Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Uploaded by
Romeo Belvis JaramillaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Intentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating Client Development in A Multicultural Society 9th Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument62 pagesIntentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating Client Development in A Multicultural Society 9th Edition Ebook PDF Versionteresa.vanhorn90798% (55)
- MoH Adverse Events Policy PDFDocument33 pagesMoH Adverse Events Policy PDFnayan4uNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Celecoxib: Shadrock L. CaparidaDocument17 pagesCelecoxib: Shadrock L. CaparidaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- MEFTAL P Suspension PIDocument10 pagesMEFTAL P Suspension PIpiyush patelNo ratings yet
- Alcofan: TabletsDocument2 pagesAlcofan: Tabletskokocodename47No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drugs - Icu (Group)Document7 pagesDrugs - Icu (Group)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Week 2 Course TaskDocument6 pagesPharma - Week 2 Course TaskLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- The Treatment and Prognosis of Nephrotic Syndrome in The ElderlyDocument5 pagesThe Treatment and Prognosis of Nephrotic Syndrome in The ElderlysulemanbankerNo ratings yet
- Meftagesic DS SuspDocument14 pagesMeftagesic DS SuspPhysics with V SagarNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- MELOXICAMDocument4 pagesMELOXICAMAizat KamalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- DOLOSTAT-SP TabletsDocument15 pagesDOLOSTAT-SP TabletsVNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Combiflam Tablets PI - 08072019Document13 pagesCombiflam Tablets PI - 08072019ArunNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJi Vista MamigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- 2021.07.30 Gen Payne PIDocument16 pages2021.07.30 Gen Payne PIZach ZwaneNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen Arrow Care TabDocument9 pagesIbuprofen Arrow Care TabshajahanputhusseriNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- HypertensiveDocument2 pagesHypertensiveReinhard Lumbag PacitengNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- 2013 4 24 12 33 8Document2 pages2013 4 24 12 33 8Karim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDocument4 pagesDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Stopp Start ToolkitDocument22 pagesStopp Start ToolkitRifky IlhamiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument1 pageTelmisartanNarianne Mae Solis Bedoy75% (8)
- BNSC CVSDocument37 pagesBNSC CVSosewapeace14No ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorDocument8 pagesACE InhibitorLeonel YagoNo ratings yet
- Lofnac Suppo Diclofenac Sodium Tablets 100mg SmpcDocument15 pagesLofnac Suppo Diclofenac Sodium Tablets 100mg SmpcKemy AbohNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument58 pagesCardio DrugsMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTrojangBaboyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument3 pagesAMLODIPINEDianpratiwi22No ratings yet
- Drug FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug FurosemideJicel Camille EdeaNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Pioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011Document95 pagesPioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011ameers333No ratings yet
- HOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Document18 pagesHOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Donajei Rica100% (1)
- Medical College Choices 08 NovDocument1 pageMedical College Choices 08 NovamitNo ratings yet
- Gensler Design Forecast 2013Document43 pagesGensler Design Forecast 2013Pete PetrášNo ratings yet
- Hospitals Qatar DatabaseDocument3 pagesHospitals Qatar DatabaseShibu KavullathilNo ratings yet
- Hydroxychloroquine PELDocument3 pagesHydroxychloroquine PELscribd_deepak100% (1)
- GoutDocument75 pagesGoutVan Talawec100% (2)
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument27 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeHassan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Part Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelDocument18 pagesPart Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelIAN LAPINGNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument37 pagesOsteoarthritisChikezie Onwukwe100% (1)
- CSC138 Group Assignment 2Document3 pagesCSC138 Group Assignment 2KIRIT GOVINDARAJA PILLAI 20BCE2404No ratings yet
- ADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Document20 pagesADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument7 pagesCPRManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Are Diet Supplements The Whey Forward?Document7 pagesAre Diet Supplements The Whey Forward?Jason Darrell100% (1)
- Nebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureDocument1 pageNebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureSahib Singh Chadha0% (1)
- English TM 8Document11 pagesEnglish TM 8Budi AtmikaNo ratings yet
- RICE. Becoming The Fat GirlDocument288 pagesRICE. Becoming The Fat GirlNina NavajasNo ratings yet
- Vestige E-Catalogue India - August 2021Document145 pagesVestige E-Catalogue India - August 2021SamyamoyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document9 pagesJurnal 2Santi SantideswitaNo ratings yet
- Pha311 TellerDocument48 pagesPha311 TellerelikidpradoNo ratings yet
- SPEECHDocument13 pagesSPEECHJellai TejeroNo ratings yet
- Employee Health and Safety of BPCLDocument4 pagesEmployee Health and Safety of BPCLpooji25No ratings yet
- Personal Growth ToolkitDocument39 pagesPersonal Growth Toolkitsudhir sharma100% (3)
- SSMT ConplanDocument2 pagesSSMT ConplanJeffrey VillangcaNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Barley PDFDocument4 pagesHealth Benefits of Barley PDFYusrinaNoorAzizahNo ratings yet
- MCN Drill 1Document23 pagesMCN Drill 1Cai Velasco DecenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesDocument16 pagesClinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesdrlawrencekindoNo ratings yet
- AIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015Document24 pagesAIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015AdamAce VelasquezNo ratings yet
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Uploaded by
Romeo Belvis JaramillaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Drug Analysis Celecoxib
Uploaded by
Romeo Belvis JaramillaCopyright:
Available Formats
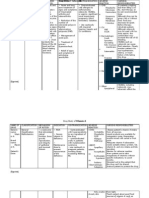
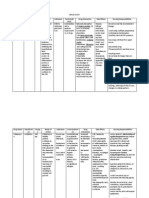
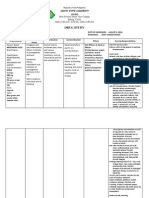
Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Drug Analysis
MEDICATION
MECHANISM OF ACTION Thought to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, impeding COX-2, to produce antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects.
INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE / SIDE EFFECTS
DRUG-TO-DRUG INTERACTION ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II antagonists: May decrease antihypertensive effects. Monitor patients blood pressure. Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium: May decrease celecoxib level. Separate doses. Aspirin: May increase risk of ulcers; low aspirin dosages can be used safely to reduce the risk of CV events. Monitor patient forsigns and symptoms of GI bleeding. Fluconazole: May increase celecoxib level. Reduce dosage of celecoxib to minimal effective dose. Furosemide, thiazides: May reduce sodium excretion caused by diuretics, leading to sodium retention. Monitor patient for swelling and increased blood pressure. Lithium: May increase lithium level. Monitor lithium level closely during treatment. Warfarin: May increase PT and bleeding complications.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
GENERIC NAME: Celecoxib BRAND NAME: Celebrex CLASSIFICATION: NSAIDs Pharmacologic: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor
Acute pain and primary dysmenorrhea
Contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain after CABG surgery. Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug, sulfonamides, aspirin, or other NSAIDs. Contraindicated in those with severe hepatic impairment. Avoid use in the third trimester of pregnancy and with any dose of a nonaspirin Use cautiously in patients with history of ulcers or GI bleeding, advanced renal disease, dehydration, anemia, symptomatic liver disease, hypertension, edema, heart failure, or asthma, and in poor CYP2C9 metabolizers. Use cautiously in elderly or debilitated patients.
CNS: headache, dizziness, insomnia. CV: hypertension, peripheral edema. EENT: pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis. GI: abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, GI reflux, nausea. Metabolic: hyperchloremia. Musculoskeletal: back pain. Respiratory: dyspnea, upper respiratory tract infection. Skin: erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, StevensJohnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, rash. Other: accidental injury.
Patients allergic to or with a history of anaphylactic reactions to sulfonamides, aspirin, or other NSAIDs may be allergic to this drug. NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious GI adverse events, including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. Elderly patients are at greater risk. Patient with history of ulcers or GI bleeding is at higher risk for GI bleeding while taking NSAIDs such as celecoxib. Other risk factors for GI bleeding include treatment with corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID treatment, smoking, alcoholism, older age, and poor overall health. Although drug may be used with low aspirin dosages, the combination may increase risk of GI bleeding. Watch for signs and symptoms of overt and occult bleeding. Black Box Warning NSAIDs may
Monitor PT and INR, and check for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
increase the risk of serious thrombotic events, MI, or stroke. The risk may be greater with longer use or in patients with CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. Drug can cause fluid retention; monitor patient with hypertension, edema, or heart failure. Assess patient for CV risk factors before therapy. Drug may be hepatotoxic; watch for signs and symptoms of liver toxicity. Before starting drug therapy, rehydrate dehydrated patient. Monitor patients renal function; renal insufficiency is possible in patients with preexisting renal disease. Longterm administration may cause renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury.
You might also like
- Intentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating Client Development in A Multicultural Society 9th Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument62 pagesIntentional Interviewing and Counseling Facilitating Client Development in A Multicultural Society 9th Edition Ebook PDF Versionteresa.vanhorn90798% (55)
- MoH Adverse Events Policy PDFDocument33 pagesMoH Adverse Events Policy PDFnayan4uNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Celecoxib: Shadrock L. CaparidaDocument17 pagesCelecoxib: Shadrock L. CaparidaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- MEFTAL P Suspension PIDocument10 pagesMEFTAL P Suspension PIpiyush patelNo ratings yet
- Alcofan: TabletsDocument2 pagesAlcofan: Tabletskokocodename47No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drugs - Icu (Group)Document7 pagesDrugs - Icu (Group)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Week 2 Course TaskDocument6 pagesPharma - Week 2 Course TaskLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- The Treatment and Prognosis of Nephrotic Syndrome in The ElderlyDocument5 pagesThe Treatment and Prognosis of Nephrotic Syndrome in The ElderlysulemanbankerNo ratings yet
- Meftagesic DS SuspDocument14 pagesMeftagesic DS SuspPhysics with V SagarNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- MELOXICAMDocument4 pagesMELOXICAMAizat KamalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- DOLOSTAT-SP TabletsDocument15 pagesDOLOSTAT-SP TabletsVNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Combiflam Tablets PI - 08072019Document13 pagesCombiflam Tablets PI - 08072019ArunNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJi Vista MamigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- 2021.07.30 Gen Payne PIDocument16 pages2021.07.30 Gen Payne PIZach ZwaneNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen Arrow Care TabDocument9 pagesIbuprofen Arrow Care TabshajahanputhusseriNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- HypertensiveDocument2 pagesHypertensiveReinhard Lumbag PacitengNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- 2013 4 24 12 33 8Document2 pages2013 4 24 12 33 8Karim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDocument4 pagesDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Stopp Start ToolkitDocument22 pagesStopp Start ToolkitRifky IlhamiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument1 pageTelmisartanNarianne Mae Solis Bedoy75% (8)
- BNSC CVSDocument37 pagesBNSC CVSosewapeace14No ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorDocument8 pagesACE InhibitorLeonel YagoNo ratings yet
- Lofnac Suppo Diclofenac Sodium Tablets 100mg SmpcDocument15 pagesLofnac Suppo Diclofenac Sodium Tablets 100mg SmpcKemy AbohNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument58 pagesCardio DrugsMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTrojangBaboyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument3 pagesAMLODIPINEDianpratiwi22No ratings yet
- Drug FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug FurosemideJicel Camille EdeaNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Pioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011Document95 pagesPioneered Products of Sabinsa - Sep 16, 2011ameers333No ratings yet
- HOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Document18 pagesHOPE 1 - Q1 - W3 - Mod3Donajei Rica100% (1)
- Medical College Choices 08 NovDocument1 pageMedical College Choices 08 NovamitNo ratings yet
- Gensler Design Forecast 2013Document43 pagesGensler Design Forecast 2013Pete PetrášNo ratings yet
- Hospitals Qatar DatabaseDocument3 pagesHospitals Qatar DatabaseShibu KavullathilNo ratings yet
- Hydroxychloroquine PELDocument3 pagesHydroxychloroquine PELscribd_deepak100% (1)
- GoutDocument75 pagesGoutVan Talawec100% (2)
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument27 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeHassan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Part Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelDocument18 pagesPart Iv - Level 3 Hospital: Attachment 3.A - PersonnelIAN LAPINGNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument37 pagesOsteoarthritisChikezie Onwukwe100% (1)
- CSC138 Group Assignment 2Document3 pagesCSC138 Group Assignment 2KIRIT GOVINDARAJA PILLAI 20BCE2404No ratings yet
- ADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Document20 pagesADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument7 pagesCPRManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Are Diet Supplements The Whey Forward?Document7 pagesAre Diet Supplements The Whey Forward?Jason Darrell100% (1)
- Nebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureDocument1 pageNebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureSahib Singh Chadha0% (1)
- English TM 8Document11 pagesEnglish TM 8Budi AtmikaNo ratings yet
- RICE. Becoming The Fat GirlDocument288 pagesRICE. Becoming The Fat GirlNina NavajasNo ratings yet
- Vestige E-Catalogue India - August 2021Document145 pagesVestige E-Catalogue India - August 2021SamyamoyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document9 pagesJurnal 2Santi SantideswitaNo ratings yet
- Pha311 TellerDocument48 pagesPha311 TellerelikidpradoNo ratings yet
- SPEECHDocument13 pagesSPEECHJellai TejeroNo ratings yet
- Employee Health and Safety of BPCLDocument4 pagesEmployee Health and Safety of BPCLpooji25No ratings yet
- Personal Growth ToolkitDocument39 pagesPersonal Growth Toolkitsudhir sharma100% (3)
- SSMT ConplanDocument2 pagesSSMT ConplanJeffrey VillangcaNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Barley PDFDocument4 pagesHealth Benefits of Barley PDFYusrinaNoorAzizahNo ratings yet
- MCN Drill 1Document23 pagesMCN Drill 1Cai Velasco DecenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesDocument16 pagesClinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesdrlawrencekindoNo ratings yet
- AIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015Document24 pagesAIDS Foundation of Chicago - Annual Report 2015AdamAce VelasquezNo ratings yet