Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Angina Outline
Angina Outline
Uploaded by
Jerick Michael FrancoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angina Outline
Angina Outline
Uploaded by
Jerick Michael FrancoCopyright:
Available Formats
ANGINA PECTORIS A MEDICAL OVERVIEW I ANGINA PECTORIS A major clinical manifestation of myocardial ischemia usually characterized by episodes of pain
n or pressure in the anterior chest Oftentimes a Precursor to Myocardial Infarction II RISK FACTORS MODIFIABLE: Atherosclerosis Obesity Diabetes Hypertension Sedentary Lifestyle Metabolic Syndrome Unopposed estrogen taking NON-MODIFIABLE: Age (Post Menopausal Women) Race Gender Familial Tendency III. TYPES Stable Angina Unstable Angina Prinzmetal | Atypical | Variant Angina Decubitus * Syndrome X IV. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS CHEST PAIN L- Retrosternal area Q- Heavy Sensation, Feeling of impending death, squeezing, burning, choking sensation R- Epigastrum, Back, Neck, Jaw, Shoulders, Inner aspects of the upper arm (usually left arm) S- Severe (rated 7-10) in pain rating scale T- Maybe precipitated or unprecipitated
Palpitations Pallor Diaphoresis Nausea and Vomiting
(+) Levines Sign S3 and S4 heart sounds Dizziness / Lightheadedness Shortness of Breath
V. DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS Blood tests Reveal: LDL, Triglyceride, VeryLDL, Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate, CReactive protein ; HDL Electrocardiography (ECG) (Usually a 12-lead ECG is used) Stable and Unstable- ST Depression Prinzmetal- ST Elevation Stress Test with ECG Echocardiography Coronary Angiography (Gold Standard) Definition A Procedure performed to detect obstruction in the coronary arteries of the heart. During the procedure a catheter is inserted into an artery into the arm or groin (subclavian / femoral) and then threaded carefully into the heart The blood vessels of the heart are then studied by injection of contrast media through the catheter. A rapid succession of Xrays (fluoroscopy) is taken to view blood flow. Nursing Considerations Assess patient allergy to iodine (seafood) Assess blood test results for possible surgical complications: hgb, aPTT, BUN, creatinine, plt, electrolyte levels During Procedure: Continuous BP and ECG monitoring, ensure IV line patency, Prepare resuscitation equipment incase any complication may occur Outpatient basis: 2-6 hours bed rest before ambulation After: Monitor for bleeding on catheter insertion site Pharmacological Treatment ANTIPLATELET Aspirin (ASA) bleeding precautions, blood coagulation tests, dont use in patients with severe anemia, caution in pt with gout Clopidogrel (Plavix) for patients with contraindications to aspirin BETA-BLOCKERS Metoprolol, Atenolol, Propanolol -Compete with endogenous catecholamines for beta-adrenergic receptors -Contraindicated in CHF, Asthma, cardiogenic shock, AV conduction abnormalities
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS Smooth muscle relaxation-peripheral arterial vasodilation Amlodipine(Norvasc), Diltiazem, Verapamil, -May increase LFT, use with caution in hepatic and renal patients, A/E include constipation (valsalva maneuver) Short-Acting Nitroglycerin Immediate relief of exertional or rest angina Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Nitro-bid, Nitrol) - Metered dose sprays and patches are used for prophylaxis Caution patients on vasodilating effects (headache), C/I in severe anemia, ischemia may worsen upon withdrawal Long Acting Nitroglycerin Causes venous and arterial dilatation Ideal for prinzmetal angina Isosorbide (Isordil, ISMO) For patients with poor prognosis ACE Inhibitors Inhibits conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II thereby breaking RAAS chain resulting to vasodilation and reduced fluid retention (lowered aldosterone secretion) Ramipril (Altace) Anti-ischemic Agents Ranolazine (Ranexa) -prolongs QT interval (Torsades de Pointes), inhibits fatty acid oxidation -indicated for Chronic Angina unresponsivce to other anti-anginal agents -does not reduce blood pressure or heart rate SURGICAL TREATMENTS Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) Description Nursing Considerations: Assess blood test results for possible surgical complications: hgb, aPTT, BUN, creatinine, plt, electrolyte levels During Procedure: Continuous BP and ECG monitoring, ensure IV line patency, Prepare resuscitation equipment incase any complication may occur After: Monitor for bleeding on catheter insertion site Place 10lbs Sandbag on catheter insertion site (Femoral Artery) for max of 6 hours after surgery Diet and Lifestyle Modifications Specifics Reduce fat, sodium and cholesterol in the diet
Avoid stimulating agents such as those that contain caffaine (coffee, chocolate) Quit/ STOP smoking Reduce Stress Exercise Treatment of Underlying Disease (DM, HTN, Obesity)
You might also like
- ACLS Pocket Card PDFDocument6 pagesACLS Pocket Card PDFdang vu hoang ducNo ratings yet
- Osce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOsce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionmmmalcampoNo ratings yet
- IU Vascular Sample SeptDocument21 pagesIU Vascular Sample SeptAlexander Edo Tondas67% (3)
- Angina Pectoris: A Medical OverviewDocument35 pagesAngina Pectoris: A Medical OverviewRose AnnNo ratings yet
- 02.emergency CardiologyDocument135 pages02.emergency Cardiologyapi-19916399No ratings yet
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- NURS 140 Exam 3 - Final Med SurgDocument11 pagesNURS 140 Exam 3 - Final Med Surgchristine.avaloNo ratings yet
- AnginaDocument37 pagesAnginaSHAHALOMGIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Hemant Mahanand (201941103034) Case StudyDocument50 pagesHemant Mahanand (201941103034) Case StudyHemiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy1Document23 pagesCardiac Disease in Pregnancy1Homeground entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Aan 204 Group Coursework: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The CourseDocument118 pagesAan 204 Group Coursework: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The CourseLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 6 KGD DeniseDocument95 pagesPemicu 6 KGD DeniseVincent VandestyoNo ratings yet
- Cardio DiseasesDocument77 pagesCardio Diseasesrea bentayaoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument42 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeGorgieNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument46 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeEmma Andaya100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Cardiovascular EmergenciesDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Cardiovascular Emergenciesعلاء البناءNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument17 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeChoga Ilham ArlandoNo ratings yet
- Stable Angina PectorisDocument27 pagesStable Angina PectorisMuhammad NurmanNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering DijumpaiDocument121 pagesPenyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering Dijumpaiandikaagus13No ratings yet
- Model Answer -I & II سبتمبر 2015تحريريDocument12 pagesModel Answer -I & II سبتمبر 2015تحريريAmr El TaherNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hipertensi KrisisDocument39 pagesTatalaksana Hipertensi KrisisImron RosyadiNo ratings yet
- Media 115008 en PDFDocument12 pagesMedia 115008 en PDFsukandeNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms-EditDocument32 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysms-EditrandikaNo ratings yet
- EmergencyDocument47 pagesEmergencymedstudy123No ratings yet
- ARRHYTHMIADocument82 pagesARRHYTHMIAjiluNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Coronary Syndrome - KOCIL 3Document69 pagesAcute and Chronic Coronary Syndrome - KOCIL 3Ino HajrinNo ratings yet
- A Fib in 60 Yr Old ManDocument32 pagesA Fib in 60 Yr Old ManNurul HikmahNo ratings yet
- Anestezia in Chirurgia CardiacaDocument179 pagesAnestezia in Chirurgia Cardiacamd.dascalescu2486No ratings yet
- PP Drug Classes and IndicationsDocument67 pagesPP Drug Classes and IndicationspninthemakinNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Content WyattDocument90 pagesCardiac Content WyattAnni BarbaNo ratings yet
- Limb IschaemiaDocument40 pagesLimb Ischaemiaqaaneta bint-e-najafNo ratings yet
- 41 Paediatric ArrhythmiasDocument4 pages41 Paediatric ArrhythmiasnasibdinNo ratings yet
- Management of Cerebrovascular AccidentsDocument42 pagesManagement of Cerebrovascular Accidentsepic sound everNo ratings yet
- Aneurisma Aorta AbdominalisDocument36 pagesAneurisma Aorta AbdominalisMutivanya Inez MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Management of Patients With Coronary Vascular and Ischemic Heart Disorders Course Pack 1Document13 pagesLesson 7 Management of Patients With Coronary Vascular and Ischemic Heart Disorders Course Pack 1maryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument85 pagesOxygenationDemuel Dee L. BertoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Roy V, Jutzy, MDDocument46 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Roy V, Jutzy, MDIrakiza jean jacquesNo ratings yet
- Case Report Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: Presented By: Dede Achmad Basofi, S. Ked I 111 12 011Document36 pagesCase Report Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: Presented By: Dede Achmad Basofi, S. Ked I 111 12 011DeproissantNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationDocument8 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationReiche GomezNo ratings yet
- 3 Ischemic Heart Disease - PPTX Year 3 2Document40 pages3 Ischemic Heart Disease - PPTX Year 3 2Danny DesuNo ratings yet
- Stable Ischemic HeartDocument217 pagesStable Ischemic HeartReda SoNo ratings yet
- Eme CVDocument35 pagesEme CVJason LinNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseasesDocument60 pagesValvular Heart DiseasesEthiopia TekdemNo ratings yet
- 5 ArrhythmiaDocument44 pages5 ArrhythmiaDanny DesuNo ratings yet
- PJK, CRS ApsDocument58 pagesPJK, CRS Apsre septian IlhamsyahNo ratings yet
- MedHOCC 13.5.2023 CardioDocument111 pagesMedHOCC 13.5.2023 Cardiofarith nasirNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease To TW FinalDocument13 pagesValvular Heart Disease To TW FinalMohammed ElSayedNo ratings yet
- ACLS SubhankarDocument87 pagesACLS SubhankarMarc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease: CPT Donald C Palma MCDocument46 pagesCardiovascular Disease: CPT Donald C Palma MCJorge RabajaNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDocument19 pagesCardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDurgesh PushkarNo ratings yet
- Investigations Management Notes For FinalsDocument138 pagesInvestigations Management Notes For FinalsThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument8 pagesCoronary Artery Diseaseqayyum consultantfpscNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rhythm and Related Disorders: - Marshell Tendean, MD - Department of Internal Medicine UKRIDA JakartaDocument50 pagesCardiac Rhythm and Related Disorders: - Marshell Tendean, MD - Department of Internal Medicine UKRIDA JakartavaiyenNo ratings yet
- Acute HF-IAIDocument49 pagesAcute HF-IAIAndita ListyannisaNo ratings yet
- 9 CsaDocument34 pages9 Csaمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease and StableDocument13 pagesCoronary Artery Disease and StableMuhammad GassanNo ratings yet
- Acs SGD 8 - 20240308 - 051618 - 0000Document13 pagesAcs SGD 8 - 20240308 - 051618 - 0000Sarah JesikaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patients With Possible Cardiovascular Disease and Physical Examination of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument79 pagesApproach To Patients With Possible Cardiovascular Disease and Physical Examination of The Cardiovascular SystemLajel S. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument12 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DM Type 2Document2 pagesPathophysiology of DM Type 2Jerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Venous CatheterDocument1 pageUmbilical Venous CatheterJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- NANDA-Approved Nursing DiagnosesDocument2 pagesNANDA-Approved Nursing DiagnosesJosie Kim100% (1)
- Factor Markets and Income DistributionDocument12 pagesFactor Markets and Income DistributionJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Factor Markets and Income DistributionDocument12 pagesFactor Markets and Income DistributionJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis Disease CycleDocument1 pageSchistosomiasis Disease CycleJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicineDocument6 pagesHerbal MedicineJerick Michael FrancoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Progressive Muscle Relaxation Combined With Deep Breathing Technique Immediately After Aerobic Exercises On Essential HypertensionDocument2 pagesEffect of Progressive Muscle Relaxation Combined With Deep Breathing Technique Immediately After Aerobic Exercises On Essential HypertensionNetraNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Agents - PharmacologyDocument3 pagesAntianginal Agents - PharmacologyChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Lutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleDocument7 pagesLutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleWayan GunawanNo ratings yet
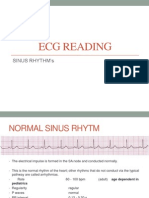
- ECG ReadingDocument7 pagesECG ReadingEricka Lj Robles DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Dynamic AuscultationDocument47 pagesDynamic AuscultationSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Hendra - EKGDocument34 pagesHendra - EKGRINANo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailureavidadarkestevilNo ratings yet
- Management of Arrhythmias in The Cardiovascular Intensive Care UnitDocument15 pagesManagement of Arrhythmias in The Cardiovascular Intensive Care UnitGabriela PachecoNo ratings yet
- 50 Cardiology Pimp Questions - LearntheHeartDocument19 pages50 Cardiology Pimp Questions - LearntheHearttrail 1No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmunary ResucitationDocument13 pagesCardiopulmunary ResucitationRussel OlivoNo ratings yet
- (:875 (: "M FlyerDocument1 page(:875 (: "M FlyerFsNo ratings yet
- Letters To The Editor: Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: An UpdateDocument1 pageLetters To The Editor: Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: An Updatesunilshinday1_456107No ratings yet
- ACCA Toolkit Abridged VersionDocument124 pagesACCA Toolkit Abridged VersionBianca BiaNo ratings yet
- Programme Gulfpcr2023Document21 pagesProgramme Gulfpcr2023Abid KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Valve Surgery: DR - Med. Dr. Yanto Sandy Tjang, SPBTKV (K), Mba, MPH, MSC, DSC, PHD, Fics, FetcsDocument20 pagesCardiac Valve Surgery: DR - Med. Dr. Yanto Sandy Tjang, SPBTKV (K), Mba, MPH, MSC, DSC, PHD, Fics, FetcsnoviNo ratings yet
- Tricuspid Valve Repair DeraniDocument15 pagesTricuspid Valve Repair Deranishoriwe68No ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Valvular Aortic Stenosis: Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesValvular Aortic Stenosis: Acute Myocardial InfarctionCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument12 pagesMyocardial InfarctionRifka Meilinda Putri IINo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Heart DiseasesDocument5 pagesHypertensive Heart DiseasesserubimNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AnginaDocument28 pagesPharmacology AnginaalijanmarwatNo ratings yet
- SymptomatologyDocument2 pagesSymptomatologyAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis and ArteriosclerosisDocument50 pagesAtherosclerosis and ArteriosclerosisApril Carter100% (1)
- Basic and Clinical Practice of Electrocardiography: Andi Wahjono Adi, SPJP (K) FihaDocument74 pagesBasic and Clinical Practice of Electrocardiography: Andi Wahjono Adi, SPJP (K) FihameutiaNo ratings yet
- Final Pathology PDFDocument294 pagesFinal Pathology PDFabdeljelile100% (1)
- Aortic Root Dilatation As The Sole Cause of Atrial FibrillationDocument2 pagesAortic Root Dilatation As The Sole Cause of Atrial FibrillationNathania HoswandiNo ratings yet
- Ventricular ArrhytmiaDocument30 pagesVentricular ArrhytmiaIkhsan AmadeaNo ratings yet
- DysrhythmiasDocument67 pagesDysrhythmiashhh hhhNo ratings yet