Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Albuterol Ventolin
Albuterol Ventolin
Uploaded by
Kristi WrayCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Astm C 423Document12 pagesAstm C 423Abhinav AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Jabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListDocument2 pagesJabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListClarence Clar100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainDanielJosephLimNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 pageAdacel Tdap VaccineKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Wiring Diagram Elevator: 123/INDSBY-ELC/1014Document22 pagesWiring Diagram Elevator: 123/INDSBY-ELC/1014Gogik Anto85% (13)
- Senior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteDocument7 pagesSenior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteNicole De AsisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- MotiliumDocument5 pagesMotiliumAkram KhanNo ratings yet
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument4 pagesKetorolacx483xDNo ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityAthena SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKorina FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNadineNo ratings yet
- Dysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseDocument5 pagesDysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseRam Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Advisory No. 12 (CV-CHD Vaccination Operation Center) : Cagayan Valley Center For Health DevelopmentDocument7 pagesAdvisory No. 12 (CV-CHD Vaccination Operation Center) : Cagayan Valley Center For Health Developmentmaria_abigailNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Immune Globulin: Deanzel Jade TrazonaDocument9 pagesTetanus Immune Globulin: Deanzel Jade TrazonaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- LansoprazoleDocument3 pagesLansoprazoleJody FelizioNo ratings yet
- NCP HemorrhoidsDocument2 pagesNCP Hemorrhoidsnurse_yramenaj0% (1)
- 3 Drug Study & 1 NCPDocument4 pages3 Drug Study & 1 NCPAnnie Christine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CholangioDocument10 pagesDrug Study - CholangioClaireMutiaNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP For AsthmawaadNo ratings yet
- Duodart: Dutasteride-Tamsulosin HydrochlorideDocument23 pagesDuodart: Dutasteride-Tamsulosin HydrochlorideYessy AndikaNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management .Document9 pagesCrisis Management .jeromeNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl (Dulcolax)Document1 pageBisacodyl (Dulcolax)ENo ratings yet
- Acute Concept Map 2 FinalDocument1 pageAcute Concept Map 2 FinalCynthia LeonNo ratings yet
- ActemraDocument7 pagesActemraLinda KvastadNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- Medical Ward Drug StudyDocument9 pagesMedical Ward Drug StudygorgeazNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug Studysandal_meenuNo ratings yet
- Mu CostaDocument6 pagesMu Costafarracholidia_867630No ratings yet
- MARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPDocument6 pagesMARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPMary grace VirayNo ratings yet
- Tamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument23 pagesTamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateGénesis GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Case Study ExampleDocument11 pagesCase Study ExampleMargeaux Deb Bartholomew CarleNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- What Is Prednisolone?Document12 pagesWhat Is Prednisolone?Chandni SeelochanNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 pagesAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument5 pagesLoperamideErick TriardiantoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plansarah hanaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDocument1 pageNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Case 1Document9 pagesModule 3 - Case 1Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: StoDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: Stoluisa bautistaNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyMark_Rebibis_8528No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJoevelyn LaynoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans ...Document16 pagesNursing Care Plans ...Santos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyJannine Bensi100% (1)
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument3 pagesTheoretical FrameworkLinus Dewey100% (1)
- Operating Room Case StudyDocument8 pagesOperating Room Case StudyJames Daniel Codamon100% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Asthma 2 Copd 2Document6 pagesAsthma 2 Copd 2Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument7 pagesGeneric NameGia Bautista-AmbasingNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument2 pagesSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNo ratings yet
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Document1 pageCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Ceftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeDocument3 pagesCeftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixDocument2 pagesClopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Clonazepam KlonopinDocument3 pagesClonazepam KlonopinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 pagesCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 pageCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine AdderallDocument2 pagesAmphetamine AdderallKristi Wray100% (1)
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 pagesAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Baclofen KemstroDocument2 pagesBaclofen KemstroKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam XanaxDocument2 pagesAlprazolam XanaxKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen TylenolDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen TylenolKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- HVLDocument44 pagesHVLlogofwood6858100% (2)
- Common Prospectus EnglishDocument293 pagesCommon Prospectus Englishven23No ratings yet
- VDRLDocument4 pagesVDRLfarazhussainkhanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The Lasing Quality of Diode Lasers by Anti-Reflective CoatingDocument21 pagesOptimizing The Lasing Quality of Diode Lasers by Anti-Reflective CoatingDannyNo ratings yet
- Maunakea Brochure C SEED and L Acoustics CreationsDocument6 pagesMaunakea Brochure C SEED and L Acoustics Creationsmlaouhi MajedNo ratings yet
- Tivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationDocument53 pagesTivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationSABRINE KHNo ratings yet
- EEET423L Final ProjectDocument7 pagesEEET423L Final ProjectAlan ReyesNo ratings yet
- HSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Document5 pagesHSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Snehal PanchalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Sample PaperDocument6 pagesClass 12 Sample PaperAaditya Vignyan VellalaNo ratings yet
- IIA IPPF PG - Quality Assurance and Improvement Program March 2012Document29 pagesIIA IPPF PG - Quality Assurance and Improvement Program March 2012Denilson MadaugyNo ratings yet
- ASTM D8210 - 19bDocument13 pagesASTM D8210 - 19bmancjaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Assignment - Jenny, Joanna, Ling PrintDocument28 pagesAuditing Assignment - Jenny, Joanna, Ling PrintJoanna EveNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Ethanol Production From Coffee Husks: Biotechnology Letters June 2009Document6 pagesFeasibility of Ethanol Production From Coffee Husks: Biotechnology Letters June 2009Jher OcretoNo ratings yet
- 2021-01-01 Good Organic GardeningDocument110 pages2021-01-01 Good Organic GardeningValéria GarcezNo ratings yet
- Linx Enterprise: Getting Results GuideDocument56 pagesLinx Enterprise: Getting Results GuideSaadullah SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Subdivision of LandDocument6 pagesSubdivision of Land林诗倩No ratings yet
- HUAWEI - SUN2000-20-40KTL-M3-UserManual GCADocument102 pagesHUAWEI - SUN2000-20-40KTL-M3-UserManual GCAReardon MetalsNo ratings yet
- VP3401 As04Document2 pagesVP3401 As04shivamtyagi68637No ratings yet
- March 16 - IM Processors DigiTimesDocument5 pagesMarch 16 - IM Processors DigiTimesRyanNo ratings yet
- Tle 7-1st Periodic TestDocument2 pagesTle 7-1st Periodic TestReymart TumanguilNo ratings yet
- APA-AP - Activity 3-Emerging Ethical and Policy Issues of STSDocument36 pagesAPA-AP - Activity 3-Emerging Ethical and Policy Issues of STSJOHN MARTIN APA-APNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection Act - SeminarDocument16 pagesConsumer Protection Act - SeminarAbdul KhadeerNo ratings yet
- Bydf3 ElectricDocument61 pagesBydf3 ElectricIvan Avila100% (1)
- ACCA P5 Question 2 June 2013 QaDocument4 pagesACCA P5 Question 2 June 2013 QaFarhan AlchiNo ratings yet
- SPE 163723 Pressure Transient Analysis of Data From Permanent Downhole GaugesDocument24 pagesSPE 163723 Pressure Transient Analysis of Data From Permanent Downhole GaugesLulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledelleNo ratings yet
Albuterol Ventolin
Albuterol Ventolin
Uploaded by
Kristi WrayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Albuterol Ventolin
Albuterol Ventolin
Uploaded by
Kristi WrayCopyright:
Available Formats
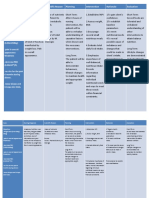
Generic Name albuterol
Trade Name Ventolin
Peak 0.52 h
Onset 515 min
Classification Dose Route BRONCHODILA 90mcg Inhaled TOR (RESPIRATORY SMOOTH MUSCLE RELAXANT); BETAADRENERGIC AGONIST Duration Normal dosage range 36 h 12 inhalations q46h
Time/frequency q6h
Why is your patient getting this medication Being used as PRN for shortness of breath.
For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Mechanism of action and indications (Why would this med be ordered) Moderately selective beta2-adrenergic agonist with comparatively long action. Acts prominently on beta2 receptors (particularly smooth muscles of trachea, bronchi, uterus, and vascular supply to skeletal muscles). Inhibits histamine release by mast cells. Produces bronchodilation by relaxing smooth muscles of bronchial tree. Bronchodilation decreases airway resistance, facilitates mucous drainage, and increases vital capacity.
Nursing Implications (what to focus on) Contraindications/warnings/interactions CONTRAINDICATIONS Albuterol or levalbuterol hypersensitivity; congenital long QT syndrome. Use of oral syrup in children younger than 2 CAUTIOUS USE Cardiovascular disease, renal impairment, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, elderly, history of seizures; hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines or to fluorocarbon propellant used in inhalation aerosols; pregnancy ( category C). INTERACTIONS With epinephrine, other SYMPATHOMIMETIC BRONCHODILATORS, possible additive effects; MAO INHIBITORS, TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS potentiate action on vascular system; BETAADRENERGIC BLOCKERS antagonize the effects of both drugs. Common side effects Body as a Whole: Hypersensitivity reaction. CNS: Tremor, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, convulsions, weakness, headache, hallucinations.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) Seroquel: There is some concern that quetiapine may have additive adverse cardiovascular effects in combination with other drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval of the electrocardiogram.
CV: Palpitation, hypertension, hypotension, bradycardia, reflex tachycardia. Special Senses: Blurred vision, dilated pupils. GI: Nausea, vomiting. Other: Muscle cramps, hoarseness. Lab value alterations caused by medicine Transient small increases in plasma glucose may occur. Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication Review directions for correct use of medication and inhaler. Avoid contact of inhalation drug with eyes. Do not increase number or frequency of inhalations without advice of physician. Notify physician if albuterol fails to provide relief because this can signify worsening of pulmonary function and a reevaluation of condition/therapy may be indicated. Albuterol can cause dizziness or vertigo; take necessary precautions. Do not use OTC drugs without physician approval. Many medications (e.g., cold remedies) contain drugs that may intensify albuterol action. Evaluation Check after giving Monitor therapeutic effectiveness which is indicated by significant subjective improvement in pulmonary function within 6090 min after drug administration. Monitor for: S&S of fine tremor in fingers, which may interfere with precision handwork; CNS stimulation, particularly in children 26 y, (hyperactivity, excitement, nervousness, insomnia), tachycardia, GI symptoms. Report promptly to physician. Lab tests: Periodic ABGs, pulmonary functions, and pulse oximetry. Consult physician about giving last albuterol dose several hours before bedtime, if drug-induced insomnia is a problem.
Nursing Process- Assessment (Pre-administration assessment) 1. Assess lung sounds, pulse, and blood pressure before administration and during peak of administration. 2. Monitor pulmonary function tests. 3. Observe for wheezing.
Assessment Why would you hold or not give this med? Undesirable side effects.
You might also like
- Astm C 423Document12 pagesAstm C 423Abhinav AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Jabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListDocument2 pagesJabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListClarence Clar100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainDanielJosephLimNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 pageAdacel Tdap VaccineKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Wiring Diagram Elevator: 123/INDSBY-ELC/1014Document22 pagesWiring Diagram Elevator: 123/INDSBY-ELC/1014Gogik Anto85% (13)
- Senior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteDocument7 pagesSenior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteNicole De AsisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- MotiliumDocument5 pagesMotiliumAkram KhanNo ratings yet
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument4 pagesKetorolacx483xDNo ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityAthena SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKorina FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNadineNo ratings yet
- Dysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseDocument5 pagesDysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseRam Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Advisory No. 12 (CV-CHD Vaccination Operation Center) : Cagayan Valley Center For Health DevelopmentDocument7 pagesAdvisory No. 12 (CV-CHD Vaccination Operation Center) : Cagayan Valley Center For Health Developmentmaria_abigailNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Immune Globulin: Deanzel Jade TrazonaDocument9 pagesTetanus Immune Globulin: Deanzel Jade TrazonaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- LansoprazoleDocument3 pagesLansoprazoleJody FelizioNo ratings yet
- NCP HemorrhoidsDocument2 pagesNCP Hemorrhoidsnurse_yramenaj0% (1)
- 3 Drug Study & 1 NCPDocument4 pages3 Drug Study & 1 NCPAnnie Christine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CholangioDocument10 pagesDrug Study - CholangioClaireMutiaNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP For AsthmawaadNo ratings yet
- Duodart: Dutasteride-Tamsulosin HydrochlorideDocument23 pagesDuodart: Dutasteride-Tamsulosin HydrochlorideYessy AndikaNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management .Document9 pagesCrisis Management .jeromeNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl (Dulcolax)Document1 pageBisacodyl (Dulcolax)ENo ratings yet
- Acute Concept Map 2 FinalDocument1 pageAcute Concept Map 2 FinalCynthia LeonNo ratings yet
- ActemraDocument7 pagesActemraLinda KvastadNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- Medical Ward Drug StudyDocument9 pagesMedical Ward Drug StudygorgeazNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug Studysandal_meenuNo ratings yet
- Mu CostaDocument6 pagesMu Costafarracholidia_867630No ratings yet
- MARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPDocument6 pagesMARY GRACE (CHN) Final Presentation For FNCPMary grace VirayNo ratings yet
- Tamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument23 pagesTamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateGénesis GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Case Study ExampleDocument11 pagesCase Study ExampleMargeaux Deb Bartholomew CarleNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- What Is Prednisolone?Document12 pagesWhat Is Prednisolone?Chandni SeelochanNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 pagesAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument5 pagesLoperamideErick TriardiantoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plansarah hanaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDocument1 pageNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Case 1Document9 pagesModule 3 - Case 1Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: StoDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cue: Sto: Stoluisa bautistaNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyMark_Rebibis_8528No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJoevelyn LaynoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans ...Document16 pagesNursing Care Plans ...Santos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyJannine Bensi100% (1)
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument3 pagesTheoretical FrameworkLinus Dewey100% (1)
- Operating Room Case StudyDocument8 pagesOperating Room Case StudyJames Daniel Codamon100% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Asthma 2 Copd 2Document6 pagesAsthma 2 Copd 2Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument7 pagesGeneric NameGia Bautista-AmbasingNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument2 pagesSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNo ratings yet
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Document1 pageCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Ceftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeDocument3 pagesCeftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixDocument2 pagesClopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Clonazepam KlonopinDocument3 pagesClonazepam KlonopinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 pagesCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 pageCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine AdderallDocument2 pagesAmphetamine AdderallKristi Wray100% (1)
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 pagesAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Baclofen KemstroDocument2 pagesBaclofen KemstroKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam XanaxDocument2 pagesAlprazolam XanaxKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen TylenolDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen TylenolKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- HVLDocument44 pagesHVLlogofwood6858100% (2)
- Common Prospectus EnglishDocument293 pagesCommon Prospectus Englishven23No ratings yet
- VDRLDocument4 pagesVDRLfarazhussainkhanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The Lasing Quality of Diode Lasers by Anti-Reflective CoatingDocument21 pagesOptimizing The Lasing Quality of Diode Lasers by Anti-Reflective CoatingDannyNo ratings yet
- Maunakea Brochure C SEED and L Acoustics CreationsDocument6 pagesMaunakea Brochure C SEED and L Acoustics Creationsmlaouhi MajedNo ratings yet
- Tivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationDocument53 pagesTivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationSABRINE KHNo ratings yet
- EEET423L Final ProjectDocument7 pagesEEET423L Final ProjectAlan ReyesNo ratings yet
- HSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Document5 pagesHSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Snehal PanchalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Sample PaperDocument6 pagesClass 12 Sample PaperAaditya Vignyan VellalaNo ratings yet
- IIA IPPF PG - Quality Assurance and Improvement Program March 2012Document29 pagesIIA IPPF PG - Quality Assurance and Improvement Program March 2012Denilson MadaugyNo ratings yet
- ASTM D8210 - 19bDocument13 pagesASTM D8210 - 19bmancjaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Assignment - Jenny, Joanna, Ling PrintDocument28 pagesAuditing Assignment - Jenny, Joanna, Ling PrintJoanna EveNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Ethanol Production From Coffee Husks: Biotechnology Letters June 2009Document6 pagesFeasibility of Ethanol Production From Coffee Husks: Biotechnology Letters June 2009Jher OcretoNo ratings yet
- 2021-01-01 Good Organic GardeningDocument110 pages2021-01-01 Good Organic GardeningValéria GarcezNo ratings yet
- Linx Enterprise: Getting Results GuideDocument56 pagesLinx Enterprise: Getting Results GuideSaadullah SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Subdivision of LandDocument6 pagesSubdivision of Land林诗倩No ratings yet
- HUAWEI - SUN2000-20-40KTL-M3-UserManual GCADocument102 pagesHUAWEI - SUN2000-20-40KTL-M3-UserManual GCAReardon MetalsNo ratings yet
- VP3401 As04Document2 pagesVP3401 As04shivamtyagi68637No ratings yet
- March 16 - IM Processors DigiTimesDocument5 pagesMarch 16 - IM Processors DigiTimesRyanNo ratings yet
- Tle 7-1st Periodic TestDocument2 pagesTle 7-1st Periodic TestReymart TumanguilNo ratings yet
- APA-AP - Activity 3-Emerging Ethical and Policy Issues of STSDocument36 pagesAPA-AP - Activity 3-Emerging Ethical and Policy Issues of STSJOHN MARTIN APA-APNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection Act - SeminarDocument16 pagesConsumer Protection Act - SeminarAbdul KhadeerNo ratings yet
- Bydf3 ElectricDocument61 pagesBydf3 ElectricIvan Avila100% (1)
- ACCA P5 Question 2 June 2013 QaDocument4 pagesACCA P5 Question 2 June 2013 QaFarhan AlchiNo ratings yet
- SPE 163723 Pressure Transient Analysis of Data From Permanent Downhole GaugesDocument24 pagesSPE 163723 Pressure Transient Analysis of Data From Permanent Downhole GaugesLulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledelleNo ratings yet