesDocument16 pagesAutoboss V30 CapabilitiesPaing Min KoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chap 1Document9 pagesUnit 2 Chap 1Sumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design BSC 01Document80 pagesEmbedded System Design BSC 01Tigabu YayaNo ratings yet
- VinayKumarV MRaghavaCharyulu 129Document7 pagesVinayKumarV MRaghavaCharyulu 129YevhenNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Automotive Cluster Device Architectures and Applications, Part IDocument9 pagesThe Basics of Automotive Cluster Device Architectures and Applications, Part IPragg AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Communications Network Communications NetworkDocument7 pagesCommunications Network Communications NetworkraghavnkNo ratings yet
- Can Bus Explained 2021Document22 pagesCan Bus Explained 2021Haji RashidNo ratings yet
- DS90UB901, DS90UB902, DS90UB903, DS90UB904: Driving High-Speed Data Against The TrafficDocument8 pagesDS90UB901, DS90UB902, DS90UB903, DS90UB904: Driving High-Speed Data Against The TrafficLungu CristianNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Applications in Automobiles ReportDocument30 pagesEmbedded System Applications in Automobiles Reportkurupathi100% (1)
- X-TOOL XT70 (Indian Version)Document4 pagesX-TOOL XT70 (Indian Version)infoNo ratings yet
- S40MY2005 ElectricalDocument34 pagesS40MY2005 ElectricalJOSE FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) Reverse Engineering: 1 BackgroundDocument3 pagesOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) Reverse Engineering: 1 BackgroundmanizzleNo ratings yet
- Car Operating Systems: Ryan BeneskyDocument31 pagesCar Operating Systems: Ryan BeneskySapari VelNo ratings yet
- Automotive TelematicsDocument23 pagesAutomotive TelematicsVivek VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument33 pagesCase StudyNathan BakerNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engine ElectronicsDocument5 pagesAutomotive Engine Electronicsmachine tunisieNo ratings yet
- 05 - F25 Driver Assistance SystemsDocument26 pages05 - F25 Driver Assistance SystemsohhmygodNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control UnitDocument2 pagesElectronic Control Unitzuron7No ratings yet
- Electronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemDocument2 pagesElectronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- BMW 07 - F25 Entertainment and CommunicationDocument44 pagesBMW 07 - F25 Entertainment and CommunicationSalisburNo ratings yet
- Risc Assessment Security Countermeasures Vehicular Instrument ClustersDocument8 pagesRisc Assessment Security Countermeasures Vehicular Instrument Clustersinesboumaiza293No ratings yet
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAutomatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'Document2 pagesYou'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'Eduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tin Whisker Analysis of Toyota's Electronic Throttle ControlsDocument6 pagesTin Whisker Analysis of Toyota's Electronic Throttle ControlsEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Alogrithm 02Document69 pagesAlogrithm 02Nebiyu Tefera ShiteNo ratings yet
- Pinpointer PetrapinDocument15 pagesPinpointer PetrapinNacer MezghicheNo ratings yet
- 2018 Annual Public Debt ReportDocument79 pages2018 Annual Public Debt ReportDr. Ọbádélé KambonNo ratings yet
- Accounting Question BankDocument217 pagesAccounting Question BankFaiza TahreemNo ratings yet
- LG 32lg3000 Chassis Ld84a LCD TV SMDocument26 pagesLG 32lg3000 Chassis Ld84a LCD TV SMEmma FrostNo ratings yet
- Watson - Packer CatalogDocument60 pagesWatson - Packer CatalogAnonymous rey6aU3ZNo ratings yet
- Cooking RubricsDocument3 pagesCooking RubricsAndrea Mae ArtiendaNo ratings yet
- Quality TrainingDocument16 pagesQuality Trainingyushma ghimireNo ratings yet
- Pantallas HITACHI DP 6X Training PackageDocument92 pagesPantallas HITACHI DP 6X Training PackagericardoNo ratings yet
- Learning Contract ETHICSDocument2 pagesLearning Contract ETHICSBUAHIN JANNANo ratings yet
- The Sine and Cosine Rule QuestionsDocument20 pagesThe Sine and Cosine Rule QuestionsJacob WilliamNo ratings yet
- Nicole Elyse NelsonDocument3 pagesNicole Elyse Nelsonapi-331206184No ratings yet
- Percentage Increase and DecreaseDocument3 pagesPercentage Increase and DecreaseLai Kee KongNo ratings yet
- Btap TCQTDocument35 pagesBtap TCQTMai Phạm Hà ThanhNo ratings yet
- AnalogI PDFDocument48 pagesAnalogI PDFJerc ZajNo ratings yet
- Timing in TTCANDocument8 pagesTiming in TTCANPOWERBASE100% (1)
- Dart New Products Feb2015Document4 pagesDart New Products Feb2015garrido.alvarez.luisNo ratings yet
- 8-Human Rights and Magna CartaDocument47 pages8-Human Rights and Magna CartaRichard Cagadas MabolocNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Wooden HousesDocument8 pagesTechnical Specification Wooden HousesNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- 134 Motion Pro Hac TantilloDocument6 pages134 Motion Pro Hac Tantillolarry-612445No ratings yet
- Prominance UPVC Windows Brochure 2018Document25 pagesProminance UPVC Windows Brochure 2018tetea_cNo ratings yet
- BRKDCN 2035 PDFDocument117 pagesBRKDCN 2035 PDFJorge Alberto Largaespada GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Universal Pump Cart: No. PC200Document1 pageUniversal Pump Cart: No. PC200herbert madariagaNo ratings yet
- HeinonlineDocument8 pagesHeinonlineSyed AsadNo ratings yet
- Total Strain CracksDocument13 pagesTotal Strain Cracksnatasha asnaNo ratings yet
- ADR Nego PlanDocument4 pagesADR Nego PlanDeeshaNo ratings yet
- Conduct Award RubricsDocument12 pagesConduct Award RubricsMark Antony M. CaseroNo ratings yet
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
Uploaded by
Eduardo ChaviraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'
Uploaded by
Eduardo ChaviraCopyright:
Available Formats
CAN do technology:
By Jeff Smit oull never have to work on that, I remember my boss telling me back in the 1970s, when, as an apprentice, I found myself staring unbelieving at the wonders of the VB Commodore and XD Falcon electronic ignition systems.
Youd better not miss the bus Y
Holdens VE Lumina I quickly learned that if we dont accept the fact that we will all have to work on that whatever that is we will never keep up in our industry. Not only do we have to repair these things, but the reality is that even that will be difficult unless we understand how they work. Lets look more closely at the technology in the new VE Holden Commodore series. Along with the now old hat systems like satellite navigation and trip computer, controlled by a scroll wheel and buttons on the steering wheel, the VE comes with two priority keys which store individual driver information. Some of the stored detail includes personalised settings for trip computer, seat and mirror settings, radio stations and even the drivers favourite instrumentation settings and illumination. At night, the interior lighting can be set to illuminate only the speedometer. To continue to deter the theft of radio systems, the radio, instrument cluster and other key components are electronically linked to the vehicle and will not operate in any other vehicle. The audio system is Blue Tooth compatible and also will accept MP3 players via an input jack on the face of the radio. A rear DVD player folds down to keep the kids happy on those long trips. The greatest advancement is in the Holden Assist telematics. This new system allows the vehicle to receive and send data. For example, if any of the air bags have been deployed, the system notifies an operator who will attempt to speak to the driver via the radio system. If the operator does not receive a response, emergency services are notified and told the vehicles exact position by the on-board satellite navigation system. If you lock yourself out of the vehicle, an operator can confirm that youre the owner, then unlock the vehicle remotely. For road side assistance, a press of a button and they will know exactly where you are.
The Automotive Technician 26 GM Corp
The VE Commodore has up to 30 computers or modules that control functions like engine operation, transmission, power steering, anti lock brakes, telematics, instrument cluster, climate control and theft deterrent. Here are just some of the control modules. Those in red are part of the high speed system and the rest are on the low speed system. Engine control module (ECM) Transmission control module (TCM) Steering wheel angle sensor (SAS) Electronic brake control module (EBCM) including Electronic stability program (ESP) Traction control system (TCS) Antilock braking system (ABS) Telematics (TELE) Instrument panel cluster (IPC) Heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC) Body control module (BCM). Theft deterrent module (TDM) Integrated radio chassis (IRC) Remote function actuator (RFA) Rear seat entertainment (RSE) Automatic headlamp levelling (AHL) Navigation interface module (NIM) Remote function actuator (RFA)
equipped vehicles because the diagnostics are essentially the same as OBD II vehicles. The only difference is that you need a CAN-compliant scan tool to read the vehicle serial data. Like many current vehicles, information in a CAN-equipped vehicle is shared over a serial data bus. The bus is the circuit that carries all the electronic chatter between modules. The new VE commodore requires a highspeed data bus to handle the volume of information going back and forth between some of the more important safety related modules. In 1995, GM introduced its own data bus to handle communication between modules. The system ran at a speed of approx 10,000 bits per second (10 Kbps), which was more than adequate for vehicles a decade ago. For the VE, GM moved to their next generation data bus system which they called GM LAN (GM Local Area Network). Holden has added the capability to operate at two speeds on two separate buses; a low speed 33 Kbps bus and a high speed 500 Kbps bus. The low speed side of the GM LAN system operates on a single wire bus to handle body-related control functions, while the high speed bus uses two wires to carry data between the powertrain, transmission and antilock brake modules. A gateway node connects the high speed bus and low speed bus and allows information to be shared back and forth. For example, the radio (which is connected to the low speed bus) may adjust volume based on engine speed and vehicle speed (from the high speed bus) to offset road noise.
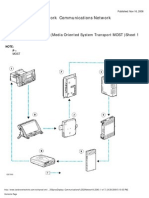
(More on controller area networks and diagnostics on these systems in future editions of TaT). The diagram on the next page shows the basic configuration of the high and low
So how do you get all these electronic modules to talk to each other?
Since about 2003, a growing number of vehicles have been built with a new onboard communications protocol called CAN (Controller Area Network). CAN is essentially an engineering standard for how computers and modules talk to one another via the serial data bus in a vehicles wiring system. The CAN protocol was created by Bosch in anticipation of future advances in onboard electronics. The first production application was on several Mercedes-Benz models. If youre not up to speed on the latest electronics and dont know a data bus from a commuter bus, diagnosing CAN systems will be a challenge. Even so, you dont have to be an engineer to perform basic diagnostics on CAN
speed GM LAN.
Latest technology in GMs VE
BCM TCM SAS EBCM AHL ECM
120
16
120
Link to low speed
High speed GM LAN X40 diagnostic plug
MCM
SIM
RFA
HVAC
TDM
SIC
IPC
RSE
IRC
TELE
NIM
SDM
Low speed GM LAN
Glossary of abbreviations
BCM TCM SAS HVAC TDM SIC IPC RSE IRC body control module transmission control module steering angle sensor heating, ventilation, a/c theft deterrent module secondary information centre instrument panel cluster rear seat entertainment integrated radio chassis EBCM electronic brake control module AHL automatic headlight levelling ECM engine control module TELE NIM SDM MCM SIM RFA telematics navigation interface module sensing diagnostic module mirror control module seat interface module remote function actuator
GM Corp
The Automotive Technician 15 The Automotive Technician 27
You might also like
- Advanced Electronics 2 - ChassisDocument227 pagesAdvanced Electronics 2 - Chassisaiigee100% (15)
- 2018 03 22 Gethsemane Eng - 2Document2 pages2018 03 22 Gethsemane Eng - 2Jorge Cavalcante67% (3)
- Mercdes w211 NetworkingDocument23 pagesMercdes w211 NetworkingOctavio Ruiz Chavez100% (9)
- Automotive Diagnostic Systems: Understanding OBD-I & OBD-II RevisedFrom EverandAutomotive Diagnostic Systems: Understanding OBD-I & OBD-II RevisedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Networking Mercedes Classe E W211Document31 pagesNetworking Mercedes Classe E W2112hard100% (8)
- CS504 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAIDDocument48 pagesCS504 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAIDHassan Tariq86% (7)
- GM Can CommunicationDocument8 pagesGM Can Communicationcherokewag100% (1)
- Electronic Control Unit ECUDocument17 pagesElectronic Control Unit ECUAhmed Hagag100% (7)
- CAN Bus - How To DiagnoseDocument12 pagesCAN Bus - How To DiagnoseHermawan 0103100% (3)
- Can BusDocument16 pagesCan Bussabtele0% (2)
- CAN BusDocument15 pagesCAN BusKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Controller Area NetworkDocument13 pagesController Area NetworkwakeamiNo ratings yet
- FSHSDHDSFHSDFHSFDSFDocument5 pagesFSHSDHDSFHSDFHSFDSFNiksa MarkovicNo ratings yet
- CAN Bus: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Vehicle Bus Microcontrollers Host Computer Message-Based Protocol MultiplexDocument25 pagesCAN Bus: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Vehicle Bus Microcontrollers Host Computer Message-Based Protocol MultiplexBenjamin HouseNo ratings yet
- CanBus WikipidiaDocument23 pagesCanBus WikipidiaZaw Min NaingNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility & CAN Bus: Todd H. HubingDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic Compatibility & CAN Bus: Todd H. HubingechostarNo ratings yet
- CAN Bus Explained - A Simple Intro (2019)Document13 pagesCAN Bus Explained - A Simple Intro (2019)Hermawan 0103100% (2)
- Automation of Cars Using Embedded Systems: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument9 pagesAutomation of Cars Using Embedded Systems: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringVaka GopiNo ratings yet
- CAN BUS Vs Ethernet Vs FTP PDFDocument5 pagesCAN BUS Vs Ethernet Vs FTP PDFonukvedat7219No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive ElectronicsDocument61 pagesUNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive Electronicsnubla mNo ratings yet
- 07 - F10 Entertainment and CommunicationDocument34 pages07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication81968No ratings yet
- OBD II Network Diagnostics StateDocument18 pagesOBD II Network Diagnostics StateCarlos CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Automation of Cars in Embedded SystemsDocument10 pagesAutomation of Cars in Embedded SystemsVijetha YadlaNo ratings yet
- Embedded System in AutomobilesDocument42 pagesEmbedded System in AutomobilesManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 15AE307J - AEES - Unit 5Document16 pages15AE307J - AEES - Unit 5Nashat MaoudNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Automation of CarDocument9 pagesAutomation of CarLakshmi NarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Design of Automotive Instrument Cluster Based On OSEK StandardDocument5 pagesDesign of Automotive Instrument Cluster Based On OSEK StandardQui PhuNo ratings yet
- Extracting Controller Area Network Data For Reliable Car CommunicationsDocument6 pagesExtracting Controller Area Network Data For Reliable Car CommunicationsRam KasyapNo ratings yet
- Senior Project 2007 Automotive Diagnostic LCD InterfaceDocument44 pagesSenior Project 2007 Automotive Diagnostic LCD InterfacelelNo ratings yet
- AC Delco Bus Diag PDFDocument8 pagesAC Delco Bus Diag PDFschraeubleNo ratings yet
- Black BoxDocument7 pagesBlack Boxlokesh_045No ratings yet
- A GSM Based Vehicle Theft Control SystemDocument115 pagesA GSM Based Vehicle Theft Control SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- 07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication PDFDocument34 pages07 - F10 Entertainment and Communication PDFSalisburNo ratings yet
- Emb System For CArsDocument12 pagesEmb System For CArsvismaywalle1No ratings yet
- MCPDocument148 pagesMCPlink2u_007No ratings yet
- Autoboss V30 CapabilitiesDocument16 pagesAutoboss V30 CapabilitiesPaing Min KoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chap 1Document9 pagesUnit 2 Chap 1Sumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design BSC 01Document80 pagesEmbedded System Design BSC 01Tigabu YayaNo ratings yet
- VinayKumarV MRaghavaCharyulu 129Document7 pagesVinayKumarV MRaghavaCharyulu 129YevhenNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Automotive Cluster Device Architectures and Applications, Part IDocument9 pagesThe Basics of Automotive Cluster Device Architectures and Applications, Part IPragg AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Communications Network Communications NetworkDocument7 pagesCommunications Network Communications NetworkraghavnkNo ratings yet
- Can Bus Explained 2021Document22 pagesCan Bus Explained 2021Haji RashidNo ratings yet
- DS90UB901, DS90UB902, DS90UB903, DS90UB904: Driving High-Speed Data Against The TrafficDocument8 pagesDS90UB901, DS90UB902, DS90UB903, DS90UB904: Driving High-Speed Data Against The TrafficLungu CristianNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Applications in Automobiles ReportDocument30 pagesEmbedded System Applications in Automobiles Reportkurupathi100% (1)
- X-TOOL XT70 (Indian Version)Document4 pagesX-TOOL XT70 (Indian Version)infoNo ratings yet
- S40MY2005 ElectricalDocument34 pagesS40MY2005 ElectricalJOSE FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) Reverse Engineering: 1 BackgroundDocument3 pagesOn-Board Diagnostic (OBD) Reverse Engineering: 1 BackgroundmanizzleNo ratings yet
- Car Operating Systems: Ryan BeneskyDocument31 pagesCar Operating Systems: Ryan BeneskySapari VelNo ratings yet
- Automotive TelematicsDocument23 pagesAutomotive TelematicsVivek VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument33 pagesCase StudyNathan BakerNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engine ElectronicsDocument5 pagesAutomotive Engine Electronicsmachine tunisieNo ratings yet
- 05 - F25 Driver Assistance SystemsDocument26 pages05 - F25 Driver Assistance SystemsohhmygodNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control UnitDocument2 pagesElectronic Control Unitzuron7No ratings yet
- Electronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemDocument2 pagesElectronic Engine Control (EEC) SystemJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- BMW 07 - F25 Entertainment and CommunicationDocument44 pagesBMW 07 - F25 Entertainment and CommunicationSalisburNo ratings yet
- Risc Assessment Security Countermeasures Vehicular Instrument ClustersDocument8 pagesRisc Assessment Security Countermeasures Vehicular Instrument Clustersinesboumaiza293No ratings yet
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAutomatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- You'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'Document2 pagesYou'd Better Not: Miss The Bus'Eduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryDocument21 pagesTom Boynton CET 249 December 2006: General Motors Computerized Vehicle Control Systems: A Short HistoryEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Tin Whisker Analysis of Toyota's Electronic Throttle ControlsDocument6 pagesTin Whisker Analysis of Toyota's Electronic Throttle ControlsEduardo ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Alogrithm 02Document69 pagesAlogrithm 02Nebiyu Tefera ShiteNo ratings yet
- Pinpointer PetrapinDocument15 pagesPinpointer PetrapinNacer MezghicheNo ratings yet
- 2018 Annual Public Debt ReportDocument79 pages2018 Annual Public Debt ReportDr. Ọbádélé KambonNo ratings yet
- Accounting Question BankDocument217 pagesAccounting Question BankFaiza TahreemNo ratings yet
- LG 32lg3000 Chassis Ld84a LCD TV SMDocument26 pagesLG 32lg3000 Chassis Ld84a LCD TV SMEmma FrostNo ratings yet
- Watson - Packer CatalogDocument60 pagesWatson - Packer CatalogAnonymous rey6aU3ZNo ratings yet
- Cooking RubricsDocument3 pagesCooking RubricsAndrea Mae ArtiendaNo ratings yet
- Quality TrainingDocument16 pagesQuality Trainingyushma ghimireNo ratings yet
- Pantallas HITACHI DP 6X Training PackageDocument92 pagesPantallas HITACHI DP 6X Training PackagericardoNo ratings yet
- Learning Contract ETHICSDocument2 pagesLearning Contract ETHICSBUAHIN JANNANo ratings yet
- The Sine and Cosine Rule QuestionsDocument20 pagesThe Sine and Cosine Rule QuestionsJacob WilliamNo ratings yet
- Nicole Elyse NelsonDocument3 pagesNicole Elyse Nelsonapi-331206184No ratings yet
- Percentage Increase and DecreaseDocument3 pagesPercentage Increase and DecreaseLai Kee KongNo ratings yet
- Btap TCQTDocument35 pagesBtap TCQTMai Phạm Hà ThanhNo ratings yet
- AnalogI PDFDocument48 pagesAnalogI PDFJerc ZajNo ratings yet
- Timing in TTCANDocument8 pagesTiming in TTCANPOWERBASE100% (1)
- Dart New Products Feb2015Document4 pagesDart New Products Feb2015garrido.alvarez.luisNo ratings yet
- 8-Human Rights and Magna CartaDocument47 pages8-Human Rights and Magna CartaRichard Cagadas MabolocNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Wooden HousesDocument8 pagesTechnical Specification Wooden HousesNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- 134 Motion Pro Hac TantilloDocument6 pages134 Motion Pro Hac Tantillolarry-612445No ratings yet
- Prominance UPVC Windows Brochure 2018Document25 pagesProminance UPVC Windows Brochure 2018tetea_cNo ratings yet
- BRKDCN 2035 PDFDocument117 pagesBRKDCN 2035 PDFJorge Alberto Largaespada GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Universal Pump Cart: No. PC200Document1 pageUniversal Pump Cart: No. PC200herbert madariagaNo ratings yet
- HeinonlineDocument8 pagesHeinonlineSyed AsadNo ratings yet
- Total Strain CracksDocument13 pagesTotal Strain Cracksnatasha asnaNo ratings yet
- ADR Nego PlanDocument4 pagesADR Nego PlanDeeshaNo ratings yet
- Conduct Award RubricsDocument12 pagesConduct Award RubricsMark Antony M. CaseroNo ratings yet