Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Plan Year6 2012
Yearly Plan Year6 2012
Uploaded by
Hasliza HasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Plan Year6 2012
Yearly Plan Year6 2012
Uploaded by
Hasliza HasCopyright:
Available Formats
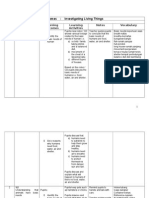
YEARLY PLAN SCIENCE YEAR 6 Wee k 1 Learning Area 1.0 Interaction among living things Learning Objective 1.
.1 Understanding that some animals live in groups and others live in solitary Suggested Learning Activities Themes: Investigating Living Things Pupils Pupils view a video on state that some animals that live in groups animals and in solitary. live in groups. state that some animals live in solitary. Pupils gather information and give examples of give examples of animals that live in group animals and in solitary. that live in groups. give examples of animals that live in solitary explain why animals live in groups. explain why animals live in solitary. Pupils discuss why animals live in groups. e.g. a) For safety b) For food Pupils discuss why animals live in solitary. e.g. a) To avoid competition for food. b) To avoid competition for space. Pupils observe how ants live together in a vivarium. Learning Outcomes SPS Notes / Vocabulary
observing solitary menyendiri safetykeselamatan cooperationbekerjasama competitionpersaingan
Teacher can prepare a vivarium of an ant colony two weeks before the lesson.
1.2 Understanding
state that cooperation is a form of interaction among animals. Pupils state that living
1
Pupils view video on interaction among living
The video should include various
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective that competition is a form of interaction among living things
Learning Outcomes things interact with one another in the environment. state that competition is a form of interaction.
Suggested Learning Activities things in various habitats. Pupils discuss and give examples of interaction among living things. Pupils discuss that competition is a form of interaction. Pupils view video or computer simulation of competition among animals. Pupils discuss and list the factors that animals compete for : a) Food b) Water c) Mate d) Shelter e) Territory/space Pupils carry out activities to observe animals competing for food. e.g. fish or bird Pupils discuss that animals compete because of : a) Limited food resources b) Limited water resources c) Trying to get a mate for breeding d) Defending or looking for territory e) Defending or looking for
SPS
list the factors that animals compete for.
5 give reasons why animals compete.
Notes / Vocabulary types of interaction such as competition and cooperation. interactioninteraksi competitionpersaingan limited resourcessumber terhad territory-wilayah breedingpembiakan mate-pasangan defendmempertahanka n space-ruang shelter-tempat perlindungan
Wee k 6 6
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities shelter.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
MONTHLY TEST 1 list factors that plants compete for. Pupils view a video or pictures of plants in the forest. Based on the video or pictures pupils discuss why plants in the forest have different heights. Pupils carry out activities to observe competition among plants. Pupils discuss that plants compete for : a) Sunlight b) Water c) Space d) Nutrient Pupils discuss that plants compete because of : a) Limited sunlight that can reach them b) Limited water resources c) Limited space d) Limited nutrient These activities can be prepared earlier because they may take some time to show results. Suggestion: green beans, maize.
give reasons why plants compete with each other
1.3 Understanding the
Pupils give examples of extinct animal.
3
Pupils view a video or pictures of animals that are extinct.
rafflesia- bunga pakma Hornbill-burung
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Learning Outcomes Objective responsibility of human beings give examples of in protecting endangered animal. endangered species give examples of endangered plant.
Suggested Learning Activities e.g. dinosaurs Pupils view a video or pictures of endangered animals and plants. e.g. tiger, turtle, orang utan, panda, rhinoceros and rafflesia and pitcher plants.
SPS
explain why certain animals or plants Pupils discuss and conclude are facing the that certain animals and threat of extinction. plants are facing the threat of extinction because of human activities such as illegal or excessive: a) Logging b) Hunting c) Development suggest ways to prevent animals Discuss ways to prevent and plants from animals and plants from extinction. extinction. e.g. a) Campaign against excessive logging b) Educating the public about the importance of protecting and conserving animals and plants. c) Avoid consuming or buying products made from endangered species. d) Enforcing the law.
Notes / Vocabulary enggang conservationpemuliharaan protectionperlindungan endangeredterancam extinct-pupus excessiveberleluasa threat- ancaman loggingpembalakan consumemenggunakan enforcementpenguatkuasaan
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
1.4 Knowing the Pupils impact of human give examples of activities on environmental environment destruction caused by human.
Pupils view video or see pictures of environmental destructions caused by human activities. e.g. a) Erosion b) Landslide c) Flash-flood d) Water pollution e) Air pollution Pupils view a video and discuss human activities that cause destruction to the environment. a) Illegal and excessive logging. b) Illegal and excessive hunting. c) Improper management of development. Pupils discuss what will happen to the Earth if human activities that caused environmental destructions are not controlled. Pupils prepare a scrap book on environmental destruction caused by human activities and steps taken to reduce its
explain how human activities cause environmental destruction.
predict what will happen to the Earth if human activities are not controlled.
balance of naturekeseimbangan alam illegal loggingpembalakan haram illegal huntingpemburuan haram landslide-tanah runtuh flash-floodbanjir kilat pollutionpencemaran erosion-hakisan disasterbencana destructionkemusnahan
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities effects.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
10
PKBS UJIAN SELARAS 1 Themes: Investigating Force And Energy
11
1.0 Force
1.1 Understanding that push and pull are forces
Pupils state that push and pull are forces. state that force cannot be seen but its effects can be observed.
Pupils push and pull each others palms to feel the effect of forces. Pupils discuss and conclude that push and pull are forces. Based on the above activity pupils discuss and conclude that a force cannot be seen but its effects can be observed. Pupils carry out activities and discuss the effects of pushing. a) A stationary ball b) A moving ball Pupils press, twist or squeeze objects such as plasticine, sponge and spring. Pupils observe and discuss the effects of forces. Pupils discuss and conclude that a force can: a) Move the stationary objects.
pull-tarikan push-tolakan force-daya palm-tapak tangan
1.2 Understanding the effects of a force
Pupils state that a force can move a stationary object. state that a force can change the motion of an object. state that a force can change the shape of an object.
speed kelajuan stationary -pegun moving - bergerak twist-pulas press- tekan
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes b) c) d) e)
Suggested Learning Activities Stop a moving object. Change the direction of a moving object. Make an object move faster or slower. Change the shape of an object.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
12
1.3 Analysing friction
Pupils state that friction is a type of force.
Pupils observe an object such as a book or a coin sliding on a surface. Pupils discuss that friction slows down a moving object and conclude that friction is a force. Pupils carry out activities that involve friction. e.g. a) Open the lid of a jar with dry hands. b) Open the lid of a jar with oily hands. Pupils discuss and conclude that it is easier to open the lid of a jar with dry hands because of greater friction. Pupils carry out activities that involve friction. e.g. a) Rubbing their palms. b) Pulling a heavy object.
friction geseran aerodynamicaerodinamik oppose -bertentangan effect kesan reduce -kurangkan increase -menambahkan surfaces in contact permukaan yang bersentuhan Friction can be reduced by using: using roller, marbles using talcum
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities c) Rubbing an eraser against a surface. Based on the above activities pupils explain the effects of friction: a) Their palms become warmer because friction produces heat. b) It is difficult to move the object because friction opposes motion.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary powder, oil, wax, grease, air cushion, smoothening the surfaces in contact.
13
describe the effects of friction.
c) The eraser becomes smaller because friction causes wear and tear. Pupils list and discuss the effects of friction in everyday life.
8
Wee k 14
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes describe ways to reduce friction. describe ways to increase friction.
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils compare the effects of friction by rubbing their palms: a) Without oil b) With oil. Pupils discuss and conclude that oil reduces friction.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
state the advantages of friction. state the disadvantages of friction. conclude that friction occurs when two surfaces are in contact.
Pupils suggest various ways to reduce friction. Pupils carry out activities to test their suggestions. Pupils gather information on the advantages and disadvantages of friction in everyday life.
design a fair test to find out how different types of surfaces affect the distance a trolley moves by deciding what to change, what to keep the same and what
9
Pupils discuss various situations where friction is produced when surfaces are in contact with one another.
Pupils plan and carry out an experiment to investigate how different types of
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes to measure.
Suggested Learning Activities surfaces affects the distance a trolley moves.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
15
2.0 Movement
2.1 Understanding speed
Pupils state that an object which moves faster travels a longer distance in a given time. state that an object which moves faster takes a shorter time to travel a given distance.
Pupils carry out activities to: a) compare the distances travelled in a given time by two moving objects b) compare the time taken by two moving objects to travel a given distance. Pupils discuss and conclude that: a) an object which moves faster travels a longer distance in a given time b) an object which moves faster takes a shorter time to travel a given distance. Pupils conclude that: speed is a measurement of how fast an object moves speed can be calculated by using the formula : speed= distance/time.
state what speed is.
10
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils solve problems using the formula.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
solve problems using the formula. MONTHLY TEST 2 Themes: Investigating Materials
16
17
1.0 Food Preservation
1.1 Understanding food spoilage
Pupils Pupils observe samples of describe what spoilt spoilt food. food is. Pupils discuss and conclude that spoilt food is unsafe to eat. identify characteristics of Pupils conclude that spoilt spoilt food. food has one or more of the following characteristics: a) unpleasant smell b) unpleasant taste c) changed colour d) changed texture e) mouldy. state that microorganisms can Pupils carry out an activity to spoil food. observe that food turns bad by leaving a slice of bread in
11
Pupils: Food used in the activity should not be tasted. medium keadaan
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities the open for a few days. Pupils discuss and conclude that microorganisms can spoil food.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
state the conditions for microorganisms to grow.
Pupils gather information and conclude that microorganisms need certain conditions to grow: a) air b) water c) nutrient d) suitable temperature e) suitable acidity Pupils find information about ways to preserve food and examples of food for each type of preservation. a) drying b) boiling c) cooling d) vacuum packing e) pickling f) freezing g)bottling/canning h)pasteurizing i) salting j) smoking k) waxing dryingpengeringan picklingpenjerukan heating -pemanasan vacuum packingpembungkusan vakum coolingpendinginan freezingpenyejuk bekuan bottling-
18
1.2 Synthesizing Pupils the concept of describe ways to food preserve food. preservation give examples of food for each type of food preservation.
12
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes give reasons why each way of food preservation is used.
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils discuss and explain why the above ways are used to preserve food. Pupils view a video or visit food factory to observe how food is processed and preserved.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary pembotolan canningpengetinan smokingpengasapan saltingpengasinan Food given can be: tapioca, banana, egg, mango, chilli.
state what food preservation is. design and carry out a project to preserve a given food. 1.3 Realising the importance of preserving food Pupils give reasons why we need to preserve food.
Pupils discuss that food preservation is a process of slowing down the food from becoming bad. Pupils carry out a project on food preservation to preserve a given food. Pupils discuss and give reasons why we need to preserve food. e.g. a) the food will last longer. b) the food is easy to store. c) to reduce wastage of food.
19 20 2.0 Waste Manage2.1 Understanding the effects of
MID-YEAR EXAMINATION PKSR 1 Pupils identify types of waste in the
13
Pupils observe various waste in a rubbish bin. e.g. plastic, glass, chemical
harmful effectskesan buruk
Wee k
Learning Area ment
Learning Objective improper disposal of waste on the environment
Learning Outcomes environment.
Suggested Learning Activities waste, organic waste and metal.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary waste disposal pembuangan bahan buangan
Pupils view a video on identify sources of waste. various waste from factories, food stalls and market. Pupils gather information on: a) sources of waste. b) various ways of waste disposal.
Pupils discuss and classify state the the proper and improper improper ways of ways of waste disposal. waste disposal. state the proper ways of waste disposal. Pupils discuss the harmful effects of improper waste describe the disposal. e.g. harmful effects of a) air pollution improper waste b) water pollution disposal. c) sickness and diseases d) acid rain e) flash-flood Pupils gather information on how waste in a local area is disposed.
describe how waste is disposed in a local area.
14
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes suggest ways to improve waste disposal.
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils discuss and suggest ways to improve waste disposal in a local area. Pupils visit a waste management centre or listen to a talk to gather information on how waste is treated.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
21
2.2 Pupils Understanding state that certain that some waste waste can decay. can decay
Pupils view videos and timelapse clipping about waste that decay and waste that do not decay. Pupils separate waste in a rubbish bin according to the categories such as vegetables, paper, glass, plastics and wood. Put each type into separate thick plastic bags. Place these bags in the open and observe the changes over a period of time. Pupils discuss and give examples of waste that: a) decay
Biodegradable materials are materials that can be decayed by microorganisms. Certain plastics are biodegradable. decay-reput harmfulmerbahaya separateasingkan
give examples of waste that can decay. give examples of waste that do not decay.
15
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes state that microorganisms can cause waste materials to decay.
Suggested Learning Activities b) do not decay Pupils discuss and conclude some microorganisms caused waste to decay During the decaying process nutrients are returned to the soil, in this way they can be used again. Pupils gather information and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of decay of waste.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
state the dvantages of waste decaying. state the disadvantages of waste decaying.
predict what will happen to human and the environment if waste do not decay.
Pupils discuss and predict what will happen to human and the environment if waste do not decay.
Themes: Investigating The Earth and The Universe 22 1.0 Eclipses 1.1 Understanding the eclipse of the moon Pupils state what eclipse of the moon is. Pupils use models to simulate the movement of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun. eclipse-gerhana position -kedudukan partial eclipse-
16
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes state the position of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the moon. explain why eclipse of the moon occurs
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils view a video or computer simulation about partial and total eclipse of the moon. Pupils discuss and conclude that eclipse of the moon occurs because: a) the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun and b) the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are positioned in a straight line. Pupils draw diagrams to show the positions of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the moon.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary gerhana separa total eclipsegerhana penuh
22
1.2 Understanding the eclipse of the sun
Pupils state what eclipse of the sun is. state the position of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun
17
Pupils use models to simulate the movement of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun. Pupils discuss that the eclipse of the sun occurs
Wee k
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes during the eclipse of the sun. explain why eclipse of the sun occurs.
Suggested Learning Activities during daytime.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
Pupils view videos or computer simulations about partial and total eclipse of the sun. Pupils discuss and conclude that eclipse of the sun occurs because: a) the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun. b) the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are positioned in a straight line. Pupils draw diagrams to show the position of the Moon, the Earth and the Sun during the eclipse of the sun.
predict the scenario on the Earth during the eclipse of the sun.
Pupils discuss and predict the scenario on the Earth during the eclipse of the sun.
Themes: Investigating Technology
18
Wee k 23
Learning Learning Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Area Objective Activities 1.0 Machine 1.1 Pupils Pupils try to remove the lid Understanding explain what simple of a tin using simple machines a) hands machine is. b) spoon Pupils compare the difficulty to complete the task and discuss the function of tool. state types of simple machines. give an example for each type of simple machine. Pupils discuss that a simple machine is a device that allows us to use less force to make work easier or faster. Pupils examine and manipulate the following simple machines: a) wheel and axle b) lever c) wedge d) pulley e) gear f) inclined plane g) screw Pupils discuss that types of simple machines. Pupils walks around the school compound and identify various type of simple machines.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary lid- penutup wheel and axleroda dan gandar lever-tuas wedge-baji pulley-takal gear-gear inclined planesatah condong screw-skru
19
Wee k 23
Learning Area
Learning Objective 1.2 Analysing a complex machine
Learning Outcomes Pupils identify simple machines in a complex machine. conclude that a complex machine is made up of more than one simple machine. give examples of complex machines. Pupils predict how life is without machines.
Suggested Learning Activities Pupils identify the simple machines in a bicycle or a wheel barrow. Pupils discuss and conclude that a complex machine is a machine made up of more than one simple machine. Pupils prepare scrap books on examples of complex machine. Pupils carry out simulation to find out how life would be without machines. Pupils discuss and predict how life would be without machines. Pupils discuss and explain how machines make our lives easier Pupils identify a problem and design a machine to solve the problem.
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary wheel barrowkereta sorong
1.3 Appreciating the invention of machines that make life easier
Encourage pupils to reuse materials and recycle materials.
explain how machines can make our lives easier. design a machine to solve a problem.
24 25 -
MONTHLY TEST - 3 REVISION
20
Wee k 26 27 28 29 30 32 33 34 37 40
Learning Area
Learning Objective
Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
SPS
Notes / Vocabulary
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN UPSR REVISION MONTHLY TEST - 4 REVISION PEPERIKSAAN UPSR AKTIVITI SELEPAS UPSR PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR TAHUN PKSR 2
21
You might also like
- Lesson Plan On Components of EcosystemDocument3 pagesLesson Plan On Components of EcosystemZM Laureta85% (34)
- Pollution Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesPollution Lesson Planapi-300889911100% (9)
- Water Conservation LessonDocument4 pagesWater Conservation Lessonapi-269984318No ratings yet
- S5 LT-II-h-8Document6 pagesS5 LT-II-h-8Kristine Joy PitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Demo Teaching in Science 6Document5 pagesLesson Plan For Demo Teaching in Science 6Mike Casañas100% (18)
- Stage 1 Wet and Dry EnvironmentsDocument5 pagesStage 1 Wet and Dry Environmentsapi-184739074100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 5Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 5Jayral Sidon Prades78% (9)
- Sewer Lice Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSewer Lice Lesson PlanCraigLichtenberg0% (1)
- Birds of Coastal Georgia ShorebirdsDocument15 pagesBirds of Coastal Georgia ShorebirdsBernatNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Inventory Population Dynamics Sept 2013Document18 pagesConceptual Inventory Population Dynamics Sept 2013Abdelaziz Abdelghany0% (1)
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6Document16 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year 6shaharinsulongNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Wan Shahlan FatimahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008Document13 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2008ff_fadzli275No ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011Document20 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Science Six 2011Syahida IslamNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahDocument23 pagesSekolah Rendah Agama Integrasi: Tengku Ampuan Fatimah, Batu BelahMohd HafizanNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6: Investigating Living ThingsDocument16 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year 6: Investigating Living ThingsGunamathyGanesanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)Document17 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Yr6 (New)HairulIzhamIshakNo ratings yet
- ScienceYearlyPlanYear 6 UPDATED 2013Document16 pagesScienceYearlyPlanYear 6 UPDATED 2013Raja Letchemy Bisbanathan MalarNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains t6Document17 pagesRancangan Tahunan Sains t6ramlybmsNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Document14 pagesScience Yearly Plan: Year 6 2013Rajesware GovindasamyNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Y6 SC 2014Document27 pagesYearly Plan Y6 SC 2014selvadz00No ratings yet
- Kecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Document23 pagesKecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Asnal KamalNo ratings yet
- Teaching Con 6Document16 pagesTeaching Con 6alyasserbinmdisa82No ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDocument27 pagesWeek Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyThamil ArasiNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Science Year 4Document26 pagesYearly Plan For Science Year 4Muhammad Azrieen SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 6Document18 pagesYearly Plan Science Yr 6Joe SabriNo ratings yet
- SN SN SNDocument23 pagesSN SN SNmaya_niranjNo ratings yet
- Lessonplan 4Document5 pagesLessonplan 4api-272727134No ratings yet
- RPT Sains Tahun 6Document12 pagesRPT Sains Tahun 6Iroet MarteniNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Document20 pagesRancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Dilla FadillahNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Document15 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6Diana LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document13 pagesLesson 5api-280508148No ratings yet
- Resources AlexiaDocument11 pagesResources Alexiaalexia alferezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education: Action Plan in School: Involve CommunityDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Education: Action Plan in School: Involve CommunityHafizul SyarafiNo ratings yet
- Yearly Planner Science Year 4 2006Document51 pagesYearly Planner Science Year 4 2006sulia81No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Heart Plant 4th Quarter Session 5 8Document7 pagesGrade 7 Heart Plant 4th Quarter Session 5 8jezilbanayo01No ratings yet
- Unit 8Document24 pagesUnit 8spicypandarok4No ratings yet
- 1.interaction Among Living ThingsDocument4 pages1.interaction Among Living ThingsRain KipliNo ratings yet
- Science Year 6 2012Document12 pagesScience Year 6 2012Hirdawati Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- GradeDocument5 pagesGradeapi-273334698No ratings yet
- Year 5 Science Sceme of WorkDocument30 pagesYear 5 Science Sceme of WorkJc JoliatiNo ratings yet
- RPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang GulaDocument29 pagesRPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang Gulavargan_ramoNo ratings yet
- Suggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarDocument16 pagesSuggested Yearly Plan / Please Change or Edit Based On Your School CalendarMuhamad Hamadi IthninNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science - EcosystemDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in Science - Ecosystemchristinejem.geligNo ratings yet
- KC D. Macahilig 7'E Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesKC D. Macahilig 7'E Lesson PlanKc MacahiligNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Level: Junior High School Lesson: Science Class: Ix Time: 1 X 15 Minutes Topic: Sustainability of Living Organism Subtopic: AdaptationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Level: Junior High School Lesson: Science Class: Ix Time: 1 X 15 Minutes Topic: Sustainability of Living Organism Subtopic: AdaptationatakhoirulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 IsitlivingcandidateDocument2 pagesLesson 6 Isitlivingcandidateapi-322160452No ratings yet
- TG - SCIENCE 5 Q2 S5LT-II - I-J 10Document7 pagesTG - SCIENCE 5 Q2 S5LT-II - I-J 10jellyB Rafael100% (1)
- Lesson Plans For The Unit On Salt Marshes By: Erika Limkilde, Rebecca Messer and Rebecca RichardDocument42 pagesLesson Plans For The Unit On Salt Marshes By: Erika Limkilde, Rebecca Messer and Rebecca Richardapi-333161760No ratings yet
- Build A Habitat Lesson 1Document3 pagesBuild A Habitat Lesson 1mgizzareNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan OverviewDocument5 pagesUnit Plan Overviewapi-354338223No ratings yet
- Weird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionDocument28 pagesWeird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionBecky BrownNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument5 pagesSemi-Detailed Conservation of Natural ResourcesRichelle SaludezNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson Plan Day 3Document2 pagesSiop Lesson Plan Day 3api-273275279No ratings yet
- Day 2 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDay 2 Lesson Planapi-532490346No ratings yet
- AP Audit Syllabus Environmental Science 1Document14 pagesAP Audit Syllabus Environmental Science 1Barry DementesNo ratings yet
- A.Bonifacio Integrated SchoolDocument8 pagesA.Bonifacio Integrated SchoolCharlyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Competition Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesEcosystems and Competition Lesson Planapi-251520607No ratings yet
- Tiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1Document8 pagesTiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1api-644963967No ratings yet
- Ocean's World Educator's Guide: An Island Tale of Discovery and AdventureFrom EverandOcean's World Educator's Guide: An Island Tale of Discovery and AdventureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final Outline (Charming Sotelo) PDFDocument19 pagesFinal Outline (Charming Sotelo) PDFjcNo ratings yet
- (Cô Vũ Mai Phương) Bộ đề nắm chắc điểm 8 cho mùa thi 2024 - Đề số 07Document6 pages(Cô Vũ Mai Phương) Bộ đề nắm chắc điểm 8 cho mùa thi 2024 - Đề số 07Hải Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Western Pond TurtleDocument2 pagesWestern Pond TurtleGirraj ojhaNo ratings yet
- International Conservation Project Funders: Institution Award/Scholarship Description Award Amount WebsiteDocument22 pagesInternational Conservation Project Funders: Institution Award/Scholarship Description Award Amount WebsitenicdonatiNo ratings yet
- Avian SystematicsDocument74 pagesAvian SystematicsArdhina ardhinaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Vehicular Traffic On Herpetofaunal Mortality (Sri Lanka)Document11 pagesImpact of Vehicular Traffic On Herpetofaunal Mortality (Sri Lanka)D.M.S. Suranjan KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Environment Protection QuizDocument3 pagesEnvironment Protection QuizAndreea PaulaNo ratings yet
- Fatal Flaws of Living FossilsDocument3 pagesFatal Flaws of Living Fossilseustoque2668No ratings yet
- Background Paper 13Document47 pagesBackground Paper 13AverageNo ratings yet
- (TO8) Bai Tap Bo Tro Tuan 1Document7 pages(TO8) Bai Tap Bo Tro Tuan 1Quân Bùi VănNo ratings yet
- Science PPT AutosavedDocument27 pagesScience PPT AutosavedKimchiNo ratings yet
- 05) Reading Inference and Rhetorical Purpose QuestionsDocument4 pages05) Reading Inference and Rhetorical Purpose Questions鄭少綸No ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, Lucknow: International Trade Law Project OnDocument22 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, Lucknow: International Trade Law Project Onsakshi singhNo ratings yet
- CDFW White Shark ESA Status ReviewDocument365 pagesCDFW White Shark ESA Status ReviewLakeCoNewsNo ratings yet
- Classification: Down FeathersDocument2 pagesClassification: Down FeathersCarlo QuinlogNo ratings yet
- Rule: Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act Title VIII Implementation (Subsistence Priority) : Vernal Pool Crustaceans, Et Al.Document77 pagesRule: Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act Title VIII Implementation (Subsistence Priority) : Vernal Pool Crustaceans, Et Al.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Mock Data ExcelDocument28 pagesMock Data Exceltaqi319No ratings yet
- Species ConceptDocument2 pagesSpecies ConceptMayhaaa100% (1)
- Town and Village of Cape Vincent FINAL Joint Comprehensive Plan - August 1, 2012Document67 pagesTown and Village of Cape Vincent FINAL Joint Comprehensive Plan - August 1, 2012pandorasboxofrocksNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Its Conservationjoshivishwanath100% (1)
- Trinity Gese Grade 8 PDFDocument7 pagesTrinity Gese Grade 8 PDFMVictoria TiradoNo ratings yet
- Project Plan - 2013-14Document10 pagesProject Plan - 2013-14api-252683864No ratings yet
- Sensitive Land Protection - U.S. Green Building CouncilDocument2 pagesSensitive Land Protection - U.S. Green Building CouncilrNo ratings yet
- FAQ Q: Pleurotus Nidiformis Is Probably The Most Common and Best KnownDocument2 pagesFAQ Q: Pleurotus Nidiformis Is Probably The Most Common and Best KnownStephen GreenNo ratings yet
- Animals Words SearchDocument14 pagesAnimals Words Searchlavievan99No ratings yet
- Pink Dolphin FactsDocument5 pagesPink Dolphin FactsMa Yumi IINo ratings yet
- Notice: Endangered and Threatened Species: Columbia River Salmon and Steelhead Recovery PlanDocument6 pagesNotice: Endangered and Threatened Species: Columbia River Salmon and Steelhead Recovery PlanJustia.comNo ratings yet
- PAS Inggris XDocument5 pagesPAS Inggris XMIBNo ratings yet