Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Client Side Operation
Client Side Operation
Uploaded by
shijonj5508Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Client Side Operation
Client Side Operation
Uploaded by
shijonj5508Copyright:
Available Formats
1.a) Discuss architecture of WWW.Ans: WWW stands for World Wide Web. It is an architectural framework for accessing linkeddocuments.
Following points describe about the architecture of WWW:i)Form user point of view, www is the collection of web pages or simply pages. Each pagecontain links to other pages which may be present elsewhere on machines in the internet.ii) The idea of one page pointing to another one is called hypertext. iii) Pages are viewed with a program called browser, which fetches the requested pages, formatsand display them. iv) On a web page, string of texts which is underlined are link to other pages. These are calledhyperlinks. v) Pages fetching is done by the browser.Entire process of obtaining the web pages on the client machine divided into majorprocesses:a) The dynamics happening on the client machine. b) The dynamics happening on the server machine. b) Explain client side and server side operations.Ans: Client Side Operation:In Client Side operation, browse follows the hyperlinks on the webpages, so its need a way to name the pages on other machine in the web. Web pages are namedusing URL which has three part Name of protocol, DNS name of the machine where the page islocated, and Name of the file containing the page.When a hyperlink is clicked:-*The browser locates the URL and asks DNS for IP address *When DNS replies with IP address browser makes TCP connection to port 80 onthe machine and sends a request for the required file. *The server sends the required file and TCP connection has closed. *Browser displays all text file info, images and other information.
Server Side Operation :- In server side operation, when URL is clicked the server offersfollowing operations:*Accept a TCP connection from a client. *Get the name of the file requested disk. *Get the file from the disk. *Return the file to the client. *Release the TCP connection. 2. a) Explain different forms of routing.Ans: Different forms of Routing:i) Next-hop routing:- The technique to make the content of routing table smaller is called next-hop routing. In this, the routing table holds only the addressof the next hop instead of holding information about the complete route. ii) Network-specific routing:- It makes the routing table smaller and searching process simpler.In this, routing tables contain only one entry for define the address of all host connected withsame physical network instead of an entry for each host. iii) Host-specific routing:- This is the inverse of network-specific routing. In this, the hostaddress is given in the routing table and it also contains specific entry for each host. But it isgood for certain purpose such as the route or providing security measure. iv) Default routing:- Default routing is a routing technique that used a default network address toroute the packets to host connected to the network. 3. a) Explain the BGP protocol in detail. National ISP (IBGP)AS3 Ans: The Border Gateway Protocol is a inter autonomous system (AS) routing protocol. BGP isused to exchange routing information for the internet and is the protocol used
between ISP.Customers connect to ISPs, and ISPs use BGP to exchange customer and ISP route. When BGP
is used between AS, the protocol is referred as External BGP (EBGP). If ISP is using BGP toexchange routes within an AS, the protocol is called Interior BGP. Regional ISP AS2 Customer3 Customer4 Regional ISP AS1 customer1 Customer2 BGP is very robust and scalable routing protocol. To achieve scalability BGP uses someattributes.a) Weight:- Weight is a Cisco defined attribute that is local to a router. This is not advertised toneighboring routers. If the router learns about more than one route to the same destination, theroute with the highest weight will be preferred. b) Local preference: - This attribute is used to prefer an exit point the local AS. The localpreference attribute is propagated throughout the local AS. If there are multiple exit points fromthe AS, the local preference attribute is used to select the exit point for a specific route. c) Multi-exit discriminator:- The multi-exit discriminator (MED) is used as a suggestion to anexternal AS regarding the preferred route into the AS that is advertising the metric. d) Origin:- This indicates how BGP learned about a particular route. The origin attribute canhave three possible values. i) IGP: The route is interior to the originating AS
ii) EGP: The route is learned via the Exterior BGP. iii) Incomplete: The origin of the route is unknown or learned in other way.e) AS _Path:f) Next hop:- The EBGP next-hop attribute is the IP address that is used to reach the advertisingrouter.g) Community:- This attribute provides a way of grouping destinations called communities, towhich routing decisions can be applied b) Discuss on IP RIP packet format. An IP RIP Packet format consists of nine fields:
i) Command: - This field indicates whether the packet is a request or a response. The requestasks that a router send all or part of its routing table. The response can be an unsolicited regularrouting update or a reply to a request. ii) Version number:- It specifies the RIP version which is in use. This field can signal differentpotentially incompatible versions. iii) Zero: - This field was added to provide backward compatibility with pre-standard varieties of RIP. It is not used by RFC 1058 RIP. iv) AFI: - It stands for Address-family Identifier. RIP is designed to carry routing information forseveral different protocols. Each entry has an AFI to indicate the type of address being specified.The AFI for IP is 2. v) IP Address: - It specifies the IP address for the entry. vi) Metric: - It indicates how many internetwork hops have been traversed in the trip to thedestination. This value is between 1 and 15 for a valid route, or 16 for an unreachable route. 5. a) Explain internet security model?Ans: When two parties exchanging their information through internet. They need security
so that no one could access their information or messages. To accomplish it, a security modelwill designed to protect the information transmission form an opponent who may present a threatto confidentiality. This technique has two components:-i) A security-related transformation onthe information to be sent. ii) Some secret information shared by the two principals and it is hoped, unknown to theopponent.A third party is needed to achieve secure transmission Or a third party is needed to arbitratedispute the two principals concerning the authenticity of a message transmission.Designing of Internet Security Model include following:-i) ii) iii) iv) Design an algorithm forperforming the security-related transformation. Generate secrete information to be used with the algorithm. iDevelop methods for the distribution and sharing of the secret information. Specify a protocol to be used by the two principals that makes use of the security algorithmand the secret information to achieve a particular security service. b) What is STEGANOGRAPHY? Explain.Ans: Steganography:-This is technique that hides the message in other messages. The senderwrites an innocuous message and then conceals on the same piece of paper. Some methods of stenography are: -Character marking:- Selected letters of printed written text are over written in pencil. Thesemarks are ordinarily not visible unless the paper is held at an angle to bright light. Invisible inks:- A number of substances can be used for writing but leave no visible trace untilheat or some chemical is applied to the paper. Pin punctures:-Small pin punctures on selected letters are ordinarily not visible unless the paperis held up in front of a light. Typewriter correction ribbon:- It is used between lines typed with a black ribbon, the results of typing with the correction tape are visible only under a strong light.The advantage of steganography is that the parties can employ the stenographer to reveal thesecrecy of the message. It main disadvantage is that it requires a lot of overhead to hide few bitsof information and once the system is discovered, it becomes useless without maintaining thesecrecy.
6. What is multimedia? What is streaming server? Explain audio streaming process.Ans: Multimedia:The combination of sound, graphics, animation, and video is calledmultimedia. It is a subset of hypermedia, which combines the aforementioned elements withhyper text. Streaming Server A server technology designed by Apple Computer to send streamingQuickTime media files over the internet. It is built on RTP and RTSP standard internet protocolsand it can set up a QuickTime streaming media Web broadcasting station capable of streamingdigital videos and music files to the users over the network.Process of Audio Streaming: In audio streaming, clients request compressed audio files thatreside on servers. Upon client request, the server directs an audio file to the client by sending fileinto socket. Before sending the files to the network, the file is segmented and encapsulated (byRTP) with special headers appropriate for audio traffic. 7. Explain classical encryption techniques.
Classical Encryption Technique: i) Substitution Cipher:- A substitution cipher is one inwhich each character in the plaintext is substituted for another character in the cipher text. Thereceiver decrypts the cipher text to recover the plaintext. ii) Monoalphabetic Cipher:- This is one in which each character of the plaintext is replaced witha corresponding character of cipher text. The cryptogram in the news papers is monoalphabaticcipher. iii) Playfair Cipher: Playfair is multiple letter encryption cipher, which treats diagrams in theplaintext as single units and translates these units into cipher text diagram. The playfairalgorithm is based on the use of a 5x5 matrix of letters constructed using keyword. The matrix isconstructed by filling the letter of the keyword from left to right and from top to bottom, andthen
filling in the reminder of the matrix with the remaining letters in alphabetic order. iv) Hill Cipher: - This is a multi letter cipher algorithm. This encryption algorithm takes msuccessive plaintext letters and substitutes for them m cipher text letters. The substitution isdetermined by m linear equation in which each character is assigned a numerical values (a=0, b=1z=25). v) Transposition Cipher:- In a transposition cipher, the plaintext remains the
same, but the orderof character is shuffled around. In columnar transposition, the plaintext is written horizontallyonto a piece of graph paper of fixed width and the cipher text vertically. A pure transpositioncipher is easily recognized because it has the same letter frequencies as the original plaintext. In decryption, cipher text written vertically onto a piece of graph of identical width and thenreading the plaintext off horizontally. 1.a) Write a brief note on SMTP. SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. I is a simple ACII protocol. To deliver amail, the source machine establishes a TCP connection to port 25, of the destination computer.The sending machine, operating as a client waits for the receiving machine, operating as a serverto talk first. The server starts by sending a line of text giving its identity and telling whether it isready for receive a mail or not. If it is not, the client releases the connection and tries again later.If the sever is ready to accept email then the client announces from where the email is comingand where it is going. If such a recipient exists at the destination then server gives instructions toclient to send email. No checksums are needed because TCP provide a reliable byte stream.When all the email has exchanged in the both directions, the connection is released.To get a better feel for SMTP first go to a machine connected to the internet. On a Unixsystem, type telnet mail.isp.com 25 . In windows system, click on start then run and type thecommand in the dialog box. 2. a) Discuss the following techniques of Routing:i) Next hop Routing: The technique to make the content of routing table smaller is called next-hop routing. In this, the routing table holds only the address of the next hop instead of holdinginformation abo
ut the complete route. Thats why routing table becomes consistent with each other. ii) Network Specific Routing: It makes the routing table smaller and searching process simpler.In this, routing tables contain only one entry for define the address of all host connected withsame physical network instead of an entry for each host. Ex- If 1000 hosts are attached to thesame network, only one entry exists in the routing table instead of 1000. iii) Host Specific Routing: This is the inverse of network-specific routing. In this, the hostaddress is given in the routing table and it also contains specific entry for each host. But it isgood for certain purpose such as the route or providing security measure. Ex- If 1000 hosts areattached to the same network, 1000 entry exists in the routing table instead of 1. iv) Default Routing: Default routing is a routing technique that used a default network addressto route the packets to host connected to the network. 3. a) With all nine fields explain OSPF packet format.Ans: OSPF packet format contain nine fields:-
An OSPF packet begins with a 24-byte header. i) ii) Version number:- It Identifies the OSPF version used. Type:- This identifies the OSPF packet type. Packet types can be:-
a) Hello:- It establishes and maintains neighbor relationships.
b) Database description:- It describes the contents of the topological database. c) Link-state update:- It responds to a link-state request packet. These messages arealso used for the regular dispersal of LSAs. d) Link-state request:- It requests pieces of the topological database from neighbor routers. e) Link-state knowledgment
iii)
Packet length:- It specifies the length of packet, including the OSPF header. iv) Router ID:- This indentifies the source of the packet.
v)
Area ID:- It indentifies the area to which the packet belongs. All OSPF
packets are associatedwith a single area. vi) Checksum:- It check the entire packet content for any damage suffered in
transit. vii) Authentication type:- All OSPF protocol exchanges are authenticated. The
authenticationtype is configurable on per-area basis. viii) ix) Authentication:- It contains authentication information. Data:- This contains encapsulated upper-layer information.0
5. a) Explain Infrared vis Radio transmission.Ans: Infrared Transmission: Infrared technologies uses diffuse reflect light or directed lightexists between sender and receivers to set up ad hoc connections. Sender can be LED or laserdiodes while photodiodes act as a receiver Advantages : i) infrared technology is simple and extremely cheap senders and receivers, whichare integrated in almost all mobile devices and receivers. ii) There is no license are required for infrared technology..
iii) IrDA implements data rates of up to 115 kbps while IrDA version 1.1 implements data ratesof 1.152 and 4Mbps.Disadvantages: It has low band width. Infrared is quite easily shielded. They cannot penetratewalls or other obstacles for good transmission.Radio Transmission: It works in the range of 2.4GHz. It is also used to set up ad hoc connectionfor work group. A dvantages: i) Radio transmission includes long term experience with radio transmission forWAN and mobile devices. ii) It covers large area and can penetrate walls, plants etc. iii) It offers transmission rate up to 10mbps.Disadvantages: In radio transmission shielding is not simple so it can interfere with other sendersor electrical devices can destroy data transmission via radio. It requires licenses. 1. a) Explain Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol.Ans: OSPF is a routing protocol developed for Internet Protocol (IP) networks by the InteriorGateway Protocol (IGP). OSPF is a link-sate routing protocol that calls for the sending of link-state advertisements to all other routers within same hierarchical area. Information on attachedinterfaces, metrics used, and other variables are included in OSPFLSAs.OSPF has two primary characteristic: i) This is an open protocol, which means that itsspecification is in the public domain.ii) OSPF is based on the SPF algorithm which sometimes is referred to as the Dijkstra algorithm. b) Discuss the features of real time protocol . The features of Real Time Protocol (RTP) are:i)RTP provides end-to-end delivery services for data with real-time characteristics such asinteractive audio and video. However, it does not provide any mechanism to timely delivery. Itneeds support from the lower layers of OSI model that actually have control over resources inswitches and routers.
ii) RTP provides timestamps, sequence numbers as hooks for adding reliability, flow, andcongestion control for packet delivery, but implementation is totally left to the application. iii) RTP is a protocol framework that is deliberately not complete. It is open to new payloadformats and new multimedia software. By adding new profile and payload format specifications,one can tailor RTP to new data formats and new applications. iv) The flow and congestion control information of RTP is provided by Real-Time ControlProtocol (RTCP) sender and receiver reports. v) RTP provides functionality and control mechanisms for carrying real-time content. 4. a) Explain different types of attacks.Ans: There are two types of attack: i) Passive Attack:- In this attack the goal of opponent is toobtain information that is being transmitted. It exists in two ways. One is release of messagecontent that is easily understood. E-mail, sms and a transferred file may contain sensitive orconfidential information. It is necessary to prevent the opponent from learning the content of thetransmission. Another one is traffic analysis is more subtle and often is more applicable tomilitary situation. It is used to guessing the nature of the communication taking place. ii) Active Attack:- It divided into four categories. a) Masquerade: This takes place when on entity pretends to be a different than other entity. b) Replay: This involves the passive capture of a data unit and its subsequent retransmission toproduce an unauthorized effect. c) Modification of messages: It means that some portion of the message is altered or thatmessages are delayed or reordered to produce an unauthorized effect.
d) Denial of service: It prevents or inhibits the normal use or management of communicationfacilities. 5.a) What is cryptography ? Explain one cryptographic algorithm. Or
Write a short note on transposition cipher. Cryptography:- Cryptography is the science of using mathematics to encrypt and decryptdata. It enables us to store sensitive information or transmit it across insecure network so that itcannot be read by anyone except the intended recipient. Cryptography is the science of securingdata.Transposition Cipher:- In a transposition cipher, the plaintext remains the same, but theorder of character is shuffled around. In columnar transposition, the plaintext is writtenhorizontally onto a piece of graph paper of fixed width and the cipher text vertically. A pure transposition cipher is easily recognized because it has the same letter frequencies as the originalplaintext. In decryption, cipher text written vertically onto a piece of graph of identical width andthen reading the plaintext off horizontally. Ex: Plaintext Computer Graphics COMPUTERGRAP HICS Cipher text CEHORIMGCPRSUATP.A pure transposition cipher is easily recognized because it has the same letter frequencies as the original plaintext. 7. Compare IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g WLAN architectures and blue tooth.
1.a) With the help of a neat diagram explain the architecture of WWW .
Ans:b) Discuss the working of POP3 in an E-mail System. What are its limitations?Ans: POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3. It begins when a user starts the mailreader. The mail reader calls up the ISP and establishes a TCP connection with the messagetransfer agent at port 110.Once the connection has been established, the POP3 protocol goesthrough three stages in sequence:Authorization:- This state deals with the user log inTransactions:- This state deals with the user collecting e-mail messages and marking them fordeletion from the mailbox.Update:- The update state causes the e-mail messages to be deleted. During the authorizationstate, at times, when the server is set for three passwords trials, if you give the wrong passwordthrice, your mail box will get locked.Limitations: i) There is no folder structure for sorting e-mail messages that are saved on thePOP3 server b) Discuss the working of POP3 in an E-mail System. What are its limitations?Ans: POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3. It begins when a user starts the mailreader. The mail reader calls up the ISP and establishes a TCP connection with the messagetransfer agent at port 110.Once the connection has been established, the POP3 protocol goesthrough three stages in sequence:Authorization:- This state deals with the user log inTransactions:- This state deals with the user collecting e-mail messages and marking them fordeletion from the mailbox.Update:- The update state causes the e-mail messages to be deleted. During the authorizationstate, at times, when the server is set for three passwords trials, if you give the wrong passwordthrice, your mail box will get locked.Limitations: i) There is no folder structure for sorting e-mail messages that are saved on thePOP3 server ii) The server has only one folder for incoming mails, which is the inbox. iii) No rules can be set at the POP3 server. All rules are set at the client end only. iv) To check e-mail, users have to download them first, they cannot see mails first beforedownloading the required mails. 2. a) What is Routing? Discuss direct and indirect Routing. 8
Ans: Routing: - Routing is a process of sending data packets or IP packets from the source to thedestination with the help of protocols (IP, and TCP), and routers using connectionoriented or aconnectionless network services.Direct Routing: - It occurs when the source and destination of the packet are on same physicalnetwork. In direct routing the final destination of the packet is a host connected to the samephysical network.In direct routing, the sender extracts the network address of the destination packet andcompares this address with the addresses of the network to which it is connected. If match isfound, then packet is delivered directly. The sender uses the destination IP address to find thedestination physical address. ARP maps the address of final destination to its correspondingphysical address.Indirect Routing: - In an indirect delivery, the data packet goes from router to router until itreaches to its final destination connected to the same physical network.In an indirect routing, the sender uses the destination IP address and a routing table to findthe IP address of the next router to which the packet should be delivered. ARP protocol is alsoused to find the physical address of next router. ARP maps the address of the next router and thephysical address of the next router. 4. a) Briefly explain the WLAN architecture.Ans: WLAN architecture consists of three components:i) Wireless end stations: The wireless end station can be any device that can communicate usingthe 802.11 standard. These devices include laptops, workstations, and PDAs, as well as printersand scanners.ii) Access points: The access point (AP) is a device. It acts as a network platform for connectionsbetween WLANs or to a wired LAN and as a relay between stations attached to the same APiii) Basic service sets (BSS): BSS is the logical component of wireless architecture. In general, itis a set of wireless stations controlled by a single management function and has twoconfiguration options that is, Infrastructure BSS (IBSS) and Extended Service Set (ESS).
In an IBSS, the stations communicate directly to one another without the need for an accesspoint. An ESS is a set of infrastructure BSSs that appear as a single BSS. This is
important forconnection redundancy but has some security issues that need to be addressed. 5. a) Discuss MAC layer of WLAN.Ans: MAC Layer stands for Medium Access Control Layer. It completes several tasks. It has tocontrol medium access. It supports for roaming, authentication, and power conservation. Thebasic services provided by MAC are data service and optional timebounded service. Bothservices can be offered by using an infrastructure-based network with the access pointcoordinating medium access.The mandatory basic method based on a version of CSMA/CA, an optional methodavoiding the hidden terminal problem, and finally a contention-free polling method for time-bounded service. The first two methods are summarized as distributed coordination function(DCF), the third method is called point coordination function (PCF). DCF offers onlyasynchronous service while PCF offers both asynchronous and time-bounded service but needsan access point to control medium access and avoid contention. The MAC mechanism are alsocalled (Distribution foundation wireless) DFWMAC. Three parameters which defines thepriorities of MAC are i) DCF inter-frame spacing (DIFS) ii) PCF inter-frame spacing(PIFS). iii) Short interframe spacing (SIFS). 7. a) Explain why audio and video need to be compressed.
Ans: Audio and video need to be compressed because uncompressed audio and video consume atremendous amount of storage and bandwidth. Compression also removes the inherentredundancies from digitized audio and video which reduce the amount of data that needs to bestored and transmitted by order of magnitude.An audio is compressed in following way: i) The analog signal is first sampled at some fixedrate. ii) Each of the samples is then rounded to one of a finite number of values.
iii) Each of the quantization values is represented by a fixed number of bits.Video is compressed to remove spatial redundancy means to much white spaces in an imageand temporal redundancy means repetition from image to subsequent image. b) What is iterative resolution?
Ans: This is a resolution technique in which, a server sends back the information to the client orsends the name of the server that has the information. The client then iterates by sending a
request to this referred server. This server may return the information itself or send the name of another server. This process continues till the time the client received the required informations.
2. a) Explain the client and server side events when user click on a URL . Ans: Client Side Operation:In Client Side operation, browse follows the hyperlinks on theweb pages, so its need a way to name the pages on other machine in the web. Web pages arenamed using URL which has three part Name of protocol, DNS name of the machine where thepage is located, and Name of the file containing the page.When a hyperlink is clicked:-* The browser locates the URL and asks DNS for IP address. * When DNS replies with IP address browser makes TCP connection to port 80 onthe machine and sends a request for the required file.
* The server sends the required file and TCP connection has closed. * Browser displays all text file info, images and other information. Server Side Operation:- In server side operation, when URL is clicked the server offersfollowing operations:* Accept a TCP connection from a client. * Get the name of the file requested disk. * Get the file from the disk. * Return the file to the client. * Release the TCP connection 3. a) Explain any one routing algorithm with the help of an example.Ans: SPF (Shortest Path First) is a routing algorithm. When SPF router powered up, it initializesits routing protocol data structure and then waits for indications from lowerlayer protocols thatits interfaces are functional. To acquire neighbors, it uses OSPF Hello protocol. The router sendshello packets to its neighbors and receives their hello packets.On multi-access networks, the hello protocol elects a designed router and a backup designatedrouter which allow a reduction in network traffic and in the size of the topological database andgenerates LSA for the entire network. These LSA is send by each router to inform others when a routers state changes and provide information about router adjacencies. By comparing established adjacencies to link states, failed routers can be detected and the network topology can be altered appropriately. From the topological database generated from LSAs, each routercalculates a shortest path tree which turn into a routing table. 4. Discuss the various features of WLAN and its protocol architecture. 15 Feature : i) WLANs are more flexible. With in radio coverage, nodes can communicatewithout further restriction. It is easy to carry.ii) Wireless network allow communication without previous planning.iii) Wireless networks can survive in disasters.iv) Wireless networks can be used everywhere we want.Protocol architecture of WLAN: In a typical WLAN
setup, the IEEE 802.11 standard WLAN(Access Point) gets connected to an IEEE 802.3 standard Ethernet (Switch/HUB) via a bridge.The higher layers (application, TCP, IP) look the same for the wireless node as for the wirednode. The IEEE 802.11 standard only covers the physical layer (PHY) and medium access layer(MAC) like the other 802.x LANs do. The physical layer is sub divided into the Physical LayerConvergence Protocol (PLCP) and the Physical Medium Dependent Sub Layer. The basic tasksof the MAC layer comprise medium access, fragmentation of user data, and encryption. ThePLCP sublayer provides a carrier sense signal called Clear Channel Assessment (CCA), andprovides a common PHY interface for the MAC, which is independent of the transmissiontechnology. b) Explain accessing of audio and video through a web server.
Audio accessing: To access audio from a web server, first user hears the audio file, andthen establishes a TCP connection with the web server and sends the HTTP request for theobject. After receiving the request the web server encapsulates the audio file in an HTTPresponse message and sends that message back to the user through TCP connection.Video accessing: Since video file stored in two different file audio and video. So, to access thevideo the user sends two separate requests to the server over two separate TCP connections.When the requests are reached to the server, then server also send back two separate HTTPresponses one for audio and another for video which arrived at the client in parallel. 4. a) Explain Real-time streaming protocol.Ans: RTSP is a protocol that enables a media player to control the transmission of a mediastream. RTSP messages use the port number 544 from the media stream. The RTSPspecification, RFC 2326, permits RTSP messages to be sent over TCP or UDP.RTSP server keeps a track of the state of the client for each ongoing RTSP session. For example,the server keeps track of whether the client is in an initialization state, a play state, or a pausestate. The session and sequence numbers, which are part of each RTSP request and response,help the server to keep track of the session state. The session number is fixed throughout theentire session; the client increments the sequence number each time it sends a new message; theserver echoes back the session number, and the current sequence number.
b) Explain transmission of multimedia data from a streaming server to a helperapplication.Ans: Getting data from streaming server to helper application like the media player requires atleast two servers where data is placed. One server is the HTTP server, and the second server is the streaming server.For example, when a user visits any songs/news web site, the web browser communicateswith the web server where the user chooses the file that has m usic or news. The moment theuser clicks any media file; media player requests for the media file to the streaming server anduser receives the media file on the media player. b) Explain the architecture of an infrastructure-based IEEE 802.11.Ans: Infrastructure-based IEEE 802.11 architecture :In this, several nodes, called station (STA)are connected to access point (AP). Stations are terminals with access mechanism to the wirelessmedium and radio connect to the AP. The stations an AP which are within the same radiocoverage form a basic service set (BSS). A distribution system connects several BSSs via the APto form a single network and there by extends the wireless coverage area. This network is calledan extended service set (ESS). Next, the distribution system connects the wireless networks viathe APs with a portal, which forms the internetworking unit to other LANs.Instead of distribution system, distribution system services are defined in the standard. The APsprovide synchronization with in a BSS, support power management, and can control mediumaccess to support time bounded service. 6. a) Explain the CSMA/CA mechanism.Ans: CSMA/CA is a network contention protocol that listens to a network in order to avoidcollisions, unlike CSMA/CD that deals with network transmissions once collisions have beendetected. The basic mechanism is shown in following figure:If the mechanism is sensed idle for at least the duration of DIFS, a node can access the mediumat once. This allows for short access delay under light load. If the medium is busy, nodes have to wait for the duration of DIFS, entering a contention phaseafterwards. Each node now chooses a random back off time with a contention window andadditionally delays medium access for this random amount of
time.The additionally waiting time is measured in multiples of slots. Slots time is derived from themedium propagation delay, transmitter delay and other PHY dependent parameters. 7. a) Briefly explain substitution ciphers. Substitution Cipher:- A substitution cipher is one in which each character in the plaintext issubstituted for another character in the cipher text. The receiver decrypts the cipher text torecover the plaintext.
There are four types of substitution: i) Monoalphabetic cipher:- In this each character of the plain text is replaced with acorresponding character of cipher text. ii) Homophonic cipher:- This is like a simple substitution cryptosystem, except a single characterof plain text can map to one of several characters of cipher text. iii) Polygram cipher:- In this blocks of characters are encrypted in groups. iv) Polyalphabetic cipher:- It is made up of multiple simple substitution ciphers. The particularone used changes with the position of each character of plaintext. 7. What is video? List and explain the drawback of the current internet to drive themultimedia data. Ans:8. Write short notes on:-
a) RTSP: RTSP stands for Real Time Streaming Protocol. It is defined in RFC2326. It providesfacilities to the user such as- RTSP is a protocol that allows a media player to control thetransmission of a media stream. Controlling of playback means pushing, forwarding, rewinding,repositioning and so on. It is an out-of-band protocol. In particular the RTSP messages are sentout-of-band, whereas the media stream, whose packet structure is not defined is considered inband.
a) Time out timer
Ans: Time out timer is used to help purge invalid routes from a RIP node. Routes that are notrefreshed for a given period of time are likely to be invalid because of some change in thenetwork. Thus, RIP maintains a timeout timer for each known route. When a route's timeout
timer expires, the route is marked invalid but is retained in the table until the routeflush timerexpires. c) Best effort service.
a) BGP path selection
A BGP selects only one path as the best path. When a path is selected it puts the selected pathin the IP routing table and propagates the path to its neighbors.BGP uses following criteria to select a path:-i)If the path specifies a next hop that is in accessible, drop the update.ii) Prefer the path with the largest weight.iii) If the weights are the same, prefer the path with the largest local preference.iv) If the local preferences are the same, prefer the path that was originated by BGP.v) If no route is originated, prefer the route that has the shortest AS_path.vi) If all paths have same AS_path length, prefer the path with the lowest origin type.vii) If the origin codes are same, prefer the path with lowest MED attribute.viii)If the paths have the same MED, prefer the external path over the internal path.ix) If the paths are also same, prefer the path through the closest IGP neighbor.x) Prefer the path with the lowest IP address as specified by the BGP router ID. b) Multimedia on internetAns: Today, multimedia over the internet has achieved significant but limited success. Forexample, streaming stored audio/video with user interactivity delays of five to ten
seconds isnow commonplace in the internet. But during peak traffic periods, performance may beunsatisfactory, particularly when intervening links are congested. Internet phone and real timeinteractive video has, to date, been less successful than streaming stored audio/video.The design of multimedia application would certainly be more straightforward if there weresome sort of first-class and second-class internet services, whereby first class packets werelimited in number and received priority service in router queues. Now we have best effort service by which we can make several design decisions and employ a few tricks to improve the user-perceived quality of a multimedia networking application. c) Cryptography and Cryptanalysis Cryptography:- Cryptography is the science of using mathematics to encrypt and decryptdata. It enables us to store sensitive information or transmit it across insecure network so that itcannot be read by anyone except the intended recipient. Cryptography isthe science of securing data.Cryptanalysis: It is the science of analyzing and breaking secure communication. Cryptanalystsare also called attackers. Classical cryptanalysis involves an interesting combination of analyticalreasoning, application of mathematical tools, pattern finding,patience and determination 1. What is POP? Explain the working of POP. Or
Explain Post Office Protocol (POP). POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3. It begins when a user starts the mail reader.The mail reader calls up the ISP and establishes a TCP connection with the message transferagent at port 110.Once the connection has been established, the POP3 protocol goes throughthree stages in sequence:Authorization:- This state deals with the user log inTransactions:- This state deals with the user collecting e-mail messages and marking them fordeletion from the mailbox.Update:- The update state causes the e-mail messages to be deleted. During the authorizationstate, at times, when the server is set for three passwords trials, if you give the wrong passwordthrice, your mail box will get locked 2. Explain why audio and video to be compressed?
Uncompressed audio and video consume a tremendous amount of storage and bandwidth.So these need to be compressed. Compression also removes the inherent redundancies fromdigitized audio and video which reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored andtransmitted by order of magnitude. 3. What is DNS? Explain working of DNS. DNS stand for Domain Name System. It translates the domain name into IP address andalso maps the domain name into Common Generic Name.Working of DNS:Whenever an application program calls a library procedure called Resolver with its domain name as parameter. The Resolver sends an UDP packet to the local DNS server.The DNS server searches its table and returns the IP address which matches the domain name.Now, the program can establish a connection or send UDP packets. 4. Explain conventional encryption model.
Ans:5. Explain IEEE 802.11 standards.
Ans:6. What are the five basic functions that an E-mail system supports?Ans: Function of E-mail system:- i) Composition:- It helps in creating message, and supportfunction such as insertion of address after extraction from the original message during replying. ii) Transfer:- It helps in sending messages to the destination. iii) Reporting:- This function repots the origin of E-mail whether it is delivered, lost orabandoned.iv) Displaying:- It displays the attached files comes with the E-mail using plug-in program. v) Disposition:- This is the final action of an E-mail. This constitutes the last stage. 7. Discuss different approaches used to make the routing table more efficient.Ans:8. What are the limitations of the best effort service? Explain.Ans:
Limitations of the best effort service are
Packet loss: As an IP datagram crosses through a network over UDP, it passes through buffers inthe routers in order to access outbound links. It is possible that one or more of the buffers in theroute from sender to receiver is full and cannot admit the datagram. In this case, the IP datagramis discarded, never to arrive at the receiving application. Loss could be eliminated by sending thepackets over TCP rather than over UDP.Excessive end-to-end delay: End-to-end delay is the accumulation of transmission, processing,and queuing delays in routers, propagation delays in the links, and end-system processing delays.Packet jitter: A crucial component of end-to-end delay is the random queuing delays in therouters. Because of these varying delays within the network, the time from when a packet isgenerated at the source until it is received at the receiver can fluctuate from packet to packet.This phenomenon is called jitter. 10. Briefly explain classification of security services. Security services are classified as follows: i) Confidentiality: It ensures that the informationin a computer system and transmitted information are accessible only for reading by authorizedparty. ii) Authentication: This ensures that the origin of a message or electronic document is correctlyidentified, with an assurance that the identity is not false. iii) Integrity: It ensures that only authorized parties are able to modify the computer assets andtransmitted information.iv) Non-repudiation: This requires that neither the sender nor the receiver of a message be able todeny the transmission. v) Access control: It requires that access to information resources may be controlled by or for thetarget system. vi) Availability: This requires that the computer system assets be available to authorized userwhen needed. 11. Explain Domain Name System (DNS).
DNS stand for Domain Name System. It translates the domain name into IP address andalso maps the domain name into Common Generic Name. It is a hierarchical scheme whichemploys domain based naming and uses a distributed database. It primarily maps host names andE-mail servers to IP addresses. DNS found in RFC 1034, 1035. 13. Compare direct and indirect forms of routing Ans: Direct Routing: - It occurs when the source and destination of the packet are on samephysical network. In direct routing the final destination of the packet is a host connected to thesame physical network.In direct routing, the sender extracts the network address of the destination packet andcompares this address with the addresses of the network to which it is connected. If match isfound, then packet is delivered directly. The sender uses the destination IP address to find thedestination physical address. ARP maps the address of final destination to its correspondingphysical address.Indirect Routing: - In an indirect delivery, the data packet goes from router to router until itreaches to its final destination connected to the same physical network.In an indirect routing, the sender uses the destination IP address and a routing table to findthe IP address of the next router to which the packet should be delivered. ARP protocol is alsoused to find the physical address of next router. ARP maps the address of the next router and thephysical address of the next router 16. What is an audio? What is a video? Audio: An audio is collection of an analog signal that is only audible.Video: A video is sequence of frames, with frames typically being displayed at a constant rate. 17. List the drawbacks of the current internet to drive the multimedia data.Ans: The Internet has some drawbacks with regard to multimedia data. For example, the mediaplayer does not communicate with the streaming server directly. This delay, before play-outbegins, is typically unacceptable for audio/video clips of moderate length. For this reason,audio/video streaming implementations typically have the server send the audio/video filedirectly to the media player process. In other words, a direct socket connection is made betweenthe server process and the media player process.
18. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of wireless LAN. Advantages:- i) WLANs are more flexible. With in radio coverage, nodes cancommunicate without further restriction.ii) Wireless network allow communication without previous planning.iii) Wireless networks can survive in disasters.
Disadvantages:i) WLANs offer lower quality due to less bandwidth than wired networks. ii) WLAN adapter are very costly. Ex- PC-Card is available in the range from 100 pounds. iii) WLANs are limited to low power senders and certain license-free frequency bands. iv) Using radio waves for data transmission might interfere with other high-tech equipment. 20. What is the purpose of time out timer? The purpose of the route timeout timer is to help purge invalid routes from a RIP node.Routes that are not refreshed for a given period of time are likely to be invalid because of somechange in the network. Thus, RIP maintains a timeout timer for each known route. When aroute's timeout timer expires, the route is marked invalid but is retained in the table until theroute-flush timer expires. 21. Discuss in detail the architecture of WWW? The architecture of WWW is two tiered. It consists of the client and the server. The client(web browser) requests for a web page. This page is retrieved from the server. The architecturedepends on three key standards: HTML for encoding document content, Uniform ResourceLocator (URL) for naming remote information objects in a global namespace, and HTTP forstaging the transfer. The following figure shows the twotiered architecture of WWW.If the web pages are interacting with the database, then the architecture becomes three-tiered, asshown in the following figure. 22. What is cryptography? List the different cryptographic algorithms
Cryptography:- Cryptography is the science of using mathematics to encrypt and decryptdata. It enables us to store sensitive information or transmit it across insecure network so that itcannot be read by anyone except the intended recipient. Cryptography isthe science of securing data.Different cryptographic algorithms are: Substitution cipher,, Monoalphabetic cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, Transposition cipher.
You might also like
- The Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingDocument55 pagesThe Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingAravind Dhananjeyan83% (6)
- MCSE Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesMCSE Questions and Answersnareshgotad65No ratings yet
- 10961C ENU CompanionDocument156 pages10961C ENU Companionshijonj5508No ratings yet
- 10979B ENU TrainerHandbook PDFDocument218 pages10979B ENU TrainerHandbook PDFshijonj5508No ratings yet
- t220 Building Drawing n3 QP Aug 2014Document8 pagest220 Building Drawing n3 QP Aug 2014Balungile0% (1)
- Advanced Computer NetworkDocument24 pagesAdvanced Computer NetworkAshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- Name: Hilal Rauf Subject: Advance Computer Networks Subject Code: BSIT - 62 Part: TBDocument7 pagesName: Hilal Rauf Subject: Advance Computer Networks Subject Code: BSIT - 62 Part: TBMukesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CN Unit Iv QBSDocument17 pagesCN Unit Iv QBS82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument13 pages1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The InternetCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 - Routers and NetworkingDocument12 pagesCh.7 - Routers and NetworkingpravinuttamNo ratings yet
- Lab - Mapping The Internet: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLab - Mapping The Internet: ObjectivesDelaida MuminovicNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The Internet PDFDocument12 pages1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The Internet PDFShah GeNo ratings yet
- DCCN Assignment 3Document7 pagesDCCN Assignment 3Usman ManiNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v6 Chapter 3Document8 pagesCCNA 1 v6 Chapter 3Webber JonxNo ratings yet
- 7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument8 pages7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetParthPatel0% (5)
- Networkin AssigmentDocument7 pagesNetworkin AssigmentanilNo ratings yet
- DCCN AssignmentDocument3 pagesDCCN AssignmentUsman ManiNo ratings yet
- FAQ'sDocument24 pagesFAQ'sduvvuruvitNo ratings yet
- 263 Exp3 CNSDocument15 pages263 Exp3 CNSneha.shroffNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument11 pages1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetHugoSantaellaSr100% (1)
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final ExamDocument62 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final ExamDonald TientcheuNo ratings yet
- Asiignment With SolutionDocument56 pagesAsiignment With SolutionmaulikNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument10 pages1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetGEOVANNYNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument50 pagesChapter IIIpapiNo ratings yet
- Interview Question and Answers of CCNADocument14 pagesInterview Question and Answers of CCNAPraveen Prakasan100% (1)
- Assesment 3 AnswersDocument4 pagesAssesment 3 AnswersMaja ChagorskyNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 6 Reading Guide FinishedDocument17 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 6 Reading Guide FinishedShriRam HegdeNo ratings yet
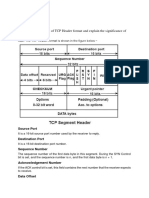
- Unit - 4: Source PortDocument13 pagesUnit - 4: Source PortthirumalreddyNo ratings yet
- Subnetting: Network ID Subnet ID Host IDDocument22 pagesSubnetting: Network ID Subnet ID Host IDmbaakanyiNo ratings yet
- 166 Exp4Document15 pages166 Exp4neha.shroffNo ratings yet
- Notes FinalDocument34 pagesNotes FinalNasir AliNo ratings yet
- Answer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?Document37 pagesAnswer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?dijeshkelothNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument13 pagesFinal Examcristiaan_schipper_147263100% (5)
- RIHT A Novel Hybrid IP Traceback SchemeDocument8 pagesRIHT A Novel Hybrid IP Traceback SchemeJAYAPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- ANS Part1 20171122 Partial SolutionDocument3 pagesANS Part1 20171122 Partial SolutionFouziNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1 - Mapping The Internet: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLab 3.1 - Mapping The Internet: Objectivesasd asdNo ratings yet
- CN Sem4Document16 pagesCN Sem4FFshivaNo ratings yet
- Network Monitoring Analysis Using Wireshark Tools (Term Project)Document19 pagesNetwork Monitoring Analysis Using Wireshark Tools (Term Project)Md. Anisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Name: K.Sai Manas Reddy REG NUM: 19BIT0027: Data Communication and Computer Networks Digital Assesment 1Document19 pagesName: K.Sai Manas Reddy REG NUM: 19BIT0027: Data Communication and Computer Networks Digital Assesment 1Manas ReddyNo ratings yet
- CN 2Document60 pagesCN 2Vinayaka HegdeNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument17 pagesPractice Finalawan kNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document17 pagesLecture 10تُحف العقولNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 Chapter 3Document8 pagesCCNA1 Chapter 3wahyuNo ratings yet
- Section 1:-Introduction To Networking Concepts NetworkingDocument35 pagesSection 1:-Introduction To Networking Concepts NetworkingManoj SainiNo ratings yet
- IFaru Chp7-9 Set3Document11 pagesIFaru Chp7-9 Set3Ishmael Faru100% (1)
- IT221 T Project Template (BGP)Document12 pagesIT221 T Project Template (BGP)1021shiroe1021No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Okech MableNo ratings yet
- Cisco HomeDocument42 pagesCisco HomeformycandyNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument13 pages1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetMuwien0% (2)
- C3. Objectives: Communication From Host To Host Network Layer and Internet Protocol (IP)Document5 pagesC3. Objectives: Communication From Host To Host Network Layer and Internet Protocol (IP)ciarmelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CNDocument30 pagesUnit 2 CNniharikaNo ratings yet
- Comptia-Network Study GuideDocument36 pagesComptia-Network Study GuideJonathan Velez Velazquez100% (3)
- Elementary TCP SocketsDocument13 pagesElementary TCP SocketsJV PriyaaNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- CCNA Certification All-in-One For DummiesFrom EverandCCNA Certification All-in-One For DummiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesFrom EverandWireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Innerpages Students Corner Previous Exam Papers BSIT Jun 2013 PDFDocument53 pagesInnerpages Students Corner Previous Exam Papers BSIT Jun 2013 PDFMilan SahuNo ratings yet
- Fina SoftDocument37 pagesFina Softshijonj5508No ratings yet
- Instructions: 1) Part A Is Compulsory: 2) Answer Any FIVE Questions From Part BDocument3 pagesInstructions: 1) Part A Is Compulsory: 2) Answer Any FIVE Questions From Part Bshijonj5508No ratings yet
- Form 10C RevisedDocument4 pagesForm 10C Revisedshijonj5508No ratings yet
- Vastu Labh: PresentsDocument8 pagesVastu Labh: PresentsSandesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Amendment of Fourth ScheduleDocument50 pagesAmendment of Fourth ScheduleSyerifaizal Hj. MustaphaNo ratings yet
- HINDU TEMPLE ARCHITECTURE of BHARAT-SOME PDFDocument30 pagesHINDU TEMPLE ARCHITECTURE of BHARAT-SOME PDFSonal KaranjikarNo ratings yet
- Zebra BoardsDocument5 pagesZebra BoardsAlfaro ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Design: A B C D E F G H I JDocument1 pageDetailed Design: A B C D E F G H I JTyrone PotterNo ratings yet
- Work Bills (LS - Last & Final Bill)Document11 pagesWork Bills (LS - Last & Final Bill)Joshua AbbottNo ratings yet
- Coo ProcessorDocument6 pagesCoo ProcessorFOUAD EL BRAHMINo ratings yet
- 3 4 7 AcutandfilloptionalDocument5 pages3 4 7 Acutandfilloptionalapi-355856202No ratings yet
- LAD PORTFOLIO 210201 Marketing With Engr. A2Document57 pagesLAD PORTFOLIO 210201 Marketing With Engr. A2Charmaine De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SAP TechEd Las Vegas Lectures Workshops PDFsDocument20 pagesSAP TechEd Las Vegas Lectures Workshops PDFsYo MeroNo ratings yet
- Configuring and Administering Microsoft® SharePoint® 2010Document324 pagesConfiguring and Administering Microsoft® SharePoint® 2010Pam LansingNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleManav GuptaNo ratings yet
- GCC Lab Manual Mahesh Kumar PDFDocument130 pagesGCC Lab Manual Mahesh Kumar PDFMohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- P85 PreCastWood Fired Oven PlansDocument30 pagesP85 PreCastWood Fired Oven PlansMarcelo del desiertoNo ratings yet
- Baroque Period INTRO DoneDocument4 pagesBaroque Period INTRO DoneJemar CulladoNo ratings yet
- FRS - Fire SPECS - EOI PDFDocument32 pagesFRS - Fire SPECS - EOI PDFRitesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Monocoque Bus DesignDocument88 pagesMonocoque Bus DesignAmit Garag100% (1)
- Details For R.C Floor Slabs, Beam, Lintel, Columns and Stair Details See Structural DrawingsDocument1 pageDetails For R.C Floor Slabs, Beam, Lintel, Columns and Stair Details See Structural DrawingsNana BarimaNo ratings yet
- Testing The Simulink Model by CompactRIODocument5 pagesTesting The Simulink Model by CompactRIOErne514No ratings yet
- Ospf Neighbor States Explained With ExampleDocument19 pagesOspf Neighbor States Explained With ExampleMark BrownNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Process FractalsDocument124 pagesContemporary Process Fractalsrishad mufas100% (2)
- Metal Door - SteelDocument18 pagesMetal Door - Steelmidenistis2No ratings yet
- BD-F - Reinforcement Cement Concrete: R.C.C. Work in FoundationsDocument8 pagesBD-F - Reinforcement Cement Concrete: R.C.C. Work in FoundationsdigvijayjagatapNo ratings yet
- Design of A Landfill Final Cover SystemDocument9 pagesDesign of A Landfill Final Cover SystemWagner TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- House Plans, 2 Story House Plans, 40 X 40 House Plans, 100121Document6 pagesHouse Plans, 2 Story House Plans, 40 X 40 House Plans, 100121MittuNo ratings yet
- Discover THE Beauty of Engineering: Aluminium WindowsDocument16 pagesDiscover THE Beauty of Engineering: Aluminium Windowsmathew1965No ratings yet
- Comos COMOS 10.1 - Readme: A5E32016431-AADocument94 pagesComos COMOS 10.1 - Readme: A5E32016431-AASri Surya LankapalliNo ratings yet
- Crack WidthDocument5 pagesCrack WidthchanakyaNo ratings yet
- ArchibusDocument12 pagesArchibusapi-256135737No ratings yet