Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 - SDOF - Free Vibrations
2 - SDOF - Free Vibrations
Uploaded by
Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 - SDOF - Free Vibrations
2 - SDOF - Free Vibrations
Uploaded by
Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziCopyright:
Available Formats
Civil Engineering Department
Structural Analysisspring 2013
(single degree of freedom - free vibrations)
Fawad Muzaffar
M.Sc. Structures (Stanford University) Ph.D. Structures (Stanford University)
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
Free Vibration: When a structure is disturbed from its equilibrium position and allowed to vibrate without any external force. Components of Dynamic System: i. Mass ii. Elastic Properties (Stiffness) iii. Energy Loss Mechanism (Damping) iv. The External Force Acting on the System The First Derivation Use dAlemberts Principle to express equilibrium of forces acting on the block ------Equation 1
Fawad Muzaffar 2
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
Note: DAlemberts Principle (named after French Mathematician Jean le
Rond dAlembert) states that different of sum of forces acting on a system of mass particles and time derivative of momenta of the system is equal to zero. From Newtons Second Law:
Assuming Viscous Damping:
Finally, the Elastic Force can be obtained from Plugging all of the above values into Equation 1, we have
Fawad Muzaffar
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
The virtual work Derivation
If mass is given a virtual displacement , the total work done by equilibrium of forces must be equal to zero.
The negative signs in the above equation indicates that force act in the negative direction relative to the direction of motion. Plugging in all constituent values, we have Since 0
Fawad Muzaffar
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
Influence of Gravitational Forces
From Equilibrium of forces Expressing The component forces can be evaluated as The equation of motion can then be written Noting that , we have
Fawad Muzaffar
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
Since does not vary with time The equation of motion can then be written as Note: equation of motion expressed with reference to static-equilibrium position of dynamic system is not effected by gravity.
Influence of Support Excitation
Dynamic deflections can be induced by motion of support points e.g. i) Excitation of supports by E.Q. ii) Motions of base of equipment due to vibration of foundation
Fawad Muzaffar 6
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
Assumptions
The Girder is Rigid. The Columns are Weightless. The Columns are Inextensible in Axial Direction. Resistance to Lateral Displacement id Provided by Columns. The Damper Provides a Velocity Proportion Response to Displacement From Equilibrium in Horizontal Direction. The Inertial Force is given by where represents total displacement of mass from fixed reference axis.
Fawad Muzaffar 7
Equation of Motion of The Basic Dynamic System
The total motion of mass, can be expressed as Plugging this value of back into equation of motion results in The above expression can then be manipulated to yield Note: () is called effective support excitation An alternate form of above equation can be obtained by using instead of ().
R.H.S. depends on velocity and displacement of earthquake motion. L.H.S. depends on quantities depending on total displacement.
Fawad Muzaffar 8
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures Math Preliminaries
Math Preliminaries
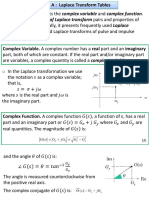
The Complex Number Concept
A Complex Number G has real and imaginary parts The Polar form of Complex Number in complex plane. where = || is the length of the vector. Using Eulers Identity, the polar form can be expressed as Note: Multiplying G by rotates it by /2 e.g. = + = +
Fawad Muzaffar
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures Math Preliminaries
Eulers Identity
Taylors Series = +
=
= +
Using Taylor Expansion to express and with = and 0 = 0 = + + ! ! !
sin =
Expressing with = and 0 = 0 = + . . + . + . . . + . + . ! ! ! ! ! ! !
= + . . + . + . . + . . + . ! ! ! ! ! ! ! = + . sin
10
Fawad Muzaffar
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures
For a freely vibrating structure, the equation of motion becomes The solution of the above linear, 2nd order homogeneous differential equation is
where G is a complex constant and s is a real constant. Plugging in the value of into the equation of motion results in
The equation of motion becomes ----Equation 2
Fawad Muzaffar 11
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures
Case 1 - Damping c=0:
When c=0, the values of s becomes The general solution of the differential equation then comes out to be ----Equation 3 The complex constants can be expressed as Also from Eulers Identity Plugging all values in Equation 3 results in
Fawad Muzaffar
12
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures
The free vibration response HAS TO BE REAL. Terms inside square brackets should be zero. Only possible if 1 and 2 are complex conjugate pair. The solution equation becomes Using Euler Identity to expand in the above equation results in where The value of A and B can be determined from initial conditions (0) and 0 , resulting in
Fawad Muzaffar
13
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures
The equation of motion becomes The Solution Represents SHM The time required to complete 1- Cycle, T is given by
The frequency of motion is given by T is measured in secs and f is measured in Hertz (Hz). The maximum value of displacement is given by The phase angle is given by
Fawad Muzaffar 14
Analysis of Free Degree of Freedom Structures
The equation of motion becomes The Solution Represents SHM The time required to complete 1- Cycle, T is given by
The frequency of motion is given by
Fawad Muzaffar
15
You might also like
- Moving Man Phet Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesMoving Man Phet Lab Activityuflilla50% (4)
- FIDIC Question & Answer - 2Document59 pagesFIDIC Question & Answer - 2segar12382% (17)
- Ec8 1 PDFDocument40 pagesEc8 1 PDFAugusto MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-265544103No ratings yet
- 2 - SDOF - Free VibrationsDocument25 pages2 - SDOF - Free VibrationsTalha EjazNo ratings yet
- Hamilton's Equations of Motion: Second OrderDocument26 pagesHamilton's Equations of Motion: Second OrderPranay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document20 pagesChapter 04api-3728553No ratings yet
- Multi Degree of Freedom MDOF VibaratoryDocument40 pagesMulti Degree of Freedom MDOF Vibaratoryhanumantharaya100% (1)
- Week 1 Vibration IntroductionDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Vibration IntroductionSaya SantornoNo ratings yet
- Name - Ashesh Kumar GuptaDocument23 pagesName - Ashesh Kumar GuptaAsheshNo ratings yet
- SD GRDocument17 pagesSD GRApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument49 pagesChapter TwoAbenezer MarkNo ratings yet
- Va&C - Unit - II (Part-One)Document76 pagesVa&C - Unit - II (Part-One)Dame AyaneNo ratings yet
- Langrangian MechanicsDocument41 pagesLangrangian MechanicsLuthfiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: 1 Concurrent Forces in A Plane 1.5 Equilibrium of Three Forces in A Plane 1.6 Method of MomentsDocument22 pagesEngineering Mechanics: 1 Concurrent Forces in A Plane 1.5 Equilibrium of Three Forces in A Plane 1.6 Method of MomentsSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Preliminary CommentsDocument5 pagesLecture 1: Preliminary CommentsRavi Harish MaulanaNo ratings yet
- DSLL1Document53 pagesDSLL1simon maaaklaNo ratings yet
- Vibrations of Multi-Degree of Freedom Systems: Simple Harmonic Motion That Passes Through Their Equilibrium PositionsDocument15 pagesVibrations of Multi-Degree of Freedom Systems: Simple Harmonic Motion That Passes Through Their Equilibrium PositionsMï XavierNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics 2020 Lecture 4Document48 pagesEngineering Dynamics 2020 Lecture 4Muhammad ShessNo ratings yet
- 01 Automatic Control System Modeling and RepresentationDocument55 pages01 Automatic Control System Modeling and RepresentationPaul BonaNo ratings yet
- Lindsey Hines Final Report PDFDocument21 pagesLindsey Hines Final Report PDFclimax1364No ratings yet
- D'Alembert-Lagrange!s Principal Equations, Their Origin and ApplicationsDocument45 pagesD'Alembert-Lagrange!s Principal Equations, Their Origin and ApplicationsBagulSurabhiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Week 1Document57 pagesMechanical Vibrations Week 1mrb87No ratings yet
- Force (Flexibility) Method of Structural AnalysisDocument48 pagesForce (Flexibility) Method of Structural AnalysisthareendaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mathematical Modeling Based On Physics LawsDocument38 pages5 - Mathematical Modeling Based On Physics LawsJosueNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Internal Forces in FramesDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Internal Forces in FramesLahlou DahmaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle - Work and EnergyDocument130 pagesChapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle - Work and EnergyPapaeng ChantakaewNo ratings yet
- Generalized CoordinatesDocument8 pagesGeneralized CoordinatesJoshua WoodNo ratings yet
- Week 12 - Impulse+Momentum+ImpactDocument56 pagesWeek 12 - Impulse+Momentum+Impactiwhy_No ratings yet
- Rigid BodyDocument9 pagesRigid BodyChernet TugeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 VibrationDocument9 pagesUNIT 2 VibrationAnonymous POUAc3zNo ratings yet
- Spring Mass DamperDocument15 pagesSpring Mass DamperAeitesham Ul Huq SubedarNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mathematical Modeling Based On Physics LawsDocument37 pages5 - Mathematical Modeling Based On Physics LawsJosueNo ratings yet
- System Requires Only One Coordinate To Describe Its Position at Any InstantDocument11 pagesSystem Requires Only One Coordinate To Describe Its Position at Any Instantsrinu.boyaNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics (CE 661)Document25 pagesStructural Dynamics (CE 661)santoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 SlidesDocument40 pagesChapter 14 SlidessuperwebonNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics 1.2-090921Document22 pagesStructural Dynamics 1.2-090921santoshNo ratings yet
- Mth-382 Analytical Dynamics: MSC MathematicsDocument51 pagesMth-382 Analytical Dynamics: MSC MathematicsediealiNo ratings yet
- Theory of VibrationDocument30 pagesTheory of VibrationCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document45 pagesModule 1MD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- W3a PDFDocument26 pagesW3a PDFShujah RashidNo ratings yet
- MDOF Structural DynamicsDocument13 pagesMDOF Structural Dynamicspanos2244662864100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics: Statics: General PrinciplesDocument45 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Statics: General PrinciplesnabilahNo ratings yet
- Week 1B - Online Classes - S2020Document25 pagesWeek 1B - Online Classes - S2020Muhammad Tayyab YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document28 pagesChap 5Mï XavierNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas and ConceptsDocument23 pagesPhysics Formulas and ConceptsShivam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2محمد فائزNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document18 pagesChapter 2-1الخليل إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Goldstein Classical Mechanics Notes: 1 Chapter 1: Elementary PrinciplesDocument149 pagesGoldstein Classical Mechanics Notes: 1 Chapter 1: Elementary PrinciplesPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Lecture TwoDocument22 pagesDynamics - Lecture TwoKassimNo ratings yet
- Statics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisDocument69 pagesStatics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisSam SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Quadrotor Equations of MotionDocument4 pagesQuadrotor Equations of MotionKaran ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 2C - 4 Quadrotor Equations of MotionDocument4 pagesAerial Robotics Lecture 2C - 4 Quadrotor Equations of MotionIain McCullochNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Control Systems and Viscosity SolutionsDocument30 pagesHybrid Control Systems and Viscosity SolutionsdharmattiNo ratings yet
- Vibrations Part OneDocument44 pagesVibrations Part OneRicardo ColosimoNo ratings yet
- Machine Control SystemsDocument9 pagesMachine Control SystemsHisham SyedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Mathematical Models of Systems - W2015Document75 pagesChapter - 2 - Mathematical Models of Systems - W2015120200421003nNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Integrals and Integro-Differentials EquationsFrom EverandExercises of Integrals and Integro-Differentials EquationsNo ratings yet
- View Topic - Flat Slab Under Wall LoadingDocument6 pagesView Topic - Flat Slab Under Wall LoadingSheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Audit ReportDocument9 pagesFire Safety Audit ReportSheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab BestDocument25 pagesTwo Way Slab BestErnest Christian Nanola100% (1)
- Construction Methodology For Test PIle NPBDocument8 pagesConstruction Methodology For Test PIle NPBSheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Date Dia Quantity Length of Each (M)Document5 pagesDate Dia Quantity Length of Each (M)Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Tender Boq - xls139170140Document12 pagesTender Boq - xls139170140Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- 16.02-GuideLines For Preparing Weekly Project Performance Report (Rev-8)Document8 pages16.02-GuideLines For Preparing Weekly Project Performance Report (Rev-8)Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- (Engineersdaily - Com) RCC62 Retaining WallDocument12 pages(Engineersdaily - Com) RCC62 Retaining WallMuhammad WaqasNo ratings yet
- How Do I Calculate Steel Reinforcement and Its Quantity in Slab, Beams, Columns and Footing For Given Dimensions - QuoraDocument6 pagesHow Do I Calculate Steel Reinforcement and Its Quantity in Slab, Beams, Columns and Footing For Given Dimensions - QuoraSheikh Nouman Mohsin Ramzi50% (2)
- What Is Development Length, Anchorage Length and Lap Length in RCC - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhat Is Development Length, Anchorage Length and Lap Length in RCC - QuoraSheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Location Member Bar Mark Bar Size Total No. A (MM) C (MM) Bar Type No. of Memb. No of Bars in Each Len. of Each Bar (M) Shape Code B (MM) D (MM)Document8 pagesLocation Member Bar Mark Bar Size Total No. A (MM) C (MM) Bar Type No. of Memb. No of Bars in Each Len. of Each Bar (M) Shape Code B (MM) D (MM)Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- ENR Top 250 International Contractors-2015Document77 pagesENR Top 250 International Contractors-2015OnurUmanNo ratings yet
- D SoftwareUpdates Nov12Document1 pageD SoftwareUpdates Nov12Sheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Analysis & RatesDocument9 pagesAnalysis & RatesSheikh Nouman Mohsin RamziNo ratings yet
- Science 4: Isabela B. LabasaDocument22 pagesScience 4: Isabela B. LabasaKim BantaoNo ratings yet
- CSE 513-1 Structural Forms and Modeling TechniquesDocument50 pagesCSE 513-1 Structural Forms and Modeling TechniquesVincent YeungNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Stand UpDocument6 pagesAnalysis of The Stand UpSafar Al InseNo ratings yet
- Power Point 2 Study IslandDocument15 pagesPower Point 2 Study Islandapi-294483847No ratings yet
- NACA Duct VsDocument10 pagesNACA Duct VsewaigeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Section 1 PhysicsDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Section 1 PhysicsMaria PittNo ratings yet
- MEM22443 2019 Summer Model Answer PaperDocument15 pagesMEM22443 2019 Summer Model Answer PaperRohit VaityNo ratings yet
- Basics of Contamination by Electrostatic Attraction: Douglas W. Cooper, TexwipeDocument4 pagesBasics of Contamination by Electrostatic Attraction: Douglas W. Cooper, TexwipeNilesh NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Centrifuges, Sediment IngDocument6 pagesCentrifuges, Sediment IngLatif Hasan Çite100% (2)
- Splice Check - 07282020 PDFDocument3 pagesSplice Check - 07282020 PDFAngelo MoralNo ratings yet
- NAC Theory of Flight SyllabusDocument2 pagesNAC Theory of Flight SyllabusHana LeransoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measuring Instrument: Assignment of Subject NVHDocument28 pagesVibration Measuring Instrument: Assignment of Subject NVHSandeep Kadam60% (5)
- Estimating in Situ Rock Mass Strength and Elastic Modulus of Granite From The Soultz Sous Forêts Geothermal Reservoir (France)Document29 pagesEstimating in Situ Rock Mass Strength and Elastic Modulus of Granite From The Soultz Sous Forêts Geothermal Reservoir (France)Frehiwot TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Building Analysis On Staad With Raft FoundationsDocument4 pagesSeminar On Building Analysis On Staad With Raft FoundationsAWOUNANGNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- Elements of Polymer Structure and Viscoelasticity: David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 18, 2004Document15 pagesElements of Polymer Structure and Viscoelasticity: David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 18, 2004Jeffrey GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 Aplicación de Derivadas PDFDocument7 pagesTarea 1 Aplicación de Derivadas PDFOscarDaniel Tello ChinguelNo ratings yet
- Notes On Static and Dynamic FrictionDocument2 pagesNotes On Static and Dynamic FrictiondrhillNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument55 pagesFluid MechanicsRixzyli Coqui SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Hoop Stress and Wall Thickness in Storage TanksDocument7 pagesHoop Stress and Wall Thickness in Storage Tanksandi suntoroNo ratings yet
- Exercise EC4Document23 pagesExercise EC4babel_stanNo ratings yet
- 2007 H2 Combined SolutionsDocument203 pages2007 H2 Combined SolutionsAmos YapNo ratings yet
- Summative Test (Physics)Document3 pagesSummative Test (Physics)Allen Paul GamazonNo ratings yet
- Swept Back WingDocument7 pagesSwept Back WingYashNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Ii Year/ Iv Semester Unit I Stress and Strain Part - ADocument14 pagesMechanics of Solids Ii Year/ Iv Semester Unit I Stress and Strain Part - AMohsin MullaNo ratings yet
- 6.fatigue Failures Resulting From Variable LoadingDocument148 pages6.fatigue Failures Resulting From Variable LoadingAekkasit SenaartNo ratings yet
- Brace Compression and Tension Capacity Design Charts As Per CSA S16 09 Rev1.5Document44 pagesBrace Compression and Tension Capacity Design Charts As Per CSA S16 09 Rev1.5Antonio LópezNo ratings yet