Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
270 viewsConditions Step by Step
Conditions Step by Step
Uploaded by
LazinessPerSeThis document outlines 4 steps for determining conditions in a contract: 1) Determine if the term is a promise, condition, or promissory condition. 2) Determine if the condition is express, implied in fact, or constructive. 3) Determine if the condition is precedent, concurrent, or subsequent. 4) Determine if the condition requires strict or substantive compliance to affect the contract.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Gilbert Law Summaries On Torts (2008) 726 PagesDocument726 pagesGilbert Law Summaries On Torts (2008) 726 PagesBILLYNo ratings yet
- Brown Machine v. Hercules (p153) 9.09Document3 pagesBrown Machine v. Hercules (p153) 9.09Stephen LindseyNo ratings yet
- Leg Reg Pre WriteDocument19 pagesLeg Reg Pre WriteashleyamandaNo ratings yet
- Battle of The Forms FlowchartDocument1 pageBattle of The Forms Flowchartncallan9No ratings yet
- Contracts 2 OutlineDocument37 pagesContracts 2 OutlineBrandon YeboahNo ratings yet
- Ucc and Restatement OutlineDocument7 pagesUcc and Restatement OutlineLauren WoodsonNo ratings yet
- Contracts II OutlineDocument16 pagesContracts II OutlineEva CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro Personal Jurisdiction Essay A+ OutlineDocument5 pagesCiv Pro Personal Jurisdiction Essay A+ OutlineBianca Dacres100% (1)
- Contracts - OutlineDocument25 pagesContracts - OutlineN FinkelsNo ratings yet
- Torts II ChartsDocument8 pagesTorts II Chartsmodwilli100% (1)
- Sales Final OutlineDocument44 pagesSales Final OutlineCole Hoffmeister75% (8)
- Contracts 1 - OutlineDocument17 pagesContracts 1 - OutlineMarlene MartinNo ratings yet
- La Salle National Bank V VegaDocument1 pageLa Salle National Bank V VegacrlstinaaaNo ratings yet
- Pro Resp Law ChartDocument22 pagesPro Resp Law ChartGud104No ratings yet
- CrimLaw AttackDocument31 pagesCrimLaw AttackLazinessPerSe100% (10)
- Pleadings Step by StepDocument3 pagesPleadings Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (3)
- Preclusion Step by StepDocument2 pagesPreclusion Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- Joinder of Parties StepbyStepDocument3 pagesJoinder of Parties StepbyStepLazinessPerSe100% (5)
- Interpretation - Construction Step by StepDocument2 pagesInterpretation - Construction Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Contracts Outline PDFDocument71 pagesContracts Outline PDFsierraNo ratings yet
- Contracts II Final OutlineDocument24 pagesContracts II Final Outlinepmariano_5No ratings yet
- Contracts Outline II Professor Knapp I. Parol Evidence Under The UCCDocument43 pagesContracts Outline II Professor Knapp I. Parol Evidence Under The UCCieaeaea100% (1)
- Contracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3Document15 pagesContracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3champion_egy325No ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument22 pagesContracts Outlinerealtor.ashley100% (1)
- Contracts Outline - Alces 2012Document15 pagesContracts Outline - Alces 2012dogsgonewildNo ratings yet
- Bartlett - Contracts Attack OutlineDocument4 pagesBartlett - Contracts Attack OutlinefgsdfNo ratings yet
- Chevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)Document2 pagesChevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)GeneTeam100% (1)
- Contract Law OutlineDocument13 pagesContract Law Outlinesomeguy8133100% (1)
- Contract II Short SheetsDocument10 pagesContract II Short Sheetsbetasteve100% (1)
- Contracts Final OutlineDocument19 pagesContracts Final OutlineCatherine Merrill100% (1)
- Contracts 2 Outline Spring20Document66 pagesContracts 2 Outline Spring20Amelia PooreNo ratings yet
- Contracts Succinct OutlineDocument21 pagesContracts Succinct OutlineAmanda100% (1)
- Civ Pro Attack OutlineDocument3 pagesCiv Pro Attack OutlineDeeNo ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument33 pagesContracts OutlinejesharerNo ratings yet
- Ucc r2 Chart Contracts 1LDocument21 pagesUcc r2 Chart Contracts 1LAsh Ley100% (2)
- Fall Civil Procedure Outline FinalDocument22 pagesFall Civil Procedure Outline FinalKiersten Kiki Sellers100% (1)
- Contracts OutlineDocument25 pagesContracts OutlineSabrina Peterman100% (1)
- Sales OutlineDocument41 pagesSales Outlineesquire1010100% (1)
- Supplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartDocument1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartYenisNo ratings yet
- Sales Outline: "The Good Guy Always Wins"Document15 pagesSales Outline: "The Good Guy Always Wins"zachroyusiNo ratings yet
- Contracts 1 SchoonerDocument23 pagesContracts 1 SchoonerJennifer Wilson100% (1)
- Frier Contracts Outline 2Document80 pagesFrier Contracts Outline 2oaijfNo ratings yet
- Contrascts II Memorize OutlineDocument3 pagesContrascts II Memorize OutlineAndrew BassNo ratings yet
- Fall 18 Sales - OutlineDocument71 pagesFall 18 Sales - OutlineKatlyn Taylor Milligan100% (1)
- How To Win A Cali AwardDocument30 pagesHow To Win A Cali AwardS King100% (1)
- Sec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistDocument4 pagesSec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistNicole Marie Torres100% (1)
- Contracts FlowchartDocument1 pageContracts Flowchartfunkchunk33100% (1)
- Accomplice Common LawDocument1 pageAccomplice Common LawLiliane KimNo ratings yet
- Products Liability OutlineDocument108 pagesProducts Liability OutlineFaris YoungNo ratings yet
- Bender Contracts Outline - Best Outline EverDocument49 pagesBender Contracts Outline - Best Outline EverLaura C100% (1)
- Civ Pro (Discovery) FlowchartDocument1 pageCiv Pro (Discovery) FlowchartJack EllisNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure - Freer Fall 00 01Document27 pagesCivil Procedure - Freer Fall 00 01lssucks1234No ratings yet
- Applying The Hanna/Erie Doctrine: Yes No Yes Yes NoDocument1 pageApplying The Hanna/Erie Doctrine: Yes No Yes Yes NoMolly EnoNo ratings yet
- One Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Document3 pagesOne Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Naadia Ali-Yallah100% (1)
- Bar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFDocument7 pagesBar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFno contractNo ratings yet
- Final Civil Procedure Outline!Document7 pagesFinal Civil Procedure Outline!Kate BroderickNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro I ChecklistDocument4 pagesCiv Pro I ChecklistDario Rabak0% (1)
- Products Liability 3Document46 pagesProducts Liability 3phil_edelsonNo ratings yet
- E&E Products LiabilityDocument6 pagesE&E Products Liabilitytbolling1No ratings yet
- Restatement ChartDocument10 pagesRestatement ChartJanice HallyceNo ratings yet
- Corporation Essay ChecklistDocument5 pagesCorporation Essay ChecklistCamille2221No ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument18 pagesContracts OutlineSam Levine100% (2)
- Jason Contracts OutlineDocument26 pagesJason Contracts Outlinethekaybomb100% (1)
- Habeas Corpus AnalysisDocument6 pagesHabeas Corpus AnalysisLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Supervening Issues Step by StepDocument2 pagesSupervening Issues Step by StepLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Property Review OutlineDocument22 pagesProperty Review OutlineLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Property OutlineDocument14 pagesProperty OutlineLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- UE - MO Step by StepDocument2 pagesUE - MO Step by StepLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Improper Bargaining Step by StepDocument3 pagesImproper Bargaining Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Interpretation - Construction Step by StepDocument2 pagesInterpretation - Construction Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Parol Evidence Rule Step by StepDocument2 pagesParol Evidence Rule Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (4)
- Joinder of Claims StepbyStepDocument1 pageJoinder of Claims StepbyStepLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- 12 (B) (6) Vs Summary Judgment StepbyStepDocument1 page12 (B) (6) Vs Summary Judgment StepbyStepLazinessPerSe50% (2)
Conditions Step by Step
Conditions Step by Step
Uploaded by
LazinessPerSe100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
270 views1 pageThis document outlines 4 steps for determining conditions in a contract: 1) Determine if the term is a promise, condition, or promissory condition. 2) Determine if the condition is express, implied in fact, or constructive. 3) Determine if the condition is precedent, concurrent, or subsequent. 4) Determine if the condition requires strict or substantive compliance to affect the contract.
Original Description:
Conditions Step by Step
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines 4 steps for determining conditions in a contract: 1) Determine if the term is a promise, condition, or promissory condition. 2) Determine if the condition is express, implied in fact, or constructive. 3) Determine if the condition is precedent, concurrent, or subsequent. 4) Determine if the condition requires strict or substantive compliance to affect the contract.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
270 views1 pageConditions Step by Step
Conditions Step by Step
Uploaded by
LazinessPerSeThis document outlines 4 steps for determining conditions in a contract: 1) Determine if the term is a promise, condition, or promissory condition. 2) Determine if the condition is express, implied in fact, or constructive. 3) Determine if the condition is precedent, concurrent, or subsequent. 4) Determine if the condition requires strict or substantive compliance to affect the contract.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
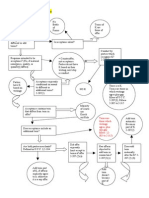
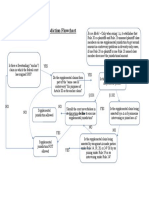
CONDITIONS STEP BY STEP
Condition Note: Interpretation/construction rules apply. 1) Determine NATURE OF TERM
a) Promise: An undertaking to act or refrain from acting in a specified way at some future time. b) Condition: An event that is not certain to occur. c) Promissory Condition: An event that is not certain to occur, but one party has promised will occur.
2) Determine TYPE OF CONDITION
a) Express: Language in K directly creates condition. i.e. On condition that, Provided that, or some other very obvious means of conveying that the K is conditional somehow. b) Implied in Fact: No language present, but contextual evidence supports understanding that condition was meant by the parties. c) Constructive: No language/context supports condition, but implied at law if the circumstances and nature of the K compel the conclusion that the condition should exist as a matter of policy, or that if the parties had addressed the issue, they reasonably would have intended it to be part of their K.
3) Determine SEQUENCE OF CONDITION (no specified order = interpretation/construction)
a) Precedent: Conditions fulfillment must precede the performance contingent upon it. i.e. Zoning board outcome either creates Buyers duty to perform or duty does not arise. b) Concurrent: Conditions fulfilled at the same time. i.e. Buyer paying and Seller conveying title. c) Subsequent: Condition occurs after performance. i.e. Zoning board outcome after K is signed either keeps Buyers duty to perform in effect or discharges the duty that arose at the K.
4) Determine CONDITIONS EFFECT ON K
a) Strict Compliance: Apply express/implied in fact condition terms strictly, even if result is harsh. b) Substantive Compliance: Apply construed condition terms reasonably.
You might also like
- Gilbert Law Summaries On Torts (2008) 726 PagesDocument726 pagesGilbert Law Summaries On Torts (2008) 726 PagesBILLYNo ratings yet
- Brown Machine v. Hercules (p153) 9.09Document3 pagesBrown Machine v. Hercules (p153) 9.09Stephen LindseyNo ratings yet
- Leg Reg Pre WriteDocument19 pagesLeg Reg Pre WriteashleyamandaNo ratings yet
- Battle of The Forms FlowchartDocument1 pageBattle of The Forms Flowchartncallan9No ratings yet
- Contracts 2 OutlineDocument37 pagesContracts 2 OutlineBrandon YeboahNo ratings yet
- Ucc and Restatement OutlineDocument7 pagesUcc and Restatement OutlineLauren WoodsonNo ratings yet
- Contracts II OutlineDocument16 pagesContracts II OutlineEva CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro Personal Jurisdiction Essay A+ OutlineDocument5 pagesCiv Pro Personal Jurisdiction Essay A+ OutlineBianca Dacres100% (1)
- Contracts - OutlineDocument25 pagesContracts - OutlineN FinkelsNo ratings yet
- Torts II ChartsDocument8 pagesTorts II Chartsmodwilli100% (1)
- Sales Final OutlineDocument44 pagesSales Final OutlineCole Hoffmeister75% (8)
- Contracts 1 - OutlineDocument17 pagesContracts 1 - OutlineMarlene MartinNo ratings yet
- La Salle National Bank V VegaDocument1 pageLa Salle National Bank V VegacrlstinaaaNo ratings yet
- Pro Resp Law ChartDocument22 pagesPro Resp Law ChartGud104No ratings yet
- CrimLaw AttackDocument31 pagesCrimLaw AttackLazinessPerSe100% (10)
- Pleadings Step by StepDocument3 pagesPleadings Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (3)
- Preclusion Step by StepDocument2 pagesPreclusion Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- Joinder of Parties StepbyStepDocument3 pagesJoinder of Parties StepbyStepLazinessPerSe100% (5)
- Interpretation - Construction Step by StepDocument2 pagesInterpretation - Construction Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Contracts Outline PDFDocument71 pagesContracts Outline PDFsierraNo ratings yet
- Contracts II Final OutlineDocument24 pagesContracts II Final Outlinepmariano_5No ratings yet
- Contracts Outline II Professor Knapp I. Parol Evidence Under The UCCDocument43 pagesContracts Outline II Professor Knapp I. Parol Evidence Under The UCCieaeaea100% (1)
- Contracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3Document15 pagesContracts II Checklist - Maggs - Spring 2003 - 3champion_egy325No ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument22 pagesContracts Outlinerealtor.ashley100% (1)
- Contracts Outline - Alces 2012Document15 pagesContracts Outline - Alces 2012dogsgonewildNo ratings yet
- Bartlett - Contracts Attack OutlineDocument4 pagesBartlett - Contracts Attack OutlinefgsdfNo ratings yet
- Chevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)Document2 pagesChevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)GeneTeam100% (1)
- Contract Law OutlineDocument13 pagesContract Law Outlinesomeguy8133100% (1)
- Contract II Short SheetsDocument10 pagesContract II Short Sheetsbetasteve100% (1)
- Contracts Final OutlineDocument19 pagesContracts Final OutlineCatherine Merrill100% (1)
- Contracts 2 Outline Spring20Document66 pagesContracts 2 Outline Spring20Amelia PooreNo ratings yet
- Contracts Succinct OutlineDocument21 pagesContracts Succinct OutlineAmanda100% (1)
- Civ Pro Attack OutlineDocument3 pagesCiv Pro Attack OutlineDeeNo ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument33 pagesContracts OutlinejesharerNo ratings yet
- Ucc r2 Chart Contracts 1LDocument21 pagesUcc r2 Chart Contracts 1LAsh Ley100% (2)
- Fall Civil Procedure Outline FinalDocument22 pagesFall Civil Procedure Outline FinalKiersten Kiki Sellers100% (1)
- Contracts OutlineDocument25 pagesContracts OutlineSabrina Peterman100% (1)
- Sales OutlineDocument41 pagesSales Outlineesquire1010100% (1)
- Supplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartDocument1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartYenisNo ratings yet
- Sales Outline: "The Good Guy Always Wins"Document15 pagesSales Outline: "The Good Guy Always Wins"zachroyusiNo ratings yet
- Contracts 1 SchoonerDocument23 pagesContracts 1 SchoonerJennifer Wilson100% (1)
- Frier Contracts Outline 2Document80 pagesFrier Contracts Outline 2oaijfNo ratings yet
- Contrascts II Memorize OutlineDocument3 pagesContrascts II Memorize OutlineAndrew BassNo ratings yet
- Fall 18 Sales - OutlineDocument71 pagesFall 18 Sales - OutlineKatlyn Taylor Milligan100% (1)
- How To Win A Cali AwardDocument30 pagesHow To Win A Cali AwardS King100% (1)
- Sec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistDocument4 pagesSec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistNicole Marie Torres100% (1)
- Contracts FlowchartDocument1 pageContracts Flowchartfunkchunk33100% (1)
- Accomplice Common LawDocument1 pageAccomplice Common LawLiliane KimNo ratings yet
- Products Liability OutlineDocument108 pagesProducts Liability OutlineFaris YoungNo ratings yet
- Bender Contracts Outline - Best Outline EverDocument49 pagesBender Contracts Outline - Best Outline EverLaura C100% (1)
- Civ Pro (Discovery) FlowchartDocument1 pageCiv Pro (Discovery) FlowchartJack EllisNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure - Freer Fall 00 01Document27 pagesCivil Procedure - Freer Fall 00 01lssucks1234No ratings yet
- Applying The Hanna/Erie Doctrine: Yes No Yes Yes NoDocument1 pageApplying The Hanna/Erie Doctrine: Yes No Yes Yes NoMolly EnoNo ratings yet
- One Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Document3 pagesOne Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Naadia Ali-Yallah100% (1)
- Bar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFDocument7 pagesBar Essays Contracts Short Review Outline PDFno contractNo ratings yet
- Final Civil Procedure Outline!Document7 pagesFinal Civil Procedure Outline!Kate BroderickNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro I ChecklistDocument4 pagesCiv Pro I ChecklistDario Rabak0% (1)
- Products Liability 3Document46 pagesProducts Liability 3phil_edelsonNo ratings yet
- E&E Products LiabilityDocument6 pagesE&E Products Liabilitytbolling1No ratings yet
- Restatement ChartDocument10 pagesRestatement ChartJanice HallyceNo ratings yet
- Corporation Essay ChecklistDocument5 pagesCorporation Essay ChecklistCamille2221No ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument18 pagesContracts OutlineSam Levine100% (2)
- Jason Contracts OutlineDocument26 pagesJason Contracts Outlinethekaybomb100% (1)
- Habeas Corpus AnalysisDocument6 pagesHabeas Corpus AnalysisLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Supervening Issues Step by StepDocument2 pagesSupervening Issues Step by StepLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Property Review OutlineDocument22 pagesProperty Review OutlineLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Property OutlineDocument14 pagesProperty OutlineLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- UE - MO Step by StepDocument2 pagesUE - MO Step by StepLazinessPerSeNo ratings yet
- Improper Bargaining Step by StepDocument3 pagesImproper Bargaining Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Interpretation - Construction Step by StepDocument2 pagesInterpretation - Construction Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (1)
- Parol Evidence Rule Step by StepDocument2 pagesParol Evidence Rule Step by StepLazinessPerSe100% (4)
- Joinder of Claims StepbyStepDocument1 pageJoinder of Claims StepbyStepLazinessPerSe100% (2)
- 12 (B) (6) Vs Summary Judgment StepbyStepDocument1 page12 (B) (6) Vs Summary Judgment StepbyStepLazinessPerSe50% (2)