Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Race Ways
Race Ways
Uploaded by
Jula CandorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Race Ways
Race Ways
Uploaded by
Jula CandorCopyright:
Available Formats
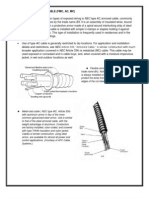
RACEWAYS Book definition: raceways are wiring accessories or channels designed for holding wires, cables, or busbars which
are either made of metal or any insulating material. Ehow definition: A wide variety of covered plastic or metal troughs or channels, known as raceways, hide various sorts of wires and cables, protecting them from physical damage. Raceways keep wires out of the way in home, office, commercial and industrial areas.
IMPORTANCE OF RACEWAYS IN PRACTICAL USE
Household -Raceways can run along the walls at the baseboards, ceilings or in corners. They hide wiring to just about anything, including speakers and home entertainment systems.
On Floors -Raceways with slanted edges placed on floors protect the wires and also people from tripping over them or getting tangled. The slanted edges allow wheels to pass over easily.
Raceway Systems -Different types of raceways can be joined together in complex arrays to hide wiring to multiple locations. Raceways help greatly where many computers are installed in a small area.
Power Poles -Some vertically mounted, stand-alone raceways have electrical outlet sockets to power multiple appliances that need AC power.
Corner Ducts Raceways -Raceways designed to fit into corners along ceilings use an adhesive, requiring no tools to install. They can be painted to match the walls or ceilings.
TYPES OF RACEWAYS: 1.) CONDUITS 2.) CONNECTORS 3.) CONDUIT COUPLINGS, ELBOWS, AND OTHER FITTINGS 4.) CONDUITS SUPPORTS, SUCH AS CLAMPS, HANGERS, ETC. 5.) CABLE TRAYS, CABLE BUS ETC. 6.) METAL RACEWAYS, NON-METAL RACEWAYS AND OTHERS
1.) CONDUITS (closed raceways/ conduit pipes/ tubings) They are the most common electrical raceways.
a rigid tube or duct for carrying and protecting electrical wires or cables
TYPES OF CONDUITS:
a.) STEEL CONDUIT- they provide enclosed wiring from mechanical injury and corrosion
Provides a ground metal enclosure for the wiring in order to avoid shock hazard. Provides a system ground path Protects surrounding against firehazard as a result of overheating or arching or enclosed conductors Supports the conductors
b.) ALUMINUM CONDUITS- its use has greatly increased over the years because of its weigh advantage over steel. -it has better corrosion resistance in most atmosphere. -it is non-magnetic, giving a lower voltage-drop -its non-sparkling and does not generally require painting. - its major drawback is its harmful effects on many types of concrete causing spalling and cracking when embedded.
c.) FLEXIBLE METAL CONDUIT It is known as Greenfield It is principally for motor connections or other locations where vibration is present, when movement is encountered or where physical obstruction make its use necessary. It should always be used in connections to motors, transformers, ballasts and the like.
d.) LIQUID-TIGHT FLEXIBLE METAL CONDUIT This conduit is of the same construction as flexible conduit, except that it is covered with a liquid-tight jacket.
It is not intended as general purpose conduit, its use is being restricted to connections where flexibility and imperviousness to liquid is required.
e.) NON-METALLIC CONDUIT They are raceways formed from materials such as fiber, asbestos cement, soapstone, rigid poly-vinyl chloride and high-density polyethylene. Its made to be resistant to moisture and chemical corrosion.
f.) METAL SURFACE RACEWAYS They may be utilized only in dry, non-hazardous, uncorrosive locations, and may generally contain only wiring operating below 300v. They are normally installed in places not subject to physical injury.
IMPORTANCE OF ELECTRICAL CONDUITS: a.) To provide a means for running wires frim one point to another. b.) To physically protect the wires. c.) To provide a grounded enclosure. d.) To protect the surroundings against the effects of fault in the wiring. e.) To protect the wiring system from damage by the building and the occupant. f.) To protect the building and the occupant from damage by electrical system.
2.) CONNECTORS They are metal sleeve usually made of copper that slipped over and secured to the butted ends of conductors in making a joint. It is also called splicing sleeve.
3.) CONDUIT COUPLINGS, ELBOWS, AND OTHER FITTINGS 4.) CONDUITS SUPPORTS, SUCH AS CLAMPS, HANGERS, ETC. 5.) CABLE TRAYS, CABLE BUS ETC.
Cable trays are used in industrial areas where many insulated cables are run together.
Individual cables can exit the tray at any point, simplifying the wiring installation and reducing the labour cost for installing new cables. Power cables may have fittings in the tray to maintain clearance between the conductors, but small control wiring is often installed without any intentional spacing between cables.
6.) METAL RACEWAYS, NON-METAL RACEWAYS AND OTHERS
2 RACEWAY SYSTEMS (WIRING METHOD) 1.) FLOOR RACEWAYS 2.) CEILING RACEWAYS
1.) FLOOR RACEWAYS A.) UNDERFLOOR RACEWAYS The raceways may be installed beneath or flush with door, are covered find their widest application in office spaces, since their use permits placements of power and signal outlets immediately under desks and other furniture, regardless of furniture layout. Some necessary methods are: a.) Channel the floor and install a conduit in the chase, connecting it to the nearest wall outlet. Patch the chased out portion. b.) Drill through the floor and run a conduit on the ceiling below to an outlet below. c.) Drill through the floor twice and connect the new outlet to an existing outlet via a conduit on the ceiling below. d.) Install a surface floor raceways. B.) METAL CELLULAR FLOOR RACEWAYS C.) PRECAST CELLULAR FLOOR RACEWAYS The structural concrete system is similar to cellular metal floor in application. A cell Is defined as a single, enclosed, tubular space in a floor made of precast cellular concrete slabs, the direction of the cell being parallel to the direction of the floor member. Feed for these cells is provided by header ducts, which is normally installed in concrete fill above the hollow core structural slab, although feed from the ceiling below is also practical. The cells can be used in air distribution and even for piping.
2.) CEILING RACEWAYS this system is actually more flexible than under floor raceways, since they energize lighting as well as provide power and telephone facilities; furthermore, they permit very rapid changes in layout at low cost. An additional advantage is that it itself can be altered at will since it is not cast in concrete. HEADER DUCTS- connect electrical panels and telephone cabinets in the power and telephones closets respectively. DISTRIBUTION DUCTS- tap onto the headers. This later acts as subdistribution wireways or may feed fixtures poles directly.
You might also like
- Proper Intallation of Wireway and Cable TrayDocument6 pagesProper Intallation of Wireway and Cable TrayJocelyn G. Esmena100% (3)
- Volume 1 - Bogie Maintenance ManualDocument276 pagesVolume 1 - Bogie Maintenance ManualManjunath AithalNo ratings yet
- Conduits and FittingsDocument6 pagesConduits and FittingsRapha RachoNo ratings yet
- UAP Docs 200-208Document85 pagesUAP Docs 200-208Julia Esquivias-Virtucio60% (5)
- Truth of The History of The WorldDocument154 pagesTruth of The History of The WorldBilly Carlson100% (1)
- Overhead DistributionDocument31 pagesOverhead DistributionZvandaziva NelisherNo ratings yet
- BG UTIliies 3Document8 pagesBG UTIliies 3Ken ChiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 202.3 Erecting Trunking and Cable TrayDocument16 pagesUnit 202.3 Erecting Trunking and Cable TraystanlyfulgensiNo ratings yet
- Flexible Armored CableDocument2 pagesFlexible Armored CableAldrin SantosNo ratings yet
- Cable RoutingDocument17 pagesCable RoutingBhagyanath GopinathNo ratings yet
- Review On Electrical Wiring (Types, Sizes and Installation) : December 2019Document11 pagesReview On Electrical Wiring (Types, Sizes and Installation) : December 2019Vinayak JenaNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ElectricalWiringDocument11 pagesReview 2 ElectricalWiringPriyaranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electrical CodeDocument6 pagesPhilippine Electrical CodeDia Necson Nicole SapongNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument44 pagesChapter Twoaregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Raceways and ConduitsDocument43 pagesLecture Raceways and Conduitsthomas goNo ratings yet
- Overhead Distribution LinesDocument53 pagesOverhead Distribution LinesJunry Tatoy MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ElectricalWiringDocument11 pagesReview 2 ElectricalWiringjonathan labajoNo ratings yet
- How To Install and Erect TrunkingDocument13 pagesHow To Install and Erect TrunkingDaniel Madulu CharlesNo ratings yet
- Testing TET113 NOTE 444Document37 pagesTesting TET113 NOTE 444bello musaNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ElectricalWiringDocument11 pagesReview 2 ElectricalWiringPogii AkooNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Research On The Following:: Matthew D. Madriaga AUGUST 23, 2016 TVL-1 Electrical Installation & MaintenanceDocument4 pagesAssignment: Research On The Following:: Matthew D. Madriaga AUGUST 23, 2016 TVL-1 Electrical Installation & MaintenanceGabriel Enrico EstoniloNo ratings yet
- Basic Elect Rial - CompiledDocument73 pagesBasic Elect Rial - CompiledElsha OlegarioNo ratings yet
- EI Lecture No.2Document9 pagesEI Lecture No.2Hassen Lazhar100% (1)
- Eccu 211 Manual T07Document40 pagesEccu 211 Manual T07Kevin MuñozNo ratings yet
- Bu RSW 2 Types of Conductors and Special Types of WiringsDocument4 pagesBu RSW 2 Types of Conductors and Special Types of WiringsANGELU MARIE GUMIRANNo ratings yet
- WiringDocument9 pagesWiringnithyasreeNo ratings yet
- Eccu 211 Manual T07Document34 pagesEccu 211 Manual T07karol villaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By-: Chetan Vasani Ashish Varghese Pravin Fating Umesh Tiple Gaurav MeshramDocument28 pagesSubmitted By-: Chetan Vasani Ashish Varghese Pravin Fating Umesh Tiple Gaurav MeshramRemya R. KumarNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument53 pagesReportJunry Tatoy MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Undergroud Power Cable Considerations Alternatives To OverheadDocument10 pagesUndergroud Power Cable Considerations Alternatives To Overheadkaushikray06No ratings yet
- Electrical Wires and Cables TypesDocument10 pagesElectrical Wires and Cables TypesMarlo AristorenasNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringDocument15 pagesLearning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringJEFFREY BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Bộ Môn Hệ Thống Điện Khoa Điện-Đhbk ĐànẵngDocument46 pagesBộ Môn Hệ Thống Điện Khoa Điện-Đhbk ĐànẵngA3 Phòng Điều ĐộNo ratings yet
- Trunking System of Electrical Systems76927 - 10 PDFDocument14 pagesTrunking System of Electrical Systems76927 - 10 PDFLeila Cherop100% (3)
- Ballast Ch12 ElectricalDocument19 pagesBallast Ch12 ElectricalSk Abdul RavoofNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 EX Wiring Methods - IECDocument51 pagesChapter 13 EX Wiring Methods - IECdanishaslNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electrical Industry TermsDocument3 pagesGlossary of Electrical Industry Termscurt4_756632202No ratings yet
- AKARSHDocument6 pagesAKARSHGreeshma PuttannaNo ratings yet
- 1armoured CableDocument23 pages1armoured CableScala PinkerNo ratings yet
- Scope: Lectrical Aterials and EthodsDocument9 pagesScope: Lectrical Aterials and EthodsAnonymous uXEdLjNo ratings yet
- Standards and Applications of Medium Voltage Bus DuctDocument5 pagesStandards and Applications of Medium Voltage Bus DuctsabeerNo ratings yet
- Cable TraysDocument13 pagesCable TrayssabeerNo ratings yet
- Draft: Central Electricity Authority 2018Document14 pagesDraft: Central Electricity Authority 2018binodeNo ratings yet
- Vanshi Dhar PDFDocument6 pagesVanshi Dhar PDFKhadse PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Re: Isolated Phase BusductDocument8 pagesRe: Isolated Phase BusductRamesh AnanthanarayananNo ratings yet
- Type of Cable TrayDocument10 pagesType of Cable TrayregistraraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design 101 PDFDocument104 pagesElectrical Design 101 PDFjungatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Second Year Wiring MethodsDocument19 pagesSecond Year Wiring MethodsReshmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in Electrical DesignDocument21 pagesBasic Concept in Electrical DesignEm Pee100% (1)
- 7 Types of Electrical Conduit: - by Juan RodriguezDocument15 pages7 Types of Electrical Conduit: - by Juan Rodriguezmany pinkNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wires and CablesDocument7 pagesElectrical Wires and CablesAUDI MCKYLA S. INOSANTONo ratings yet
- 11Document3 pages11Kurimaw SyNo ratings yet
- Cable TrunkingDocument5 pagesCable TrunkingLeo GeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring Estimation 170529115347Document45 pagesElectrical Wiring Estimation 170529115347habib AnsariNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design 1Document134 pagesElectrical Design 1Genisis Sangalang Nolledo100% (1)
- Nema Ve1 PDFDocument27 pagesNema Ve1 PDFvijayachidu60% (5)
- 8 Electrical SystemsDocument12 pages8 Electrical SystemsaguanoluNo ratings yet
- Electrical System of BuildingDocument86 pagesElectrical System of BuildingCatherineNo ratings yet
- Cables SelectionDocument17 pagesCables SelectionKhaldoon Alnashi100% (1)
- Cable: Electrical System TN-S Grand Coulee Dam Fire Test Sweden FireDocument7 pagesCable: Electrical System TN-S Grand Coulee Dam Fire Test Sweden FireSanjeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design and Corona Effect Overhead Transmission LineDocument60 pagesMechanical Design and Corona Effect Overhead Transmission LineGetahun shankoNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeFrom EverandA Guide to Some of the Equations used in Constructing a Suspension BridgeNo ratings yet
- Urban AestheticsDocument4 pagesUrban AestheticsJula CandorNo ratings yet
- LegaspiDocument11 pagesLegaspiJula CandorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Materials Electrical MaterialDocument7 pagesElectrical Materials Electrical MaterialJula CandorNo ratings yet
- Coping With Stress: A Special Addition To Staying Healthy: An EnglishDocument14 pagesCoping With Stress: A Special Addition To Staying Healthy: An EnglishJula Candor100% (1)
- Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and DiffractionDocument4 pagesReflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and DiffractionJula CandorNo ratings yet
- MetrologyDocument1 pageMetrologyMeet BakotiaNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Proper Residual Current Device Selection For Solar InvertersDocument5 pagesGuidance On Proper Residual Current Device Selection For Solar InvertersJake JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CDFT D18mp-A 104ts 17jan 2023 Fauzi, DevidDocument14 pagesCDFT D18mp-A 104ts 17jan 2023 Fauzi, DevidbobbyNo ratings yet
- Brother CP1800, CP2000, CB200 Service Manual PDFDocument92 pagesBrother CP1800, CP2000, CB200 Service Manual PDFStefanNo ratings yet
- Swiss Type Colles Guide BushingsDocument24 pagesSwiss Type Colles Guide BushingsKyi ZawNo ratings yet
- ShopNotes Comprehensice Index and Cut List PDFDocument16 pagesShopNotes Comprehensice Index and Cut List PDFJoe CNo ratings yet
- Assembly 2 DRWDocument2 pagesAssembly 2 DRWapi-576392651No ratings yet
- Air Conditioner Presentation A1Document29 pagesAir Conditioner Presentation A1Nova KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Expert 1100-2100-3100 Series ManualDocument4 pagesExpert 1100-2100-3100 Series ManualdiegoNo ratings yet
- SCTR Performa LHBDocument4 pagesSCTR Performa LHBTechnical CellNo ratings yet
- Total Mechanical Course PDFDocument17 pagesTotal Mechanical Course PDFbiranchi satapathy100% (3)
- Amphenol - 05022017 - TP 101 CP 1156596Document2 pagesAmphenol - 05022017 - TP 101 CP 1156596Fredson SidileneNo ratings yet
- Cheat SniperDocument4 pagesCheat SniperLadleyBibih KingbabehNo ratings yet
- Rotary Kiln Hydraulic Oil Station User ManualDocument44 pagesRotary Kiln Hydraulic Oil Station User ManualDIAGNE100% (1)
- VUETRADE Installation Guide T Blade Post Supports - Vers2Document3 pagesVUETRADE Installation Guide T Blade Post Supports - Vers2saagar8No ratings yet
- Classification of Tools and EquipmentDocument38 pagesClassification of Tools and EquipmentRodel de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes - AstecDocument34 pagesManual de Partes - AstecChristian Adan Rosas ZertucheNo ratings yet
- 02 Optical Fibre With VESDAnet LoresDocument8 pages02 Optical Fibre With VESDAnet LoresIVAN ANDRES PizarroNo ratings yet
- Lift Schedule of Tender SpecificationDocument33 pagesLift Schedule of Tender Specificationchia yeewahNo ratings yet
- Water Flow Test: Case StudyDocument5 pagesWater Flow Test: Case StudycwiejkowskaNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio CalipersDocument4 pagesGolden Ratio CalipersFrancois VaaltynNo ratings yet
- Quest 105 155 205 Dual Quick Start GuideDocument4 pagesQuest 105 155 205 Dual Quick Start GuidePhzi PhziNo ratings yet
- 50 Series Mechanical - Pins and BushingsDocument55 pages50 Series Mechanical - Pins and BushingsLuis Torres100% (1)
- Clutch Hino 5.5Document5 pagesClutch Hino 5.5Yeam_90No ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Careta Warrior Tech 9-13 Helmet EsabDocument2 pagesFicha Tecnica Careta Warrior Tech 9-13 Helmet EsabJACQUELINE CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Autroprime Marine Fire Alarm Control Panel BS-200MDocument2 pagesAutroprime Marine Fire Alarm Control Panel BS-200MTanesan WyotNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter Testing Not Applicable For This PanelDocument3 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter Testing Not Applicable For This Paneleswaran005No ratings yet
- 230313-MEP Client RequirementDocument19 pages230313-MEP Client RequirementSelcen yeniçeriNo ratings yet