Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Do You Know
Do You Know
Uploaded by
Amit ShuklaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Do You Know
Do You Know
Uploaded by
Amit ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
Do You Know?
From the invention of the decimal system in mathematics to the noble philosophy of ahims, Hindus have contributed their share in all fields of knowledge and learning. Over five thousand years ago, when Europeans were only nomadic forest dwellers, ancient Hindus had established a civilization, known as the Harappan culture, in the Indus Valley, the northwestern region of India. When much of the world was still sunk in sleep, people of the Harappan culture were conducting trade workshops in weaving, bead-making, pottery, dying of fabrics, and metallurgy. Although modern images & descriptions of India often show poverty, India was one of the richest countries till the time of British in the early 17th Century. Christopher Columbus was attracted by India's wealth and was looking for route to India when he discovered America by mistake. If readers, who have diligently read their schoolbooks on India, are surprised that they haven't been told of these ideas before, the fault is of the books they have used. Such books are as worthless as would be books on America, two hundred years from now, that describe only matters of conflict between race, language, and gender, ignoring completely the achievements of science, art, and imagination. The official Sanskrit name for India is Bharat. INDIA has been called Bharat even in satya yuga. Charaka Samhita: Worlds first physician The west is fond of proclaiming Hippocrates (460 377 BC) as the father of medicine, but way before him in 500 BC Maharishi Charaka wrote the famous Charaka Samhita or Physicians Handbook. The Charaka Samhita went into great detail to describe human anatomy, pathology, diagnostic procedures, and treatment for various diseases. Charaka defined eight major medical disciplines of Ayur Veda: Shailya Chikitsa (surgery), Shaalakya Chikitsa (head, eye, nose, throat), Kaaya Chikitsa (mental health), Kaumarbhrutya Chikitsa (pediatrics), Agada Tantra (toxicology), Rasaayana Tantra (Pharmacology), Vaajeekarna Tantra (reproductive medicine). Charaka also described the functions of the heart and the circulatory system in great detail. The Charaka Samhita was widely translated in various languages and Charaka was a respected medical authority in both the Arab and Roman empires.
Dice The dice is attributed to India by some accounts. Some of the earliest archaeological evidence of oblong dice have been found in Harrapan sites such as Kalibangan, Lothal, Ropar, Alamgirpur, Desalpur and surrounding territories, some dating back to the third millennium BCE, which were used for gambling. The oblong or cubical dice (aka) is the precursor of the more primitive vibhakasmall, hard nuts drawn randomly to obtain factors of a certain integer. Dicing is believed to have later spread westwards to Persia, influencing Persian board games. Early references to dicing can be found in the ig Veda as well as the newer atharvaveda.
Metallurgy India was the world-leader in Metallurgy for more than 5,000 years. Gold jewelery is available from 3,000 BCE. Brass and bronze pieces are dated back to 1,300 BCE. Extraction of zinc from ore by distillation was used in India as early as 400 BCE while European William Campion patented the process some 2,000 years later. Copper statues can be dated back to 500 CE. There is an iron pillar in Delhi dating back to 400 CE that shows no sign of rust or decay. The earliest know book on metallurgy was known to be written by Nagarjuna in 10th century. The book Rasaratnanakara addresses various metallurgical topics such as: Preparation of liquids (rasas) such as Mercury Extraction of metals like Gold, Silver, Tin, and Copper from their ores and their purification The processes of liquefaction, distillation, sublimation, and roasting India was invaded by Mohammedans during the time of Nagarjuna. It is possible that Nagarjuna's texts fell into the hands of the invaders, who could have transmitted these Indian Metallurgical sciences to the outside world.
Oral tradition of Vedic Chanting is declared an intangible heritage of humanity by UNESCO The oral tradition of Vedic chanting has been declared an intangible heritage of humanity by UNESCO. In a meeting of jury members on November 7, 2003, at Paris, Mr. Koichiro Matsuura, Director-General of UNESCO, declared the chanting of Vedas in India an outstanding example of heritage and form of cultural expressions. The proclamation says that in the age of globalization and modernization when cultural diversity is under pressure, the preservation of oral tradition of Vedic chanting, a unique cultural heritage, has great significance.
The oldest book in the library of humans is the Rigveda The existence of the Vedas go beyond recorded history and are said to be passed down from the Gods to the great seers of Bharat. For many human generations the Vedas were passed on through word of mouth, until finally documented by the great Rishis and Swamis. 'The Vedas are written in Sanskrit, a complex language that Sir William Jones - in 1786 - demonstrated to be related to Greek, Latin, German and Celtic (giving rise to the expression 'Indo-European languages'). And if the Vedas speak of the Sarasvati River, then it would seem clear that they were written before about 2000 BC, and not later than 1500 BC, as scholars originally believed. And if - as seems likely - Sanskrit was the language of the Aryans, then it was also clear that they could not have invaded as late as 1500 BC. There are four major collections of Vedic hymns - the Rig-Veda, the Samaveda, the Yajurveda and the Atharvaveda, of which the Rigveda is recognized as the oldest and most important. In the 1980's, a Vedic scholar, David Frawley, observed that the hymns of the Rigveda are full of an oceanic symbolism that seems to argue that they sprang from the maritime culture - which certainly contradicted the assumption that the Aryans came from somewhere in central Europe. He also noted hymns that spoke of the 'ancestors' as coming from across the sea, having been saved from the great flood. Studying the astronomical references in the Vedic hymns, Frawley concluded that one reference to a summer solstice in Virgo indicated a date of about 4000 BC, while a reference to a summer solstice in Libra pointed to about 6000 BC. He also concluded that the authors of the Vedas were familiar with the precession of the equinoxes. These revolutionary ideas were set out in a book called Gods, Sages and Kings (1991). Mother of Martial Arts Do you know that Kalari is considered to be the most complete and scientific martial art and is the mother of all martial arts? Bodhidharma, a Buddhist monk from India, introduced Kalari into China and Japan in the 5th century. He taught this art in a temple This temple is today known as the Shaolin temple. The Chinese called him Po-ti-tama. What he taught has evolved into Karate and Kung Fu. One can find a lot of similarities among the three. Thus Judo, Karate, Kung Fu and other similar marshal arts which are today identified with the far-east actually originated from India. At times the changes made in the original nature of the Indian sport-forms were so many and so fundamental that the game lost all similarity with its original form in India. Some Indian games were not transmitted abroad and remained confined to India. For instance we have Kabbadi, Kho-Kho, AtyaPatya, Malkhamb, Gulli-danda, etc., which are being played today exclusively in India. In this chapter we shall look into how the games like Chess and Ludo (Snakes and Ladders), the martial art of Karate, and Playing cards had existed in India for the past 2000 years and how in some cases the indigenous form of the game became totally extinct erasing the fact that the game had ever been played in India. The teacher here is not looked upon only as a coach as in western martial arts like boxing and fencing. This relationship between a teacher and student in Judo and Karate could have its roots in the Guru-Shishya tradition of India. Bharatanatyam Bharatanatyam is amongst the oldest of the classical dance forms of India, with a history that goes back more than two thousand years. Integrating elements of music, theater, poetry, sculpture, and literature, this multi-dimensional art has come down through the centuries, as part of a dynamic, vital, living tradition, that offers infinite scope for understanding and exploring the body, mind and spirit. Mother of all Higher Languages The Sanskrit language has helped shape many European languages including French, German, Russian, and English. It shows many ancient forms of words such as father, through, shampoo, trigonometry, and mouse, while guru, pundit, dharma, bandh, and yoga are among hundreds of Sanskrit words that can now be found in the Oxford dictionary.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Vedicmaths EbookDocument212 pagesVedicmaths Ebooksaurab83100% (9)
- A Review of Robotics in Onshore Oil-Gas Industry PDFDocument8 pagesA Review of Robotics in Onshore Oil-Gas Industry PDFAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Peshwa Bajirao I and Maratha ExpansionDocument258 pagesPeshwa Bajirao I and Maratha ExpansionAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Vaisnava CalendarDocument48 pagesVaisnava CalendarAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2: Topic: Motion Models and Robot OdometryDocument6 pagesSheet 2: Topic: Motion Models and Robot OdometryAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- MMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 5: Student Name Student IDDocument1 pageMMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 5: Student Name Student IDAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Seekur JRDocument2 pagesSeekur JRAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- MMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 4: Student Name Student IDDocument1 pageMMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 4: Student Name Student IDAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
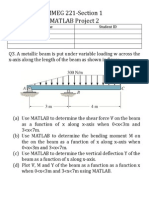
- MMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 2: Student Name Student IDDocument1 pageMMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 2: Student Name Student IDAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
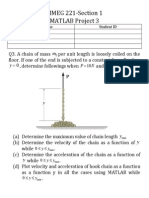
- MMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 3: 10N 0.2kg / MDocument1 pageMMEG 221 - Section 1 Matlab Project 3: 10N 0.2kg / MAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Course ID MEEG221 Course Name Engineering MATLAB Instructor Dr. Amit Shukla Section 01Document1 pageCourse ID MEEG221 Course Name Engineering MATLAB Instructor Dr. Amit Shukla Section 01Amit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2: Script FileDocument3 pagesProblem 2: Script FileAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- The Vedānta-Philosophy Described by Bhavya in His MadhyamakahrdayaDocument16 pagesThe Vedānta-Philosophy Described by Bhavya in His Madhyamakahrdayacha072No ratings yet
- Customer Name Industry Contact Person NameDocument12 pagesCustomer Name Industry Contact Person NameAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Music of Indonesia - PDFDocument19 pagesMusic of Indonesia - PDFbidowa1895No ratings yet
- Guieline FullDocument460 pagesGuieline FullArohi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Evolution of Hindu ArchitectureDocument112 pagesUnit 3 - Evolution of Hindu Architecturearchitectfemil6663No ratings yet
- KaulaDocument10 pagesKaulaDamon MontclareNo ratings yet
- Ganpati Aarti Sukhkarta Dukhharta Download PDFDocument1 pageGanpati Aarti Sukhkarta Dukhharta Download PDFpoonam mehraNo ratings yet
- About The Institution: Department of ECEDocument2 pagesAbout The Institution: Department of ECESelva KumarNo ratings yet
- The Upside-Down King Unusual Tales About Rama and Krishna (Murty, Sudha)Document160 pagesThe Upside-Down King Unusual Tales About Rama and Krishna (Murty, Sudha)Rasputin Rasputin100% (2)
- Second Entrance Result 2074Document11 pagesSecond Entrance Result 2074Sachin Chakradhar0% (1)
- 33 VOICE Newsletter May 19 PDFDocument11 pages33 VOICE Newsletter May 19 PDFYadavkurlagunda LavanyaykNo ratings yet
- Non WovenDocument7 pagesNon WovenRaveesh MittalNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Indian Chemical Council Icc Executive Commette PDFDocument20 pagesVdocuments - MX - Indian Chemical Council Icc Executive Commette PDFBhavin SagarNo ratings yet
- List of All Publications With The KRI Seal of Approval: Name of Publication Yoga and Meditation ManualsDocument3 pagesList of All Publications With The KRI Seal of Approval: Name of Publication Yoga and Meditation ManualsRosely PereiraNo ratings yet
- Contacts With The Gods From Space Free ExtractDocument44 pagesContacts With The Gods From Space Free Extractrajeshiitd0% (1)
- Designing A TempleDocument138 pagesDesigning A Templebaabjitvk100% (1)
- Tinkle 185Document36 pagesTinkle 185Ved PatelNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Lesson 3: The Human Body As An Embodied SpiritDocument27 pagesPhilosophy Lesson 3: The Human Body As An Embodied SpiritLeigh MNo ratings yet
- Area Wise Onboarding As On 04062021Document87 pagesArea Wise Onboarding As On 04062021himanshu ranjanNo ratings yet
- J Rajaram PDFDocument3 pagesJ Rajaram PDFEmrald ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Submission of Loc by Schools Comptt. 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesSubmission of Loc by Schools Comptt. 2019 PDFBaharul IslamNo ratings yet
- Zoroastrianism in AzerbaijanDocument12 pagesZoroastrianism in AzerbaijanUlvi YusifliNo ratings yet
- Dharma DevataDocument4 pagesDharma DevataRakesh VenaktachalamNo ratings yet
- A Sordid Reality in the World of Dalits- a Critical Study of Mulk Raj Anand’s Coolie and Untouchable With an Evaluation of Wretched Condition in Arundhati Roy’s the God of Small Things by Mukesh KumarDocument6 pagesA Sordid Reality in the World of Dalits- a Critical Study of Mulk Raj Anand’s Coolie and Untouchable With an Evaluation of Wretched Condition in Arundhati Roy’s the God of Small Things by Mukesh Kumarijr_journalNo ratings yet
- Transgressive Territories - Queer Space in Indian Fiction and FilmDocument196 pagesTransgressive Territories - Queer Space in Indian Fiction and FilmPrantik BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ReduplicationDocument21 pagesReduplicationBrinzei Lucian100% (1)
- Annamayya kIRTHISDocument15 pagesAnnamayya kIRTHISkjegadeeshNo ratings yet
- Himachal Pradesh HP State Coop. M & C Fed. Ltd. (Himfed)Document1 pageHimachal Pradesh HP State Coop. M & C Fed. Ltd. (Himfed)ASHUOSH RANANo ratings yet
- Surya Namaskar, The 11000 Year Old Vedic Sun Salutation - Capt Ajit VadakayilDocument21 pagesSurya Namaskar, The 11000 Year Old Vedic Sun Salutation - Capt Ajit VadakayilAMITH OKNo ratings yet