Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nasal Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NoseDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NoseManveer DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Describe The Osteology of The Nasal Cavity and Indicate Sites of Drainage For Each Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesDescribe The Osteology of The Nasal Cavity and Indicate Sites of Drainage For Each Paranasal Sinuskep1313No ratings yet
- Demo For Typing PDFDocument14 pagesDemo For Typing PDFGurpreet Kaur DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR - Mohamed Talaat ElghonemyDocument49 pagesProf. DR - Mohamed Talaat Elghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nose 2Document23 pagesAnatomy Nose 2Max Fax100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesMusfique RashidNo ratings yet
- Sinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFDocument4 pagesSinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Airway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2Document49 pagesAirway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2agatakassaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity - WikipediaDocument23 pagesNasal Cavity - Wikipediaراوند اعبيدNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The NoseDocument19 pagesAnatomy of The NoseYuka Puspita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 The NoseDocument8 pagesLecture 3 The Nosenatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- 8-The NoseDocument97 pages8-The NoseM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesAnatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfabubakar rizviNo ratings yet
- PBL - THT HidungDocument35 pagesPBL - THT Hidungdian novitasariNo ratings yet
- Lectures, WordDocument27 pagesLectures, Word9xymc5pcyzNo ratings yet
- Aj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusDocument117 pagesAj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusTradigrade PukarNo ratings yet
- Nose Dr. A. S. D' SouzaDocument18 pagesNose Dr. A. S. D' SouzaNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Nose ENT D&R AgamDocument131 pagesNose ENT D&R AgamS Balagopal SivaprakasamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.1 Nasal Cavities and Paranasal SinusesDocument21 pagesAnatomy Lec.1 Nasal Cavities and Paranasal Sinusesزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- 3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)Document28 pages3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- 1 RHINOLOGY NoseDocument116 pages1 RHINOLOGY NoseWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Modul Anatomi Blok 11Document40 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 11AyuNo ratings yet
- Nose and Nasal Cavity - 1Document39 pagesNose and Nasal Cavity - 1Sonali SudhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 The Nose and The Paranasal SinusesDocument6 pagesChapter - 15 The Nose and The Paranasal Sinusesmanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- The Nose and SinusesDocument40 pagesThe Nose and SinusesPraiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-1Document12 pagesChapter 8-1Syafrianda PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal Sinusbayoe_pra100% (1)
- Respiratory System-2cgf2Document42 pagesRespiratory System-2cgf2Nzenwa Jedidiah KimizuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NoseDocument35 pagesAnatomy Noseضبيان فرحانNo ratings yet
- Экзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРDocument98 pagesЭкзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРканизаNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4Document9 pagesScenario 4Syaema MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesNuardi YusufNo ratings yet
- Things To From BD: 1 PriorityDocument9 pagesThings To From BD: 1 PriorityFarah KhanNo ratings yet
- Nasal AnatomyDocument23 pagesNasal AnatomyArchanaShenoyNo ratings yet
- NOSEDocument6 pagesNOSEAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- FORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteDocument1 pageFORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteRusseiNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEDocument4 pagesNasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEAnna AyumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory Systemsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- Test 1: 1. A. F B.T C.F D.T E.FDocument34 pagesTest 1: 1. A. F B.T C.F D.T E.Famiumi2No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The EarBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Pretest AnatomyDocument3 pagesPretest AnatomyIndrias SalisaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Anatomy of The NoseDocument32 pages12 - Anatomy of The Nosehanizulfani13No ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes 2Nia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocument22 pagesB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.2 Pterygopalatine FossaDocument10 pagesAnatomy Lec.2 Pterygopalatine Fossaزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- G5 Nasal CavityDocument41 pagesG5 Nasal CavityGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Nasal AnatomyDocument2 pagesNasal Anatomycocstudio25No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Is A Common Disease Worldwide Characterized by at Least One Symptom Between Nasal ObstructionDocument10 pagesRhinitis Is A Common Disease Worldwide Characterized by at Least One Symptom Between Nasal ObstructionWii YangNo ratings yet
- NaaaaaaaaaaaDocument64 pagesNaaaaaaaaaaaRhea RaveloNo ratings yet
- 9pterygopalatine FossaDocument9 pages9pterygopalatine FossaAaaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory SystemThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - HandoutsDocument35 pagesRESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - Handoutsfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDocument137 pagesAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinus AnatomyDocument69 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinus AnatomyfitsumalemayehudNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy NotesEmerald BunnyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal SinusesDocument7 pagesLecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal Sinusesadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 5Document4 pagesCase Studies 5kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 4Document4 pagesCase Studies 4kep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - BSDocument15 pagesPsychiatry - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDocument2 pages2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- Anemia DifferentialDocument1 pageAnemia Differentialkep1313No ratings yet
- 2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative DisordersDocument7 pages2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV DiseaseDocument2 pages2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV Diseasekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in DiseaseDocument2 pages2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in Diseasekep1313No ratings yet
- MeimaDocument203 pagesMeimaAr Prateek KapilaNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite First AidDocument6 pagesSnake Bite First Aidmelchor bangaoilNo ratings yet
- A-Attrition and BruxismDocument5 pagesA-Attrition and BruxismBob Permana Simanungkalit100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Shobhit NirwanDocument9 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Shobhit NirwanygdfjjNo ratings yet
- Mudras. 02pdfDocument9 pagesMudras. 02pdfarunsrlNo ratings yet
- Gordon's Functional Health Pattern For DMDocument2 pagesGordon's Functional Health Pattern For DMAj Miranda100% (1)
- Ncert Xii Biology - Solutions - All ChaptersDocument106 pagesNcert Xii Biology - Solutions - All ChaptersKumar VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Animal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Document2 pagesAnimal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Chinmay KotkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Basic GeneticsDocument6 pagesIntroduction Basic GeneticscsamarinaNo ratings yet
- Hasna Arrywn - PART 1Document4 pagesHasna Arrywn - PART 1hasna arrywnNo ratings yet
- CFJ Anatomy Physiology PrimerDocument46 pagesCFJ Anatomy Physiology PrimerMarcelo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus CASE PRESDocument18 pagesStatus Asthmaticus CASE PRESNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- 7c SyllabusDocument5 pages7c Syllabusapi-421573700No ratings yet
- Rabbit FarmingDocument4 pagesRabbit FarmingNana Kwaku Duah IINo ratings yet
- Morning ReportDocument107 pagesMorning ReportMuhammad RezaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument37 pagesApproach To A Case of Ambiguous GenitaliaDR.MAULIK SHAHNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Phlebostatic Axis: Ask An ExpertDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Phlebostatic Axis: Ask An ExpertAnonymous r0XMWbsYAYNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument41 pagesThe Skeletal SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- WrwerDocument251 pagesWrwerRaheelNo ratings yet
- Possible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsDocument4 pagesPossible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsVivi rikkaNo ratings yet
- Injection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteDocument1 pageInjection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteAnonymous vGIfNflwEPNo ratings yet
- Rogo Se Bachav by Mohan GuptaDocument244 pagesRogo Se Bachav by Mohan GuptaAnonymous 3g66foKcWq75% (4)
- BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy, Volume 1 Upper Limb Thorax, 6th EditDocument18 pagesBD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy, Volume 1 Upper Limb Thorax, 6th EditGanjuNo ratings yet
- Goldenhar Syndrome AnesthesiaDocument4 pagesGoldenhar Syndrome AnesthesiaTysonNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Monitoring ToolDocument6 pagesCOVID 19 Monitoring ToolAmelinda ManigosNo ratings yet
- Mod 7 PoisoningDocument12 pagesMod 7 Poisoningrez198767% (3)
- Biology Term2 Assessment Y10Document10 pagesBiology Term2 Assessment Y109hgdpyk96jNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living at Your FingertipsDocument14 pagesHealthy Living at Your FingertipsazerNo ratings yet
- Gracevetsky Interview PDFDocument5 pagesGracevetsky Interview PDFdavidescu5costinNo ratings yet
Nasal Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Uploaded by
kep1313Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nasal Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright:
Available Formats
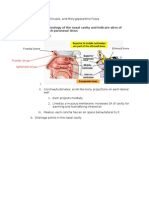
Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses, and Pterygopalantine Fossa April 16, 2010 1.
Describe the osteology of the nasal cavity and indicate sites of drainage for each paranasal sinus a. Lateral Wall
Frontal bone
Ethmoid bone
Frontal sinus Sphenoid sinus
Nasal
Palatine bone Maxilla
i. ii. Conchae/turbinates: scroll-like bony projections on each lateral wall 1. Each projects medially 2. Lined by a mucous membrane: increases SA of cavity for warming and humidifying inhaled air iii. Meatus: each concha has an air space below/lateral to it b. Drainage points in the nasal cavity
i. 1. Nasolacrimal duct: where excess tears drain into from the eyes 2. Middle meatus: frontal, maxillary, and anterior/middle ethmoids 3. Superior meatus: posterior ethmoids
4. Sphenothmoidal recess: where sphenoid sinus drains into
2. Indicate the relationships of the paranasal sinuses to other regions of the head
Ethmoid air cells ethmoid sinusitis may erode orbits Frontal sinus cause headache Sphenoid sinus most posterior
Maxillary sinus sinusitis causes pain/tenderness in cheek area
a.
3. Trace the course of the nerve and blood supply to the nasal cavity and indicate areas where nose bleeds are most common a. Blood supply i. External carotid artery maxillary artery enters pterygomaxillary fissure from the infratemporal fossa three pathways: 1. exits pterygomaxillary fossa on the medial side though the sphenopalatine foramen as the sphenopalatine artery 2. exits pterygomaxillary fossa on the superior side through the inferior orbital fissure as the infraorbital artery 3. exits pterygomaxillary fossa on the inferior side through the greater palatine canal as the descending palatine artery
Sphenopalatine artery
Maxillary artery
ii.
Descending palatine artery
b. Nerve supply
Trigeminal ganglion V2
Infraorbital nerve SS
Nerve of pterygoid canal para/pre (VII) Pterygopalatine ganglion SS, para Greater/lesser palatine nerves SS, para/post
Nasal mucosal branches SS, para/post
i. 4. Probe the six foramina leading into or out of the pterygopalatine fossa and list the structures passing through each opening
a. 5. Describe the nerve pathways related to parasympathetic innervations of the lacrimal gland and the nasal and palatine mucous glands a. Superior salivatory nucleus CN VII geniculate ganglion greater petrosal nerve nerve of the pterygoid canal pterygopalatine ganglion b. Pterygopalatine ganglion: site of para/post cell bodies c. For lacrimal gland: i. Pterygopalatine ganglion lacrimal gland d. For nasal/palatine glands i. Pterygopalatine ganglion greater palatine nerve nasal/palatine mucosa
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NoseDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NoseManveer DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Describe The Osteology of The Nasal Cavity and Indicate Sites of Drainage For Each Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesDescribe The Osteology of The Nasal Cavity and Indicate Sites of Drainage For Each Paranasal Sinuskep1313No ratings yet
- Demo For Typing PDFDocument14 pagesDemo For Typing PDFGurpreet Kaur DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR - Mohamed Talaat ElghonemyDocument49 pagesProf. DR - Mohamed Talaat Elghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nose 2Document23 pagesAnatomy Nose 2Max Fax100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesMusfique RashidNo ratings yet
- Sinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFDocument4 pagesSinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Airway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2Document49 pagesAirway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2agatakassaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity - WikipediaDocument23 pagesNasal Cavity - Wikipediaراوند اعبيدNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The NoseDocument19 pagesAnatomy of The NoseYuka Puspita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 The NoseDocument8 pagesLecture 3 The Nosenatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- 8-The NoseDocument97 pages8-The NoseM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesAnatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfabubakar rizviNo ratings yet
- PBL - THT HidungDocument35 pagesPBL - THT Hidungdian novitasariNo ratings yet
- Lectures, WordDocument27 pagesLectures, Word9xymc5pcyzNo ratings yet
- Aj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusDocument117 pagesAj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusTradigrade PukarNo ratings yet
- Nose Dr. A. S. D' SouzaDocument18 pagesNose Dr. A. S. D' SouzaNariska CooperNo ratings yet
- Nose ENT D&R AgamDocument131 pagesNose ENT D&R AgamS Balagopal SivaprakasamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.1 Nasal Cavities and Paranasal SinusesDocument21 pagesAnatomy Lec.1 Nasal Cavities and Paranasal Sinusesزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- 3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)Document28 pages3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- 1 RHINOLOGY NoseDocument116 pages1 RHINOLOGY NoseWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Modul Anatomi Blok 11Document40 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 11AyuNo ratings yet
- Nose and Nasal Cavity - 1Document39 pagesNose and Nasal Cavity - 1Sonali SudhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 The Nose and The Paranasal SinusesDocument6 pagesChapter - 15 The Nose and The Paranasal Sinusesmanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- The Nose and SinusesDocument40 pagesThe Nose and SinusesPraiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-1Document12 pagesChapter 8-1Syafrianda PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal Sinusbayoe_pra100% (1)
- Respiratory System-2cgf2Document42 pagesRespiratory System-2cgf2Nzenwa Jedidiah KimizuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NoseDocument35 pagesAnatomy Noseضبيان فرحانNo ratings yet
- Экзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРDocument98 pagesЭкзам.тесты ИГ 4курс ЛОРканизаNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4Document9 pagesScenario 4Syaema MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesNuardi YusufNo ratings yet
- Things To From BD: 1 PriorityDocument9 pagesThings To From BD: 1 PriorityFarah KhanNo ratings yet
- Nasal AnatomyDocument23 pagesNasal AnatomyArchanaShenoyNo ratings yet
- NOSEDocument6 pagesNOSEAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- FORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteDocument1 pageFORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteRusseiNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEDocument4 pagesNasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEAnna AyumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory Systemsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- Test 1: 1. A. F B.T C.F D.T E.FDocument34 pagesTest 1: 1. A. F B.T C.F D.T E.Famiumi2No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The EarBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Pretest AnatomyDocument3 pagesPretest AnatomyIndrias SalisaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Anatomy of The NoseDocument32 pages12 - Anatomy of The Nosehanizulfani13No ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes 2Nia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocument22 pagesB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.2 Pterygopalatine FossaDocument10 pagesAnatomy Lec.2 Pterygopalatine Fossaزينب فؤاد موسىNo ratings yet
- G5 Nasal CavityDocument41 pagesG5 Nasal CavityGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Nasal AnatomyDocument2 pagesNasal Anatomycocstudio25No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Is A Common Disease Worldwide Characterized by at Least One Symptom Between Nasal ObstructionDocument10 pagesRhinitis Is A Common Disease Worldwide Characterized by at Least One Symptom Between Nasal ObstructionWii YangNo ratings yet
- NaaaaaaaaaaaDocument64 pagesNaaaaaaaaaaaRhea RaveloNo ratings yet
- 9pterygopalatine FossaDocument9 pages9pterygopalatine FossaAaaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory SystemThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - HandoutsDocument35 pagesRESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - Handoutsfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDocument137 pagesAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinus AnatomyDocument69 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinus AnatomyfitsumalemayehudNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy NotesEmerald BunnyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal SinusesDocument7 pagesLecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal Sinusesadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 5Document4 pagesCase Studies 5kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 4Document4 pagesCase Studies 4kep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - BSDocument15 pagesPsychiatry - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDocument2 pages2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- Anemia DifferentialDocument1 pageAnemia Differentialkep1313No ratings yet
- 2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative DisordersDocument7 pages2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV DiseaseDocument2 pages2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV Diseasekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in DiseaseDocument2 pages2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in Diseasekep1313No ratings yet
- MeimaDocument203 pagesMeimaAr Prateek KapilaNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite First AidDocument6 pagesSnake Bite First Aidmelchor bangaoilNo ratings yet
- A-Attrition and BruxismDocument5 pagesA-Attrition and BruxismBob Permana Simanungkalit100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Shobhit NirwanDocument9 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Shobhit NirwanygdfjjNo ratings yet
- Mudras. 02pdfDocument9 pagesMudras. 02pdfarunsrlNo ratings yet
- Gordon's Functional Health Pattern For DMDocument2 pagesGordon's Functional Health Pattern For DMAj Miranda100% (1)
- Ncert Xii Biology - Solutions - All ChaptersDocument106 pagesNcert Xii Biology - Solutions - All ChaptersKumar VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Animal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Document2 pagesAnimal Classification Chapter Assessment Science and Technology Part 2 STD 10th English Medium1572016893Chinmay KotkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Basic GeneticsDocument6 pagesIntroduction Basic GeneticscsamarinaNo ratings yet
- Hasna Arrywn - PART 1Document4 pagesHasna Arrywn - PART 1hasna arrywnNo ratings yet
- CFJ Anatomy Physiology PrimerDocument46 pagesCFJ Anatomy Physiology PrimerMarcelo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus CASE PRESDocument18 pagesStatus Asthmaticus CASE PRESNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- 7c SyllabusDocument5 pages7c Syllabusapi-421573700No ratings yet
- Rabbit FarmingDocument4 pagesRabbit FarmingNana Kwaku Duah IINo ratings yet
- Morning ReportDocument107 pagesMorning ReportMuhammad RezaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument37 pagesApproach To A Case of Ambiguous GenitaliaDR.MAULIK SHAHNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Phlebostatic Axis: Ask An ExpertDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Phlebostatic Axis: Ask An ExpertAnonymous r0XMWbsYAYNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument41 pagesThe Skeletal SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- WrwerDocument251 pagesWrwerRaheelNo ratings yet
- Possible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsDocument4 pagesPossible Interview Questions: Posted by at LabelsVivi rikkaNo ratings yet
- Injection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteDocument1 pageInjection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteAnonymous vGIfNflwEPNo ratings yet
- Rogo Se Bachav by Mohan GuptaDocument244 pagesRogo Se Bachav by Mohan GuptaAnonymous 3g66foKcWq75% (4)
- BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy, Volume 1 Upper Limb Thorax, 6th EditDocument18 pagesBD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy, Volume 1 Upper Limb Thorax, 6th EditGanjuNo ratings yet
- Goldenhar Syndrome AnesthesiaDocument4 pagesGoldenhar Syndrome AnesthesiaTysonNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Monitoring ToolDocument6 pagesCOVID 19 Monitoring ToolAmelinda ManigosNo ratings yet
- Mod 7 PoisoningDocument12 pagesMod 7 Poisoningrez198767% (3)
- Biology Term2 Assessment Y10Document10 pagesBiology Term2 Assessment Y109hgdpyk96jNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living at Your FingertipsDocument14 pagesHealthy Living at Your FingertipsazerNo ratings yet
- Gracevetsky Interview PDFDocument5 pagesGracevetsky Interview PDFdavidescu5costinNo ratings yet