Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vector V
Vector V
Uploaded by
Naruttam BorahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vector V
Vector V
Uploaded by
Naruttam BorahCopyright:
Available Formats
Vector V/s Bitmap Graphics 1.
Vector-based images generally contain well-defined elements such as curves and shapes of various colors. These elements can either be pure graphics, western alphabets or Asian characters. Vector-based files are more suitable for illustrations that require precise measurements. They are also easily scalable due to their mathematical nature. However, the vector-based file format has its drawbacks as well. It is not good for displaying photo-realistic images such as a photograph because images of this type generally do not contain well-defined shapes and curves.
Bitmap-based images, on the other hand, do not rely on mathematical formulas to define their various elements. Each bitmap-based image is mapped into a grid. The size of the grid is based on the image's resolution. For example, a bitmap-based image of 1 inch x 1 inch with a 600 dpi resolution would be defined by a grid of 600 x 600 pixels. Hence, a bitmap-based image is like a mosaic of pixels with each pixel holding a specific color value.
Bitmap-based files are more suitable for photo-realistic images that require complex color variations. They are, however, not easily scalable because each bitmap-based image is mapped to a non-flexible grid. If a bitmap-based image were to be enlarged, it would lose its sharpness. All edges within the image would appear to be jagged.
Base of Raster Scan System Random Scan System Difference Electron The electron beam is swept across the screen, one row at a The electron beam is directed only to the parts of Beam time, from top to bottom. screen where a picture is to be drawn. Its resolution is good because this system produces Its resolution is poor because raster system in contrast Resolution smooth lines drawings because CRT beam directly produces zig-zag lines that are plotted as discrete point sets. follows the line path. Picture Picture definition is stored as a set of intensity values for all Picture definition is stored as a set of line drawing Definition screen points, called pixels in a refresh buffer area. instructions in a display file. The capability of this system to store intensity values for pixel Realistic These systems are designed for line-drawing and makes it well suited for the realistic display of scenes contain Display cant display realistic shaded scenes. shadow and color pattern. Draw an Screen points/pixels are used to draw an image. Mathematical functions are used to draw an image. Image
Painting and Drawing Tools
Painting software, such as Photoshop, Fireworks, and painter is dedicated to producing crafted bitmap images. Drawing software, such as CorelDraw, Freehand, Designer and Canvas, is dedicated to producing vectorbased line art easily printer to paper at high resolution. Some software applications combine drawing and painting capabilities, but many authoring systems can import only bitmapped images. Typically, bitmapped images provide the greatest choice and power to the artist for rendering fine detail and effects, and today bitmaps are used in multimedia more often than drawn objects. Some vector-based packages such as Macromedia's Flash are aimed at reducing file download times on the web and may contain both bitmaps and drawn art.
What is the difference between hypermedia and hypertext?
Answer:
Hypertext - Hypertext is basically the same as regular text - it can be stored, read, searched, or edited - with an important exception: hypertext is text with pointers to other text. The browsers let you deal with the pointers in a transparent way -select the pointer, and you are presented with the text that is pointed to.
Hypermedia - Hypermedia is a superset of hypertext. Hypermedia documents contain links not only to other pieces of text, but also to other forms of media - sounds, images, and movies. Images themselves can be selected to link to sounds or documents. This means that browsers might not display a text file, but might display images or sound or animations. Hypermedia simply combines hypertext and multimedia.
GIF
GIF is best for images that have solid colors, text, and line art. It is good for computergenerated images, such as those produced by a drawing program like Corel Draw. It is also best when the image has detail, like text, where every pixel (dot on the screen) counts. It does well with images that are made up of a limited number of colors. It does not compress photographs very well, especially images that show texture or color gradations, or that are 24-bit color. GIF is a "lossless" form of compression. Every pixel in the original image is preserved. GIFs are rarely used for large images on web pages because the benefits of noloss are not visible to all but the most technical of viewers, but the huge differences in file size, and therefore download time, are noticeable to all.
JPG (JPEG)
JPG is best for photographs, and scanned photographs, of natural images. JPG gets its good compression by doing approximations, and is not as good for images where every pixel counts, or when you can get compression by using less than 24-bit color. It is usually a "lossy" compression, where you do not get back every pixel exactly as it was in the original image. There are different levels of JPG compression, ranging from little loss of detail and poor compression ("higher quality") to possible loss of detail with
great compression ("lower quality"). On web sites, it's often best to use the greater compression, even if it means loss of detail ("lower quality") because it savesdownload time. The software you use to edit or scan your images often has a setting to control the JPG quality. You can always link the low quality image to another page with a higher quality, perhaps larger, image for people who want to print out as good a copy as possible.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Simulation and Modeling Question - BSC - CSIT 2070 Final ExamDocument2 pagesSimulation and Modeling Question - BSC - CSIT 2070 Final ExamAakash Floydian Joshi83% (6)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fundamentals of Database System PQ1 PRELIM EXAMDocument25 pagesFundamentals of Database System PQ1 PRELIM EXAMAlbert SwakNo ratings yet
- JavaintroDocument14 pagesJavaintroMr.PNo ratings yet
- Informatica MDM SetupDocument17 pagesInformatica MDM SetupbabjeereddyNo ratings yet
- Uniform Color QuantizationDocument5 pagesUniform Color Quantizationpi194043No ratings yet
- Graphics6 BresenhamCirclesAndPolygonsDocument48 pagesGraphics6 BresenhamCirclesAndPolygonsSourabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- mgt202 ForecastingDocument4 pagesmgt202 ForecastingKathleen MarcialNo ratings yet
- BPM NotesDocument2 pagesBPM NotesLakshmi KakarlaNo ratings yet
- Food Ordering System: Department of Computer Science Object Oriented Lab Project Proposal FormDocument3 pagesFood Ordering System: Department of Computer Science Object Oriented Lab Project Proposal Formabdul moizNo ratings yet
- 5 SQLDocument71 pages5 SQLRohit KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3c - Conceptual Data Modeling Excercise ContDocument15 pagesLecture 3c - Conceptual Data Modeling Excercise ContHurair khanNo ratings yet
- Msuic DynamicDocument2 pagesMsuic DynamicCarina Concepcion BermilNo ratings yet
- Linear Classifiers in Python: Chapter4Document24 pagesLinear Classifiers in Python: Chapter4NishantNo ratings yet
- IDS Assignment # 4 Name Obaid Ullah: University of Engineering and Technology (Mardan)Document3 pagesIDS Assignment # 4 Name Obaid Ullah: University of Engineering and Technology (Mardan)Obaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Model Driven Engineering (MDE) : ITC-708 by Dr. Mir Sajjad Hussain Talpur Dated: 08-2-2021Document17 pagesModel Driven Engineering (MDE) : ITC-708 by Dr. Mir Sajjad Hussain Talpur Dated: 08-2-2021Abdul WahidNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems Shells PDFDocument2 pagesExpert Systems Shells PDFSally100% (1)
- Crossword Puzzle - Question WordsDocument10 pagesCrossword Puzzle - Question WordsrhariharancseNo ratings yet
- CA2 Practical JournalDocument37 pagesCA2 Practical JournalK HNo ratings yet
- Archmodels Vol 1 LWDocument15 pagesArchmodels Vol 1 LWPurwo YuliyantoNo ratings yet
- DIP3E Chapter03 ArtDocument64 pagesDIP3E Chapter03 ArtThippeswamy KhNo ratings yet
- CSC 201-Lecture 10Document31 pagesCSC 201-Lecture 10pavanilNo ratings yet
- LG 55LM6700 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDocument7 pagesLG 55LM6700 CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - DBMS-II BSCDocument74 pagesUnit 1 - DBMS-II BSCsaravana AriyalurianNo ratings yet
- Archi CADDocument2 pagesArchi CADTheresa CostalesNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument104 pagesJavashruthig29111988No ratings yet
- BuildingSMART IFC4 What Is NewDocument25 pagesBuildingSMART IFC4 What Is Newlaurenssen0% (1)
- Introduction of ER Model: Entity, Entity Type, Entity SetDocument8 pagesIntroduction of ER Model: Entity, Entity Type, Entity SetRahul SheikhNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab: Project 01Document4 pagesDbms Lab: Project 01tHe tecHniquEsNo ratings yet
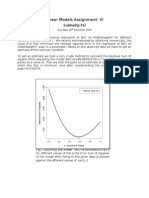
- Linear Models Assignment: VI: Subhadip PalDocument6 pagesLinear Models Assignment: VI: Subhadip PalsubhadippalNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument22 pagesRegression AnalysisNanthitha BNo ratings yet