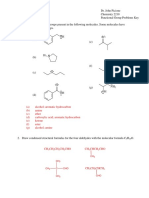
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Qualitative Tests
Summary of Qualitative Tests
Uploaded by
danavalerieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Qualitative Tests
Summary of Qualitative Tests
Uploaded by
danavalerieCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 1.
Reaction with bromine
Reagents/Apparatus Br2 in methylene chloride
Visible Results Decolorization of bromine
Summary of Tests Formula of the compound responsible for the visible result TESTS FOR UNSATURATION
Significance of the test Differentiates alkenes from aromatic and aliphatic compounds Shows the presence of = bonds (+) test: decolorization of bromine (-) test: no change in the color of bromine Differentiates unsaturated from saturated and aromatic compounds Shows the presence of unsaturation (+) test: decolorization of KMnO4 (-) test: no change in the color of the solution Differentiates unsaturated and aromatic compounds from saturated aliphatic compounds Shows the presence of unsaturation and aromaticity (+) test: yellow flame with soot (-) test: blue/yellow flame without soot Differentiates aromatic compounds from aliphatic compounds (+) test: yellow solution and evolution of odor (-) test: No change in the color of the solution, no evolution of odor Differentiates aromatic compounds from aliphatic compounds (+) test: formation of a cherry red solution (-) test: no change in the color of the solution Differentiates acidic form basic and neutral compounds (+) test for acid: pH < 7 (+) test for base: pH > 7
2. Baeyer Test
1% KMnO4
Decolorization of KMnO4 from purple into lighter color
MnO4- MnO2 (violet) (brown) 2KMnO4 + H2O 2KOH + 2MnO2 + 3(O)
3. Ignition Test
Bunsen Flame
Formation of a yellow flame and soot
Compound + O2 C (soot) + CO2
1. Nitration
Concentrated HNO3 Concentrated H2SO4
Formation of yellow solution and aromatic odor
TESTS FOR AROMATICITY ArH + (HNO3/H2SO4) ArNO2
2. Le Rosens Test
Formaldehyde in H2SO4
Change into a cherry red/ pink solution
CH3 RCHO H2SO4 Colorless
Par quinone (cherry red)
1. pH of the solution
pH paper
Depending on the color of the pH paper and matching it with the color in
TESTS FOR ACIDITY AND BASICITY H3O+ and OH-
2. NaHCO3 Test
5% NaHCO3 solution
the chart Dissolves strong acids but not weak acids and all bases Precipitate formation Gray precipitate
NaHCO3 + C6H5COOH Na+C6H5COO- + H2CO3
3. AgNO3 Test 4. Silver Acetylhalide Test
2% ethanolic AgNO3 solution Ammoniacal AgNO3 solution
RCHO-Ag
C2Ag + 2NH4NO3 + 2H2O
(+) test for neutral: pH = 7 Differentiates strong acids from weak acids (+) test: dissolution of strong acid (-) test: no dissolution taking place Differentiates acids from bases (+) test: formation of a precipitate (-) test: no precipitate formation Differentiates acids from bases (+) test: formation of a metal acetylhalide (acidic) (-) test: no precipitate formation Shows the presence of alkyl halides (+) test: either blue, blue-green or green flame (-) test: absence of the (+) flame color Shows the presence of alkyl halide in a compound (+) test: precipitate formation with AgNO3 (-) test: absence of precipitate/ no precipitate formed Differentiates alcohols with intermediate molecular weight from alcohols with large molecular weights (+) test: evolution of bubbles (-) test: no evolution of bubbles NOTE: The rate of bubble formation Differentiates primary from secondary from tertiary alcohols (+) tests for different degrees 1o alcohol no reaction o 2 alcohol cloudy solution (3-5 minutes) 3o alcohol, allyl and benzyl alcohol formation of layers (separate phases)
1. Beilstein Test
Copper Wire
2. Alcoholic AgNO3 Test
2% ethanolic AgNO3
Blue flame presence of I2 Blue-green flame presence of Br2 Green flame presence of Cl2 Precipitate formation with different colors AgI - yellow AgBr pale yellow AgCl - white Evolution of gas/bubbles
TEST FOR ALKYL HALIDES RX + CuO(s) CuX2 (source of flame) CuI2 CuBr2 CuCl2 RX + AgNO3 AgX + R+ + NO3AgI AgBr AgCl TEST FOR ALCOHOLS 2ROH + 2Na 2RONa + H2 2R2NH + 2Na 2R2NNa + H2 2RSH + 2Na 2RSNa + H2
1. Na+ Test
Na metal
2. Lucas Test
ZnCl2 in HCl
3. K2Cr2O7
3% K2Cr2O7
Formation of layers 1o alcohol no reaction 2o alcohol cloudy solution (3-5 minutes) 3o alcohol, allyl and benzyl alcohol formation of layers (separate phases) Formation of layers
RX, R2X, R3X (alkyl chloride)
RCOOH (Blue green) and CH3CH2COOH (green)
Differentiates primary from
Test
2M H2SO4
upon reacting with K2Cr2O7 Formation of colored solution (whether blue, violet, green, redbrown solution) TEST FOR PHENOLS AND ENOLS Fe(OAr)3 complex
secondary from tertiary alcohols
1. FeCl3 Test
3% FeCl3
2. Bromine water Test
Br2 in H2O
Change in color ranging from orange to black
Tribromophenols
3. Millons Test
Hg(NO3)2 in HNO3
Formation of precipitates and colored solutions ranging from red to brown
Hydroxyphenol groups
Differentiates phenols from alcohols and other organic compounds (+) test: formation of an aromatic iron complex (-) test: no change in color of solution nor formation of complex ion Differentiates phenols from alcohols and other organic compounds (+) test: formation of colored solutions (-) test: no change in the color of bromine and no change in the color of the solution of precipitate formation Detects the presence of phenols/ hydroxyl groups (phenol group in tyrosine) (+) test: formation of precipitates and colored solutions due to the presence of hydroxy group upon heating (-) test: no change in color after heating Shows the presence of a C=O of aldehyde or ketone (+) test: formation of an insoluble crystalline solid (-) test: no precipitate formation
TEST FOR ALDEHYDES AND KETONES 1. 2-4-DNPH Test 2,4Dinitrophenylhydrazine Formation of an insoluble yellow/ yellow orange solid (oily and crystalline)
2. Bisulfite Test
NaHSO3
Precipitate formation
Shows the presence aldehydes (+) test: precipitate formation (aldehydes) (-) test: no precipitate formation (ketones or other compounds)
3. Schiffs Test
Fuschine in NaHSO3 solution
Purple/violet solution
Shows the presence of aldehydes (+) test: formation of a violet solution (for aldehydes only) (-) test: no purple solution formed (ketones or other compounds)
4. Tollens Test
Ammoniacal AgNO3 solution
5. Iodoform Test
10% NaOH I2KI solution
Deposition of Silver metal to form the so called Silver mirror Formation of a solid yellow iodoform
RCHO + 2Ag(NH3)2OH 2Ag(s) + RCOOHNH4 + H2O + 3NH3
Shows the presence of aldehydes (+) test: Silver mirror (-) test: No silver mirror formed Shows the presence of CH3C=O in a molecule (+) test: solid yellow iodoform formation (-) test: no iodoform formed Differentiates reducing sugars from non-reducing sugars Shows the presence of an aldehyde (+) test: precipitate formation (Cu2O) (-) test: no precipitate formed
CH3COCH3 + 3I2 CH3COCI3 + 3HI (ketones) CH3COCI3 + OH- CHI3 + CH3COO- (aldehydes) 2 NaOH + I2 + CH3CH(OH)CH3 2 NaI + CH3COCH3 + 2 H2O (alcohols)
6. Fehlings Test
Sodium tartrate; NaOH; CuSO4
Formation of a red precipitate (Cu2O)
7. Molischs Test
-naphthol and conc. H2SO4
Formation of blue violet ring
1. C5H10O5 (pentose) + (conc.) H2SO4 C5H4O2 + 3 H2O 2. C5H4 + 2 C10H8OH (-naphthol) colored product
8. Barfoeds Test
Cu(OAc)2 in HOAc
Formation of a red precipitate (Cu2O)
Shows the presence of carbohydrates (+) test: formation of a blue-violet ring (-) test: no blue-violet ring formation Test for detecting the presence of monosaccharides (+) test: formation of a red precipitate (-) test: no precipitate formation
9. Seliwanoffs Test
Resorcinol and conc. H2SO4
Formation of a red precipitate and a pink solution
Test to differentiate aldose from ketose sugars (-) test: light pink (aldose) (+) test: red (ketose) Shows the presence of reducing sugars such as glucose, fructose, galactose, lactose and maltose. (+) tests: no precipitate green yellow orange red TEST FOR AMINES 1o Amine a trace + ++ +++
10. Benedicts Test
Sodium citrate; CuSO4; sodium bicarbonate
no precipitate green yellow orange red
a trace + ++ +++
1. Hindsberg Test
10% NaOH Benzylsulfonyl chloride
1o amines dissolves in base and precipitates from acid is a positive test. 2o amines precipitates from base and no change from acid is a positive test. 3o amines precipitates from base and dissolves in acid is a positive test.
Differentiates the different degrees of amines (+) test: 1o amines - dissolves in base and precipitates from acid is a positive test. 2o amines - precipitates from base and no change from acid is a positive test. 3o amines - precipitates from base and dissolves in acid is a positive test.
2o Amine
3o Amine
2. Nitrous acid Test
2M HCl 20% NaNO2
Evolution of gas
1o Aliphatic Amine
Differentiates the different degrees of amines 1o aliphatic amines- rapid bubbling upon addition of sodium nitrite is a positive test. 1o aromatic amines- rapid bubbling after addition of sodium nitrite (with heating) is a positive test. 2o amines- pale yellow oil with no evolution of gas is a positive test. 3o aliphatic amines- immediate positive test for nitrous acid with no evolution of gas is a positive test. 3o aromatic amines- dark-orange solution or orange solid, when treated with base turns green is a
1o Aromatic Amine
2o Amine
positive test.
3o Aliphatic Amine
3o Aromatic Amine
Amino Acid
1. Reaction of RCOOH
Methanol Concentrated H2SO4
Evolution of odor
TEST FOR CARBOXYLIC ACID AND ITS DERIVATIVES Ester
Shows the presence of an ester due to the reaction between an acid and
and ROH
2. Schotten Baumann Reaction 3. Hydrolysis of Benzamide 4. Hydrolysis of Ester
Ethanol Water Benzoyl Chloride 25% NaOH 10% NaOH Litmus paper (red)
Formation of an amides from an acyl halide and amine Change of the color of litmus paper and odor of the mixture Neutral to litmus and changes in odor RCONH2 + NaOH RCOONa + NH3 RCONHR + NaOH RCOONa + RNH2 RCONHR2 + NaOH RCOONa + R2NH RCN + NaOH + H2O RCOONa + NH3
an alcohol (+) test: evolution of odor/aroma (-) test: no evolution of odor/aroma Shows the reaction between an acyl halide and an alcohol to form an ester Shows the production of amines that can confirmed using Hinsberg test Shows the production of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The breaking of an ester (+) test: change in the odor of the mixture (-) test: neutral to litmus
25% NaOH
5. Hydrolysis of an anhydride
H2O
Change from blue litmus paper to red litmus paper
(RCO)2O + H2O 2RCOOH
6. Hydroxamic acid Test
7% Methanolic hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution 10% methanolic KOH 3% FeCl3
Acid Anhydride
Acyl Halide
Shows the conversion of an anhydride into a carboxylic acid (+) test: change from blue litmus to red litmus paper (-) test: no change in odor and color of the litmus paper (+) test: for RCOOH derivatives A distinct burgundy or magenta color of the ferric hydroxamate complex is a positive test. Compare the color of this solution with the yellow observed when the original compound is tested with ferric chloride in the presence of acid to assure the color is due to the formation of ferric hydroxamate complex. (+) test: for amides, amines A red to violet color constitutes a positive test. Yellow colors indicate negative tests, and brown colors or precipitates are indeterminate.
Ester
Ferric Hydroxamate Complex Formation
Nitrile
Amide
Ferric Hydroxamate Complex Formation
You might also like
- Chemistry: Qualitative Analysis - Idenitfication of Acidic Radicals - ManualDocument3 pagesChemistry: Qualitative Analysis - Idenitfication of Acidic Radicals - Manualzaid mansuri60% (10)
- Biochemical TestsDocument4 pagesBiochemical TestsNxxx0% (2)
- Handout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)Document9 pagesHandout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)twelvefeetNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nfpa 497 2012Document1 pageNfpa 497 2012Kaka Baba100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Organic ChemistryShamarie Love MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Poc One Shot Bounce BackDocument123 pagesPoc One Shot Bounce BackCOOLTEX YTNo ratings yet
- TestDocument52 pagesTestShivam Mittal100% (1)
- Chem 12 Organic DistinguishDocument5 pagesChem 12 Organic DistinguishNabaratna Biswal0% (1)
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Organic CompoundDocument11 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Organic CompoundHishq Dhiman100% (1)
- Distinguish by A Single Chemical Test: Prepared By-A.P. Singh Pgt-Chemistry - KV Aliganj LucknowDocument1 pageDistinguish by A Single Chemical Test: Prepared By-A.P. Singh Pgt-Chemistry - KV Aliganj LucknowChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- Test For SugarsDocument1 pageTest For SugarsVetina Lirio100% (1)
- Chemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Document4 pagesChemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Mukesh GanjawalaNo ratings yet
- Distinction Test Org - Chem.Document3 pagesDistinction Test Org - Chem.ht.9.hitakshiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 19Document3 pagesExperiment 19Beenu SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsDocument5 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsHarshwardhan100% (1)
- Experiment 8Document85 pagesExperiment 8Are-nim Hanim100% (1)
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsDocument5 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsIshika Singh100% (2)
- Files-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)Document56 pagesFiles-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)mmiliyasNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 16 - 22 PDFDocument60 pagesChem Lab 16 - 22 PDFKram GonzalesNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Compounds - 0Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Compounds - 0Ritu Raj100% (9)
- Qualitative Analysis Test For and Identify Organic Functional GroupsDocument6 pagesQualitative Analysis Test For and Identify Organic Functional GroupsChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument7 pagesQualitative AnalysisDavid MorganNo ratings yet
- Practical Organic Chemistry: (A) Functional Group AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractical Organic Chemistry: (A) Functional Group AnalysisManjunath NaikNo ratings yet
- Distiguishing Tests For Pairs of Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesDistiguishing Tests For Pairs of Organic CompoundsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- Anion AnalysisDocument6 pagesAnion AnalysisdiptafaraNo ratings yet
- Notes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIDocument52 pagesNotes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIMahesh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Pratical Organic Chemistry (13th)Document4 pagesPratical Organic Chemistry (13th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Dil. H SO Group: Experiment Observation InferenceDocument6 pagesDil. H SO Group: Experiment Observation InferencepranjaliNo ratings yet
- Pratical Organic Chemistry (12th)Document4 pagesPratical Organic Chemistry (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- Acidic Radical Part-1 T BatchDocument16 pagesAcidic Radical Part-1 T BatchAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations and AnionsDocument24 pagesQualitative Analysis of Cations and AnionsNidhi Chaudhary33% (3)
- Expt 8ADocument74 pagesExpt 8APearl Azucena100% (3)
- POST LAB DISCUSSION Activity 21 29 PDFDocument80 pagesPOST LAB DISCUSSION Activity 21 29 PDFDC BalangueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis Cheatsheet v1Document5 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis Cheatsheet v1lalit8888No ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Guide Sheet For Chemistry PracticalDocument4 pagesQualitative Analysis Guide Sheet For Chemistry PracticalquinzhangNo ratings yet
- Element AnalysisDocument28 pagesElement AnalysisSoumya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Test WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesDistinguishing Test WORKSHEETqwertyytrewqNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Qualitative Element AnalysisDocument6 pagesExp 1 Qualitative Element AnalysisNurin Afrina Syasya AzrenNo ratings yet
- Woah! So Practicool!Document6 pagesWoah! So Practicool!fuzzy pillowNo ratings yet
- Testing For ProteinsDocument7 pagesTesting For ProteinskulangkatunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis Cheat SheetsSumit Sapra83% (12)
- Lab Manual MSc. ChemistryDocument21 pagesLab Manual MSc. ChemistryGovardhan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Org. Chem 2Document8 pagesOrg. Chem 2JamesShiqNo ratings yet
- Ion Test PDFDocument11 pagesIon Test PDFAnderson XiaoNo ratings yet
- Handout For Qualitative AnalysisDocument9 pagesHandout For Qualitative AnalysisJarvin TanNo ratings yet
- Selected Reactions of Some AnionsDocument5 pagesSelected Reactions of Some AnionsJay JayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt AnalysisDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt AnalysisBiswajit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SALT ANALYSIS (Test For Anion)Document5 pagesChemistry SALT ANALYSIS (Test For Anion)Shivank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry Revision NotesFarhan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Identification of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesIdentification of Organic Compoundsrkushi0205No ratings yet
- Single Organic Test PDFDocument15 pagesSingle Organic Test PDFgreatNo ratings yet
- Acidic, Basic RadicalDocument13 pagesAcidic, Basic RadicalWael Elwekel100% (2)
- Let Me Give Some General DetailsDocument7 pagesLet Me Give Some General DetailsNimra IqbalNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of ProteinsDocument1 pageColor Reactions of ProteinsZarah Pauline JimenezNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 10 Organic NomenclatureDocument45 pages10 Organic NomenclatureAnubhab100% (2)
- Unit 14 - Organic ChemistryDocument56 pagesUnit 14 - Organic ChemistryRey GoldNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupDocument42 pagesAldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupIrfan HanifNo ratings yet
- Organic 1 CompressedDocument4 pagesOrganic 1 CompressedMD MoonNo ratings yet
- Topic: General Organic Chemistry-IDocument21 pagesTopic: General Organic Chemistry-IWTF GammerNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Acyl Chloride and AnhydrideDocument44 pagesReaction of Acyl Chloride and AnhydrideChyNaluri89No ratings yet
- Oer000000143 1Document235 pagesOer000000143 1mshahzaibjutt3636No ratings yet
- Naming Hydrocarbons Worksheet1 KDocument2 pagesNaming Hydrocarbons Worksheet1 KRare RootNo ratings yet
- Structure of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument42 pagesStructure of Aldehydes and KetonesPaul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups KeyDocument2 pagesFunctional Groups KeyalfredNo ratings yet
- Chem SyllabusDocument5 pagesChem Syllabusamuradyan1996No ratings yet
- Reactions of TrichlorotriazineDocument16 pagesReactions of Trichlorotriazinebebo4gpaNo ratings yet
- AlkaneDocument2 pagesAlkanePerfidious PriestNo ratings yet
- 11th-2022-23 Assignment - 05 Common Name Dt. 17-05-22 - 922612Document7 pages11th-2022-23 Assignment - 05 Common Name Dt. 17-05-22 - 922612Ravindra PatilNo ratings yet
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsBhai JaanNo ratings yet
- Refined VersionDocument3 pagesRefined VersionChemistry Department Government City CollegeNo ratings yet
- 13.E ExercisesDocument13 pages13.E ExercisesSadan ShawabikahNo ratings yet
- Esterification: DefinationDocument7 pagesEsterification: DefinationKamran Ashraf KamranNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesOrganic ChemistryKim SeungminNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument2 pagesAlkanesAnn DayritNo ratings yet
- NMRshifts1H GeneralDocument1 pageNMRshifts1H GeneralJeric CestinaNo ratings yet
- MS Fragmentation Functional Groups (Compatibility Mode)Document68 pagesMS Fragmentation Functional Groups (Compatibility Mode)Adriana Estefanía HPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Lipids: 17.4 Chemical Properties of TriacylglycerolsDocument20 pagesChapter 17 Lipids: 17.4 Chemical Properties of TriacylglycerolsAser SerNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab EXPERIMENTDocument3 pagesPre Lab EXPERIMENTEyy DeeNo ratings yet
- CHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument32 pagesCHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsKharl Roei SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 11.alkenes and Alkynesexercise PDFDocument68 pages11.alkenes and Alkynesexercise PDFMohammed Owais KhanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes KetonesDocument16 pagesCarboxylic Acid Aldehydes KetonesNorman Rafael EspejoNo ratings yet
- Alkanes (Multiple Choice) QPDocument4 pagesAlkanes (Multiple Choice) QPSandra MonicaNo ratings yet