Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics MA 1505 Mathematics I Tutorial 1
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics MA 1505 Mathematics I Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
gilbertllhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics MA 1505 Mathematics I Tutorial 1
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics MA 1505 Mathematics I Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
gilbertllhCopyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE
Department of Mathematics
MA 1505 Mathematics I
Tutorial 1
1. Find the rst derivative of each of the following functions:
(a)
ax + b
cx + d
; (b) y = sin
m
x cos (nx), where m and n are constant positive integers;
(c) y =
e
4x
+ 5
e
2x
+ 3
; (d) y = [8x + ln (3 + 8x)]
1/8
, where x > 0.
Ans. (a)
ad bc
(cx + d)
2
(b) sin
m1
x[mcos x cos (nx) nsin x sin (nx)]
(c)
2e
2x
_
e
4x
+ 6e
2x
5
_
(e
2x
+ 3)
2
(d)
4 + 8x
3 + 8x
[8x + ln (3 + 8x)]
7/8
2. Find
dy
dx
and
d
2
y
dx
2
for each of the following:
(a) x
2/3
+ y
2/3
= a
2/3
, where a is a positive constant, 0 < x < a and y > 0;
(b) y = (ln x)
ln x
, where x > 1;
(c) x = a cos t, y = a sin t, where a is a positive constant.
Ans. (a)
_
_
a
x
_
2/3
1 ;
a
2/3
3x
4/3
_
a
2/3
x
2/3
(b) (ln x)
ln x
ln (ln x) + 1
x
; (ln x)
ln x
_
_
ln (ln x) + 1
x
_
2
+
1 [ln (ln x) + 1] ln x
x
2
ln x
_
(c) cot t ;
1
a sin
3
t
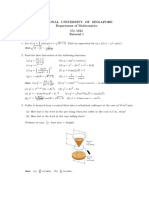
3. Sand falls from an open end of a pipe at the rate of 10 cubic metres per minute onto the top
of a conical pile. The height of the pile is always three-quarters of the base diameter. Find
the rate at which the base radius is changing when the pile of sand is 4 metres high.
Ans.
15
16
metres per minute
MA1505 Tutorial 1
4. A police car chases a car of robbers on a straight southbound road. At a road intersection,
the robbers car turns left and heads down the straight eastbound road. When the police
car is still 0.3 km from the intersection on the southbound road, the radar in the police car
shows that the robbers car is 0.5 km away and the (instantaneous) rate of change of distance
between the two cars is 0 km/hr. If the police car is travelling at 120 km/hr, nd the speed
of the robbers car.
Ans. 90 km/hr
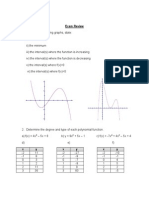
5. For each of the following functions f(x)
(a) f(x) =
x + 1
x
2
+ 1
, x [3, 3]; (b) f(x) = (x 1)
3
x
2
, x (, )
nd
(i) the values of x, if any, that give critical points, local extrema, and absolute extrema;
(ii) the (maximal) open intervals on which f(x) is (1) increasing, and (2) decreasing.
Ans.
(a) Critical points at x = 1
2; local max. at x = 3; local min. at x = 3;
absolute min. at x = 1
2; absolute max. at x = 1 +
2;
decreasing on (3, 1
2) and (1 +
2, 3); increasing on (1
2, 1 +
2)
(b) Critical points at x = 0 and x =
2
5
; local max. at x = 0; local min. at x =
2
5
;
no absolute extrema;
increasing on (, 0) and
_
2
5
,
_
; decreasing on
_
0,
2
5
_
6. A (circular) cylindrical container with no top cover is to be constructed to hold a xed volume
V cm
3
of liquid. The cost of the material used for the base is 8 cents/cm
2
, and the cost of
the material used for the curved surface is 3 cents/cm
2
. Find the radius r cm (in terms of V )
of the least expensive container.
Ans.
3
_
3V
8
2
You might also like
- Mcv4u Calculus ReviewDocument2 pagesMcv4u Calculus ReviewVoormila NithianandaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Overview: 0.1 Limits and ContinuityDocument14 pagesCalculus Overview: 0.1 Limits and Continuitytanmoy bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter CalculusDocument3 pages3rd Quarter CalculusLador GiovanniNo ratings yet
- MA1505 Tutorial 1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesMA1505 Tutorial 1 QuestionsBilguun BatboldNo ratings yet
- m7 REVIEW PDFDocument6 pagesm7 REVIEW PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- UDPG1673 - Tutorial 7 - 201601Document4 pagesUDPG1673 - Tutorial 7 - 201601chinNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Final Review SetDocument10 pagesCalculus - Final Review SetAaron David ReidNo ratings yet
- MATH 103 (Calculus 1) Sample Questions For The Final ExaminationDocument3 pagesMATH 103 (Calculus 1) Sample Questions For The Final ExaminationMustafa FarragNo ratings yet
- CLASS - XII-MATHS Diff&Appl of DiffDocument11 pagesCLASS - XII-MATHS Diff&Appl of DiffNICKNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 (Week 5)Document3 pagesTutorial 4 (Week 5)kbxw9s7x6jNo ratings yet
- MCV 4U1 Exam Review 1Document52 pagesMCV 4U1 Exam Review 1Eduardo Yépez M.No ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesDocument13 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoNo ratings yet
- Maths Xii Class 21-08-23Document3 pagesMaths Xii Class 21-08-23manishgup6879No ratings yet
- Review For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Document16 pagesReview For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Ian StantonNo ratings yet
- FinalReviewSem1 (2010)Document11 pagesFinalReviewSem1 (2010)Benjamin NgNo ratings yet
- Calculus Solved ProblemsDocument23 pagesCalculus Solved ProblemscloudNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - ExercisesDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - ExercisesVillamorchard0% (2)
- 2014 2 PENANG SMJK Jit Sin Maths QADocument11 pages2014 2 PENANG SMJK Jit Sin Maths QASK100% (2)
- Cal Review1Document4 pagesCal Review1Carlos MotosNo ratings yet
- Applied CalculusDocument12 pagesApplied CalculusRonald MulindeNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Mayur Vihar Subject: Mathematics Class: Xii Chapter: Applications of DerivativesDocument5 pagesAmity International School, Mayur Vihar Subject: Mathematics Class: Xii Chapter: Applications of DerivativesKOMAL AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Reviewer - Differential CalculusDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Exam Reviewer - Differential CalculusHarold MangaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1MatthewNo ratings yet
- Honors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesDocument16 pagesHonors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesKent MillerNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument121 pagesMultiple ChoicecathyNo ratings yet
- HW Assignment #3Document4 pagesHW Assignment #3oanh TrầnNo ratings yet
- 12th Application of Derivatives AssignmentDocument2 pages12th Application of Derivatives Assignmentsumankaswa841No ratings yet
- MATH Practice With Answer (Besavilla)Document121 pagesMATH Practice With Answer (Besavilla)aj100% (1)
- REVIEW - QuadraticsDocument2 pagesREVIEW - QuadraticsPranav KNo ratings yet
- Text 1b emDocument13 pagesText 1b emkrishNo ratings yet
- 2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Document5 pages2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Matthew LuNo ratings yet
- 010RDocument4 pages010RninokargigogoaNo ratings yet
- N R N N N R N N N 0 N 0 N N N (n-1) NDocument16 pagesN R N N N R N N N 0 N 0 N N N (n-1) N9stepsNo ratings yet
- MATH 150-Practice Test #1 (Spring 2013)Document2 pagesMATH 150-Practice Test #1 (Spring 2013)mytemp2544No ratings yet
- Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesExam ReviewvasdevharishNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 2 The DerivativeDocument3 pagesTutorial - 2 The DerivativeDurah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- ClassXII Topper Sample Paper 50Document26 pagesClassXII Topper Sample Paper 50Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- KEE - Model Question PaperDocument19 pagesKEE - Model Question PaperPremKumarKalikiriNo ratings yet
- tUGAS CHECKPOITNDocument2 pagestUGAS CHECKPOITNMohammad Rifaldi AgustienNo ratings yet
- MTH-101 Quiz File by Attiq KundiDocument19 pagesMTH-101 Quiz File by Attiq KundiSeHr Biz100% (1)
- HW Assignment2 Saturday Spring2018Document7 pagesHW Assignment2 Saturday Spring2018Quỳnh Ngân Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- CONAIP Mathematics Exam With CorrectionsDocument20 pagesCONAIP Mathematics Exam With CorrectionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Maths Cs em r1 2021 GTDocument8 pagesMaths Cs em r1 2021 GTIBA PrepworksNo ratings yet
- MT4 MathDocument4 pagesMT4 MathRicardo Aguilar Banal Jr.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Snehal SolankeNo ratings yet
- HW Assignment #3Document4 pagesHW Assignment #3Ayase YukiNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument62 pagesMultiple ChoiceJohnCarloDBautistaNo ratings yet
- Two Marks QuestionsDocument12 pagesTwo Marks QuestionsSsNo ratings yet
- 13 - Applications of DerivativesDocument9 pages13 - Applications of DerivativeskapilNo ratings yet
- 2003 Test BDocument10 pages2003 Test BDerny FleurimaNo ratings yet
- Winter Break PKT 2009Document5 pagesWinter Break PKT 2009Mandy Pan BohmbachNo ratings yet
- 1 Limit and Continuity: Review Final Exam Math1003 Math Learning Centre Department of MATH & STATSDocument4 pages1 Limit and Continuity: Review Final Exam Math1003 Math Learning Centre Department of MATH & STATSPenellapheNo ratings yet
- 1 03s c3Document1 page1 03s c3ABC CheckNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Previous Year Question Paper - 1Document7 pagesApplication of Derivatives Previous Year Question Paper - 1Brijesh MNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter5 In-Class Activities #11Document2 pagesChapter5 In-Class Activities #11Youssef KamounNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Advanced Principle of Inclusion & Exclusion (Pie)Document9 pagesLesson 6: Advanced Principle of Inclusion & Exclusion (Pie)James WigtonNo ratings yet
- Problem Score Problem Score Problem Score 1 (14 PTS) 4 (12 PTS) 7 (11 PTS) 2 (15 PTS) 5 (11 PTS) 8 (15 PTS) 3 (12 PTS) 6 (10 PTS) TotalDocument12 pagesProblem Score Problem Score Problem Score 1 (14 PTS) 4 (12 PTS) 7 (11 PTS) 2 (15 PTS) 5 (11 PTS) 8 (15 PTS) 3 (12 PTS) 6 (10 PTS) Totalrcherry calaorNo ratings yet
- Grading Aggregates by C Furnas 1931 1Document7 pagesGrading Aggregates by C Furnas 1931 1Ali HendiNo ratings yet
- Optimization For ML: CS771: Introduction To Machine Learning NisheethDocument18 pagesOptimization For ML: CS771: Introduction To Machine Learning NisheethRajaNo ratings yet
- IZhO 2022 Exp - Eng - SolDocument7 pagesIZhO 2022 Exp - Eng - SolAydın MammadovNo ratings yet
- Lo, Mamaysky &wang - Foundations of Technical Analysis PDFDocument61 pagesLo, Mamaysky &wang - Foundations of Technical Analysis PDFkhrysttalexa3146No ratings yet
- Calculus (BMAT101L), Module 1 - Dr. T. PhaneendraDocument26 pagesCalculus (BMAT101L), Module 1 - Dr. T. PhaneendraAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2ehmyggasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Optimisation: Kausik ChaudhuriDocument52 pagesLecture Notes: Optimisation: Kausik ChaudhuriRollins John100% (1)
- MATH140 Final Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageMATH140 Final Cheat Sheet: by ViaKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- CS 546: Module 2: Spring 2014Document73 pagesCS 546: Module 2: Spring 2014drsimrankaurNo ratings yet
- Partial DerivativesDocument15 pagesPartial DerivativesAien Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 LP Modeling and Selected IE ApplicationsDocument137 pagesUnit 4 LP Modeling and Selected IE ApplicationsYosser BelhediNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Practice AnswersDocument35 pagesAlg 2 Practice Answersbalakama67% (3)
- Actix Cellopt AFP User Guide 3 14Document158 pagesActix Cellopt AFP User Guide 3 14Ali Raza SabriNo ratings yet
- PSBB Code 1Document5 pagesPSBB Code 1Vibushitha KabardineshwarNo ratings yet
- MA 101 HandoutDocument3 pagesMA 101 HandoutCustomizedMENo ratings yet
- Maths Lab BookDocument30 pagesMaths Lab BookAhana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Percentage Questions For CATDocument17 pagesPercentage Questions For CATStartup SkillsNo ratings yet
- Unconstrained OptimizationDocument11 pagesUnconstrained OptimizationSuparna2No ratings yet
- FPM Formula Sheet 2Document13 pagesFPM Formula Sheet 2Yolo Gamer DudeNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Apostol PDFDocument77 pagesSolutions Manual Apostol PDFjrsduran80% (10)
- Cbse Xii Hots Application of Derivatives Chapter 6Document4 pagesCbse Xii Hots Application of Derivatives Chapter 6Om Prakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Formula - Engg Maths 1 PDFDocument7 pagesFormula - Engg Maths 1 PDFDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Mapper Manual PRODocument71 pagesMapper Manual PROroyerarangoasisNo ratings yet
- PROJECTMean Value Theorem and Its Applicationby DRP 12Document25 pagesPROJECTMean Value Theorem and Its Applicationby DRP 12Ujjwal RaiNo ratings yet
- Least Squares Quantization in PCMDocument9 pagesLeast Squares Quantization in PCMKoundinya ChunduruNo ratings yet
- Honors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesDocument16 pagesHonors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesKent MillerNo ratings yet