Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quality Standards Manual Tightening Loads and Torques For Standard Metric Bolts and Foundation Bolts
Quality Standards Manual Tightening Loads and Torques For Standard Metric Bolts and Foundation Bolts
Uploaded by
gabriel_517180914Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quality Standards Manual Tightening Loads and Torques For Standard Metric Bolts and Foundation Bolts
Quality Standards Manual Tightening Loads and Torques For Standard Metric Bolts and Foundation Bolts
Uploaded by
gabriel_517180914Copyright:
Available Formats
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING LOADS AND TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS AND FOUNDATION BOLTS
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 1 of 6
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
CONTENTS
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 Scope....................................................................................................... 1 Strength designation system .................................................................... 1 Mechanical strength example................................................................... 1 Loads and Methods.................................................................................. 1 Torque Values.......................................................................................... 2 Table of Tightening Torques and Preloads............................................... 3 Table of Torques and Pre-loads for Civil Use ........................................... 5
1.0
Scope
This document provides recommended tightening forces and torques for standard metric bolts and screws and for foundation bolts. Recommendations are also provided for applications where a high strength bolt is screwed into a weaker material (e.g. an 8.8 bolt holding a wearplate onto an A1 cast steel housing)
2.0
Strength designation system
In accordance with ISO 898-1, the strength grade designation system for steel bolts and screws consists of two figures e.g. 4.6. The first figure indicates one hundredth of the nominal tensile strength in Newtons per square millimetre. The second indicates 10 times the ratio between lower yield stress RcL (or stress at 0.2% non-proportional elongation Rp0.2) and nominal tensile strength R m,nom (yield stress ratio). The multiplication of these two figures will give 1/10 of the yield stress in Newtons per square millimetre.
3.0
Mechanical strength example
The symbol 4 gives the nominal tensile strength = 100 X 4 = 400 N/mm2 The symbol .6 gives the lower yield stress = 0.6 X 400 = 240 N/mm2 Strength Grade Designation Nominal Tensile Strength Rm nom N/mm2 Nominal Lower yield stress ReL N/mm2 Nominal Stress at 0.2% nonproportional elongation Rp0.2 N/mm2 Stress under proof load Sp N/mm2 Ratio Sp/ ReL (Clause 5.9 of ISO 898-1) 4.6 400 240 225 0.94 6.8 600 480 440 0.92 8.8 800 640 600 0.91 12.9 1200 1080 970 0.88
4.0
Loads and Methods
The loads given in section 5.0 Table of Tightening Torques and Preloads are for static loading. If a soft material is in the joint, or if the nut strength does not match the bolt properties then a calculation is required. 1/ Determine the external loads and hence minimum preload for the bolts.
Issue / Revision Issue Date
ISSUE 1 NOV. 02
ISSUE 2 JULY 05
ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08
ISSUE 4 MARCH 10
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING LOADS AND TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS AND FOUNDATION BOLTS 2/ Determine size and number of bolts.
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 2 of 6
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
If the joint is subject to fatigue loads and is critical then this MathCAD calculation should be used:N:\TECHPROG\MATHCAD\v13\bolt.xmcd A help file can be found here: N:\TECHPROG\MATHCAD\v11\bolt.mcx Tightening methods can be divided into two types: axial and rotary (or torque). Torque based methods have poor accuracy as most of the torque goes into overcoming friction so a small change in friction means a big change in the axial force developed. Axial loading methods are preferred. These include hydraulic loading tools, hydraulic nuts, and load washers. Bolt extension can also be used.
5.0
Torque Values
Torque values are derived from this formula: T=CDF Where C = torque coefficient dependent on friction conditions D = Bolt diameter F = Preload C varies from 0.1 to 0.34 or more. For lubricated threads C=0.15. For as received threads C=0.20. The values in the tables use C=0.153 for compatibility with previous tables. If threads are not lubricated the preload will be lower than expected for a given torque. (Ref Design of Machine Elements 4th Edition VM Faires) The accuracy of the preload achieved using torque is 25% (Design Procedures DP6) For this reason one off use values based on torque have been removed from this issue. (One off uses 90% of the yield strength so an error of +25% would cause the bolt to yield.)
6.0
High Strength Threads Screwed into Weaker Materials
For critical applications, the method outlined in 4.0 Loads and Methods must be followed. For non critical applications, if a high strength screw or bolt is screwed into a lower strength material, the yield strength of the nut material should be used to determine the correct tightening force. An example is an 8.8 bolt screwed into a housing cast in EN10293 GE240. The bolt has a yield strength of 640 MN/m2 and the cast steel has a yield strength of 240 MN/m2 It can be seen that the yield strength of the cast steel is identical with the values for a 4.6 material, so the loading figures for 4.6 bolts should be used. If the cast steel was grade GE300 which has a yield strength of 300 MN/m2 then a ratio of the next highest value could be used. Comparing the yield strengths bolt grade 6.8 is the next strength grade up (480 MN/m2 ) If the bolt size is M16, then the torque table value is 94.9 Nm. Value to be used = 94.9 x 300/480 = 59 Nm. The stripping strength is non linear: increasing the depth of thread engagement does not give a linear increase in joint strength. Use the MathCAD calculation mentioned above if a check is needed for the stripping strength. Note that it is rare for a socket head capscrew to be used with a nut, and so the 12.9 values will not normally be required.
Issue / Revision Issue Date
ISSUE 1 NOV. 02
ISSUE 2 JULY 05
ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08
ISSUE 4 MARCH 10
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 3 of 6
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
7.0
Table of Tightening Torques and Preloads
This table does not apply to foundation bolts. Notes and larger bolt sizes are on the next page.
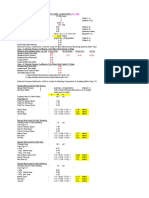
NOMINAL THREAD SIZE THREAD AREA (mm2) Pitch (mm) STRENGTH GRADE OF BOLTS & SCREWS 4.6 225 ONE OFF USE Preload kN 4.1 7.4 11.7 17.1 31.7 49.6 71.4 114 165 227 298 411 542 701 880 1132 1416 1732 2266 ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08 6.8 8.80 Stress under Proof Load from EN 898-1 Clause 5.9 440 600 ONE ONE OFF OFF RE-USE USE RE-USE USE Preload Torque Preload Preload Torque Preload kN Nm kN kN Nm kN 6.6 4.6 8.0 9.0 6.2 10.9 12.1 11.1 14.5 16.5 15.1 19.8 19.1 22.0 23.0 26.1 29.9 31.3 27.8 38.3 33.4 37.9 52.2 45.5 51.7 94.9 62.1 70.5 129 84.6 80.8 185 96.9 110 253 132 116 320 140 159 437 190 185 637 222 252 868 303 270 1113 323 368 1518 441 370 1783 444 504 2431 605 486 2678 583 663 3651 795 670 4305 804 914 5870 1096 883 6485 1060 1204 8844 1445 1142 9433 1370 1557 12863 1868 1434 13160 1720 1955 17945 2346 1845 19054 2214 2516 25983 3019 2308 26487 2770 3148 36119 3777 2823 35638 3388 3850 48597 4620 3693 52974 4432 5036 72237 6043 ISSUE 4 MARCH 10 12.9 970 ONE OFF USE Preload kN 17.5 32.0 50.6 73.6 137 214 308 489 713 979 1286 1772 2336 3020 3792 4881 6106 7469 9770
6 8 10 12 16 20 24 30 36 42 48 56 64 72 80 90 100 110 125 Issue / Revision Issue Date
20.1 36.6 58 84.3 156.7 244.8 352.5 560.6 816.7 1120.9 1473.1 2030 2676 3460 4344 5591 6995 8556 11191 ISSUE 1 NOV. 02
1 1.25 1.5 1.75 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
RE-USE Preload Torque kN Nm 3.4 2.3 6.2 5.7 9.8 11.2 14.2 19.6 26.4 48.5 41.3 94.8 59.5 164 94.6 326 138 569 189 912 249 1369 343 2201 452 3316 584 4824 733 6729 943 9743 1180 13544 1444 18224 1889 27089 ISSUE 2 JULY 05
RE-USE Preload Torque kN Nm 14.6 10.1 26.6 24.4 42.2 48.4 61.3 84.4 114 209 178 409 256 706 408 1404 594 2454 815 3930 1072 5903 1477 9490 1947 14297 2517 20795 3160 29012 4067 42005 5089 58392 6224 78565 8142 116784
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 4 of 6
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
NOMINAL THREAD SIZE THREAD AREA (mm2) Pitch (mm) STRENGTH GRADE OF BOLTS & SCREWS 4.6 225 ONE OFF USE Preload kN 2872 3790 2374 6.8 8.80 Stress under Proof Load from EN 898-1 Clause 5.9 440 600 ONE ONE OFF OFF RE-USE USE RE-USE USE Preload Torque Preload Preload Torque Preload kN Nm kN kN Nm kN 4680 75179 5616 6381 102516 7658 6176 113398 7412 8422 154634 10107 3869 55502 4643 5276 75684 6332 12.9 970 ONE OFF USE Preload kN 12380 16339 10236
140 160 125
14181 18716 11725
6 6 3
RE-USE Preload Torque kN Nm 2393 38444 3158 57988 1979 28381
RE-USE Preload Torque kN Nm 10317 165735 13616 249992 8530 122356
Note 1: These values are to be used unless other values are defined on the arrangement drawing. Note 2: If the male thread is screwed into a weaker material then the preloads must be reduced as defined in paragraph 6.0 High Strength Threads Screwed into Weaker Materials Note 3: The Re-use values are for bolts and screws which may be re-used during maintenance. These values are based on 75% of yield stress. Note 4: The one off use values are for bolts and screws which will be replaced after unscrewing following the initial tightening. These values are based on 90% of yield stress. Note 5: These values are for lubricated threads. Note 6: These values do not apply to foundation bolts.
Issue / Revision Issue Date
ISSUE 1 NOV. 02
ISSUE 2 JULY 05
ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08
ISSUE 4 MARCH 10
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 5 of 6
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
8.0
Table of Torques and Pre-loads for Civil Use
Admissible Force [kN] For pre-tensioning 4.6 grade steel Admissible Force [kN] For pre-tensioning 5.6 grade steel Tightening Method Anchoring f. FAr (2.) [kN] 36 57 82 113 148 205 270 349 438 564 705 862 1128 1429 1650 75% FAa Rotary Pre-tension f. FVr (4.) [kN] Rotary 59 94 137 188 247 341 450 581 730 939 1175 1437 1880 2382 2750 75%Fva Tighten. Torque MA (5.) [Nm] 217 432 756 1210 1818 2922 4402 6403 8933 12934 17979 24190 35958 51030 63116 0.153*D*FVr Direct Pull PreAnchoring f. tension f. FAa (2.) FVa (3.) [kN] [kN] Direct Pull 47 79 75 126 110 183 151 251 198 330 273 455 360 599 465 775 584 973 751 1252 940 1567 1150 1916 1504 2507 1906 3176 2200 3667 60% Fva 80% Proof
Bolt Dia
Pitch
ISO Stress Area Anchoring f. FAr (2.) [kN] 29 45 66 91 119 164 217 280 352 453 567 693 907 1149 1326 75% FAa
Tightening Method Rotary Pre-tension f. FVr (4.) [kN] Rotary 48 76 110 151 199 274 361 467 586 755 944 1155 1511 1914 2210 75%FVa Tighten. Torque MA (5.) [Nm] 175 347 607 972 1461 2348 3537 5145 7178 10393 14447 19439 28895 41007 50718 0.153*D*FVr Direct Pull Anchoring Pre-tension f. f. FAa (2.) FVa (3.) [kN] [kN] Direct Pull 38 63 61 101 88 147 121 202 159 265 219 365 289 482 374 623 469 782 604 1006 755 1259 924 1540 1209 2014 1532 2553 1768 2947 60% FVa 80% Proof
[mm] 24 30 36 42 48 56 64 72 80 90 100 110 125 140 150
[mm] 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0
[mm2] 353 561 817 1121 1473 2030 2676 3460 4344 5591 6995 8556 11191 14181 16370
See notes on next page
Issue / Revision Issue Date ISSUE 1 NOV. 02 ISSUE 2 JULY 05 ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08 ISSUE 4 MARCH 10
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
Prepared By
GROUP PART PAGE
QS12 1 6 of 6
QUALITY STANDARDS MANUAL TIGHTENING TORQUES FOR STANDARD METRIC BOLTS
R Donkin
Approved
J Roberts
Notes :1.) IMPORTANT - Bolt sizes M24 up to M150 must be to the figures indicated above, unless it is physically impossible to operate a pre-tensioning tool, in which case revert to conventional tightening. Exclusion - Roller Tables in general do not require pre-tensioning via hydraulic tool, conventional tightening is acceptable. This exclusion does not apply to the Roughing and Finishing Mill Main Entry & Exit tables. 2.) The admissible anchoring forces FA are applicable for tube anchor bolts of a 4.6 grade steel material. 3.) Admissible pre-tightening force at controlled pre-stressing of the bolt by direct pull tightening process 4.) Admissible pre-tightening force at controlled tightening of the bolt to their stated torque by the rotary tightening process. 5.) During the rotary tightening process, torsional and frictional moments occur as well as friction losses. These are attributable to the thread pitch, lubrication and surface conditions. The values stated for pre-tightening force and tightening torque take account of these factors when 75% of the yield strength of the 4.6 grade steel material is used. The accuracy of rotary tightening methods is less than that of direct pull methods, hence the lower allowable loads. 6.) The locknut must only be screwed on after the bolt has been pre-tensioned. 7.) The values of Fa assume a length to diameter ratio greater than 6. The allowable values drop if the ratio is lower. The values of Fa are designed to resist fatigue failure. If they are exceeded, no guarantee against fatigue failure can be given.
Issue / Revision Issue Date
ISSUE 1 NOV. 02
ISSUE 2 JULY 05
ISSUE 3 DECEMBER 08
ISSUE 4 MARCH 10
This standard is no longer controlled if copied from the network
You might also like
- CanRig Top Drive - 275T - Manual PDFDocument537 pagesCanRig Top Drive - 275T - Manual PDFNelly Beltrán Cuellar100% (2)
- Machine Design Elements and AssembliesFrom EverandMachine Design Elements and AssembliesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Kipor GeneratorDocument39 pagesKipor GeneratorWebdesign Webmasters87% (15)
- Torques PDFDocument2 pagesTorques PDFarmin_fernandez75% (4)
- Service Manual - 6198135m2gb Pre h100 1 3904Document652 pagesService Manual - 6198135m2gb Pre h100 1 3904abip201556% (9)
- 6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlDocument30 pages6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlcenicercNo ratings yet
- S70me-C8 5 PDFDocument397 pagesS70me-C8 5 PDFIgor Tabulynsky100% (1)
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet
- VRC 430 Operating InstructionsDocument40 pagesVRC 430 Operating Instructionsdstoic1No ratings yet
- Service Instruction For Servo Cylinder Type PBEDDocument2 pagesService Instruction For Servo Cylinder Type PBEDДжон Диллинджер100% (1)
- F 2054Document8 pagesF 2054yadu100% (1)
- Uncoated, Weldless, 2-And 3-Wire Steel Strand For Prestressed ConcreteDocument4 pagesUncoated, Weldless, 2-And 3-Wire Steel Strand For Prestressed ConcreteGustavo SuarezNo ratings yet
- 3948Document20 pages3948Jigneshkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- ARI Standard 780/790-1997, Definite Purpose and Limited Duty Definite Purpose Magnetic ContactorsDocument10 pagesARI Standard 780/790-1997, Definite Purpose and Limited Duty Definite Purpose Magnetic ContactorsEng-JRNo ratings yet
- Bolt Torque Chart - Portland BoltDocument6 pagesBolt Torque Chart - Portland BoltkNdashNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel - Torque Guidelines A2 & A4 - Grampian FastenersDocument1 pageStainless Steel - Torque Guidelines A2 & A4 - Grampian FastenerschandravadiyaketanNo ratings yet
- Informe Análisis Esfuerzos RuedaDocument33 pagesInforme Análisis Esfuerzos RuedaARS MECHANICA SAC César Ruiz OroscoNo ratings yet
- Collar EyeBolt To BS4278 Table 1Document9 pagesCollar EyeBolt To BS4278 Table 1Rajesh N Priya GopinathanNo ratings yet
- Sag Tension ReportDocument3 pagesSag Tension ReportKC ColinNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Journal BearingDocument3 pagesHydrodynamic Journal BearingJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- Torque EspiraladasDocument7 pagesTorque EspiraladasDanielDeFrancescoNo ratings yet
- MSM Series Brushless Servo Motor Manual: © 2003 Sheffield Automation, LLC. All Rights ReservedDocument11 pagesMSM Series Brushless Servo Motor Manual: © 2003 Sheffield Automation, LLC. All Rights Reservedsppa1No ratings yet
- SECTION 11 05 12 General Motor Requirements For Equipment Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionDocument4 pagesSECTION 11 05 12 General Motor Requirements For Equipment Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionRima Baz FadousNo ratings yet
- Tightening ForceDocument1 pageTightening ForceLuisLauShNo ratings yet
- 70 - Am5k Measuring Head User Manual 4-20ma RevhDocument37 pages70 - Am5k Measuring Head User Manual 4-20ma Revhbaggo81No ratings yet
- Hen ACSRDocument3 pagesHen ACSRkapilsharma404No ratings yet
- RS 385SHDocument3 pagesRS 385SHshahpinkalNo ratings yet
- Nadella - Needle BearingsDocument230 pagesNadella - Needle Bearingsג'ון ירוקNo ratings yet
- 1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Document4 pages1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- PDF Braking Resistor Calculation enDocument10 pagesPDF Braking Resistor Calculation enarc_cdsplNo ratings yet
- Laurus As Built BOP Part Numbers - UnlockedDocument166 pagesLaurus As Built BOP Part Numbers - UnlockedEstuardo OlanNo ratings yet
- Development of Shear-Key Consisted of Steel Disk and Anchor Bolt For Seismic RetrofittingDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Shear-Key Consisted of Steel Disk and Anchor Bolt For Seismic RetrofittingJothi ManiNo ratings yet
- TSKDocument4 pagesTSKar174_569868987No ratings yet
- EMF ResultsDocument6 pagesEMF ResultsRaghbendra JhaNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual DBDocument27 pagesTechnical Manual DBRentu Philipose100% (2)
- Screeing Method Fea FatigueDocument34 pagesScreeing Method Fea FatigueGokul Amarnath0% (1)
- New Standards For Transformers-Year 2022Document7 pagesNew Standards For Transformers-Year 2022salemg82No ratings yet
- Balancing Tip # 105 C D International, IncDocument3 pagesBalancing Tip # 105 C D International, IncAnonymous PVXBGg9TNo ratings yet
- Sag-Tension ReportDocument4 pagesSag-Tension ReportHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Fastrak Parts 333559 - 0510Document100 pagesFastrak Parts 333559 - 0510Mike Hunter-MallettNo ratings yet
- Sarpanta LemnDocument4 pagesSarpanta LemnEla TeodorescuNo ratings yet
- IRC5-IRB1400 Prod Man Part2 3HAC021111-001 - References - Rev - enDocument52 pagesIRC5-IRB1400 Prod Man Part2 3HAC021111-001 - References - Rev - enadriano_falavinha9186No ratings yet
- Gen00001-00 (PC400-7 Field Assembly Instruction)Document17 pagesGen00001-00 (PC400-7 Field Assembly Instruction)Ebrahim SabouriNo ratings yet
- MtE325-Assignment 3Document3 pagesMtE325-Assignment 3Hacker YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Section 429 Alternate Design Method: Not MM B To MinimumDocument7 pagesSection 429 Alternate Design Method: Not MM B To Minimumtabsze heyNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument25 pagesTorquesami4330100% (3)
- Drum Motor 80SDocument5 pagesDrum Motor 80SManekGorisNo ratings yet
- A 391 - A 391M - 98 Qtm5ms9bmzkxts1sruqDocument6 pagesA 391 - A 391M - 98 Qtm5ms9bmzkxts1sruqClaudia Patricia Magaña RabanalesNo ratings yet
- Clivet CCWG550EVD 550TR - 2 CompressorDocument7 pagesClivet CCWG550EVD 550TR - 2 CompressorniedhaNo ratings yet
- ActuatorDocument12 pagesActuatorDeepu RockzzNo ratings yet
- Kaiser 308A PDFDocument132 pagesKaiser 308A PDFCTN2010No ratings yet
- Method of Test FOR Compressive Deformation of Laminated BearingsDocument6 pagesMethod of Test FOR Compressive Deformation of Laminated Bearingsming_zhu10No ratings yet
- 124 - Bench Am5k Manual Standard 11-05-06Document100 pages124 - Bench Am5k Manual Standard 11-05-06Ayman MaezaNo ratings yet
- Bolt Torque ChartDocument6 pagesBolt Torque Chartsethu1091No ratings yet
- WSA 109 - Flange Assembly Torque Calculator v5Document12 pagesWSA 109 - Flange Assembly Torque Calculator v5MouchartStéphanieNo ratings yet
- Catalogo New PrecisionDrill ML HB r2 PDFDocument214 pagesCatalogo New PrecisionDrill ML HB r2 PDFDei AdrianzaNo ratings yet
- Specs Motor Grader Power TrainDocument52 pagesSpecs Motor Grader Power Trainkaswade Brian100% (1)
- Asanor Compact Iran 2 PDFDocument71 pagesAsanor Compact Iran 2 PDFSatisNo ratings yet
- Gosan - Barrel Coupling - AGBSDocument7 pagesGosan - Barrel Coupling - AGBSAndré RosolemNo ratings yet
- 1104d-E44ta sbl@96.5kw (Tpd1575e1)Document10 pages1104d-E44ta sbl@96.5kw (Tpd1575e1)pricopdaniel50% (2)
- Metal Forming: Processes and AnalysisDocument10 pagesMetal Forming: Processes and AnalysissadewaamNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial DrivesFrom EverandModel Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial DrivesNo ratings yet
- Surveying Activity 4-13 SuarezDocument14 pagesSurveying Activity 4-13 SuarezDante M Suarez Jr.No ratings yet
- Nanda ResumeDocument2 pagesNanda ResumeMac MillanNo ratings yet
- ADocument22 pagesAPrasun Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- ASTM A304-05e2 ÓÐÄ© Ë Ã Ð Ãí ÐÔÒ Çó ÄºÏ Ð Ö°ô Ä Ä Êõ Æ (Ó ÎÄ) PDFDocument50 pagesASTM A304-05e2 ÓÐÄ© Ë Ã Ð Ãí ÐÔÒ Çó ÄºÏ Ð Ö°ô Ä Ä Êõ Æ (Ó ÎÄ) PDFcvazquez999No ratings yet
- Time Delay CalculationsDocument16 pagesTime Delay Calculationsraghuramu23456100% (1)
- DAT Belt ConveyorDocument8 pagesDAT Belt ConveyorEDUARDONo ratings yet
- SC CalculationsDocument97 pagesSC CalculationsshrieersNo ratings yet
- WSTP 112ME: Metrology and Benchwork: Learning ModuleDocument54 pagesWSTP 112ME: Metrology and Benchwork: Learning ModulesheeellyyyNo ratings yet
- Elektor Electronics 2016-03,04Document132 pagesElektor Electronics 2016-03,04Adrian_Andrei_443388% (8)
- Maintenance Manual ElectricDocument30 pagesMaintenance Manual ElectriceveraldoNo ratings yet
- SimuPlot5 ManualDocument25 pagesSimuPlot5 Manualikorishor ambaNo ratings yet
- A Duplex Stainless Steel With PREN 24 SPDocument2 pagesA Duplex Stainless Steel With PREN 24 SPFarhad MalikNo ratings yet
- Assignment RAMDocument8 pagesAssignment RAMnawab2588No ratings yet
- MSDS TaecDocument7 pagesMSDS TaecMuhammad FikriansyahNo ratings yet
- Delhi Sites. SBCDocument20 pagesDelhi Sites. SBCPankaj SherwalNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual: Non-Cycling Refrigerated Dryer 1000-2400 SCFMDocument32 pagesOperator's Manual: Non-Cycling Refrigerated Dryer 1000-2400 SCFMjael.gm10No ratings yet
- Duty Cycle of Circuit Breaker - Operating Sequence of Circuit BreakerDocument3 pagesDuty Cycle of Circuit Breaker - Operating Sequence of Circuit BreakerHawaz BeyeneNo ratings yet
- Tpl-Pml3-An-901 R0Document1 pageTpl-Pml3-An-901 R0suvraNo ratings yet
- X InternetDocument17 pagesX Internetmayankkansal19No ratings yet
- 9820 - 1015P - 3DX Super Parts Manual From 1855501-2583230Document445 pages9820 - 1015P - 3DX Super Parts Manual From 1855501-2583230Moussa HamzaNo ratings yet
- Wind - PZ CalculationDocument4 pagesWind - PZ CalculationPradip NikamNo ratings yet
- FENEX - Urban Planning QuestionsDocument3 pagesFENEX - Urban Planning QuestionsAbdul Rahman A RNo ratings yet
- Book Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDocument57 pagesBook Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDanny OxinaNo ratings yet
- Instalacion V2Track - Boletin Bi 25/17 Rev.0 - Ec-Gpf: EMC Source/Victim MatrixDocument1 pageInstalacion V2Track - Boletin Bi 25/17 Rev.0 - Ec-Gpf: EMC Source/Victim MatrixJonathan Miguel Gómez MogollónNo ratings yet
- Catalog Parts 1Document171 pagesCatalog Parts 1Fernanda AndradeNo ratings yet
- Vologzhanina Resume ADocument1 pageVologzhanina Resume Aapi-309047901No ratings yet
- ARMDocument226 pagesARMapi-3783901No ratings yet