Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiplication Rules For Probability
Multiplication Rules For Probability
Uploaded by
momathtchrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multiplication Rules For Probability
Multiplication Rules For Probability
Uploaded by
momathtchrCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
Objectives: Find the probability of two or more independent events all occurring. Find the probability of two or more dependent events all occurring Find conditional probabilities
A. Independent and Dependent Events
The probability of consecutive events depends on whether the first event affects the second. Two events A and B are independent if the fact that A occurs has no effect on the probability of B occurring. Two events A and B are dependent if the outcome of A has some effect on the probability of B occurring. Examples of dependent events could be: Drawing a card from a deck, not replacing it, and then drawing a second card. Parking in a no-parking zone and getting a parking ticket.
An example of independent events could be: Rolling a die and getting a 6, and then rolling a second die and getting a 3.
B. Multiplication Rules
When two events A and B are independent, the probability of both occurring is When two events A and B are dependent, the probability of both occurring is
(A d d t y )i h s ( ) A Po ( B r g c v e r a a P P Pnu ( B(Ahe A ( Blc a A a tr) n ) ) Ba d n ad ) PP e
When we are interested in finding the probability of consecutive events that are dependent, we can still use the multiplication rule, but with a minor modification.
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
1. A coin is flipped and a die is rolled. Find the probability of getting heads on the coin and a 4 on the die.
Video
2. As part of a psychology experiment on perception and memory, colored balls are picked from an urn. The urn contains three red balls, two green balls, and five white balls. A ball is selected and its color is noted. Then it is replaced. A second ball is selected and its color is noted. Find the probability of each of these. Video (a) Selecting two green balls.
(b) Selecting a green ball and then a white ball.
(c) Selecting a red ball and then a green ball.
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
3. Three cards are drawn from a deck. After each card is drawn, its denomination and suit are noted and it is replaced before the next card is drawn. Find the probability of getting Video (a) Three kings.
(b) Three clubs.
4. According to a Gallup Poll in 2007, 47 percent of all parents in America with children under 18 feel frequent stress. If three parents are chosen randomly, find the probability that all three will say they feel frequent stress.
Video
5. An appliance store gets a shipment of 25 plasma TVs, and 3 of them are defective. If two of the TVs are chosen at random, find the probability that both are defective. (The first TV is not replaced after its tested.) Video
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
6. Three cards are drawn from an ordinary deck and not replaced. Find the probability of Video (a) Getting three jacks.
(b) Getting an ace, a king, and a queen in order.
(c) Getting a club, a spade, and a heart in order.
(d) Getting three clubs.
C. Conditional Probability
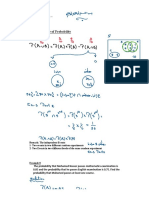
We know that to find the probability of two dependent events occurring, its important to find the probability of the second event occurring given that the first has already occurred. We call this the conditional probability of event B occurring given that event A has occurred, and denote it P(B | A).
P n) ( aB A d P) (A B P () A
4
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
7. Suppose that your professor goes stark raving mad and chooses your final grade from A, B, C, D, F, or Incomplete totally at random. Find the probability of getting an A given that you get a letter grade higher than D.
Video
8. Hate crimes are defined to be crimes in which the victim is targeted because of one or more personal characteristics, such as race, religion, or sexual orientation. The table below lists the motivation for certain crimes as reported by the FBI for 2007.
(a) Find the probability that a hate crime was racially motivated given that it was a crime against persons.
Video
(b) Find the probability that a hate crime was against property given that it was motivated by the victims sexual orientation.
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
9. A group of buses is rented for an away game, and they are numbered from 1-8. All students are randomly assigned to a bus. What is the probability that you get an evennumbered bus given that your bus number is less than 6? Video
10. In a group of eight Olympic track stars, five are hurdlers. If three are selected at random without replacement, find the probability that they are all hurdlers. Find the probability that none of them are hurdlers. Video
Lesson 11-8 The Multiplication Rules and Conditional Probability
11. Three red cards are numbered 1, 2, and 3. Three black cards are numbered 4, 5, and 6. The cards are placed in a box and one card is selected at random.
a. Find the probability that a number less than 5 was selected given that the card was a black card.
Video
b. Find the probability that a black card was selected given that the number on the card was an even number.
You might also like
- Worksheet Independent EventsDocument6 pagesWorksheet Independent EventsHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- CH1 Prob SuppDocument6 pagesCH1 Prob SuppMuhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Maths - CHANCE & PROBABILITY Unit Plan Year 5/6Document20 pagesMaths - CHANCE & PROBABILITY Unit Plan Year 5/6mbed201050% (4)
- Supplementary Problems Set 2Document5 pagesSupplementary Problems Set 2malaik hiraNo ratings yet
- Session 2 2014 Version Part 1Document12 pagesSession 2 2014 Version Part 1Remalyn Quinay CasemNo ratings yet
- 2.1 ProbabilityDocument17 pages2.1 ProbabilityJon Zeth AslorNo ratings yet
- Independence & Conditional ProbabilityDocument7 pagesIndependence & Conditional Probabilityapi-235607885No ratings yet
- T1 SampleQuestionsDocument4 pagesT1 SampleQuestionsQuame Enam KunuNo ratings yet
- HW1Document9 pagesHW1Pallavi RaiturkarNo ratings yet
- Probability Laws, Demorgans Laws: Chris Morgan, Math G160 Csmorgan@Purdue - Edu January 11, 2012Document24 pagesProbability Laws, Demorgans Laws: Chris Morgan, Math G160 Csmorgan@Purdue - Edu January 11, 2012Anima AnwarNo ratings yet
- Probability (Introduction) : Random Experiments Sample Spaces EventsDocument37 pagesProbability (Introduction) : Random Experiments Sample Spaces EventsrammableNo ratings yet
- Addition Rules For ProbabilityDocument4 pagesAddition Rules For ProbabilitymomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Stat Chapter 4-3Document17 pagesStat Chapter 4-3sambaNo ratings yet
- HW3Document2 pagesHW3Cem TahtakıranNo ratings yet
- Session 6-7Document14 pagesSession 6-7AniketNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Bach Tran HuuNo ratings yet
- Maths in Focus Chapter 11Document52 pagesMaths in Focus Chapter 11eccentricftw450% (2)
- Jan S Day 3Document12 pagesJan S Day 3Hassan SaadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Mth3003Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Mth3003nasonex91No ratings yet
- Probability: Prepared byDocument40 pagesProbability: Prepared byYato QtNo ratings yet
- Probability - PPPT - 2Document23 pagesProbability - PPPT - 2BEFIRE TVNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document5 pagesCH 5BakerFieldNo ratings yet
- 2 - Probability (Part 1)Document37 pages2 - Probability (Part 1)Stephanie CañeteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Practice of Statistics 9Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesIntroduction To The Practice of Statistics 9Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrichard.nichols145100% (18)
- Introduction To The Practice of Statistics 9th Edition Moore Test Bank 1Document76 pagesIntroduction To The Practice of Statistics 9th Edition Moore Test Bank 1dorothy100% (60)
- Practice Problems in Chapter 2Document4 pagesPractice Problems in Chapter 2mirandatwongNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument7 pagesProbabilityJanaka PriyalalNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument11 pagesQuizSerge Mandhev SwamotzNo ratings yet
- AdHStat1 1notesDocument5 pagesAdHStat1 1notesDavid ClellandNo ratings yet
- 06 - HW Assignment # 13Document3 pages06 - HW Assignment # 13yayaxiiNo ratings yet
- Supporting Problem - Probabbility Part 2Document16 pagesSupporting Problem - Probabbility Part 2Danice ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- IB A&I 7.4 ProbabilityDocument19 pagesIB A&I 7.4 ProbabilitythodgesNo ratings yet
- Class 7 S09Document3 pagesClass 7 S09madhu_angel20018484No ratings yet
- 6 Probability ExperimentDocument42 pages6 Probability ExperimentTruKNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Probability ConceptsDocument42 pagesA Survey of Probability ConceptsBor ShonNo ratings yet
- A. Classical Probability: Lesson 11-3 Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocument4 pagesA. Classical Probability: Lesson 11-3 Basic Concepts of ProbabilitymomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Grade 10Document2 pagesQuestionnaire Grade 10Julie Ann DefitaNo ratings yet
- Sm2205es1 7Document12 pagesSm2205es1 7JooSie241No ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 ProbabilityDocument3 pagesProblem Set 2 ProbabilityVignesh NagarajanNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2Tristan WaNo ratings yet
- 1 ElementProbDocument5 pages1 ElementProbtin nguyenNo ratings yet
- MBA First Semester AssignmentDocument14 pagesMBA First Semester AssignmentMukeshKumarNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument47 pagesProbabilitylieynna4996100% (1)
- Data Analysis Week 3Document7 pagesData Analysis Week 3Christian John Paul LijayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Betty TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 ProbabilityDocument24 pagesChapter - 3 ProbabilityVikram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Week 3Document18 pagesData Analysis Week 3Christian John Paul LijayanNo ratings yet
- 4Document17 pages4Anonymous 3hrzMH7No ratings yet
- Cambridge TextbookDocument40 pagesCambridge TextbookwedwdwNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Engineering StatisticsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - Engineering StatisticsNamra FatimaNo ratings yet
- 6 ProbabilityDocument56 pages6 Probabilityaavneet21No ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument16 pagesProbabilitylitille mae diolaNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 STS3006 SS VL2019205007330 Reference Material I 14-Dec-2019 Probability-STS3006 3007Document21 pagesWINSEM2019-20 STS3006 SS VL2019205007330 Reference Material I 14-Dec-2019 Probability-STS3006 3007Srinivasan Saai Mahesh 16BCE0559No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Probability of Independent EventsDocument47 pagesLESSON 1 Probability of Independent EventsCarbon CopyNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems For Exam 2Document3 pagesSample Problems For Exam 2Kerby Gail RulonaNo ratings yet
- MIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Document14 pagesMIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Ryan SooknarineNo ratings yet
- Summary of Avinash K. Dixit & Barry J. Nalebuff's Thinking StrategicallyFrom EverandSummary of Avinash K. Dixit & Barry J. Nalebuff's Thinking StrategicallyNo ratings yet
- Probability, Decisions and Games: A Gentle Introduction using RFrom EverandProbability, Decisions and Games: A Gentle Introduction using RNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Envelopes: Dimension Reduction for Efficient Estimation in Multivariate StatisticsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Envelopes: Dimension Reduction for Efficient Estimation in Multivariate StatisticsNo ratings yet
- Jeopardy ReviewDocument27 pagesJeopardy ReviewmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.4 Video TutorialsDocument2 pagesLesson 4.4 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.5 Video TutorialsDocument4 pagesLesson 4.5 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 Video TutorialsDocument7 pagesLesson 2.3 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Sets and Venn Diagrams To Solve ProblemsDocument4 pagesSets and Venn Diagrams To Solve ProblemsmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Hesterfield Illage: Annual Board Meeting-Your Help Is Needed!Document4 pagesHesterfield Illage: Annual Board Meeting-Your Help Is Needed!momathtchrNo ratings yet
- Rational Exponents VideosDocument2 pagesRational Exponents VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- 2014-April 7 Meeting MinutesDocument9 pages2014-April 7 Meeting MinutesmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- 2014-August 11 Meeting MinutesDocument8 pages2014-August 11 Meeting MinutesmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- July 2014 MinutesDocument2 pagesJuly 2014 MinutesmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratic Functions VideosDocument7 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Pool Opening Information: Hesterfield IllageDocument2 pagesPool Opening Information: Hesterfield IllagemomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Radicals VideosDocument2 pagesAdding and Subtracting Radicals VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Square Root Property and Completing The Square VideosDocument4 pagesSquare Root Property and Completing The Square VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Multiplying Radical Expressions VideosDocument4 pagesMultiplying Radical Expressions VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Radical Expressions VideosDocument3 pagesSimplifying Radical Expressions VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula VideosDocument2 pagesQuadratic Formula VideosmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of A Relation: Video Tutorial For #1-6Document5 pagesA. Definition of A Relation: Video Tutorial For #1-6momathtchrNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CDocument10 pagesA. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Review MidtermII Summer09Document51 pagesReview MidtermII Summer09Deepak RanaNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument28 pagesProbabilityVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Loss DistributionDocument19 pagesLoss Distributionelifeet123No ratings yet
- Distribution Function of A Random Variable: X If X IfDocument8 pagesDistribution Function of A Random Variable: X If X IfNomad Soul MusicNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory Random ExperimentDocument4 pagesProbability Theory Random ExperimentArjun SukumaranNo ratings yet
- PRP (Unit-I QB) BmeDocument8 pagesPRP (Unit-I QB) BmeMaan Karate KamalNo ratings yet
- PSD Ceu 177may11Document9 pagesPSD Ceu 177may11Del MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Quỳnh Nga 20203275Document3 pagesNguyễn Quỳnh Nga 20203275Quỳnh NgaNo ratings yet
- تأثير الأزمات المالية على عائد ومخاطر المحفظة المالية الدولية - - حالة مجموعة من بورصات الأسهم المتطورة والناشئة 2007-2012 -Document16 pagesتأثير الأزمات المالية على عائد ومخاطر المحفظة المالية الدولية - - حالة مجموعة من بورصات الأسهم المتطورة والناشئة 2007-2012 -MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Risk and Its Treatment SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Risk and Its Treatment SummaryIbrahim Nur Sufi100% (1)
- Binomial DistributionDocument3 pagesBinomial Distributionnskaz2067No ratings yet
- Stat 244 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesStat 244 CheatsheetguanyucNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument28 pagesProbabilitytamann2004No ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument1 pageBinomial DistributionToni SerbanNo ratings yet
- Belarusian National Annex To Eurocode 3 Basic Variables Formulation For The Partial Factors CalibrationDocument10 pagesBelarusian National Annex To Eurocode 3 Basic Variables Formulation For The Partial Factors CalibrationmaNo ratings yet
- Probability-Assignment 1Document4 pagesProbability-Assignment 1ibtihaj aliNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis of Gas Distribution Network PDFDocument206 pagesRisk Analysis of Gas Distribution Network PDFHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1802 06071Document107 pages1802 06071Raymond N CoxNo ratings yet
- 732 CHAPTER 72 Probability: Problem SolvingDocument3 pages732 CHAPTER 72 Probability: Problem SolvingEspen ZahlNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STATISTICS Notes UNIT 2Document6 pagesBUSINESS STATISTICS Notes UNIT 2Sherona ReidNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 296.1 Auctions With Risk Averse Bidders PDFDocument2 pagesEXERCISE 296.1 Auctions With Risk Averse Bidders PDFzuimaoNo ratings yet
- R1 Factor GraphDocument2 pagesR1 Factor GraphN EMNo ratings yet
- PAS206 Exercises Unit 2A (Answers)Document6 pagesPAS206 Exercises Unit 2A (Answers)Johannah ManokoNo ratings yet
- Acme CorporationDocument5 pagesAcme Corporationjuanmateus680No ratings yet
- Math 4441 - Course OutlineDocument4 pagesMath 4441 - Course OutlineMehedi AhamedNo ratings yet
- Lab5 - Independence of EventsDocument9 pagesLab5 - Independence of EventsA BNo ratings yet
- How Many Lives Has Schrodinger's Cat?Document20 pagesHow Many Lives Has Schrodinger's Cat?kdf2113No ratings yet
- Statistic Engineering Topic 1Document9 pagesStatistic Engineering Topic 1harisNo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument5 pagesCentral Limit TheorembossishereNo ratings yet