Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Uploaded by
Kirin JoiezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
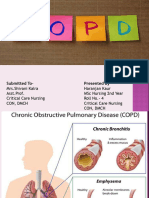
Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Uploaded by
Kirin JoiezCopyright:
Available Formats
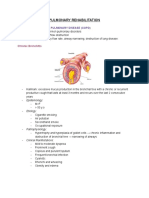
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) Sputum: Colorless; clear Thick; yellow; creamyPinkish fruityGreenishRustyLayeredMalodorBlood streak-
viral infection staphylococcus infection pulmonary edema pseudomonas infection pneumonia Bronchiectasis lung abscess or depression of the lungs PTB, Ca Lung Asthma Allergens (dust, chalk, pollens, chicken, seafoods) Abnormal antigen-antibody reaction (a A-A reaction) Stimulates mast cells with presence of inflammation response)
Release of mediators *histamine- (prolonged inside the body but slow) constriction/ narrowing of the airway *SRS-A slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis Potent than histamine *ECF-A Eusinophils chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis
Bronchial wall Asthma cough
hyper secretion Spasm/ of bronchial mucus constriction of the bronchi/ dyspnea bronchioles Wheezing
Narrowing the airway of the patient CHRONIC BRONCHITIS Cough will last for more than 3 months for 2 consecutive years ACUTE for pedia patient pathologic/ microorganism
Pathophysiology same with asthma Cardinal sign: bronchial edema; hypersecretion; spasm Airway obstruction Airway resistance Impaired gas exchange Impaired ventilation Hypoxia Cyanosis (Called BLUE BLOATERS) Predisposing factors: cigarette/ tabacco smoking
EMPHYSEMA Over inflation of alveoli/ distended alveoli No elastic recoil Problem during exhalation Predisposing factor: smoking, hereditary, and age. Smoking Presence of Nicotine old age wear and tear Destruction of Alveolar epithelium hereditary enzyme inhibitor deficiency of alpha antityrpsin
Stimulate release of Alveolar macrophages Release of protease/elastase *protease theory*elastase theoryconnective tissues: collagen and elastin Lung compliance and elastic recoil (expand) (go back to resting state)
Loss elastic recoil Over inflation/ distention of the alveoli Compression of the diaphragm RR Reddish skin pink puffer surfactant (phospholipid) closure of alveoli pulmonary Hypertension (HPN) stiffening Right ventricular hypertrophy Right ventricular failure Coronary pulmonale Arrest due to failure due to HPN constriction of pulmonary casculatures pulmonary vascular resistance Poor ventilation
atelectasis
hypercarbia ( CO2) hypoxia/ hypoxemia
respiratory acidoses
Surfactant decreases the tension of the surface of your alveoli Status Asthmaticus lock of the bronchioles spasm of larynx ER (1:1000 subcutaneous Epinephrine, adrenaline)
Management: 1. Avoid allergens 2. Desensitization- gradually introduce of allergens 3. Steroids- decrease bronchial edema and decrease bronchospasm Inhalation- decrease toxicity Fluticasone Budesonide Dont abrupt stop of hydrocortisone (IV) Tapper into prednisone (oral) 4. Bronchodilators Relaxes the smooth muscles of bronchus/bronchioles Salbutamol Ventolin Terbutalin- Bricanyl (oral) Salmeterol- Seravet Albuterol _Volmax 5. Mucolytics- decrease stixkiness of the mucus Ambroxol- Mucosolvan Carbocistene- Loviscol, Solmux Aciitylcysteine- Fluilucil 6. Inhalation USLOG 7. Chest tapping- loosen the secretion (after inhalation) 8. Postural drainage drainage of secretion through gravity 9. Pursed lip breathing- prevent air trapping 10. Diet low CHO (carbohydrates) presence of CO2 .. ( hypercarbia patient) 11. Small frequent feeding avoid abdominal distention 12. Regular exercise (modified) tolerable of the patient Prevent hypoxia
13.
14.
15.
Secretions move to be easy to cough out Environment Smoke free Wear mask Avoid perfume, powder Provide well ventilated room Too hot increase energy expenditure (needs more oxygen - May develop hypoxia Too cold- constrict - SOB because of spasm Psychologically prepare Counsel, talk, provide more information Psychologically prepare from : stress, fear . These may cause bronchospasm that may lead to SOB O2 therapy 2L/ min - average
You might also like
- Process Recording Mental Health PDFDocument5 pagesProcess Recording Mental Health PDFCeline Cabading90% (29)
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocument91 pagesPart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüNo ratings yet
- Brain Gym ExercisesDocument21 pagesBrain Gym Exercisesapi-380547950% (4)
- General Nursing Departmental ManualDocument532 pagesGeneral Nursing Departmental Manualarahman16850% (2)
- SofasDocument2 pagesSofasZizieAzizahZahwaNo ratings yet
- ElecrolytesDocument4 pagesElecrolytesKrizzia Allyssa CotingjoNo ratings yet
- Medical and Psychiatric Social WorkDocument36 pagesMedical and Psychiatric Social WorkSaravana Kadirvel64% (25)
- 1respiratory System DisordersDocument10 pages1respiratory System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- Cough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Document24 pagesCough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Meghana PatilNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation NotesDocument23 pagesOxygenation NoteschikaycNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDDocument49 pagesAcute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDHendraDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Document41 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Kristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Onchi & CopdDocument8 pagesOnchi & CopdAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Tina ThankachanDocument50 pagesTina ThankachanBharat JamodNo ratings yet
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure: For EMT ProvidersDocument44 pagesContinuous Positive Airway Pressure: For EMT ProvidersYabetsNo ratings yet
- DR Ambreen Shams NephrologistDocument58 pagesDR Ambreen Shams NephrologistAamer NaeemNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDocument23 pagesApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- COPDDocument70 pagesCOPDDr. Rizwana SamrinNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument6 pagesCOPDAubrey PerezNo ratings yet
- Respiration CH 43.Dr SarahDocument59 pagesRespiration CH 43.Dr Sarahaiman siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Patho Exam 3: Deficiency in Alpha-1-Antitrypsin-Unchecked Elastase Destruction of The AlveoliDocument5 pagesPatho Exam 3: Deficiency in Alpha-1-Antitrypsin-Unchecked Elastase Destruction of The AlveoliTaran LuthraNo ratings yet
- COPD Bat NoteDocument6 pagesCOPD Bat NoteLankeshwaraNo ratings yet
- Obstructive DisordersDocument23 pagesObstructive DisordersMartha ChaseNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument6 pagesAsthmaJay Hipulan QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Asthma and The COPDsDocument133 pagesAsthma and The COPDsShania robertsNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument18 pagesCOPDMae CalicaNo ratings yet
- Copd 200412082048Document139 pagesCopd 200412082048Richard ArceNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Obstructive DisorderDocument79 pagesWeek 3 Obstructive Disorderdelrosariojm87No ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Pathology of The Respiratory System 2Document76 pagesPathology of The Respiratory System 2Fabian ChapimaNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Airway DiseasesDocument56 pagesObstructive Airway Diseaseskalanakariyawasam99No ratings yet
- ATI Respiratory PowerpointDocument90 pagesATI Respiratory PowerpointAnn KelseaNo ratings yet
- Normal Changes of AgingDocument9 pagesNormal Changes of AgingGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- COPD PTDocument49 pagesCOPD PTSathish RathnamNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDocument55 pagesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- SS Visser, Pulmonology Internal Medicine UPDocument33 pagesSS Visser, Pulmonology Internal Medicine UPRonnie JaderNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System2Document134 pagesRespiratory System2Darell M. BookNo ratings yet
- Emphysema Fall 2019Document3 pagesEmphysema Fall 2019Mary MarshNo ratings yet
- Athira UDocument22 pagesAthira UJuvana LachuNo ratings yet
- Feline Brochial DiseaseDocument7 pagesFeline Brochial DiseaseDimas SetiawanNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument4 pagesCopdapi-3739910100% (2)
- The System: RespiDocument219 pagesThe System: Respilalaine22dale100% (1)
- Pathohys II-respiratory DiseasesDocument89 pagesPathohys II-respiratory DiseasesSophia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cough: Dr. Amit Adhikari Medical Officer Siddhi Memmorial Hospital Paediatric DepartmentDocument31 pagesApproach To Cough: Dr. Amit Adhikari Medical Officer Siddhi Memmorial Hospital Paediatric DepartmentAmit AdhikariNo ratings yet
- The System: RespiDocument247 pagesThe System: RespiKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- COPD & RLDDocument17 pagesCOPD & RLDhis.thunder122No ratings yet
- Patho Respiratory - KatherineDocument9 pagesPatho Respiratory - KatherineKayla MayerNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument3 pagesConcept MapKevin T. KatadaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document36 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Tuesday, October 3 (Ellen)Document6 pagesTuesday, October 3 (Ellen)api-26938624No ratings yet
- CopdDocument30 pagesCopdsalmanhabeebekNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument30 pagesCOPDAmila SirisingheNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology: Several Diseases Airflow ObstructionDocument11 pagesEpidemiology: Several Diseases Airflow ObstructionBharat Singh BanshiwalNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary FailureDocument29 pagesPulmonary FailureWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument11 pagesChronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary Diseasepreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- Resp System. ExamDocument145 pagesResp System. ExamIrina CornilovNo ratings yet
- k12, Pa, Pathology of Copd - rts1-k12Document46 pagesk12, Pa, Pathology of Copd - rts1-k12ashtridNo ratings yet
- COPD:RLDDocument11 pagesCOPD:RLDKhiara Yapha AlfarNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Wassim Mehboobali NooranyDocument12 pagesAsthma: Wassim Mehboobali NooranyMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersDocument3 pagesChapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersPeej Reyes100% (1)
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument46 pagesPulmonary PathologyMuostafa KamelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PathologyDocument26 pagesRespiratory PathologyIshali NuwanjiniNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument31 pagesRespiratoryRebecca Hughes100% (4)
- 2cough and ExpectationDocument37 pages2cough and ExpectationMar ClrNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Manual IPL AESTHETICDocument16 pagesManual IPL AESTHETICIrene Chandra100% (1)
- Chamomilla: Materia MedicaDocument29 pagesChamomilla: Materia MedicaA.H. Lammert Holdijk100% (1)
- Manupatra - The Consumer Protection Act, 1986Document25 pagesManupatra - The Consumer Protection Act, 1986samiaNo ratings yet
- Liam 1 ADocument1 pageLiam 1 ASelina MaycockNo ratings yet
- Spring 2013.1 Aromatherapy JournalDocument52 pagesSpring 2013.1 Aromatherapy JournalNAHAAdmin100% (3)
- PIID 184 Post Mortem April 17Document7 pagesPIID 184 Post Mortem April 17Rey Loro PongautanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase Studyapi-401961702No ratings yet
- Homoeo at A Glance PDFDocument12 pagesHomoeo at A Glance PDFNarasimharao VennelakantiNo ratings yet
- Hard WordsDocument29 pagesHard WordsIlluminate ValorantNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Teeth For Functional Harmony - PPTX 1Document102 pagesArrangement of Teeth For Functional Harmony - PPTX 1ChaithraNo ratings yet
- Alb2.Js02 (1) AlbuminaDocument2 pagesAlb2.Js02 (1) AlbuminaJuan SánchezNo ratings yet
- Ginkgobiloba: Indications, Mechanisms, and SafetyDocument11 pagesGinkgobiloba: Indications, Mechanisms, and SafetyEmirgibraltarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmacologic Pain Management in OrthodonticsDocument21 pagesNon-Pharmacologic Pain Management in OrthodonticsDr. Kanak100% (1)
- 3786 Frequency & Severity Rates For Industrial InjuriesDocument30 pages3786 Frequency & Severity Rates For Industrial InjuriesVk Seshadri100% (1)
- National Family Health SurveyDocument21 pagesNational Family Health SurveyNamita Goyal100% (1)
- Fundamental of NursingDocument5 pagesFundamental of Nursingsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- The PhilCAT Certification Self-Assessment and Survey ToolDocument25 pagesThe PhilCAT Certification Self-Assessment and Survey ToolEivenn PanerioNo ratings yet
- Catherine M. Metra BSN IvDocument18 pagesCatherine M. Metra BSN IvCatherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Prescription Drug Abuse Crisis in NYS - Comprehensive ApproachDocument26 pagesPrescription Drug Abuse Crisis in NYS - Comprehensive ApproachNew York SenateNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Effects of Twelve Signs of The ZodiacDocument6 pagesPathogenic Effects of Twelve Signs of The ZodiacParamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology and Clinical Use of DiureticsDocument5 pagesPharmacology and Clinical Use of DiureticsvivianNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Temporary Anchorage Devices: Dr. Chelza X, Dr. Anand SivadasaDocument3 pagesNanotechnology in Temporary Anchorage Devices: Dr. Chelza X, Dr. Anand SivadasajayashreeNo ratings yet
- Cleft Case Chief Complaint Brief History (I) Present IllnessDocument6 pagesCleft Case Chief Complaint Brief History (I) Present IllnessArchanaShenoyNo ratings yet