Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Equation Notes
Linear Equation Notes
Uploaded by
Matthew0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageThis document contains notes on linear equations, defining slope-intercept form, standard form, point-slope form, and how to find the x-intercept and y-intercept. It also defines slope as the ratio of the rise over the run between two points on a line and discusses horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines.
Original Description:
Notes on Linear Equations
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains notes on linear equations, defining slope-intercept form, standard form, point-slope form, and how to find the x-intercept and y-intercept. It also defines slope as the ratio of the rise over the run between two points on a line and discusses horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageLinear Equation Notes
Linear Equation Notes
Uploaded by
MatthewThis document contains notes on linear equations, defining slope-intercept form, standard form, point-slope form, and how to find the x-intercept and y-intercept. It also defines slope as the ratio of the rise over the run between two points on a line and discusses horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
”Do not worry about your problems with mathematics,
I assure you mine are far greater.” - Albert Einstein Linear Equation Notes Created by: Matthew Westerhoff, 2006
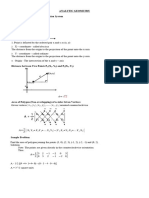
Slope-Intercept Form:
y = mx + b , where
m = slope and b = ordinate of the y-intercept.
x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable.
To find x-intercept let y = 0 and solve for x.
To find y-intercept let x = 0 and solve for y.
Standard Form:
Ax + By = C, where
A, B, and C are constants.
Point-Slope Form:
y − y1 = m(x − x1 ) where
m = slope and (x1 , y1 ) is a point on the line
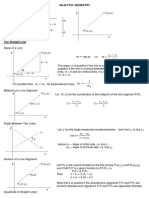
Definition of Slope:
Given two points (x1 , y1 ) and (x2 , y2 ) on a line then
y −y change of y ∆y
m = x2 − x1 = = ∆x = rise
run
2 1 change of x
Horizontal Lines have 0 slope.
Vertical Lines have an undefined slope.
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines:
Given two linear equations y1 = m1 x1 + b1 and y2 = m2 x2 + b2 , then
If m1 = m2 then y1 k y2 (y1 is parallel y2 )
If m1 · m2 = −1 then y1 ⊥ y2 (y1 is perpendicular to y2 )
You might also like
- Basic Integration Formula SheetDocument1 pageBasic Integration Formula SheetMatthewNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Formula SheetDocument1 pageBasic Integration Formula SheetMatthewNo ratings yet
- Advanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedDocument299 pagesAdvanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedShikhar Gupta92% (36)
- Derivatives and Integrals Formula SheetDocument1 pageDerivatives and Integrals Formula SheetMatthew100% (2)
- Families of CurvesDocument2 pagesFamilies of CurvesJoshua RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Maths For ManagementDocument53 pagesMaths For ManagementMwalimu Hachalu FayeNo ratings yet
- Maths Chapter - 1Document9 pagesMaths Chapter - 1AbushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Studentgerearegawi721No ratings yet
- 20 Dec 2021Document5 pages20 Dec 2021AbhimanyuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note 5Document35 pagesLesson Note 5Solange AtabongNo ratings yet
- AnalyticDocument25 pagesAnalyticshotsfiredsxiiiNo ratings yet
- 7760lecture 3 NotesDocument19 pages7760lecture 3 NotesSyed Osama GhaniNo ratings yet
- 0 A Brief Summary of Asymptotes PDFDocument13 pages0 A Brief Summary of Asymptotes PDFAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Lines: ObjectivesDocument16 pages1.3 Lines: ObjectivesWEDD FAWAZNo ratings yet
- Man Sci Reviewer para Sa Crush KoDocument3 pagesMan Sci Reviewer para Sa Crush KoJerickho JNo ratings yet
- Cgunit 1Document4 pagesCgunit 1Mr. K.Kasikumar Head of the Dept (CS)No ratings yet
- What Is A Linear Function?Document23 pagesWhat Is A Linear Function?Fernando Lipardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Pair of LinesDocument58 pagesPair of LinesKahaan KakabaliaNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument8 pagesLinear EquationkleyrgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsDocument11 pagesChapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsJiregna Gadisa KumsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Gia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- Study Unit 2: Linear Functions Chapter 2: Sections 2.1 - 2.4 and 2.6 1. FunctionDocument15 pagesStudy Unit 2: Linear Functions Chapter 2: Sections 2.1 - 2.4 and 2.6 1. FunctionMarionNo ratings yet
- Response CurveDocument11 pagesResponse CurveGrt grtNo ratings yet
- Int. Ext. Division Notes OneDocument7 pagesInt. Ext. Division Notes OneSeznie St. RemyNo ratings yet
- MGMT 221 Ch. 1Document13 pagesMGMT 221 Ch. 1kebron100% (1)
- MathsDocument138 pagesMathssolomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter One MathsDocument11 pagesChapter One Mathsየገጠር ልጅNo ratings yet
- 01 02 Functions Business SettingDocument35 pages01 02 Functions Business SettingFernando Lipardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Reviewer SlopeDocument3 pagesReviewer SlopeJashmine Mhae Mercado ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Linear Equations and Their Interpretative Applications in BusinessDocument14 pagesUnit 1: Linear Equations and Their Interpretative Applications in BusinessBetiy YitbarekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsDocument11 pagesChapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationstemedebereNo ratings yet
- Business MathematicsDocument135 pagesBusiness MathematicsEbsa Ademe100% (1)
- Chap 08Document29 pagesChap 08Giancarlo Libreros LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Study GuideDocument16 pagesCoordinate Geometry Study GuideAdair Contemarero100% (1)
- Linear Functions Review 20-50Document9 pagesLinear Functions Review 20-50Alberto EcheverriNo ratings yet
- Battery Exam ReviewerDocument11 pagesBattery Exam ReviewerLA WritesNo ratings yet
- Bus MathsDocument22 pagesBus MathsReal JoyNo ratings yet
- Lec 18 Linear Regression 02122022 010556pmDocument21 pagesLec 18 Linear Regression 02122022 010556pmsadia sagheerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1Document23 pagesLecture Notes 1Lucas ZogbiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1ghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper On MathDocument151 pagesA Research Paper On MathFafa AgbakpeNo ratings yet
- Slope and Linear Eq - Section 1.4Document13 pagesSlope and Linear Eq - Section 1.4Tere SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations: Different FormsDocument6 pagesLinear Equations: Different FormsStephanie BANGTANNo ratings yet
- Transformations of GraphsDocument21 pagesTransformations of GraphsChuah Xin YuNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts:) y y X X (Document5 pagesKey Concepts:) y y X X (virat gandhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4KelleyNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Formulae NewDocument2 pagesStraight Line Formulae New卂丂卄山丨几ツNo ratings yet
- Maths MicroprojectDocument1 pageMaths MicroprojectNarendra PalseNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument4 pagesLinear EquationthatweirdchildpNo ratings yet
- 32 Linear EquationsDocument5 pages32 Linear Equationsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry StudentsDocument10 pagesAnalytic Geometry StudentsRiza May BaisaNo ratings yet
- NotesLinearFunctions 1Document8 pagesNotesLinearFunctions 1Zhang SaNo ratings yet
- 08 Lines and Linear ModelsDocument12 pages08 Lines and Linear ModelsharshilNo ratings yet
- Slope and Intercept Form ReviewerDocument3 pagesSlope and Intercept Form Reviewerzh4hft6pnzNo ratings yet
- Biaxial Bending of Asymmetric Section: TensionDocument29 pagesBiaxial Bending of Asymmetric Section: Tensionnasser KhattabNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument286 pagesExperimental DesignIhsanaNo ratings yet
- CH IDocument10 pagesCH Igech95465195No ratings yet
- ASYMPTOTESDocument2 pagesASYMPTOTESJoan Christine Marie AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Further Concepts For Advanced Mathematics - FP1 Unit 2 Matrices - Section2i Invariant Points and Invariant LinesDocument4 pagesFurther Concepts For Advanced Mathematics - FP1 Unit 2 Matrices - Section2i Invariant Points and Invariant LinesEmmaculate OngumNo ratings yet
- 1e Sketching Cubic and Reciprocal GraphsDocument5 pages1e Sketching Cubic and Reciprocal GraphsZonish BakshNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic and Inverse Integral and Derivative FormulasDocument2 pagesHyperbolic and Inverse Integral and Derivative FormulasMatthewNo ratings yet
- Newton's MethodDocument9 pagesNewton's MethodMatthew100% (1)
- Variation of ParametersDocument1 pageVariation of ParametersMatthewNo ratings yet
- ALT CodesDocument1 pageALT CodesElle RalukNo ratings yet
- Writing A Matrix Into Row Echelon FormDocument1 pageWriting A Matrix Into Row Echelon FormMatthewNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation NotesDocument1 pageQuadratic Equation NotesMatthew100% (2)
- Related Rates ExamplesDocument6 pagesRelated Rates ExamplesMatthewNo ratings yet
- Factoring Using Greek MethodDocument1 pageFactoring Using Greek MethodMatthewNo ratings yet
- Least Common Multiple of NumbersDocument3 pagesLeast Common Multiple of NumbersMatthew100% (4)
- Least Common Multiple of Algebraic ExpressionsDocument1 pageLeast Common Multiple of Algebraic ExpressionsMatthew100% (1)