Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Uploaded by
henrylewiskennedyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: Team SmartDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: Team SmartJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Cannock Chase GeologyDocument30 pagesCannock Chase Geologypeter_alford3209No ratings yet
- Folds and FaultsDocument11 pagesFolds and FaultsfosteckhNo ratings yet
- GeoEng - JD HendersonDocument4 pagesGeoEng - JD HendersonARIANNE JADE ORBISTANo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting in The EarthDocument5 pagesFolding and Faulting in The Earthdiannereyes23No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 GEOLOGYDocument10 pagesLecture 4 GEOLOGYnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Geology (Unit 3) : Rock Deformation (Cause of Folding and Faulting)Document9 pagesGeology (Unit 3) : Rock Deformation (Cause of Folding and Faulting)chhabra994143No ratings yet
- Deforming Earth's Crust: Section 3Document12 pagesDeforming Earth's Crust: Section 3Argeena Agao-AgaoNo ratings yet
- High School Earth Science - Stress in The Earth's Crust - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument59 pagesHigh School Earth Science - Stress in The Earth's Crust - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldAngellene TumilapNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument48 pagesChapter Threeone loveNo ratings yet
- C3ed2znol Module 4 Earth and Life Science Rocks Deformation and Metamorphism 1.docx UPDATED JULY 20 2020Document17 pagesC3ed2znol Module 4 Earth and Life Science Rocks Deformation and Metamorphism 1.docx UPDATED JULY 20 2020Philippines QuestionNo ratings yet
- Geol 11 Week 10 - Rock Deformation - Annotated Lecture SlidesDocument12 pagesGeol 11 Week 10 - Rock Deformation - Annotated Lecture SlidesAssignment ForNo ratings yet
- Science 11 LAS Geologic ProcessDocument2 pagesScience 11 LAS Geologic ProcessKimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Causes and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Causes and MeasurementsMahfuzul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Explanation: 1 Episode: These Sedimentary Layers Were Originally Deposited Horizontally. They've Been FoldedDocument5 pagesExplanation: 1 Episode: These Sedimentary Layers Were Originally Deposited Horizontally. They've Been FoldedMubashirKhattakNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Q2 Week3Document10 pagesEarth Science Q2 Week3MCAPUZ, MARK JOHN, V.No ratings yet
- Faulting and FoldingDocument3 pagesFaulting and FoldingchikwambaNo ratings yet
- Strike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockDocument16 pagesStrike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockGanguli Tutor RajNo ratings yet
- LP4 w4 Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesLP4 w4 Earth and Life ScienceJiego PabiaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Geological StructuresDocument50 pagesGroup 6 Geological StructuresAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 8: Faults, Folds, and Cross-Cutting RelationshipsDocument8 pagesLaboratory 8: Faults, Folds, and Cross-Cutting RelationshipsXuan PhuongNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci 7Document13 pagesEarth Sci 7Cyrus GabutenNo ratings yet
- Earth QuakeDocument16 pagesEarth QuakeJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology Group 5Document35 pagesStructural Geology Group 5richethan25No ratings yet
- Geologic StructuresDocument6 pagesGeologic Structurescris ortonero100% (1)
- Unit Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map InterpretationDocument45 pagesUnit Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map InterpretationBennet Nii Tackie-OtooNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology: A) Geological Maps B) Folds, Fault, & JointsDocument42 pagesStructural Geology: A) Geological Maps B) Folds, Fault, & JointsRolandNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisGue Gitu LochNo ratings yet
- Report in ElsDocument2 pagesReport in ElsRowe AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ELSDocument50 pagesLesson 2 - ELSalshawy0909No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document100 pagesChapter 5samajikpraani97No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Earth 'S Geological ProcessesDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science: Earth 'S Geological ProcessesGentila LancheNo ratings yet
- Forces in Earth - S CrustDocument55 pagesForces in Earth - S CrustBlanche Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth ScienceAutumn ZakyNo ratings yet
- Rock Deformation and Earthquake FinalDocument131 pagesRock Deformation and Earthquake Finalniaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Faulting and Folding of Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesFaulting and Folding of Plate TectonicsJailian Rhainne Delloso BretañaNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology GroundwaterDocument109 pagesStructural Geology Groundwaterkiran_ran99No ratings yet
- DiastrophismDocument31 pagesDiastrophismEunice Rean SamonteNo ratings yet
- DiastrophismDocument7 pagesDiastrophismhilaliusvalentine67No ratings yet
- MergeResult 2022 10 01 11 04 58Document114 pagesMergeResult 2022 10 01 11 04 58Mark Justine MallariNo ratings yet
- Module-3: Structural Geology & Rock MechanicsDocument76 pagesModule-3: Structural Geology & Rock MechanicsLeon FouroneNo ratings yet
- 5.structural GeologyDocument46 pages5.structural Geologysamir bardewaNo ratings yet
- Perlita Rock StructureDocument29 pagesPerlita Rock StructureJohn Rey DumaguinNo ratings yet
- 4 Geological StructuresDocument35 pages4 Geological StructuresZahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Unconformities Joints Faults and FoldsDocument8 pagesUnconformities Joints Faults and FoldsTrue ConfessorNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Sec 1: Forces in Earth's Crust: Guide For ReadingDocument3 pagesCH 2 Sec 1: Forces in Earth's Crust: Guide For ReadingOper SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Faults 1Document3 pagesFaults 1christophermike.ozoa.magadanNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Structural GeologyDocument32 pagesLecture9 Structural Geologyadia kajunaNo ratings yet
- Exp-7 Priya SharmaDocument15 pagesExp-7 Priya SharmaSPACE GHOSTNo ratings yet
- Unit IV STRUCTURAL GEOLOGYDocument16 pagesUnit IV STRUCTURAL GEOLOGYRubel RanaNo ratings yet
- Examples of FoldsDocument9 pagesExamples of FoldsSoumita MondalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFDocument26 pagesOverview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFMahmoud Eloribi100% (1)
- Tectonic Forces & ProcessesDocument3 pagesTectonic Forces & ProcessesMery NohanaNo ratings yet
- Structure GeologyDocument51 pagesStructure Geologyusama_veronNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.7 The Formation of Faults and FoldsDocument7 pagesLesson 2.7 The Formation of Faults and FoldsJessa Sumayang100% (1)
- Deformations PDFDocument4 pagesDeformations PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab Inclined BeddingDocument7 pagesLab Inclined BeddingAbu HIsyam0% (1)
- Structural GeologyDocument35 pagesStructural GeologyYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Tectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFDocument20 pagesTectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFVladimir AmorinNo ratings yet
- Movement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Document24 pagesMovement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Jester DayaoNo ratings yet
- Bab I: 1. To Know The Description About Fold 2. To Know What Factors Affect About Fold FormationDocument6 pagesBab I: 1. To Know The Description About Fold 2. To Know What Factors Affect About Fold FormationlianNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument85 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleRemil CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Seismic ContouringDocument142 pagesSeismic ContouringHuỳnh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Diastrophism - Folding, Faulting and MoreDocument58 pagesDiastrophism - Folding, Faulting and MoremayankNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain PPTDocument34 pagesStress Strain PPTStephen CeresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Reservoir CharacterizationDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Reservoir CharacterizationMohFekry100% (1)
- Cretaceous Stratigraphy of Central Andes of PeruDocument34 pagesCretaceous Stratigraphy of Central Andes of PeruPetro1111No ratings yet
- EPS171 - Lab 3 - Stereonets: PurposeDocument7 pagesEPS171 - Lab 3 - Stereonets: PurposeZamzuri ZaidinNo ratings yet
- Aparajita Das: Geological Field Traverse and Mapping Along The Baula Nuasahi Complex, Keonjhar, OdishaDocument55 pagesAparajita Das: Geological Field Traverse and Mapping Along The Baula Nuasahi Complex, Keonjhar, OdishaMilan SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cross Sections: A. DahlstromDocument15 pagesBalanced Cross Sections: A. DahlstromMuhammad Waqas100% (1)
- Mitra2003 PDFDocument15 pagesMitra2003 PDFGonzaloLopezNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument86 pagesStructural GeologyDiwyacitta Dirda Danoedoro100% (1)
- Iptc-19182-Ms An Innovative Reservoir Engineering Method To Identify Bypassed Oil and Derisk The Further Development of A Complex Mature FieldDocument16 pagesIptc-19182-Ms An Innovative Reservoir Engineering Method To Identify Bypassed Oil and Derisk The Further Development of A Complex Mature FieldGilbert OmittaNo ratings yet
- Glossary GeologyDocument128 pagesGlossary GeologyMeraGurdaspurNo ratings yet
- Amayapampa PDFDocument15 pagesAmayapampa PDFAnonymous EIAoKOoLlv100% (1)
- Exercise 2Document15 pagesExercise 2warrior_2008No ratings yet
- Bedir Et Al. 2016Document33 pagesBedir Et Al. 2016fatenNo ratings yet
- LAB 2a) &2b)Document13 pagesLAB 2a) &2b)Ae Asyraaf100% (1)
- Estimation of Fault Propagation Distance From Fold ShapeDocument4 pagesEstimation of Fault Propagation Distance From Fold ShapestephenNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas EngineeringDocument106 pagesNatural Gas Engineeringnerioalfonso100% (1)
- Geology of Bahariya Oasis in The Western Desert of EgyptDocument66 pagesGeology of Bahariya Oasis in The Western Desert of Egyptnilecruised100% (3)
- Baram Delta PDFDocument43 pagesBaram Delta PDFYTF RystadNo ratings yet
- OIL - From Pore To PipelineDocument49 pagesOIL - From Pore To PipelineMarcos Serrão100% (1)
- Basic GeologyDocument39 pagesBasic Geologyduncmcleod100% (1)
- Physical Geography EssayDocument7 pagesPhysical Geography EssayKieran KingNo ratings yet
- Geology Reviewer 2Document11 pagesGeology Reviewer 2Loki PagcorNo ratings yet
- AAPG EXPLORER 2018 03 Agua Caliente Oilfield Boiling River Peruvian AmazonDocument4 pagesAAPG EXPLORER 2018 03 Agua Caliente Oilfield Boiling River Peruvian AmazonAlejandro VegaNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingTikTok ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Gams - Geomorphogenetics of The Classical Karst - KrasDocument18 pagesGams - Geomorphogenetics of The Classical Karst - KrasCaegeoNo ratings yet
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Uploaded by
henrylewiskennedyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Anticlines Are Caused by Extensional Stress On The Rocks, and Syncline Is Caused by Compressional Stress. The
Uploaded by
henrylewiskennedyCopyright:
Available Formats
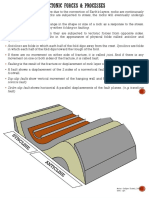
1. Picture No 1 This image is a syncline folds.
A syncline is a fold that is concave upward,or, in more complicated fold,is infererred to have had such an attitude at some stage in its development(plateVI).factors that cause this syncline folds can happen are : a. Generally a fold with younger rock toward the center of curvature b. Another set of term refers to the attitude of the axial plane c. In the asymmetrical fold the axial plane in inclined ; the two limbs dip in opposite directions but a different angle d. In the overturned fold or overfold the axial plane is inclined,and both limbs dip in the same action direction,usually at different angle. 2. Picture No 2 The image is a isoclinal fold.Isoclinal fold is one in which the axial plane is inclined.A recumbent isoclinal is one in which the axial plane is horizontal. Isoclinal is a major factor in the direction of the force exerted on the crease.Because it is formed by the folds of activity tectonics.
3. Picture No 3
The image is a anticline fold. An anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships between various strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. anticlines are caused by extensional stress on the rocks, and syncline is caused by compressional stress. The
stress is always pushing from the oldest layer of rock toward the youngest layer of rock, so in an anticline, where the oldest rocks are in the center of the rock fold, they push outward toward the younger rocks. In a syncline the youngest rocks are in the center of the fold and the oldest rocks are on the outer edge, the older rocks push inward toward the youngest rock. 4. Picture No 4 The image is a syncline fold.In this figure is the same type of fold with Figure 1, which syncline. Cause of the difference is the direction of the force forming the crease. Force that work is stressful and compress
5. Picture No 5 The image is a unconformity. The structural geologist is concerned with unconformities for several reasons.Unconformities are definitely structural features,although their origin involves erosional and depositional as wll as tectonic processes..An unconformity is a buried erosional or nondepositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentar geologic record.
6. Picture No 6 This image is mass movement.Mass movement or mass wasting is movements of masses of bodies of soil, bed rock, rock debris, soil, or mud which usually occur along steep-sided hills and mountains because of the pull of gravity. This slipping of large amounts of rock and soil is seen in landslides, mud slides, and avalanches. Mass movements are caused by various conditions:
Volcanic activity many times causes huge mudflows when the icy cover of a volcano melts and mixes with the soil to form mud as the magma in the volcano stirs preceding an eruption. Mudslides can also develop when water rapidly accumulates in the ground, such as during heavy rainfall or rapid snow melt, changing the earth into a flowing river of mud or "slurry.". Earthquake shocks cause sections of mountains and hills to break off and slide down. Human modification of the land or weathering and erosion help loosen large chunks of earth and start them sliding downhill. Vibrations from machinery, traffic, weight loading from accumulation of snow; stockpiling of rock or ore; from waste piles and from buildings and other structures. However, the trigger mechanism for mass movement is the gravitational pull of the earth on soil, rocks, and mud.
7. Picture No 7 The image is Isoclinal fault. in this picture is the same picture in picture No. 2Different causes is a fault. the fault occurred as a result of the movement of the plates. The movement of the plates are always moving constantly - constantly so that the elasticity of this layer to be broken.
8. Picture No 8 The image is joint. In geology the term joint refers to a fracture in rock where the displacement associated with the opening of the fracture is greater than the displacement due to lateral movement in the plane of the fracture (up, down or sideways) of one side relative
to the other. Typically, there is little to no lateral movement across joints. The main factor in the formation of the joint is the process of movement of the plates but have not yet experienced the movement. This makes joints different from a fault which is defined as a fracture in rock in which one side slides laterally past the other with a displacement that is greater than the separation between the blocks on either side of the fracture. Joints normally have a regular spacing related to either the mechanical properties of the individual rock or the thickness of the layer involved. Joints generally occur as sets, with each set consisting of joints sub-parallel to each other.
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: Team SmartDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: Team SmartJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Cannock Chase GeologyDocument30 pagesCannock Chase Geologypeter_alford3209No ratings yet
- Folds and FaultsDocument11 pagesFolds and FaultsfosteckhNo ratings yet
- GeoEng - JD HendersonDocument4 pagesGeoEng - JD HendersonARIANNE JADE ORBISTANo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting in The EarthDocument5 pagesFolding and Faulting in The Earthdiannereyes23No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 GEOLOGYDocument10 pagesLecture 4 GEOLOGYnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Geology (Unit 3) : Rock Deformation (Cause of Folding and Faulting)Document9 pagesGeology (Unit 3) : Rock Deformation (Cause of Folding and Faulting)chhabra994143No ratings yet
- Deforming Earth's Crust: Section 3Document12 pagesDeforming Earth's Crust: Section 3Argeena Agao-AgaoNo ratings yet
- High School Earth Science - Stress in The Earth's Crust - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument59 pagesHigh School Earth Science - Stress in The Earth's Crust - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldAngellene TumilapNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument48 pagesChapter Threeone loveNo ratings yet
- C3ed2znol Module 4 Earth and Life Science Rocks Deformation and Metamorphism 1.docx UPDATED JULY 20 2020Document17 pagesC3ed2znol Module 4 Earth and Life Science Rocks Deformation and Metamorphism 1.docx UPDATED JULY 20 2020Philippines QuestionNo ratings yet
- Geol 11 Week 10 - Rock Deformation - Annotated Lecture SlidesDocument12 pagesGeol 11 Week 10 - Rock Deformation - Annotated Lecture SlidesAssignment ForNo ratings yet
- Science 11 LAS Geologic ProcessDocument2 pagesScience 11 LAS Geologic ProcessKimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Causes and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Causes and MeasurementsMahfuzul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Explanation: 1 Episode: These Sedimentary Layers Were Originally Deposited Horizontally. They've Been FoldedDocument5 pagesExplanation: 1 Episode: These Sedimentary Layers Were Originally Deposited Horizontally. They've Been FoldedMubashirKhattakNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Q2 Week3Document10 pagesEarth Science Q2 Week3MCAPUZ, MARK JOHN, V.No ratings yet
- Faulting and FoldingDocument3 pagesFaulting and FoldingchikwambaNo ratings yet
- Strike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockDocument16 pagesStrike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockGanguli Tutor RajNo ratings yet
- LP4 w4 Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesLP4 w4 Earth and Life ScienceJiego PabiaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Geological StructuresDocument50 pagesGroup 6 Geological StructuresAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 8: Faults, Folds, and Cross-Cutting RelationshipsDocument8 pagesLaboratory 8: Faults, Folds, and Cross-Cutting RelationshipsXuan PhuongNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci 7Document13 pagesEarth Sci 7Cyrus GabutenNo ratings yet
- Earth QuakeDocument16 pagesEarth QuakeJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology Group 5Document35 pagesStructural Geology Group 5richethan25No ratings yet
- Geologic StructuresDocument6 pagesGeologic Structurescris ortonero100% (1)
- Unit Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map InterpretationDocument45 pagesUnit Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map InterpretationBennet Nii Tackie-OtooNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology: A) Geological Maps B) Folds, Fault, & JointsDocument42 pagesStructural Geology: A) Geological Maps B) Folds, Fault, & JointsRolandNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisGue Gitu LochNo ratings yet
- Report in ElsDocument2 pagesReport in ElsRowe AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ELSDocument50 pagesLesson 2 - ELSalshawy0909No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document100 pagesChapter 5samajikpraani97No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Earth 'S Geological ProcessesDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science: Earth 'S Geological ProcessesGentila LancheNo ratings yet
- Forces in Earth - S CrustDocument55 pagesForces in Earth - S CrustBlanche Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth ScienceAutumn ZakyNo ratings yet
- Rock Deformation and Earthquake FinalDocument131 pagesRock Deformation and Earthquake Finalniaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Faulting and Folding of Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesFaulting and Folding of Plate TectonicsJailian Rhainne Delloso BretañaNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology GroundwaterDocument109 pagesStructural Geology Groundwaterkiran_ran99No ratings yet
- DiastrophismDocument31 pagesDiastrophismEunice Rean SamonteNo ratings yet
- DiastrophismDocument7 pagesDiastrophismhilaliusvalentine67No ratings yet
- MergeResult 2022 10 01 11 04 58Document114 pagesMergeResult 2022 10 01 11 04 58Mark Justine MallariNo ratings yet
- Module-3: Structural Geology & Rock MechanicsDocument76 pagesModule-3: Structural Geology & Rock MechanicsLeon FouroneNo ratings yet
- 5.structural GeologyDocument46 pages5.structural Geologysamir bardewaNo ratings yet
- Perlita Rock StructureDocument29 pagesPerlita Rock StructureJohn Rey DumaguinNo ratings yet
- 4 Geological StructuresDocument35 pages4 Geological StructuresZahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Unconformities Joints Faults and FoldsDocument8 pagesUnconformities Joints Faults and FoldsTrue ConfessorNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Sec 1: Forces in Earth's Crust: Guide For ReadingDocument3 pagesCH 2 Sec 1: Forces in Earth's Crust: Guide For ReadingOper SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Faults 1Document3 pagesFaults 1christophermike.ozoa.magadanNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Structural GeologyDocument32 pagesLecture9 Structural Geologyadia kajunaNo ratings yet
- Exp-7 Priya SharmaDocument15 pagesExp-7 Priya SharmaSPACE GHOSTNo ratings yet
- Unit IV STRUCTURAL GEOLOGYDocument16 pagesUnit IV STRUCTURAL GEOLOGYRubel RanaNo ratings yet
- Examples of FoldsDocument9 pagesExamples of FoldsSoumita MondalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFDocument26 pagesOverview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFMahmoud Eloribi100% (1)
- Tectonic Forces & ProcessesDocument3 pagesTectonic Forces & ProcessesMery NohanaNo ratings yet
- Structure GeologyDocument51 pagesStructure Geologyusama_veronNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.7 The Formation of Faults and FoldsDocument7 pagesLesson 2.7 The Formation of Faults and FoldsJessa Sumayang100% (1)
- Deformations PDFDocument4 pagesDeformations PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab Inclined BeddingDocument7 pagesLab Inclined BeddingAbu HIsyam0% (1)
- Structural GeologyDocument35 pagesStructural GeologyYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Tectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFDocument20 pagesTectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFVladimir AmorinNo ratings yet
- Movement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Document24 pagesMovement of Plates Lead To Formation of Folds and Faults: Lesson 5Jester DayaoNo ratings yet
- Bab I: 1. To Know The Description About Fold 2. To Know What Factors Affect About Fold FormationDocument6 pagesBab I: 1. To Know The Description About Fold 2. To Know What Factors Affect About Fold FormationlianNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument85 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleRemil CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Seismic ContouringDocument142 pagesSeismic ContouringHuỳnh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Diastrophism - Folding, Faulting and MoreDocument58 pagesDiastrophism - Folding, Faulting and MoremayankNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain PPTDocument34 pagesStress Strain PPTStephen CeresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Reservoir CharacterizationDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Reservoir CharacterizationMohFekry100% (1)
- Cretaceous Stratigraphy of Central Andes of PeruDocument34 pagesCretaceous Stratigraphy of Central Andes of PeruPetro1111No ratings yet
- EPS171 - Lab 3 - Stereonets: PurposeDocument7 pagesEPS171 - Lab 3 - Stereonets: PurposeZamzuri ZaidinNo ratings yet
- Aparajita Das: Geological Field Traverse and Mapping Along The Baula Nuasahi Complex, Keonjhar, OdishaDocument55 pagesAparajita Das: Geological Field Traverse and Mapping Along The Baula Nuasahi Complex, Keonjhar, OdishaMilan SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cross Sections: A. DahlstromDocument15 pagesBalanced Cross Sections: A. DahlstromMuhammad Waqas100% (1)
- Mitra2003 PDFDocument15 pagesMitra2003 PDFGonzaloLopezNo ratings yet
- Structural GeologyDocument86 pagesStructural GeologyDiwyacitta Dirda Danoedoro100% (1)
- Iptc-19182-Ms An Innovative Reservoir Engineering Method To Identify Bypassed Oil and Derisk The Further Development of A Complex Mature FieldDocument16 pagesIptc-19182-Ms An Innovative Reservoir Engineering Method To Identify Bypassed Oil and Derisk The Further Development of A Complex Mature FieldGilbert OmittaNo ratings yet
- Glossary GeologyDocument128 pagesGlossary GeologyMeraGurdaspurNo ratings yet
- Amayapampa PDFDocument15 pagesAmayapampa PDFAnonymous EIAoKOoLlv100% (1)
- Exercise 2Document15 pagesExercise 2warrior_2008No ratings yet
- Bedir Et Al. 2016Document33 pagesBedir Et Al. 2016fatenNo ratings yet
- LAB 2a) &2b)Document13 pagesLAB 2a) &2b)Ae Asyraaf100% (1)
- Estimation of Fault Propagation Distance From Fold ShapeDocument4 pagesEstimation of Fault Propagation Distance From Fold ShapestephenNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas EngineeringDocument106 pagesNatural Gas Engineeringnerioalfonso100% (1)
- Geology of Bahariya Oasis in The Western Desert of EgyptDocument66 pagesGeology of Bahariya Oasis in The Western Desert of Egyptnilecruised100% (3)
- Baram Delta PDFDocument43 pagesBaram Delta PDFYTF RystadNo ratings yet
- OIL - From Pore To PipelineDocument49 pagesOIL - From Pore To PipelineMarcos Serrão100% (1)
- Basic GeologyDocument39 pagesBasic Geologyduncmcleod100% (1)
- Physical Geography EssayDocument7 pagesPhysical Geography EssayKieran KingNo ratings yet
- Geology Reviewer 2Document11 pagesGeology Reviewer 2Loki PagcorNo ratings yet
- AAPG EXPLORER 2018 03 Agua Caliente Oilfield Boiling River Peruvian AmazonDocument4 pagesAAPG EXPLORER 2018 03 Agua Caliente Oilfield Boiling River Peruvian AmazonAlejandro VegaNo ratings yet
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 pagesFolding and FaultingTikTok ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Gams - Geomorphogenetics of The Classical Karst - KrasDocument18 pagesGams - Geomorphogenetics of The Classical Karst - KrasCaegeoNo ratings yet