Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Api I C4
Api I C4
Uploaded by
mihai37Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sol Activitat 3Document21 pagesSol Activitat 3Jorge Lopez BlascoNo ratings yet
- PAC1 MATI ESTUDIANTS Per PenjarDocument4 pagesPAC1 MATI ESTUDIANTS Per PenjarÀngel Dominguez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Dossier Exercicis ElectropneumàticaDocument6 pagesDossier Exercicis ElectropneumàticaSonia SoldadoraNo ratings yet
- AutomaticaDocument5 pagesAutomaticaAlexLgNo ratings yet
- Control Industrial I AutomatizaciónDocument13 pagesControl Industrial I Automatizaciónmar taNo ratings yet
- 1 Guia Gemma I Grafcet Celula FestoDocument13 pages1 Guia Gemma I Grafcet Celula FestoALBERT ROFIN ESTELLESNo ratings yet
- GrafcetDocument26 pagesGrafcetCarlos Prudecio de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Guia de La Practica 4 CIIA v3gDocument13 pagesGuia de La Practica 4 CIIA v3gAlan Reyes Rodriguez Reyee RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pengantar MATLABDocument56 pagesPengantar MATLABanon_124002009No ratings yet
- Solució Examen SR 2021Document6 pagesSolució Examen SR 2021Fineas GrozaNo ratings yet
- Info 3Document4 pagesInfo 3albaboschfreireNo ratings yet
- Tema 3Document24 pagesTema 3Hanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Tema2 1Document58 pagesTema2 1Hanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Bic Practiques.Document1 pageBic Practiques.chaimae mokhtari khaledNo ratings yet
- Activitats MP08Document24 pagesActivitats MP08Fernando Buiza AmatllerNo ratings yet
- Eps 20230827 Ra AcDocument5 pagesEps 20230827 Ra Acmakoma3772No ratings yet
- Presentacio Automatismes Al MoodleDocument56 pagesPresentacio Automatismes Al MoodleJavier SuarezNo ratings yet
- Solucionari Unitat 1Document17 pagesSolucionari Unitat 1Oliver Uriel AndrangoNo ratings yet
- NF4 INSTRUCREGISTRES PT13 Seleccio de TolvesDocument1 pageNF4 INSTRUCREGISTRES PT13 Seleccio de TolveselminycitoNo ratings yet
- Practica 4 Modelatge I Simulació de ProcessosDocument9 pagesPractica 4 Modelatge I Simulació de Processosroger campsNo ratings yet
- P3-Implementació de Cóntróladórs AnalíticsDocument8 pagesP3-Implementació de Cóntróladórs AnalíticsDavid Murillo SánchezNo ratings yet
- EE02101CDocument68 pagesEE02101CCariatore GriseldaNo ratings yet
- Daw M05 Uf2 Paf1 2324S1Document6 pagesDaw M05 Uf2 Paf1 2324S1Ainoa Piudo CabelloNo ratings yet
- IORD - Practica 1Document5 pagesIORD - Practica 1Cucu bausNo ratings yet
- Practica3 20 21Document5 pagesPractica3 20 21marc arnauNo ratings yet
- TC Cat 20232 Pac2Document9 pagesTC Cat 20232 Pac2ericfer 48No ratings yet
- 2012 Junio Lavadora y Plataforma ElevadoraDocument4 pages2012 Junio Lavadora y Plataforma ElevadoragabinosaezNo ratings yet
- Bpr1.1 - Sistemes Avançats de Control Industrial M6-UF1-provisional PDFDocument17 pagesBpr1.1 - Sistemes Avançats de Control Industrial M6-UF1-provisional PDFOriolNo ratings yet
- 1r Recull Exercicis CADocument11 pages1r Recull Exercicis CAToni LuqueNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Modul 5 Transformacions GeometriquesDocument64 pagesAlgebra - Modul 5 Transformacions GeometriquesAccount FreeNo ratings yet
- Paper de Tiro HrizontalDocument7 pagesPaper de Tiro Hrizontall.vazquezNo ratings yet
- 1 - GRAFCET v2Document95 pages1 - GRAFCET v2alextopgear33No ratings yet
- T3 Estructures LinealsDocument83 pagesT3 Estructures LinealsnaitmeirNo ratings yet
- Informe 1 CADocument14 pagesInforme 1 CAJordi Gallart MartínezNo ratings yet
- Pràctica 2 - Equips Perifèrics - C2324Document5 pagesPràctica 2 - Equips Perifèrics - C2324Jesús Oran SansNo ratings yet
- Examen D'automatització IndustrialDocument21 pagesExamen D'automatització IndustrialFineas GrozaNo ratings yet
- 4 1819 Mates2n DOSSIER FraccionsDocument15 pages4 1819 Mates2n DOSSIER Fraccionspocholo74No ratings yet
- Tipo Test 1 Parcial EconometriaDocument74 pagesTipo Test 1 Parcial EconometriaMarc MonfortNo ratings yet
- Finestra EsdevsDocument3 pagesFinestra EsdevsCarles Prat JovaniNo ratings yet
- Tema1 - Grafcet KMECDocument17 pagesTema1 - Grafcet KMECfencaladaenriquezNo ratings yet
- UF1-Pp1 PracticaInicialDocument2 pagesUF1-Pp1 PracticaInicialJosep ALCAÑIZ PRATSNo ratings yet
- ET8a 09 10 Q1 ElectronicDocument7 pagesET8a 09 10 Q1 Electronicrc7pablorNo ratings yet
- MTM II Mayo 2016 DefDocument4 pagesMTM II Mayo 2016 DefBakre ToutaiNo ratings yet
- P3 - LLEI DOHM - InformeDocument6 pagesP3 - LLEI DOHM - InformeDilan OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Installacions-Electrotecniques 2020Document25 pagesInstallacions-Electrotecniques 2020iridium2000No ratings yet
- Información GeneralDocument8 pagesInformación GeneralpovNo ratings yet
- SSII 20232 PAC1-ca v2Document4 pagesSSII 20232 PAC1-ca v2vmashchakNo ratings yet
- 06 - Moduls I TurtleDocument12 pages06 - Moduls I Turtledaniel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Pract 1 X 2014Document5 pagesPract 1 X 2014yilunNo ratings yet
- Presentacio EntregaFinalDocument19 pagesPresentacio EntregaFinalPau Chamarro LópezNo ratings yet
- 1 - GRAFCET v1Document76 pages1 - GRAFCET v1sergiNo ratings yet
- LadrilloDocument545 pagesLadrilloToni LuqueNo ratings yet
- UOC - Sistemes Operatius ExamenDocument8 pagesUOC - Sistemes Operatius ExamenMarina P.No ratings yet
- 1T Parcial 1Document4 pages1T Parcial 1xavimarticardonerNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free PAC1202021Q1Document7 pagesWuolah Free PAC1202021Q1sasha trashNo ratings yet
- CIIA Guia de Treball Tema 1 - 1 V7Document19 pagesCIIA Guia de Treball Tema 1 - 1 V7paula RPNo ratings yet
- Projecte D'automatitzacióDocument2 pagesProjecte D'automatitzacióHanna ZipaNo ratings yet
- Est ClassificacioDocument6 pagesEst ClassificacioTomas GVNo ratings yet
- IntroduccioDocument10 pagesIntroducciooriol.ibanez.rodaNo ratings yet
Api I C4
Api I C4
Uploaded by
mihai37Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Api I C4
Api I C4
Uploaded by
mihai37Copyright:
Available Formats
IST / DEEC / API
MEEC 2011-2012
Industrial Automation
(Automao de Processos Industriais)
GRAFCET (Sequential Function Chart)
http://users.isr.ist.utl.pt/~jag/courses/api1112/api1112.html
Slides 2010/2011 Prof. Paulo Jorge Oliveira Rev. 2011/2012 Prof. Jos Gaspar
Page 1
IST / DEEC / API
MEEC 2011-2012
Syllabus:
Chap. 3 PLCs Programming Languages [2 weeks] ... Chap. 4 - GRAFCET (Sequential Function Chart) [1 week] The GRAFCET norm. Elements of the language. Modelling techniques using GRAFCET. ... Chap. 5 CAD/CAM and CNC Machines [1 week]
Page 2
IST / DEEC / ACSDC API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
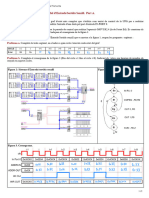
PLCs Programming Languages (IEC 1131-3) Ladder Diagram Structured Text
If %I1.0 THEN %Q2.1 := TRUE ELSE %Q2.2 := FALSE END_IF
Instruction List
LD AND ANDN OR ST %M12 %I1.0 %I1.1 %M10 %Q2.0
Sequential Function Chart (GRAFCET) 1
(1) m
2
(2) b
Right
3
(3) p
Load
4
(2) a
Left
Page 3
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
Some pointers to GRAFCETs (SFCs)
History: Tutorial: http://www.lurpa.ens-cachan.fr/grafcet/groupe/gen_g7_uk/geng7.html http://asi.insa-rouen.fr/~amadisa/grafcet_homepage/tutorial/index.html http://www-ipst.u-strasbg.fr/pat/autom/grafce_t.htm
Simulator:
http://asi.insa-rouen.fr/~amadisa/grafcet_homepage/grafcet.html http://www.automationstudio.com (See projects)
-- Petri Nets and GRAFCET: Tools for Modelling Discrete Event Systems R. David, H. Alla, New York : PRENTICE HALL Editions, 1992 -- Grafcet: a powerful tool for specification of logic controllers, R. David, IEEE Trans. on Control Systems Tech., 1995 v3n3 pp253-268 [online] -- Programao de Autmatos, Mtodo GRAFCET, Jos Novais, Fundao Calouste Gulbenkian -- Norme Franaise NF C 03-190 + R1 : Diagramme fonctionnel "GRAFCET" pour la description des systmes logiques de commande
Bibliography:
Homepage:
http://www.lurpa.ens-cachan.fr/grafcet/
Page 4
IST / DEEC / API
Page 5
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET History
1975 Decision of the workgroup "Logical Systems" da AFCET (Association Franaise de Cyberntique Economique et Technique) on the creation of a committee to study a standard for the representation of logical systems and automation.
1977 GRAFCET definition (Graphe Fonctionnel de Commande Etape-Transition).
1979 Dissemination in schools and adopted as research area for the implementation of solutions of automation in the industry. 1988 - GRAFCET becomes an international standard denominated as "Sequential Function Chart, pela I.E.C.
Page 6
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Basic Elements Steps
1 2 3
Connections
Directed Arc
Transitions
Simple Joint
(parallel junction) (1) R1
Inactive Active Initial
(2)
R2
Fork (parallel branch) Joint e fork
(3)
R3
(3)
R3
Actions can be associated with Steps.
A logical receptivity function can be associated with each Transition.
Page 7
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Basic Elements Oriented connections (arcs)
1
In a GRAFCET: An Arc can connect Steps to Transitions An Arc can connect Transitions to Steps
(1) R1
.
(2)
3
R2
Action A
A Step can have no Transitions as inputs (source); A Step can have no Transitions as outputs (drain);
4
(3) R3
The same can occur for the Transitions.
Page 8
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
State of a GRAFCET
Definition of State: The set of markings of a GRAFCET constitutes its state. Question: How does the state of a GRAFCET evolve?
(1)
1
R1
.2
(2)
3
R2
Action A
4 .
(3) R3
Page 9
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
State Evolution:
Rule 1: Initial State
It is characterized by the active Steps at the beginning of operation (at least one).
Rule 2: Transposition of a Transition
A Transition is active or enabled only if all the Steps at its input are active (if not it is inactive). A Transition can only be transposed if it is active and is true the associated condition (receptivity function).
Rule 3: Evolution of active Steps
The transposition of a Transition leads to the deactivation of all the Steps on its inputs and the activation of all Steps on its outputs.
Rule 4: Simultaneous transposition of Transitions
All active Transitions are transposed simultaneously.
Rule 5: Simultaneous activation and deactivation of a Step
In this case the activation has priority.
Page 10
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET State Evolution:
Rule 2a:
All active Transitions are transposed immediately.
Rule 4:
Simultaneous active Transitions are transposed simultaneously.
Example 1
Example 2
Example 3
.
(1)
1
a (2)
2
a (3) b
5 .
(4) b (5)
.
c
.3
.4
10
.
Page 11
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
OR Divergences:
OR Convergences:
If Step 1 is active and if a is TRUE then Step 1 is If Step 1 is active and if a is TRUE then Step 1 is deactivated deactivated and Step 2 is activated (state of Step 3 is and Step 3 is activated (state of Step 2 remains unchanged). maintained). The same happens for Step 2 and b. If a and b are TRUE and Step 1 is active then Step 1 is If both Steps 1 and 2 are active and a and b are TRUE deactivated and Steps 2 and 3 are activated then Steps 1 and 2 are deactivated and Step 3 is activated. (for any previous state of Steps 2 and 3).
AND Divergences:
AND Convergences:
If Step 1 is active and if a is TRUE then Step 1 is deactivated and Steps 2 and 3 are activated.
If Steps 1 and 2 are active and if a is TRUE then Steps 1 and 2 are deactivated and Step 3 is activated (if only one of the input steps is active, the state remains). Page 12
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Example:
(1)
1
R1
GRAFCET state evolution
2
(2)
3
R2
Action A
4
Level activated Action. Actions can also be activated during transitions - see next.
(3) R3
Page 13
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Modelling problem:
.
t1 3 4
t2
Given 4 Steps (1 to 4) and 2 Transitions (t1 and t2) write a segment of GRAFCET to solve the following problem: In the case that the Steps 1 and 2 are active: if t1 is TRUE, activate Step 3 (and deactivate Steps 1 and 2); if t2 is TRUE, activate Step 4 (and deactivate Steps 1 and 2); otherwise, the state is maintained.
Page 14
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Other modelling problem:
Given 4 Steps (1 to 4) and 2 Transitions (t1 and t2) write a segment of GRAFCET to solve the following problem: If Step 1 is active and t1 is TRUE OR If Step 2 is active and t2 is TRUE THEN Activate Steps 3 and 4.
1 t1
2 t2
Page 15
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET GRAFCET state evolution, Conflicts:
There exist Conflicts when the validation of a Transition depends on the same Step or when more than one receptivity functions can become true simultaneously. Solutions:
1
(1) a (2) ba (1) a
1
(2) b (1)
1
a b (2) ab (3) ab
Transiction 1 prioritary
Three mutualy exclusive hypotheses
Page 16
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 1: modeling a control/automation system
1
(1) m
m
load
2
b
(2) b
Right
a
left right
3
(3) p
Load
p
(4)
4
a
Left
Page 17
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 2: modeling a automated transport workcell
* Conveyor A brings parts (sensor a detects part ready to lift) * Conveyor B brings parts (sensor b detects part ready to lift) Hanging crane, commanded with D (droit) e G (gauche), uses sensors x, y e z to detect crane over the base, over A, or over B, respectively. Clamp of the crane grabs and releases parts with commands PP and DP. Limit switches fpp and fdp indicate grabbed and released part. A holding platform has two extreme positions, top and bottom, detected by switches fv+ and fv-. Part release can only be done having the holding platform up. fpfp+ fv+ * The output conveyor is always ON. fv* Conveyors A e B are commanded by other automata, independent of this workcell. * Effector pushes parts with commands P+ e P-. Limit switches fp+ and fp- indicate max and min pushing positions.
Page 18
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 2 (cont)
Solution
fp- fp+ fv+ fv-
To guarantee alternating A and B, modify the program, adding the following GRAFCET:
and changing the receptivity function * to: Explanation: grab part in y, if there exists part in a and if b has not the priority; if b is true and has priority, then grab part in z. Note: terminology X10 of PL7 changes to S_1_10 in Unity Pro Page 19
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 2 (cont) Improved solution:
a) After processing one part (P+) prepare immediately to receive the next one: fv+. b) Move crane (D) to an optimal waiting location (i.e. location that reduces delays): y.
Page 20
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 3: modeling and automation of a distribution system Objective: fill 1&2, empty 1&2 refill only after both empty Sensors: m = ON/OFF b1, h1, b2 h2 = level Actuators: V1, V2, W1 W2 = admit/exhaust
reservoir
V1 h1 b1 W1 h2 b2
V2
W2
Page 21
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 3: modeling and automation of a distribution system
1
(1) m
4
5 V2
h2
7
(1) m
2
(2) h1
V1
(4)
3
(3) b'1
W1
(5)
6
b'2
2
W2
(2) h1
V1
(4)
5
h2
V2
4
(6) =1
7
(3)
3
b'1
W1
(5)
6
b'2
W2
Page 22
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Example 3: modeling and automation of a distribution system
1
4
(1') m.X7 (1'')
7
m.X4
(1)
2
(2) h1
V1
(4)
5
h2
V2
(2)
2
h1
V1
(4)
5
h2
V2
3
(3) b'1
W1
(5)
6
b'2
W2
34
W1 se if b1
(6)
67
b'1 . b'2
W2 if se b2
Page 23
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Transitions can be conditions, events and conditions mixed with events
(a) Events f and f obtained from a condition f
(b) Event a.b obtained from event a and condition b
(c) Event a. b obtained from events a and b
(d) Event a + b obtained from events a and b
Grafcet: a powerful tool for specification of logic controllers, R. David, IEEE Trans. on Control Systems Tech., 1995 v3n3 pp253-268
Page 24
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Transitions can be conditions, events and conditions mixed with events
Properties of events (edge triggers) mixed with conditions (Boolean variables): a = a a . a = a, a . a = a, a . a = 0, a . a = 0 (a + b) = a . b + b . a a . a = a, a . a = 0
(a . b) = a . b + b . a, (a . b) . (a . c) = (a . b . c)
In general, if events a and b are independent a . b = 0
Page 25
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Other auxiliary mechanisms
Macro-steps
15 V2 2
h2 h1 (1)
E10
m
V1
5
h2
V2
16 M10
3
b'1
W1
6
b'2
W2
4
=1
17
V1
S8
Page 26
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Other auxiliary mechanisms
Pseudo Macro-steps Macro Actions Force actions Enable actions Mask actions
Page 27
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Implementation in DOLOG80
The activity of each Step is stored in an auxiliary memory. At startup do: AM128 SLMx ... AM128 SLMy (initial steps) RLM128 Store Rk evaluation in M100 AM1 AM2 AM100 SLM3 AM1 AM2 AM100 SLM4
1
(k)
AM3 AM4 RLM1 AM3 AM4 RLM2
2
Rk
Page 28
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Implementation in the TSX3722/TSX57
Steps
Page 29
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Implementation in the TSX3722/TSX57
Macro-steps
Page 30
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Implementation in the TSX3722/TSX57
Page 31
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET
Implementation in the TSX3722/TSX57
Arcs/Connectors
Page 32
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
Information associated with Steps in the GRAFCET:
Page 33
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
Information associated with Steps in the GRAFCET (bis):
And where to find information related with Transitions? Does not make sense state or activity nor timmings (only number of occurences).
Page 34
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET General structure:
Characteristics:
Page 35
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Editor: 8 pages
Pages 0 to 7 154 cells (14*11)
Characteristics:
Page 36
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET OR divergences
(OR convergences)
Characteristics:
Page 37
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET AND divergences
(AND Convergences)
Characteristics:
Page 38
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Arcs/Connectors
Page 39
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
Rules for divergences and convergences:
OR AND
Page 40
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Programming Actions
Page 41
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET Programming Actions
Example of execution of Actions
Example of Activation/deactivation
Example of continuous Action
Page 42
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET GRAFCET Section Sctructure
LD, IL, ST
GRAFCET
LD, IL, ST
Page 43
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET GRAFCET Section Initialization
Page 44
IST / DEEC / API
Chap. 4 - GRAFCET
GRAFCET GRAFCET Section Reset
Page 45
IST / DEEC / API
Properties of Transition Sections (Unity Pro) Transition sections have the following properties: Transition sections only have one single output (transition variable), whose data type is BOOL. The name of these variables are identical to the names of the transition sections. The transition variable can only be used once in written form. The transition variable can be read in any position within the project. Only functions can be used, function blocks or procedures cannot. Only one coil may be used in LD. There is only one network, i.e. all functions used are linked with each other either directly or indirectly. Transition sections can only be used once. Transition sections belong to the SFC section in which they were defined. If the respective SFC section is deleted then all transition sections of this SFC section are also deleted automatically. Transition sections can be called exclusively from transitions.
Page 46
You might also like
- Sol Activitat 3Document21 pagesSol Activitat 3Jorge Lopez BlascoNo ratings yet
- PAC1 MATI ESTUDIANTS Per PenjarDocument4 pagesPAC1 MATI ESTUDIANTS Per PenjarÀngel Dominguez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Dossier Exercicis ElectropneumàticaDocument6 pagesDossier Exercicis ElectropneumàticaSonia SoldadoraNo ratings yet
- AutomaticaDocument5 pagesAutomaticaAlexLgNo ratings yet
- Control Industrial I AutomatizaciónDocument13 pagesControl Industrial I Automatizaciónmar taNo ratings yet
- 1 Guia Gemma I Grafcet Celula FestoDocument13 pages1 Guia Gemma I Grafcet Celula FestoALBERT ROFIN ESTELLESNo ratings yet
- GrafcetDocument26 pagesGrafcetCarlos Prudecio de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Guia de La Practica 4 CIIA v3gDocument13 pagesGuia de La Practica 4 CIIA v3gAlan Reyes Rodriguez Reyee RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pengantar MATLABDocument56 pagesPengantar MATLABanon_124002009No ratings yet
- Solució Examen SR 2021Document6 pagesSolució Examen SR 2021Fineas GrozaNo ratings yet
- Info 3Document4 pagesInfo 3albaboschfreireNo ratings yet
- Tema 3Document24 pagesTema 3Hanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Tema2 1Document58 pagesTema2 1Hanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Bic Practiques.Document1 pageBic Practiques.chaimae mokhtari khaledNo ratings yet
- Activitats MP08Document24 pagesActivitats MP08Fernando Buiza AmatllerNo ratings yet
- Eps 20230827 Ra AcDocument5 pagesEps 20230827 Ra Acmakoma3772No ratings yet
- Presentacio Automatismes Al MoodleDocument56 pagesPresentacio Automatismes Al MoodleJavier SuarezNo ratings yet
- Solucionari Unitat 1Document17 pagesSolucionari Unitat 1Oliver Uriel AndrangoNo ratings yet
- NF4 INSTRUCREGISTRES PT13 Seleccio de TolvesDocument1 pageNF4 INSTRUCREGISTRES PT13 Seleccio de TolveselminycitoNo ratings yet
- Practica 4 Modelatge I Simulació de ProcessosDocument9 pagesPractica 4 Modelatge I Simulació de Processosroger campsNo ratings yet
- P3-Implementació de Cóntróladórs AnalíticsDocument8 pagesP3-Implementació de Cóntróladórs AnalíticsDavid Murillo SánchezNo ratings yet
- EE02101CDocument68 pagesEE02101CCariatore GriseldaNo ratings yet
- Daw M05 Uf2 Paf1 2324S1Document6 pagesDaw M05 Uf2 Paf1 2324S1Ainoa Piudo CabelloNo ratings yet
- IORD - Practica 1Document5 pagesIORD - Practica 1Cucu bausNo ratings yet
- Practica3 20 21Document5 pagesPractica3 20 21marc arnauNo ratings yet
- TC Cat 20232 Pac2Document9 pagesTC Cat 20232 Pac2ericfer 48No ratings yet
- 2012 Junio Lavadora y Plataforma ElevadoraDocument4 pages2012 Junio Lavadora y Plataforma ElevadoragabinosaezNo ratings yet
- Bpr1.1 - Sistemes Avançats de Control Industrial M6-UF1-provisional PDFDocument17 pagesBpr1.1 - Sistemes Avançats de Control Industrial M6-UF1-provisional PDFOriolNo ratings yet
- 1r Recull Exercicis CADocument11 pages1r Recull Exercicis CAToni LuqueNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Modul 5 Transformacions GeometriquesDocument64 pagesAlgebra - Modul 5 Transformacions GeometriquesAccount FreeNo ratings yet
- Paper de Tiro HrizontalDocument7 pagesPaper de Tiro Hrizontall.vazquezNo ratings yet
- 1 - GRAFCET v2Document95 pages1 - GRAFCET v2alextopgear33No ratings yet
- T3 Estructures LinealsDocument83 pagesT3 Estructures LinealsnaitmeirNo ratings yet
- Informe 1 CADocument14 pagesInforme 1 CAJordi Gallart MartínezNo ratings yet
- Pràctica 2 - Equips Perifèrics - C2324Document5 pagesPràctica 2 - Equips Perifèrics - C2324Jesús Oran SansNo ratings yet
- Examen D'automatització IndustrialDocument21 pagesExamen D'automatització IndustrialFineas GrozaNo ratings yet
- 4 1819 Mates2n DOSSIER FraccionsDocument15 pages4 1819 Mates2n DOSSIER Fraccionspocholo74No ratings yet
- Tipo Test 1 Parcial EconometriaDocument74 pagesTipo Test 1 Parcial EconometriaMarc MonfortNo ratings yet
- Finestra EsdevsDocument3 pagesFinestra EsdevsCarles Prat JovaniNo ratings yet
- Tema1 - Grafcet KMECDocument17 pagesTema1 - Grafcet KMECfencaladaenriquezNo ratings yet
- UF1-Pp1 PracticaInicialDocument2 pagesUF1-Pp1 PracticaInicialJosep ALCAÑIZ PRATSNo ratings yet
- ET8a 09 10 Q1 ElectronicDocument7 pagesET8a 09 10 Q1 Electronicrc7pablorNo ratings yet
- MTM II Mayo 2016 DefDocument4 pagesMTM II Mayo 2016 DefBakre ToutaiNo ratings yet
- P3 - LLEI DOHM - InformeDocument6 pagesP3 - LLEI DOHM - InformeDilan OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Installacions-Electrotecniques 2020Document25 pagesInstallacions-Electrotecniques 2020iridium2000No ratings yet
- Información GeneralDocument8 pagesInformación GeneralpovNo ratings yet
- SSII 20232 PAC1-ca v2Document4 pagesSSII 20232 PAC1-ca v2vmashchakNo ratings yet
- 06 - Moduls I TurtleDocument12 pages06 - Moduls I Turtledaniel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Pract 1 X 2014Document5 pagesPract 1 X 2014yilunNo ratings yet
- Presentacio EntregaFinalDocument19 pagesPresentacio EntregaFinalPau Chamarro LópezNo ratings yet
- 1 - GRAFCET v1Document76 pages1 - GRAFCET v1sergiNo ratings yet
- LadrilloDocument545 pagesLadrilloToni LuqueNo ratings yet
- UOC - Sistemes Operatius ExamenDocument8 pagesUOC - Sistemes Operatius ExamenMarina P.No ratings yet
- 1T Parcial 1Document4 pages1T Parcial 1xavimarticardonerNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free PAC1202021Q1Document7 pagesWuolah Free PAC1202021Q1sasha trashNo ratings yet
- CIIA Guia de Treball Tema 1 - 1 V7Document19 pagesCIIA Guia de Treball Tema 1 - 1 V7paula RPNo ratings yet
- Projecte D'automatitzacióDocument2 pagesProjecte D'automatitzacióHanna ZipaNo ratings yet
- Est ClassificacioDocument6 pagesEst ClassificacioTomas GVNo ratings yet
- IntroduccioDocument10 pagesIntroducciooriol.ibanez.rodaNo ratings yet