Professional Documents
Culture Documents
#Anatomy of The Eye
#Anatomy of The Eye
Uploaded by
ameerabestOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
#Anatomy of The Eye
#Anatomy of The Eye
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright:
Available Formats
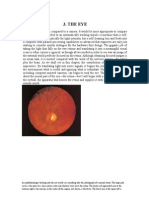
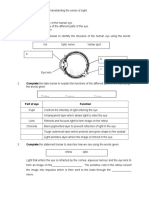
ANATOMY OF THE EYE
OUTER PROTECTIVE LAYER SCLERA CORNEA post 5/6 of outer layer anterior 1/6 of outer layer - whitish in adult - clear, transparent, - thin & bluish in children Avascular
CHOROID
MIDDLE UVEAL TRACT CILIARY BODY
thickness post equator recti insertion Apertures: Lamina cribrosa Anterior Middle
1 mm 0.6 mm 0.3mm
Posterior
Optic nerve Ant ciliary arteries Exit of 4-5 vortex veins Long & short ciliary N & Vs
horizontal 11.6 mm diameter vertical 10.6 mm diameter central 0.52 mm thickness peripheral 0.7 mm thickness anterior 7.8 mm curvature posterior 6.5 mm curvature refractive power : 42 D refractive index : 1.37 Nutrition from: - peri-limbal, episcleral Vs - aqueous humour O2 : directly from the air 1. Epithelium
- firmly attached to Bowmans layer
5-6 mm wide divided into PARS PLICATA anterior 1/3 2 mm 70 ciliary process
PARS PLANA posterior 2/3 4 mm
IRIS thin, contractile pigmented diaphragm, with central aperture(pupil) - root attached to anterior surface of CB anterior surface divided by collarette into - narrow inner zone (papillary zone) - wide outer zone ( ciliary zone)
INNER NERVOUS LAYER RETINA light sensitive layer
LENS - transparent - biconvex
Macula
Fovea
Optic disc
- 4.5 mm diameter - 3mm lateral to optic disc - 1.5 mm diameter - no BV, no rods - 1.5 mm diameter - 3 mm medial to macula
Radius of anterior curvature Radius of posterior curvature Diopteric power RI of cortex RI of nucleus
10 mm
6 mm
16 -18 D 1.38 1.42
Histo
1. Episclera 2. Sclera proper 3. Lamina fusca
2. Bowmans layer
- condensation of stroma lamellae 3. Stroma (90% of thickness)
1. Suprachoroidal lamina 2. Large-sized BVs 3. Medium-sized BVs 4. Capillaries (chorio-capillaris) 5. Bruchs membrane
1. Ciliary epithelium 2. Ciliary process produce aqueous 3. Stroma 4. Ciliary muscles
1. Stroma sphincter pupillae circular fiber in papillary zone parasympathetic constrict pupil light & near reflex dilator pupillae radial fiber ciliary zone sympathetic dilate pupil in intensity light & excess sympa actvty
4. Descemets membrane
- basement mbrane of endothelium - easily stripped from stroma
1. Pigment epithelium 2. Layer of rods & cones 3. External limiting layer 4. Outer nuclear layer 5. Outer molecular layer 6. Inner nuclear layer 7. Inter molecular layer 8. Ganglion cell layer 9. Nerve fiber layer 10. Internal limiting layer
1. Capsule 2. Lens epithelium 3. Lens fibers - cortex - nucleus
5. Endothelium
single layer of million cells
2. 2 layers of pigmented epithelium Fx 1. Protects intra-ocular structures 2. Preserve the shape of eyeball 3. Provide rigid insertion of EOM 1. Refraction of light *transparency by: - uniform spacing of collagen bundles - integrity of endothelium - Avascularity - UNmyelinated nerve fibers - uniform RI of epithelium, descemet membrane & endothelium Nourish the outer layer of retina 1. Production of aqueous humour 2. Accommodation 1. One of referactive media of the eye 2. Accommodation 3. Retinal protection from UV rays 4. Neutralize spherical & chromatic aberrations of the cornea
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Osama's Ophthalmology NotesDocument127 pagesOsama's Ophthalmology NotesMd. Abdullah Rumman100% (1)
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument30 pagesAnatomy of The Eyesukhi20mil100% (1)
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pages@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 pagesCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pages@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 pagesGenital EmbryologyameerabestNo ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 pagesSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestNo ratings yet
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pages#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- #MediastinumDocument4 pages#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- #LungDocument1 page#LungameerabestNo ratings yet
- Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)Document2 pagesExtracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)ameerabestNo ratings yet
- Parotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandDocument5 pagesParotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandameerabestNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus & StomachDocument3 pagesOesophagus & StomachameerabestNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Mouth Cavity, Palate, TongueDocument8 pagesMouth Cavity, Palate, Tongueameerabest100% (1)
- Bab 01 PDFDocument32 pagesBab 01 PDFAbdul Rahman B. NarawiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eyes: January 2009Document7 pagesAnatomy of Eyes: January 20091710105 Sean Rio SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Opthalmology NotesDocument43 pagesOpthalmology NotesKashif Khan100% (2)
- Dr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeDocument13 pagesDr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Santa Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Document10 pagesSanta Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Chapz PaczNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply, Nerve Supply and Lymphatics of The OrbitDocument28 pagesBlood Supply, Nerve Supply and Lymphatics of The OrbitPallavi Uday Naik100% (1)
- Estilistica 7Document13 pagesEstilistica 7Rafael Silva CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy PhysiologyDocument101 pagesOcular Anatomy PhysiologyĐạt VũNo ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDDocument20 pagesOcular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDMalek AldawimehNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Netra Sharir of Ayurveda in The Modern PerspectiveDocument10 pagesA Critical Review of Netra Sharir of Ayurveda in The Modern PerspectiveSambamurthi Punninnair NarayanNo ratings yet
- FIU - Eye AnatomyDocument23 pagesFIU - Eye AnatomyKira23406No ratings yet
- Estadística Básica AplicadaDocument742 pagesEstadística Básica AplicadaPaola González Mejía100% (1)
- Lens DislocationDocument13 pagesLens DislocationMuthia Fydiah JayantiNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity #3Document2 pagesAsynchronous Activity #3Gel VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyecarminaduriasNo ratings yet
- Vision: Physiology OF Vision and OpticsDocument7 pagesVision: Physiology OF Vision and OpticsMujahid Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument36 pagesThe EyeMuresan Radu CatalinNo ratings yet
- Eye & Ear Embryology ObjectivesDocument3 pagesEye & Ear Embryology ObjectivesDr. DNo ratings yet
- Example Eye EE PDFDocument46 pagesExample Eye EE PDFAva HalloranNo ratings yet
- 02 Introduction To The EyeDocument12 pages02 Introduction To The EyeMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Geriatric OptometryDocument57 pagesGeriatric OptometryMahendra singhNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The EyeDocument29 pagesEmbryology of The EyeBimo Juliansyah100% (1)
- L. Obj. 1.6Document2 pagesL. Obj. 1.6Lee DahlanNo ratings yet
- ROLE OF EYE - A CRUCIAL PATH IN HUMAN LIFE Divya Jonnala, D. Navya, D. Eswar TonyDocument4 pagesROLE OF EYE - A CRUCIAL PATH IN HUMAN LIFE Divya Jonnala, D. Navya, D. Eswar TonyiajpsNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tanpa PembahasanDocument56 pagesSkripsi Tanpa PembahasanPutri EmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Diseases of The UveaDocument102 pagesAnatomy and Diseases of The UveaVishakh IsloorNo ratings yet
- Development of EyeDocument37 pagesDevelopment of EyeshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 The Special SensesDocument8 pagesUnit 14 The Special SensesJess LNo ratings yet