Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Sci 105: Microbiology: Laboratory Activities
Bio Sci 105: Microbiology: Laboratory Activities
Uploaded by
Nerissa Dadores-PagayunanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Sci 105: Microbiology: Laboratory Activities
Bio Sci 105: Microbiology: Laboratory Activities
Uploaded by
Nerissa Dadores-PagayunanCopyright:
Available Formats
Western Philippines University Puerto Princesa Campus Puerto Princesa City
BIO SCI 105: MICROBIOLOGY
LABORATORY ACTIVITIES
Submitted to: Mrs. Violeta T. Bargoyo
Submitted by: Nerissa Mae F. Dadores BSED II
LABORATORY ACTIVITY 1 The Compound Microscope
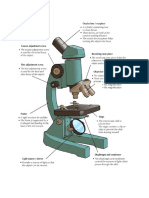
Results: 1. Tabulate the parts of a microscope and function of each part.
Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus. Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen. Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed. Stage clips: Metal clips that hold the slide in place. Stage height adjustment (Stage Control): These knobs move the stage left and right or up and down. Aperture: The hole in the middle of the stage that allows light from the illuminator to reach the specimen. On/off switch: This switch on the base of the microscope turns the illuminator off and on. Illumination/ Light Source: The light source for a microscope. Older microscopes used mirrors to reflect light from an external source up through the bottom of the stage; however, most microscopes now use a low-voltage bulb. Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen. Condenser: Gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed. Eyepiece/ Oculars: The eyepiece is the ocular lens that helps you look through to see a magnified image from the top of the microscope. The lens has a power of magnification of about 10x or 15x. Low Power Objective Lens: The low power objective helps in viewing large specimens. High Power Objective: These are used for a detailed view of the specimen and small specimens. Body tube (Head): The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Arm: The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope. Filter holder and filters: Some microscopes (like our Home 1000x) come with a swing-out filter holder at the bottom of the condenser. Blue and yellow filters can be used to enhance the image in some situations. Mechanical stage: This fits onto the stage (in some microscopes it is built in) and provides the best slide control, which makes viewing easier. Clip the slide into place and use the X and Y-axis knobs on the stage to move the slide back and forth under the objective lens. 2. Draw the position of the letter e as viewed under LPO and HPO. Compare the size. Give the total magnification of each drawing.
3. Draw several cells from the viewed prepared slides under LPO and HPO. Give the total magnification of each one.
Discussions (Guide questions) 1. For what purpose would you adjust each of the following components during a microscopy exercise? a. Iris Diaphragm-controls the amount of light that passes through the stage and, consequently, through the specimen. Reducing the iris diaphragm aperture increases contrast for an image focused under high power by reducing the amount of light that both fills the objective lens and detracts around specimen edges. Opening the iris diaphragm under high magnification increases "flare", the appearance of light "washing out" an object. By decreasing the flow of light through the specimen, the iris diaphragm limits light defraction and saturation. b. Coarse Adjustment Knob- This knob helps in focusing the specimen by adjusting the distance of the objective lens to the slide. The knob helps move the objective lens up and down till the magnified image is seen clearly. To raise or lower the body tube of the microscope.Fine
c. Adjust Knob-This helps in switching from one objective lens to the other. The specimen can be easily observed under high or low magnification with the adjustment using fine adjust knob. Use to bring specimen into sharp focus. d. Condenser- Clearly gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed. 2. Explain why the body tube of the microscope should not be lowered while looking through the ocular lens? The body tube of the microscope should not be lowered while looking through the ocular lens because you do not want to lower the body tube too much and have it crack the slide. There's a chance that you might crunch the objective lens into the slide or specimen.
3. What is xylol? Why it is used in the microscope?
Xylol is a colorless flammable volatile liquid hydrocarbon used as a solvent. Since it is a solvent it is usually used in laboratory in cleaning microscope lenses. It is used in cleaning microscope because it is polar solvent and can degrade the lens if lens left on for too long.
Conclusion:
References:
You might also like
- Lab1 LASER TransmittersDocument9 pagesLab1 LASER TransmittersManuel Fernando Santofimio Tovar0% (2)
- Biology Practical 2Document8 pagesBiology Practical 2N.THEVANo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 MicrosDocument5 pagesExercise No 1 MicrosJm Gutierrez0% (1)
- 5.30.Intro-Optics and PinholeDocument2 pages5.30.Intro-Optics and PinholeDaniel RoranzawaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 No. 2Document11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 No. 2Myles ElarcosaNo ratings yet
- Act 1 Microscope As A Biological ToolDocument14 pagesAct 1 Microscope As A Biological ToolSidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory IIDocument9 pagesLaboratory IIDecemei CuaboNo ratings yet
- EXP1Document8 pagesEXP1Marife CompraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 MicrosDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 Microscharles mepaniaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document10 pagesActivity 1Lovely Krish RazNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument6 pages1 MicroscopeAntonio Charisma100% (1)
- Sci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3Document6 pagesSci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3AlibabaNo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #1Document3 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #1Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 1Document6 pagesLab Act 1Marwin Rivarez Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 Microscope: Layka M. Sabdani BSMT 3 ZoologyDocument4 pagesActivity #1 Microscope: Layka M. Sabdani BSMT 3 ZoologyRaniaNo ratings yet
- MICROSDocument10 pagesMICROSBikram MondalNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Worksheet 3Document8 pagesGen Bio 1 Worksheet 3JJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises For BiologyDocument13 pagesLab Exercises For BiologyMari SoleiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 - Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesLab Report 2 - Cell Biologya.krakulli23No ratings yet
- Zoology Lab Activity 1 Letter EDocument7 pagesZoology Lab Activity 1 Letter EChen NnineNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument9 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 1Document10 pagesBZ Lab 1Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Ekaterina 6b MicroscopesDocument19 pagesEkaterina 6b Microscopesapi-269598196No ratings yet
- 8th 2023-III-LAB3 Using A MicroscopeDocument5 pages8th 2023-III-LAB3 Using A MicroscopeFelipe MNo ratings yet
- Module in ScienceDocument6 pagesModule in Sciencenasser pazaulan12No ratings yet
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their Functionsiammiiie0167% (3)
- Virtual Lab 1. Introduction To The Microscope: Senior High School DepartmentDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab 1. Introduction To The Microscope: Senior High School Departmentbabalo loNo ratings yet
- 01 Zoology MicrosDocument10 pages01 Zoology MicrosJohn AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesMicroscope Parts and Their FunctionsNica PinedaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Act 2 Bot LabDocument3 pagesAct 2 Bot LabAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1Kathy Mae Morales Forcadilla - DaclanNo ratings yet
- GBGuidelineDocument106 pagesGBGuidelinedoskuuunNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument5 pagesMicroscopeDinnich aaNo ratings yet
- Carol - THE MICROSCOPEDocument20 pagesCarol - THE MICROSCOPEmaryllaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab ReportDocument10 pagesMicroscope Lab ReportBrian Luo67% (3)
- Worksheet 1-Word FinalDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1-Word FinalPrince SalvaNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument30 pagesMicroscopy ReviewMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1.2: To Study Different Parts of MicroscopeDocument5 pagesWorksheet-1.2: To Study Different Parts of MicroscopeTej pattaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 Micros PDFDocument4 pagesExercise No 1 Micros PDFAlthea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 MicrosDocument4 pagesExercise No 1 MicrosAshley PapaNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2 LAB MODULE 1 WorksheetDocument7 pagesGENBIO2 LAB MODULE 1 Worksheetgnye20No ratings yet
- Module 1 - MicroscopeDocument4 pagesModule 1 - MicroscopeGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Microscopy: Exercise 1Document12 pagesMicroscopy: Exercise 1Adrelynx JoviNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Compound MicroscopeDocument2 pagesParts and Functions of Compound Microscopemydiamondstar17No ratings yet
- Assignment - Type of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesAssignment - Type of Microscopeuypaul97100% (1)
- Data Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeDocument7 pagesData Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeSohail SaripadaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A Compound MicroscopeKim Ashley Ballesteros100% (1)
- Introduction To Cell Biology: Senior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Cell Biology: Senior High School DepartmentJericho LindoNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 Microscopy 1Document5 pagesExercise No 1 Microscopy 1Diana BoladoNo ratings yet
- Microscope WorksheetDocument5 pagesMicroscope WorksheetDaxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- Jeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFDocument3 pagesJeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- 04 Microscope UseDocument3 pages04 Microscope Usepixiewinx20No ratings yet
- STE Biotechnology (Lesson 2) 0c0Document9 pagesSTE Biotechnology (Lesson 2) 0c0Sharon Cordova100% (1)
- Exercise 1 - The Microscope (BIO11A) - 1Document9 pagesExercise 1 - The Microscope (BIO11A) - 1EMNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document15 pagesLab 3aizen3881No ratings yet
- Compound Microscop EDocument26 pagesCompound Microscop EDixie MerinNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument12 pagesMicroscopeHEXALANE E. LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and MeaningDocument3 pagesMicroscope Parts and MeaningJhonLloyd DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 pagesLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Uv-Spectroscopy Handout by Vijaya Lakshmi Sada - pdf524Document13 pagesUv-Spectroscopy Handout by Vijaya Lakshmi Sada - pdf524manasjyotiray02186No ratings yet
- Electron MicrosDocument43 pagesElectron Microssmurali_sNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Antibonding OrbitalsDocument3 pagesBonding and Antibonding OrbitalsSara PereiraNo ratings yet
- Chem 10Document14 pagesChem 10Cao Thị Vân GiangNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Compound Microscope (Parts III and IV)Document11 pagesExercise 1 The Compound Microscope (Parts III and IV)BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Gr10 Ch13.4 TBDocument5 pagesGr10 Ch13.4 TBnr46jpdxbpNo ratings yet
- 2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Document175 pages2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Matter - MuldersDocument142 pagesThe Structure of Matter - MuldersJeremy MooreNo ratings yet
- Nirs Xds Rapidcontent Analyzer: Fast, Non-Destructive Analyses of Solid and Liquid SubstancesDocument4 pagesNirs Xds Rapidcontent Analyzer: Fast, Non-Destructive Analyses of Solid and Liquid SubstancesAlexNo ratings yet
- 110B - Chapter 13: Molecular SpectrosDocument26 pages110B - Chapter 13: Molecular SpectrosTuấn Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & Mole Concept (Question Paper)Document5 pagesAtomic Structure & Mole Concept (Question Paper)Param shahNo ratings yet
- 09 Particle in 1-D Box PDFDocument4 pages09 Particle in 1-D Box PDFSigit PriatmokoNo ratings yet
- Sprague Matthew Thesis App C PDFDocument26 pagesSprague Matthew Thesis App C PDFAniello LangellaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-5 Aim: To Study The Faraday Effect Using He-Ne Laser. Apparatus Required: Helium-Neon Laser, Axial Electromagnet With PowerDocument6 pagesExperiment-5 Aim: To Study The Faraday Effect Using He-Ne Laser. Apparatus Required: Helium-Neon Laser, Axial Electromagnet With PowerSarveena100% (2)
- Module 3: Physical ScienceDocument7 pagesModule 3: Physical ScienceBoycie F. TarcaNo ratings yet
- Exp. No. 16 Dynamic Light ScatteringDocument9 pagesExp. No. 16 Dynamic Light ScatteringLikhithNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 9tolisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 4 - B - Dual Nature of LightDocument18 pagesTutorial - 4 - B - Dual Nature of LightJasmine BahriNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 QuestionDocument12 pagesAssignment1 QuestionRubyat100% (1)
- Different Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesJhon Carlo Bataller Monleon100% (1)
- Hollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEDocument17 pagesHollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEsugapriya83% (6)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 9: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 9: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJanine Rocero100% (2)
- Sample Chapter On Optical and Surveying InstrumentsDocument23 pagesSample Chapter On Optical and Surveying Instrumentshaider100% (4)
- Modeling Molecules: Key Words: Chemical BondDocument4 pagesModeling Molecules: Key Words: Chemical BondAscendNo ratings yet
- 3D Holographic Projection TechnologyDocument32 pages3D Holographic Projection TechnologyPranay GoudaNo ratings yet
- Field Emission Scanning Electron Micros PDFDocument2 pagesField Emission Scanning Electron Micros PDFJenniferNo ratings yet
- Hamilton's OpticsDocument18 pagesHamilton's OpticsLoubnanNo ratings yet