Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Batch Notes Gyne DDX of Vaginal Bleeding
Batch Notes Gyne DDX of Vaginal Bleeding
Uploaded by
Pipoy AmyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Batch Notes Gyne DDX of Vaginal Bleeding
Batch Notes Gyne DDX of Vaginal Bleeding
Uploaded by
Pipoy AmyCopyright:
Available Formats
Differential Diagnosis of Vaginal Bleeding Dr.
Ursua PQ1
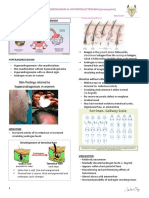
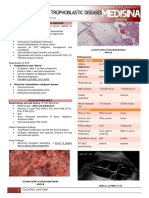
Differential Diagnosis of Vaginal bleeding *differentiate pathologic from non normal (menstruation). Take consideration the AGE of the patient. *if the patient is in age of reproduction, check SEXUAL ACTIVITY *amount of bleeding - normal bleeding : 50 ml - spotting : ectopic pregnancy *fully soaked napkin : 30-40 ml Obstetric (pregnancy related causes) *the first diagnosis PREGNANCY FIRST HALF 1. ABORTION - The fetus is less than the age of the viability (20 weeks AOG) - Depending of type of abortion 2. ECTOPIC PREGANCY - (+) bleeding is due to the hormones which affects the endometrium. - The endometrium regresses as decidualization and secreted as decidual cast - The space in the fallopian tube is not enough, hence there is no enough stimulus to stimulate corpus luteum to produce HCG, decreasing the progesterone levelsm hence decidua will not attach which then result to vaginal bleeding 3. GESTATION TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASE - Hydatidiform mole (H-mole) will result into cancer - Classic manifestation : (+) pearls, sago like consistency along with bleeding 4. LOW LYING PLACENTA - *doc said due to placenta previa SECOND HALF 1. PLACENTA PREVIA - Normal: placenta is implanted at fundal region b. Outright bleeding - The placenta peripherally is detached Placenta precedes the uterus 2. ABRUPTIO PLACENTA - Ablatio Placentae - Premature separation of placenta that is NORMALLY IMPLANTED - Types: a. Concealed - The placenta is centrally detached causing HEMATOMA - (+) BOARD LIKE RIGIDITY - (+) SEVEREDIRECT BOUND TENDERNESS
3. VASA PREVIA - Normal: all vessels are enlarged - Crisscrossing of vessels - Ddx: intrauterine fetal death Dead fetus is perceived by the body as foreign, causing the uterus to contract resulting to dilatation of cervix, hence expulsion POST PARTUM FOUR TS 1. TONE - uterine atony (failure of the uterus to contract) 2. TISSUE a. Retained Placenta fragments Placenta accrete Mismanagement of placenta b. Unclotted round 3. TRAUMA a. Ruptured vagina Use of RITGENS MANEUVER to prevent forceful release of fetus 4. THROMBIN - Coagulation factor problems a. Aplastic anemia b. Hemophilia
1 Saint Louis University School of Medicine Batch 2015
Differential Diagnosis of Vaginal Bleeding Dr. Ursua PQ1
c. d. e. f. Blood dyscrasia Decreased fibrinogen Decreased calcium Used of drugs : heparin, aspirin FIBROTHECOMA: functional bleeding produces
Gynecologic causes 1. TUMORS (please educate patient that not all tumors are malignant.) a. Benign - Polyps - Fibroids : myoma o Well circumscribed o More bleeding at intracavity
Medical Causes 1. PLATELET DISORDERS - Dengue hemorrhagic fever 2. CLOTTING FACTOR ABNORMALITY Prepubertal Period 1. PHYSIOLOGIC - Withdrawal from exposure to estrogen - Vulvar o Vulvitis
Trauma : straddle injury Lichen sclerosus : scarring around genital skin
b. Malignant - Cervical Ca : due to STDs which are highly preventable - Endometrial Ca - Fallopian tube Ca 2. INFECTION a. Endometritis b. Cervivitis 3. FOREIGN BODY - Recurrent bleeding especially in children o Toys o Coin o Lego parts o M&Ms o Wisp of cotton 4. HORMONAL ABNORMALITIES a. Endogenous : medications b. Exogenous - Breakthrough bleeding 2 Saint Louis University School of Medicine Batch 2015 Condylomata: Molloscum contagiosum: warts
- Urethral prolapsed : a. Vaginal - Vaginitis - Foreign bodies - Trauma - Vaginal tumor
Differential Diagnosis of Vaginal Bleeding Dr. Ursua PQ1
b. Hormones - Precocious puberty - Ovarian tumors (fibrothecoma) - Exogenous estrogen Adolescent Period a. Anovulation Dysfunctional uterinebleeding : follicles not maturing due to problem at hypothalamo pituitary gonadal axis b. Pregnancy related c. Exogenous hormones d. Hematologic abnormalities e. Infections f. Endogenous g. Anatomic causes Reproductive Age Group 1. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding 2. Pregnancy related bleeding 3. Exogenous hormones 4. Endocrine causes *eat mungo beans :high in estrogen 5. Anatomic derangements Post Menopausal Stage Group 1. Exogenous estrogen - To prevent osteoporosis - Thickening of vagina 2. Atrophic endometritis/ vaginitis 3. Endometrium/ cervical/ uterine/ ovarian cancer and lesions 4. Endometrial polyps and cervical polyps 5. Endometrial hyperplasia 6. Trauma 7. Urethral carunlce
3 Saint Louis University School of Medicine Batch 2015
You might also like
- EUOGS OSCE Booklet 2020Document26 pagesEUOGS OSCE Booklet 2020Amanda Leow100% (1)
- 6 10Document10 pages6 10Pipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Music EducationDocument24 pagesTherapeutic Music EducationXimena LainfiestaNo ratings yet
- 1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyDocument6 pages1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyIrene FranzNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic Lesions FinalDocument11 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions Final2012100% (4)
- (Gyne) 2.1 PCOS, Hyperandrogenism & Hyperprolactenemia (OnaCruz) - WiniDocument10 pages(Gyne) 2.1 PCOS, Hyperandrogenism & Hyperprolactenemia (OnaCruz) - WiniDexter IanNo ratings yet
- DystociaDocument8 pagesDystociaCylin Dadural100% (1)
- Name: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsDocument3 pagesName: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsAllyah Anthonette Ferwelo100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Maternal AnatomyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Maternal AnatomyRem Alfelor100% (2)
- Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesCervical CancerCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- C SectionDocument50 pagesC SectionAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Ob Revalida Samplex ZapDocument24 pagesOb Revalida Samplex ZapMariana B.No ratings yet
- Breech - Management Of: 1. PurposeDocument15 pagesBreech - Management Of: 1. PurposeMuathNo ratings yet
- History and Pe ObgynDocument4 pagesHistory and Pe ObgynCara Marrero IguidNo ratings yet
- I 1.dystociaDocument3 pagesI 1.dystociaAllan NacinoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Female Genital TractDocument4 pagesDiseases of The Female Genital Tractsarguss14No ratings yet
- HysterectomyDocument70 pagesHysterectomyYudhistira AdiNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CollapseDocument54 pagesPostpartum Collapsemedical chroniclesNo ratings yet
- Gyne ReflectionDocument18 pagesGyne ReflectionKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.06-Benign and Malignant Lesions of UterusDocument7 pagesGYNE 4.06-Benign and Malignant Lesions of UterusGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Gyno & Obs HXDocument68 pagesGyno & Obs HXJason SteelNo ratings yet
- Obgyn Osce - Ob HistoryDocument3 pagesObgyn Osce - Ob HistoryErika Leah ManaloNo ratings yet
- OSCE OB - PDF Version 1Document15 pagesOSCE OB - PDF Version 1FNaF is love FNaF is lifeNo ratings yet
- Normal Conduct of LaborDocument62 pagesNormal Conduct of LaborFaye Cabotaje LinganNo ratings yet
- Malig Ovarian TumoursDocument42 pagesMalig Ovarian TumoursSamuel InbarajaNo ratings yet
- Caesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDocument3 pagesCaesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDewi SaftariNo ratings yet
- OB 1.01 DystociaDocument9 pagesOB 1.01 DystociaRaquel Reyes100% (1)
- OSCE Reviewer 2013Document4 pagesOSCE Reviewer 2013rere choiNo ratings yet
- Uterinefibroids 130120064643 Phpapp02Document73 pagesUterinefibroids 130120064643 Phpapp02Tharun Kumar0% (1)
- Hypertension in Pregnancy PoltekesDocument41 pagesHypertension in Pregnancy PoltekesKhoerunnisa SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2Document75 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2yurie_ameliaNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument28 pagesCervical IncompetenceHoney May Rollan Vicente100% (1)
- 002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFDocument11 pages002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFale_fearNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument5 pagesObstetrics - Operative Vaginal DeliveryJonathanNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care: Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument2 pagesAntenatal Care: Physiological Changes in PregnancyAlexander Ennes100% (1)
- Multifetal Pregnancy: Nancy Margarette C. Roxas First Year ResidentDocument39 pagesMultifetal Pregnancy: Nancy Margarette C. Roxas First Year ResidentKarla LasamNo ratings yet
- Medicine 6.1b Approach To Cancer Patients - FernandoDocument7 pagesMedicine 6.1b Approach To Cancer Patients - FernandoAbigail LausNo ratings yet
- BENIGN OVARIAN DISEASES - Updated January 2018Document31 pagesBENIGN OVARIAN DISEASES - Updated January 2018daniel100% (1)
- O&G Counselling - TSPDocument6 pagesO&G Counselling - TSPTarran PhagooNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: (Hydatidiform Mole)Document12 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease: (Hydatidiform Mole)Gylle Marie PlazaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Ultrasound in The Diagnosis of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease PDFDocument37 pagesThe Role of Ultrasound in The Diagnosis of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease PDFBenn Berrigan100% (2)
- StratOG Vaginal BreechDocument17 pagesStratOG Vaginal BreechNalin AbeysingheNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.01a EndometriosisDocument4 pagesGYNE 4.01a EndometriosisGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1Document14 pagesBenign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1Charrie RagadiNo ratings yet
- CC C C: June 8, 2011 By: Santos, Edilberto DBDocument63 pagesCC C C: June 8, 2011 By: Santos, Edilberto DBHakugeiNo ratings yet
- DystociaDocument6 pagesDystociasarguss14100% (2)
- 02 Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument8 pages02 Gestational Trophoblastic Diseasemisakichan FrandoNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Screening ProceduresDocument30 pagesGynecology Screening Proceduresapi-506496190No ratings yet
- Multifetal PregnancyDocument8 pagesMultifetal PregnancyPat CabanitNo ratings yet
- Benign Gyne LesionsDocument133 pagesBenign Gyne LesionsJulie Ann ValenciaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSDocument24 pagesOSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSMohammad Saifullah100% (1)
- Multifetal PregnancyDocument42 pagesMultifetal PregnancyRisman TangdiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument8 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingEcbNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Tumors of Female Genital TractDocument14 pagesBenign and Malignant Tumors of Female Genital TractDimitrios PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LaborDocument20 pagesAbnormal LaborAiszel Angeli Pepito LigoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsRenz Francis SasaNo ratings yet
- Mal Presentations Mal PositionsDocument4 pagesMal Presentations Mal PositionsMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Benign & Precancerous Tumors of Female Genital Organs: by Assist. O.V.BakunDocument83 pagesBenign & Precancerous Tumors of Female Genital Organs: by Assist. O.V.BakunDian Permata PutraNo ratings yet
- Medical Disorders in Pregnancy: A Manual for MidwivesFrom EverandMedical Disorders in Pregnancy: A Manual for MidwivesS. Elizabeth RobsonNo ratings yet
- Remedial Law Review Case Digests 1-20Document36 pagesRemedial Law Review Case Digests 1-20Pipoy Amy100% (1)
- Commercial Law AssignmentDocument13 pagesCommercial Law AssignmentPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Theft Pros (Evid Attached)Document18 pagesTheft Pros (Evid Attached)Pipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Judicial Affidavit Philip AmilsocDocument5 pagesJudicial Affidavit Philip AmilsocPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Provisional OrdersDocument45 pagesProvisional OrdersPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Cases 157910Document13 pagesCases 157910Pipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- E Notarization PowerpointDocument27 pagesE Notarization PowerpointPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Case 10 Sps Lising V SampanaDocument1 pageCase 10 Sps Lising V SampanaPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- Legal Forms CasesDocument59 pagesLegal Forms CasesPipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- The Limits of Restorative JusticeDocument12 pagesThe Limits of Restorative JusticePipoy AmyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Architecture and Design On Mental Health and ImplicDocument34 pagesThe Effect of Architecture and Design On Mental Health and ImplicClarisse DoriaNo ratings yet
- MicroSIlver BG 11-2011Document92 pagesMicroSIlver BG 11-2011Guilherme LealNo ratings yet
- Inlays Onlays 1Document18 pagesInlays Onlays 1Alireza NaderiNo ratings yet
- Program Guide REVISED 4.26.2018Document60 pagesProgram Guide REVISED 4.26.2018Sergio Hidalgo BronfmanNo ratings yet
- Issues in Therapy With Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender ClientsDocument33 pagesIssues in Therapy With Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender ClientsOlena Baeva0% (1)
- Table of Contents Iadc Safety Meeting TopicsDocument4 pagesTable of Contents Iadc Safety Meeting TopicsfarisNo ratings yet
- LifeextensionDocument84 pagesLifeextensionhermestriNo ratings yet
- Incident First Notification Form - Rev 3Document5 pagesIncident First Notification Form - Rev 3ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Natural Treatment For Eosinophilia & CureDocument28 pagesNatural Treatment For Eosinophilia & CureVikram ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation Science Technology AssignmentDocument8 pagesPresentation Science Technology AssignmentLaura JadeNo ratings yet
- 7 Days of Mindful Living PDFDocument10 pages7 Days of Mindful Living PDFMohamed DhokkarNo ratings yet
- California BCC Required Lab Testing ChartDocument1 pageCalifornia BCC Required Lab Testing Chartsandydocs100% (2)
- Comprehensive School Safety Monitoring ToolDocument8 pagesComprehensive School Safety Monitoring ToolJane Lhyn Villaflor100% (1)
- Kabale University Private Admission List For Academic Year 20192020Document36 pagesKabale University Private Admission List For Academic Year 20192020The Campus Times100% (1)
- Deviation Permit/ConcessionDocument3 pagesDeviation Permit/ConcessionUnni AlsvikNo ratings yet
- Guide To The Quality EDQM For Human ApplicationDocument462 pagesGuide To The Quality EDQM For Human ApplicationFREDY ALONSO MANTILLA CABALLERONo ratings yet
- Novel Boswellic Acids Nanoparticles Induces Cell Death in Prostate Cancer CellsDocument9 pagesNovel Boswellic Acids Nanoparticles Induces Cell Death in Prostate Cancer CellsSaji UthamanNo ratings yet
- Awake!: November 08, 2001 - United Nations NewsDocument32 pagesAwake!: November 08, 2001 - United Nations NewssirjsslutNo ratings yet
- Userdocument 4Document7 pagesUserdocument 4Gopal SutharNo ratings yet
- Atypical CMLDocument5 pagesAtypical CMLBenyam ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Cryotech IVF Media Products and Services For Reproductive, Infertility ProfessionalsDocument9 pagesCryotech IVF Media Products and Services For Reproductive, Infertility ProfessionalsCryoTech IndiaNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Post Op Pain After 1 Appointment Endodontic Treatment of Asymptomatic Pulpal Necrosis in Single Rooted Teeth Mulhern 1982Document6 pagesIncidence of Post Op Pain After 1 Appointment Endodontic Treatment of Asymptomatic Pulpal Necrosis in Single Rooted Teeth Mulhern 1982abcder1234No ratings yet
- ADAZA - BSND 3 - Omaha SystemDocument4 pagesADAZA - BSND 3 - Omaha SystemKrizle AdazaNo ratings yet
- 6 Moving and Positioning WorkbookDocument30 pages6 Moving and Positioning WorkbookAgnieszka WaligóraNo ratings yet
- Module-5 Envirionmental Impact Assessment Dr. Saravanakumar Evs Chy1002Document33 pagesModule-5 Envirionmental Impact Assessment Dr. Saravanakumar Evs Chy1002Asheee100% (1)
- Pengaruh Work Life Balance Terhadap Kepu 3ad997e8Document9 pagesPengaruh Work Life Balance Terhadap Kepu 3ad997e8Khazz JweeNo ratings yet
- Arya 2014Document15 pagesArya 2014pratyusha vallamNo ratings yet
- Hans-Günter Ramke, HöxterDocument12 pagesHans-Günter Ramke, HöxterKalagotla PeerNo ratings yet
- LEC8 OncologyDocument19 pagesLEC8 Oncologymian gNo ratings yet