Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Related To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing Ability
Related To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing Ability
Uploaded by
Ferwina SakiliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Related To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing Ability
Related To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing Ability
Uploaded by
Ferwina SakiliCopyright:
Available Formats
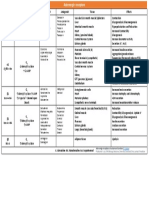
Example Nursing Diagnosis and Careplan for N205 Mini careplansPotential for Injury (Apsiration) Assessment Data Related
toNursing DiagnosisN u r s i n g D i a g n o s i s G o a l N u r s i n g I n t e r v e n t i o n s E v a l u a t i o n What Objective and SubjectiveData lead you to this one diagnosis. Objective: CVA with Left Sided ParalysisDiminished Gag ReflexDifficulty Swallowing Liquids Subjective (from patient or family)" Mom chokes every time sheeats". Potential for Injury (Aspiration) related to dimminshed gag reflexand impaired swallowing ability Goal (Should be broad statements whichsolve the Problem part of the NursingDiagnosis Statement. )Patient will not have injury related toaspiration (10/20/95 2-10pm) Outcome Criteria Specific and observable things whichallow an observer to determine if the patient met the goal1 . P a t i e n t wi l l h a v e n o c h o k i n g episodes while eating. 2. Patient color will remain cyanotic3 . P a t i e n t l u n g s o u n d s w i l l r e ma i n clear 4 . P a t i e n t C XR wi l l s h o w n o s i g n s o f aspirationInterventions should be things thatyou do (either independently or dependently) to assist the patient inreaching the goal. They should befocused on addressing the cause of the problem (the related to part of the nursing diagnosis statement) Place patient on side or with HOB toavoid aspiration of mucous.Feed patient liquids which have beenthickened, as thin liquids are morelikely to cause aspiration.Monitor lung sounds for signs of aspirationMonitor Lab and X-ray data for signs of aspiration.Evaluate based on the patients progresstowards each of theoutcome Criteria1 . P a t i e n t d i d n o t have problemswith chokingduring my shift.2 . P a t i e n t c o l o r w a s pink.3 . P a t i e n t l u n g sounds remainedclear.4 . Y o u m a y o r m a y not have lab/X-raydata to report,depending on theday and what testshave beenordered.Goal Met, ContinuePlan. ALSO INCLUDE
Was this an appropriateNursing Dx for THISPATIENT? It may turnout that after you carefor the patient, youdiscover a higherpriority nursingdiagnosis.
Sample Nursing Careplan for N205 : Fluid Volume Excess Assessment DataNursing DiagnosisGoal: Patient will not havefluid volume excessI n t e r v e n t i o n s E v a l u a t i o n (List the things your patienthas which make you suspecthe/she is overhydrated)Objective:Weight gain in past monthEdemaTight, shinny skinCrackles in lungsDecreased urine output Na level 134Hct level below 35Subjective:"My feet and legs are soswollen""I just can't breath if I'm flatin bed"Fluid volume excess RT water retentionsecondary to decreased renal perfusionand cardiac output Outcome Criteria: 1 . C l i e n t ' s w e i g h t w i l l b e WNL for Ideal BodyWeight (give numbers).2 . C l i e n t w i l l v e r b a l i z e ability to breathecomfortably.3 . L u n g s
will be clear 4.Vital Signs will Be WNL5.Relevant l a b v a l u e s (Sodium, Hct) will beWNL ( Na 135-145) etc.6 . U r i n e w i l l b e c l e a r yellow with output>30cc/hr 7 .I n t a k e wi l l n o t b e g r e a t e r than output8 . N o e v i d e n c e o f s k i n breakdown.Restrict fluids to 350 cc per shift.SR: Excessive fluids will worsen client'scondition. (Sparks, 110)Weigh client at same time each day, using samescale. SR: Provides baseline and continuingdatabase for monitoring changes and evaluatinginterventions.(Brunner, 1039)Administer diuretics (Lasix) as prescribed. SR:To increase excretion of water. (Ulrich, 508)Help client into a position that aids breathing,such as Fowler's or Semi-Fowler's.SR: To increase chest expansion and improveventilation. (Sparks, 110)Encourage client to cough and deep breathe q2h.SR: To prevent pulmonary complications.(Sparks, 110)Asculatate Lung Sounds q 4 hours. Monitor PulseOx Q 4 hours, Monitor CXR results, as performed.SR: To look for pulmonary vascular congestion, pleural peffusion, or pleural edema. (Ulrich, 508)Assess vital signs q4h.Assess lab values q shift.Monitor extremities for venous return (check pulses and capillary refill) q shift.SR: Decrease in venous blood flow results in anincrease in venous pressure, a rise in capillaryhydrostatic pressure, a net filtration of fluid outof the capillaries, and thus edema. (Brunner,625)Administer vasodilators, as ordered. SR: Toimprove renal blood flow. (Reduced renal1 . C l i e n t s w e i g h t was stable at 145lbs.2 . C l i e n t s t a t e d s h e could breathe better 3 . L u n g s h a d decreasedcrackles4 . V i t a l s i g n s w e r e T 98.6 P 87 R 24B/P 134/865 . N a w a s 1 3 5 6 . H c t w a s 3 6 7 . U r i n e w a s c l e a r yellow withoutput over 30cc/hr 8 . I n t a k e w a s 3 5 0 c c this shift withoutput of 475 = Negative fluid balance of 125 ccthis shift.9 . T h e r e w a s n o s k i n breakdown
perfusion stimulates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism) (Ulrich, 508)Encourage client to restrict Na intake.SR: Restriction of NA intake reduces theamount of Na that passes through the kidney and is reabsorbed. Thisresults in decreased retention of water. (Ulrich,37)Test urine specific gravity q8h.SR: High specific gravity indicates fluidretention. Fluid overload may alter electrolytevalues. (Sparks, 110)Examine skin q8h for signs of bruising or other discoloration.SR: Edema may cause decreased tissue perfusionwith skin changes. (Sparks, 108)Skin care q4h. (Cleanse wound with saline, dry,apply polysporin and dry gauze dressing.)SR: To prevent further skin breakdown. (Sparks,108)Reposition client q2h. References
Brunner, L.S. & Suddarth, D.S. (1988). Medicalsurgical nursing. Philadelphia: Lippincott.Sparks, S.M. (1993). Nursing diagnosis reference manual (2nd ed.). Springhouse, PA: Springhouse Corporation.Ulrich, S.P., Canale, S.W., & Wendell, S.A. (1994). Medical- surgical nursing care planning guides (3rd ed.). Philadelphia:Saunders.
You might also like
- Case Study 51 Acute PancreatitisDocument6 pagesCase Study 51 Acute PancreatitisKelsey LloydNo ratings yet
- Archer USMLE Step 3 Question BankDocument116 pagesArcher USMLE Step 3 Question Bankrolpf garri33% (3)
- SCIQuestions CaseStudyKeyDocument4 pagesSCIQuestions CaseStudyKeyDeez NutsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Simplified SheetsDocument14 pagesNursing Simplified Sheetssao sl78% (9)
- Anesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideFrom EverandAnesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- Hypovolemic Shock Case StudyDocument6 pagesHypovolemic Shock Case StudyJenn GallowayNo ratings yet
- Example Nursing Diagnosis and Careplan For N205 Mini Careplanspote Ntial ForDocument25 pagesExample Nursing Diagnosis and Careplan For N205 Mini Careplanspote Ntial ForCorina RadulescuNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis Case PresDocument29 pagesAcute Pancreatitis Case Preskristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- ClickerDocument4 pagesClickerJanae TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chapt 09Document20 pagesChapt 09brentupdegraffNo ratings yet
- Nle Tips May2015Document15 pagesNle Tips May2015Randy100% (2)
- Nle Tips Pls Read.. Dali DaliDocument15 pagesNle Tips Pls Read.. Dali DaliRandyNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument23 pagesAcute AppendicitisJack ChuaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Ankit Int MedDocument4 pagesTopic 9 Ankit Int MedAnkit Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- ICU Case StudyDocument9 pagesICU Case Studysand2123No ratings yet
- NCBI BookshelfDocument9 pagesNCBI Bookshelframzan aliNo ratings yet
- Nle Tips 3Document11 pagesNle Tips 3glenard-roble-1251No ratings yet
- NCM112 LP1 Rosales - AnswersDocument5 pagesNCM112 LP1 Rosales - AnswersChristine CalleyNo ratings yet
- Medical History Physical Exam Chest X-Ray Clinical Signs Breath Sounds Fremitus Pleural Friction Rub Egophony TrachealDocument8 pagesMedical History Physical Exam Chest X-Ray Clinical Signs Breath Sounds Fremitus Pleural Friction Rub Egophony TrachealCholo Mercado ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary SurveyDocument7 pagesPrimary and Secondary Surveyandila.muhammad20No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planapi-315741653No ratings yet
- SAQs PaediatricsDocument43 pagesSAQs Paediatricss336336anl100% (1)
- Physical Examination of Cardivascular ADocument4 pagesPhysical Examination of Cardivascular AAbdikhani Mohamed Mukhtar100% (1)
- Chapter VDocument15 pagesChapter VJellou MacNo ratings yet
- Epigastric Pain AssignmentDocument3 pagesEpigastric Pain AssignmentLauren EnglerNo ratings yet
- Check My Twitter Account @nursetopia or IG @nursetopia1 For More Nursing Test Banks, Sample Exam, Reviewers, and NotesDocument29 pagesCheck My Twitter Account @nursetopia or IG @nursetopia1 For More Nursing Test Banks, Sample Exam, Reviewers, and NotesNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument22 pagesShockDiana RamberNo ratings yet
- Resume Nasogastric Tube InstallationDocument17 pagesResume Nasogastric Tube InstallationRedmy LasmanaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care PASSTHEMRCSDocument131 pagesCritical Care PASSTHEMRCSthinzarNo ratings yet
- Documentation ExamplesDocument5 pagesDocumentation ExamplesErika HarveryNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisGeovanni Rai HermanoNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Pancytopenia: Section I: HistoryDocument12 pagesA Patient With Pancytopenia: Section I: HistoryHadia AamirNo ratings yet
- PALS Study GuideDocument12 pagesPALS Study GuidePrerna SehgalNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination DetailedDocument22 pagesAbdominal Examination Detailedsaveetha purushothamanNo ratings yet
- A Case of HypercalcemiaDocument7 pagesA Case of HypercalcemiaWitrisyah PutriNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Diagnostic Procedure) : Prepared By: Kriegel Paman Bihasa RM, RN, UsrnDocument17 pagesCardiovascular System (Diagnostic Procedure) : Prepared By: Kriegel Paman Bihasa RM, RN, UsrnKriegel Paman BihasaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument4 pagesDefinitionJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- RSM Osce Sheets 2009Document26 pagesRSM Osce Sheets 2009Derek Ho100% (2)
- Case Study Group 2 Chapter 21Document4 pagesCase Study Group 2 Chapter 21Arnold ZamoroNo ratings yet
- Extraoral Clinical Examination: Stature and Nutritional StatusDocument21 pagesExtraoral Clinical Examination: Stature and Nutritional StatusJheremy SolisNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument61 pagesChole CystitisPlain GerlNo ratings yet
- CVS Exam (RCT)Document7 pagesCVS Exam (RCT)kenners100% (11)
- Fluid Management in HFDocument47 pagesFluid Management in HFPandu AnggoroNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document10 pagesCH 1Jared Michael BergerNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination OSCE GuideDocument30 pagesAbdominal Examination OSCE Guideزياد سعيدNo ratings yet
- Shock: Ivan Mucharry Dalitan - PPDS Orthopaedi & Traumatologi Semester IVDocument5 pagesShock: Ivan Mucharry Dalitan - PPDS Orthopaedi & Traumatologi Semester IVusnulNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pediatric HemoptysisDocument5 pagesApproach To Pediatric HemoptysisAssma Haytham MuradNo ratings yet
- Guide To Clerking 2014Document24 pagesGuide To Clerking 2014Ridhwan Amid100% (1)
- Criteri Dimissione ICUDocument4 pagesCriteri Dimissione ICUgianriciNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument8 pagesRespiratory DisordersCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Daily Rounds in IcuDocument59 pagesDaily Rounds in IcutuulipNo ratings yet
- PANRE and PANCE Review Emergency MedicineDocument15 pagesPANRE and PANCE Review Emergency MedicineThe Physician Assistant Life100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Atlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringFrom EverandAtlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringNo ratings yet
- CHF Pathophys PaperDocument8 pagesCHF Pathophys PaperSarah SNo ratings yet
- Engebretsen2011, INSULINA EN B BLOQDocument7 pagesEngebretsen2011, INSULINA EN B BLOQFabiola Delia Rosas AlarcónNo ratings yet
- JURNAL GlimepirideDocument10 pagesJURNAL GlimepirideTazkiyatan IsriaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: HESI QuestionDocument1 pageMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: HESI QuestionTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Receptor 1Document1 pageReceptor 1Jeremy WongNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyDocument40 pagesLecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyRobert BakerNo ratings yet
- Transport System: Biology Unit (12/13) Kedah Matriculation CollegeDocument26 pagesTransport System: Biology Unit (12/13) Kedah Matriculation CollegegajenraoNo ratings yet
- Multivessel Pci Nejm - AppendixDocument47 pagesMultivessel Pci Nejm - Appendixmajeid saidNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To Injury, Surgical NutritionDocument8 pagesSystemic Response To Injury, Surgical NutritionCarl Earvin L. FavoritoNo ratings yet
- Path Endocrine OutlineDocument46 pagesPath Endocrine Outlineaya derweshNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Danger SignsDocument6 pagesNeonatal Danger Signsmarkus_danusantosoNo ratings yet
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483No ratings yet
- Ob Osce.04 CTG ReadingDocument6 pagesOb Osce.04 CTG ReadingDasha VeeNo ratings yet
- Evaluative Exam Gastrointestinal SystemDocument21 pagesEvaluative Exam Gastrointestinal SystemReymart AcalaNo ratings yet
- Tests From The Database Croc 2Document30 pagesTests From The Database Croc 2Андрій ВознякNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone For Atrial FibrillationDocument7 pagesAmiodarone For Atrial FibrillationARNo ratings yet
- Urine NGLDocument9 pagesUrine NGLBogdan RusuNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr 2 Sem Skills Pack 2020-21Document56 pages1st Yr 2 Sem Skills Pack 2020-21Francesca GrassiaNo ratings yet
- Aortic Valve Preservation - Concepts and Approaches 1st EditionDocument251 pagesAortic Valve Preservation - Concepts and Approaches 1st EditionSergeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesScience 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemMaricel PenaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Infective EndocarditisDocument13 pagesCase Presentation: Infective EndocarditisHillaryNo ratings yet
- Module 27Document14 pagesModule 27Jerico CastilloNo ratings yet
- Moving Exam NCM 109 LectureDocument6 pagesMoving Exam NCM 109 LectureMoneto CasaganNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 2312569Document1 pageNej Mic M 2312569lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Too Pooped To PumpDocument14 pagesToo Pooped To PumpYusar CahyadiNo ratings yet
- Q Bank 2010 WITH AnswersDocument119 pagesQ Bank 2010 WITH Answersazum77100% (7)
- Functional Relationship of The Different Organ Systems in Ensuring Animal SurvivalDocument22 pagesFunctional Relationship of The Different Organ Systems in Ensuring Animal SurvivalChristopher VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sign Symptoms Ketoacidosis DiabeticDocument4 pagesSign Symptoms Ketoacidosis DiabeticMatthew NathanielNo ratings yet