Professional Documents
Culture Documents
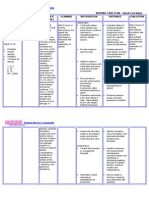
NCP Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
NCP Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Uploaded by
Vencel Mae Famas VillahermosaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
NCP Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Uploaded by
Vencel Mae Famas VillahermosaCopyright:
Available Formats
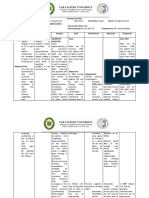
NURSING RATIONALE DIAGNOSIS Preci Acute Pain related Predis Bulging eyeballs Lack of improper to physical Headache Exercise
se position disability in the Swelling while neck area AEB conjunctiva sleeping guarding behavior, Guarding irritability, verbal behavior report of pain and Irritability altered ability to antigen stimulus Reduced continue previous activates interaction with activities. monocytes and t people lymphocytes/t cells Verbal report of Definition: pain Unpleasant Immunoglobulin Altered ability sensory or antibodies form to continue emotional immune complexes previous experience arising with antigen activities from actual or potential tissue Phagocytosis Risk factors: damage or produces described in terms leukotrienes and Poor hygiene of such damage; prostaglandins sudden or slow Strength: onset of any Leukotrienes intensity from contribute to Strong family mild to severe inflammatory support with an anticipated process by end and duration anttracting WBC to of less than 6 the area; months. prostaglandins act as modifiers to inflammation Source:Nurses th Pocket Guide 12 Both produce Edition page. 586 enzymes such as
ASSESSMENT
DESIRED OUTCOMES After 4 days of nursing care, client will be able to:
NURSING INTERVENTION Independent:
JUSTIFICATION
EVALUATION After 8 hours of nursing care, client will be able to:
Report pain is relieved or controlled
Identify ways of avoiding or minimizing pain (e.g using firm mattress and proper supporting and good body mechanics)
To reduce the pain felt by the client
Goal met. Client was able to report pain is controlled.
Monitor skin color and vital signs
Skin color and vital signs are usually altered in acute pain To promote nonpharmacologic al pain management
Provide comfort measures (e.g repositioning, use of heat or cold packs, nurses presence and quite environment) Demonstrate nonpharmacologic al methods such as therapeutic touch, biofeedback and relaxation skill
Recognize nonpharmacologica l methods that provide relief
To reduce anxiety and fear of the patient to pain
Goal met. Client was able to recognize nonpharmacologi cal methods that provide relief
21
collagenase Collagenase break down Pannus formation Erosion of articular cartilage Secondary degenerative changes in joint Mechanical stress on bone ends Stiffening of bone tissue Acute pain
Monitor use of self-administration or patient controlled analgesia for management of severe or persistent pain.
To distract attention and reduce tension
Demonstrate use of relaxation skills and diversional activities as indicated, for individual situation
Instruct in and encourage use of relaxation techniques such as focused breathing, imaging and listening to music etc.
Goal met. Client was able to demonstrate relaxation skills and diversional activities.
Source: Nursing Pocket Guide 12th Edition http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/791704-overview#a0104 22
23
You might also like
- EDF6222 Discussion Post 1Document2 pagesEDF6222 Discussion Post 1Erica LevyNo ratings yet
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Nasha Mukt Bharat PPT For VolunteersDocument27 pagesNasha Mukt Bharat PPT For Volunteersvaishali TMU student100% (4)
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pages"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Angina Pectoris NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Angina Pectoris NCPkarthi karthi100% (1)
- 1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument1 page1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusionjean_fabulaNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationHanz AlecNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryDan Leo UnicoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErica Denice CastilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageNo ratings yet
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesViii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationhehehe29No ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm Case Analysis and Concept MapDocument5 pagesCerebral Aneurysm Case Analysis and Concept Mapate NarsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment - Pediatric Clients in The Community New 1 1Document7 pagesNursing Assessment - Pediatric Clients in The Community New 1 1Ugalde AlyssakyleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Document3 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanNo ratings yet
- NCP of CavDocument3 pagesNCP of CavHenry Roque TagalagNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentGabrielLopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Planusama_salaymehNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJamaica SaranquinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VIII Drug StudyDocument14 pagesCHAPTER VIII Drug StudyAnonymous opu4ls27No ratings yet
- Imbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument3 pagesImbalnce Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementselheezaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsDocument4 pagesSurgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsAprille Claire MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- NCP Anxiety in SVTDocument2 pagesNCP Anxiety in SVTAlfadz AsakilNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute-PainDocument4 pagesNCP Acute-PainMarie CatapiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationFebee GeeNo ratings yet
- JDM Care PlanDocument5 pagesJDM Care PlangopscharanNo ratings yet
- NCP Hip FractureDocument5 pagesNCP Hip FractureCherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- BSN 1 H Case Application Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesBSN 1 H Case Application Nursing Care PlanAntonio EscotoNo ratings yet
- Thoracentesis Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesThoracentesis Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationAyra PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentjisooNo ratings yet
- Lapkas HegDocument1 pageLapkas HegkurniaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- ValeraJMP ACT3Document6 pagesValeraJMP ACT3JMICHELLE VALERANo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPBon BonNo ratings yet
- Child - Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesChild - Otitis MediawanyaminNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Stroke - NewDocument4 pagesNursing Care of Stroke - Newninda saputriNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLKevin M. VillacorteNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ludwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLudwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- AbacusDocument97 pagesAbacusأنور مازوز أبو يوسفNo ratings yet
- Test Yourself Units 1, 2, 3Document5 pagesTest Yourself Units 1, 2, 3Hieu PhuongNo ratings yet
- HTML Codes Foa WebsiteDocument180 pagesHTML Codes Foa WebsitePappu YadavNo ratings yet
- Astm G59Document4 pagesAstm G59Hà KhểnhNo ratings yet
- International Rules For Seed Testing 2020: Chapter 2: SamplingDocument52 pagesInternational Rules For Seed Testing 2020: Chapter 2: SamplingmaritzaNo ratings yet
- Management FunctionsDocument18 pagesManagement FunctionsKennethNo ratings yet
- CBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ..Light RefrectionDocument5 pagesCBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ..Light RefrectionBhardwaj Rajinder Sippy100% (2)
- Human Behavior PDFDocument12 pagesHuman Behavior PDFJameboy IbanezNo ratings yet
- Week14EdLing 102ProcessingtheMatterDocument5 pagesWeek14EdLing 102ProcessingtheMatterKevin BlasurcaNo ratings yet
- Welding Terms & DefinitionsDocument42 pagesWelding Terms & DefinitionspchakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- Yuxuan 6Document5 pagesYuxuan 6Kenton ZhengNo ratings yet
- Baby Fawn Noia LandDocument10 pagesBaby Fawn Noia LandRodrigo Pera75% (4)
- Control of HVDC Transmission System Based On MMC With Three-Level Flying Capacitor SubmoduleDocument22 pagesControl of HVDC Transmission System Based On MMC With Three-Level Flying Capacitor SubmoduleAnand Parakkat Parambil100% (1)
- Canon iPF8300 8300S 8000 Service Manual&Parts Catalog PDFDocument730 pagesCanon iPF8300 8300S 8000 Service Manual&Parts Catalog PDFHNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Self Assessment QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesInternal Control Self Assessment QuestionnaireHime Silhouette Gabriel100% (1)
- Restart Technique in AbaqusDocument24 pagesRestart Technique in AbaqusHSP19fNo ratings yet
- Rudder - Steering Gear Speed RulesDNVGL-RU-SHIP-Pt4Ch10 19Document1 pageRudder - Steering Gear Speed RulesDNVGL-RU-SHIP-Pt4Ch10 19Tolias EgwNo ratings yet
- Bard SpellsDocument5 pagesBard SpellsJake Von RührNo ratings yet
- 2.change Over Switch - L&TDocument12 pages2.change Over Switch - L&Trajpre1213No ratings yet
- Ar710 2 (Supply)Document329 pagesAr710 2 (Supply)xxal123xxNo ratings yet
- Greene - Shear Tab CalcDocument6 pagesGreene - Shear Tab CalcNagender KumarNo ratings yet
- Airon Cristobal Crim 1 D Illegal MiningDocument13 pagesAiron Cristobal Crim 1 D Illegal MiningJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Siyensikula Script (Draft) : Scene (Time Duration) Audio/ Script VisualDocument3 pagesSiyensikula Script (Draft) : Scene (Time Duration) Audio/ Script VisualJohn Nicholas TabadaNo ratings yet
- Answer Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks MarksDocument3 pagesAnswer Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks MarksanuNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & Technology: Sessional On ME 3220Document7 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & Technology: Sessional On ME 322017044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHNo ratings yet
- LS 231g3 Advanced Multifunctional Servo DriveDocument60 pagesLS 231g3 Advanced Multifunctional Servo DriveIlhami DemirNo ratings yet
- Unemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)Document16 pagesUnemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)NickNo ratings yet
- Controls Engineer InterviewDocument3 pagesControls Engineer Interviewrhoney0120% (1)