Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Uploaded by
nambu002Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BANGLOW2Document12 pagesBANGLOW2rokiahhassan100% (1)
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersFrom EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsDocument61 pagesInterpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsCiresica Sanda Cocindau100% (1)
- Concrete Surface ProfilesDocument3 pagesConcrete Surface ProfilesquaeNo ratings yet
- Gravity Die CastingDocument30 pagesGravity Die Castingwebmash100% (2)
- MC 331 Inspection TrainingDocument30 pagesMC 331 Inspection Trainingpjvergara382350% (2)
- Incoterms AssignmentDocument10 pagesIncoterms AssignmentUrbana Raquib100% (1)
- Question Bank RMGDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank RMGKawoser Ahammad100% (3)
- Case-Hardening Steel: Everything That Moves Needs Case-Hardened GearsDocument5 pagesCase-Hardening Steel: Everything That Moves Needs Case-Hardened GearsjeyakumarNo ratings yet
- Case HardeningDocument2 pagesCase HardeningdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Propiedades AISI 410Document25 pagesPropiedades AISI 410alvaroyepezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rolling Element Bearing Manufacturing ProcessDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Rolling Element Bearing Manufacturing ProcessRamakanth P JoshiNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Applications in Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesStainless Steel Applications in Electrical EngineeringUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Alloys - Group 05Document36 pagesFerrous Alloys - Group 05Nipun Harsha100% (1)
- Materials For Engine: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncDocument8 pagesMaterials For Engine: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncDzaky ArizsaNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 16Document16 pagesPage 1 of 16Wilfharry billyNo ratings yet
- Final MT-4 & 5Document31 pagesFinal MT-4 & 5RajasekharKosuruNo ratings yet
- Advanced High Strength SteelsDocument24 pagesAdvanced High Strength SteelsPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials For Marine Diesel EnginesDocument3 pagesConstruction Materials For Marine Diesel Enginesmohanrajjercy71No ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument20 pagesHeat Treatmentعزت عبد المنعمNo ratings yet
- Application of Stainless SteelDocument13 pagesApplication of Stainless Steelsweety1188No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesCivil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manualbinhlinhh9ih100% (35)
- Ebook Civil Engineering Materials 1St Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesEbook Civil Engineering Materials 1St Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtironcolossald30y100% (13)
- Surfacing of MetalsDocument9 pagesSurfacing of MetalsNixon LionelNo ratings yet
- CVS 415 Notes 2021Document20 pagesCVS 415 Notes 2021Imani LughoNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaDocument25 pagesAlloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaChandima K Priyamal100% (1)
- Bearing SteelDocument2 pagesBearing Steelarunkumar17No ratings yet
- ASTM A36/A36M Standard Specification For Carbon Structural SteelDocument4 pagesASTM A36/A36M Standard Specification For Carbon Structural SteeliuliamicutNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture Material - WatermarkDocument88 pagesWeek 1 Lecture Material - Watermarkchristi SNo ratings yet
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument83 pagesBolted Connections22ce100jinsNo ratings yet
- SubhradipDocument10 pagesSubhradipGreatNo ratings yet
- By - Shaik ShahidDocument22 pagesBy - Shaik ShahidAnonymous q6SfMddJDoNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 59Document59 pagesPage 1 of 59Wilfharry billyNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1. CrankshaDocument3 pages2.4.1. Crankshasanmin8361No ratings yet
- Bearing MaterialDocument2 pagesBearing Materialsrinivas raghavanNo ratings yet
- Case Study: CrankshaftsDocument12 pagesCase Study: CrankshaftsDHRUV SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Nickel Based Superalloys UsesDocument6 pagesNickel Based Superalloys UsesHeanjiaAlloysNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inKanwarlal KharolNo ratings yet
- Ship Building MaterialsDocument21 pagesShip Building Materialsimran5705074No ratings yet
- Steel AlloysDocument6 pagesSteel AlloysSanthosh LingappaNo ratings yet
- RTRTRTRTRDocument2 pagesRTRTRTRTRjanarthananNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolDocument56 pagesMaterial Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolPatrick Gibson100% (1)
- AHSS RKuziakDocument16 pagesAHSS RKuziakJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Grade of Steel Is Used For ShipsDocument9 pagesWhat Grade of Steel Is Used For ShipsAbdallah AlbeityNo ratings yet
- 18-6 Theoretical PartsDocument11 pages18-6 Theoretical Partshayder1920No ratings yet
- Bed Plate Main Engine BedplateDocument52 pagesBed Plate Main Engine BedplateSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- Module - 2: Materials and Manufacturing & SystemsDocument15 pagesModule - 2: Materials and Manufacturing & SystemsKushal SinghNo ratings yet
- Materials: 6.1 Hull SteelDocument13 pagesMaterials: 6.1 Hull SteelJuan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Ball BearingDocument8 pagesCeramic Ball BearingSachin Kadwadkar100% (1)
- Application - Cast Iron RepairDocument16 pagesApplication - Cast Iron RepairAnonymous L0ChmPGNo ratings yet
- Steel Bars: For Automotive ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSteel Bars: For Automotive ApplicationsSunil AundhekarNo ratings yet
- Yousuf P ReportDocument91 pagesYousuf P ReportAnonymous l1dIwmHV5mNo ratings yet
- Cold-Rolled and Galvannealed (GA) High Strength Steel Sheets For Automotive Cabin StructureDocument9 pagesCold-Rolled and Galvannealed (GA) High Strength Steel Sheets For Automotive Cabin StructureAlexandre Lima LopesNo ratings yet
- Iml213 (2 Föy)Document65 pagesIml213 (2 Föy)HilalAldemirNo ratings yet
- Metals: Microstructural and Mechanical Assessment of Camshafts Produced by Ductile Cast Iron Low Alloyed With VanadiumDocument18 pagesMetals: Microstructural and Mechanical Assessment of Camshafts Produced by Ductile Cast Iron Low Alloyed With VanadiumJainer IbarraNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument30 pagesInstant Download PDF Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapterbiadooluersa69100% (3)
- Physical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFDocument13 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFJose Merced Martinez VazquezNo ratings yet
- CrankshaftDocument11 pagesCrankshaftPankajBhamareNo ratings yet
- AK Hot Rolled Steel 062212 HSLA 60Document6 pagesAK Hot Rolled Steel 062212 HSLA 60Alexandre Lima LopesNo ratings yet
- 2 Welding On Rotors Welding On Rotors For Power Plant Turbo Sets Dr.-Ing. Wolfgang Janssen, Siemens AG, Power Generation, GermanyDocument13 pages2 Welding On Rotors Welding On Rotors For Power Plant Turbo Sets Dr.-Ing. Wolfgang Janssen, Siemens AG, Power Generation, GermanySumit RaiNo ratings yet
- 86 Weld Ability of Corten SteelsDocument1 page86 Weld Ability of Corten SteelsNattawat LeelapeerapongNo ratings yet
- (Welding) s7Document113 pages(Welding) s7Popo YuppyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Standard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsFrom EverandStandard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsNo ratings yet
- Higway, Bridge&AirportDocument7 pagesHigway, Bridge&AirportShaik Jhoir50% (2)
- Brazing ApplicationsDocument2 pagesBrazing ApplicationsLaw Hui HuangNo ratings yet
- Sample Drawings SU01, SU02 & SU03Document3 pagesSample Drawings SU01, SU02 & SU03Madan Pal SainiNo ratings yet
- HR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanyDocument55 pagesHR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanykevalNo ratings yet
- List of National Qualified FSTDs in Switzerland 110228Document1 pageList of National Qualified FSTDs in Switzerland 110228kanajuurikasNo ratings yet
- A06-90 Rock Bits CatalogDocument4 pagesA06-90 Rock Bits CatalogtifonNo ratings yet
- Istanbul High Streets 2015 enDocument14 pagesIstanbul High Streets 2015 enfbutteNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TradeDocument86 pagesUnit 6 TradeManoj SolankarNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics 101 - Mark Millar CILT HK 0212 FINAL CircDocument40 pagesReverse Logistics 101 - Mark Millar CILT HK 0212 FINAL CircfungeeeeNo ratings yet
- Explorer Hammerhead Classic: Instructions - Instructions - Gebrauchsanweisung - Instrucciones - InstructiesDocument60 pagesExplorer Hammerhead Classic: Instructions - Instructions - Gebrauchsanweisung - Instrucciones - InstructiesHerczku AnnamáriaNo ratings yet
- Gi Conduit LayingDocument5 pagesGi Conduit LayingPrasad PanchatsaramNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Crash Report NTSBDocument3 pagesHelicopter Crash Report NTSBABC15 NewsNo ratings yet
- Apron Safety-MBJ PDFDocument20 pagesApron Safety-MBJ PDFSankar CdmNo ratings yet
- ElevatorDocument10 pagesElevatorThömAs MédizàNo ratings yet
- Iron Steel GuideDocument160 pagesIron Steel GuideAtif Ahmad Khan100% (2)
- Dragon CementDocument8 pagesDragon CementPema WangdheeNo ratings yet
- Prerequisites For Diesel Generator DG Set InstallationsDocument6 pagesPrerequisites For Diesel Generator DG Set InstallationsTagel MarkosNo ratings yet
- Continuous Gas Carburising FurnaceDocument2 pagesContinuous Gas Carburising FurnaceEmba MadrasNo ratings yet
- BCA Project ListDocument7 pagesBCA Project ListPrashant BhushanNo ratings yet
- Space Syntax - Beijing CBD Case StudyDocument8 pagesSpace Syntax - Beijing CBD Case StudySpace Syntax Limited100% (1)
- Estimate Lesson 4 RSBDocument28 pagesEstimate Lesson 4 RSBBCXC LLAM100% (1)
- Astm A530Document2 pagesAstm A530Thiruvengadam75% (4)
- Stainless Steel Grade 904LDocument5 pagesStainless Steel Grade 904LMadan YadavNo ratings yet
- Survey PED-Standards 07-01-2013Document1 pageSurvey PED-Standards 07-01-2013Danut Rus100% (1)
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Uploaded by
nambu002Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Case Hardening Steel PDF
Uploaded by
nambu002Copyright:
Available Formats
Case hardening Steel
http://www.imoa.info/moly_uses/moly_grade_alloy_steels_irons/case_ha...
Case hardening Steel
Tough core and a hard case are the target properties of components made of case hardened steel. That combination of wear resistance and fatigue strength in the surface and impact strength in the core zone is achieved by carburizing the surface layer of the component, which is subsequently quenched and tempered. Components produced that way with optimized properties between core and case include gear components of all kind, camshafts, cardan joints, driving pinions, link components, axles and arbors. Applications include: Transportation: Case hardened components are needed in any engine driven vehicle, whether it's a small car, a race car, a truck or an ocean vessel. Energy generation: Gear wheels and components in large dimensions have to withstand both stress and wear in equipment such as hydroelectric power stations, wind turbine generators, propeller drives of drilling rigs or steam turbine gears of power stations. General mechanical engineering: forging presses, steel rolling equipment, machine tools; drivelines of mining equipment and heavy duty transmissions; earth moving equipment and heavy duty construction cranes. The combination of wear resiastance and fatigue strength is always a key characteristic of the case hardened steels used for these applications. For carburisation the steel is heated in a carbon releasing medium to a temperature where the base material is completely transformed into austenite (here the solubility for carbon is much higher than in the ferritic structure).
Case hardened gears for everything that moves
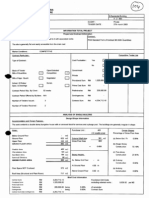
This way the surface layer is carburised up to 0.7% carbon, while the carbon content of the core material is limited to about 0.25%. Quenching and tempering following the carburisation produces a high carbon martensitic structure near the surface, with great hardness and wear resistance, while the core retains its original strength and toughness properties. Standard case hardening Steels % Alloy content SAE/ASTM C Cr Mo 5120 0.2 1.2
DI - E MnCr Steel 20MnCr5 CrMo Steel
Other 1.3 Mn
1 of 2
24/06/2012 14:07
Case hardening Steel
http://www.imoa.info/moly_uses/moly_grade_alloy_steels_irons/case_ha...
20MoCr4 20CrMo5 iCrMo Steel 20NiCrMo2-2 18CrNiMo7-6
Table 1: Standard case hardening steels
0.2 8620 0.2 0.2 0.18
0.4 1.2 0.5 1.7
0.5 0.25 0.25 0.3 0.5 Ni 1.5 Ni
Molybdenum (0.15 - 0.50%) is used in carburising steels to simultaneously increase the hardenability of the low carbon core and toughen the high carbon case. It is especially effective in large cross sections, such as in gears. Molybdenum is not oxidised during carburisation, making it an effective hardening agent which does not cause increased surface cracking and spalling.
2 of 2
24/06/2012 14:07
You might also like
- BANGLOW2Document12 pagesBANGLOW2rokiahhassan100% (1)
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersFrom EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsDocument61 pagesInterpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsCiresica Sanda Cocindau100% (1)
- Concrete Surface ProfilesDocument3 pagesConcrete Surface ProfilesquaeNo ratings yet
- Gravity Die CastingDocument30 pagesGravity Die Castingwebmash100% (2)
- MC 331 Inspection TrainingDocument30 pagesMC 331 Inspection Trainingpjvergara382350% (2)
- Incoterms AssignmentDocument10 pagesIncoterms AssignmentUrbana Raquib100% (1)
- Question Bank RMGDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank RMGKawoser Ahammad100% (3)
- Case-Hardening Steel: Everything That Moves Needs Case-Hardened GearsDocument5 pagesCase-Hardening Steel: Everything That Moves Needs Case-Hardened GearsjeyakumarNo ratings yet
- Case HardeningDocument2 pagesCase HardeningdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Propiedades AISI 410Document25 pagesPropiedades AISI 410alvaroyepezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rolling Element Bearing Manufacturing ProcessDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Rolling Element Bearing Manufacturing ProcessRamakanth P JoshiNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Applications in Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesStainless Steel Applications in Electrical EngineeringUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Alloys - Group 05Document36 pagesFerrous Alloys - Group 05Nipun Harsha100% (1)
- Materials For Engine: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncDocument8 pagesMaterials For Engine: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncDzaky ArizsaNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 16Document16 pagesPage 1 of 16Wilfharry billyNo ratings yet
- Final MT-4 & 5Document31 pagesFinal MT-4 & 5RajasekharKosuruNo ratings yet
- Advanced High Strength SteelsDocument24 pagesAdvanced High Strength SteelsPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials For Marine Diesel EnginesDocument3 pagesConstruction Materials For Marine Diesel Enginesmohanrajjercy71No ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument20 pagesHeat Treatmentعزت عبد المنعمNo ratings yet
- Application of Stainless SteelDocument13 pagesApplication of Stainless Steelsweety1188No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesCivil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manualbinhlinhh9ih100% (35)
- Ebook Civil Engineering Materials 1St Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesEbook Civil Engineering Materials 1St Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtironcolossald30y100% (13)
- Surfacing of MetalsDocument9 pagesSurfacing of MetalsNixon LionelNo ratings yet
- CVS 415 Notes 2021Document20 pagesCVS 415 Notes 2021Imani LughoNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaDocument25 pagesAlloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaChandima K Priyamal100% (1)
- Bearing SteelDocument2 pagesBearing Steelarunkumar17No ratings yet
- ASTM A36/A36M Standard Specification For Carbon Structural SteelDocument4 pagesASTM A36/A36M Standard Specification For Carbon Structural SteeliuliamicutNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture Material - WatermarkDocument88 pagesWeek 1 Lecture Material - Watermarkchristi SNo ratings yet
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument83 pagesBolted Connections22ce100jinsNo ratings yet
- SubhradipDocument10 pagesSubhradipGreatNo ratings yet
- By - Shaik ShahidDocument22 pagesBy - Shaik ShahidAnonymous q6SfMddJDoNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 59Document59 pagesPage 1 of 59Wilfharry billyNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1. CrankshaDocument3 pages2.4.1. Crankshasanmin8361No ratings yet
- Bearing MaterialDocument2 pagesBearing Materialsrinivas raghavanNo ratings yet
- Case Study: CrankshaftsDocument12 pagesCase Study: CrankshaftsDHRUV SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Nickel Based Superalloys UsesDocument6 pagesNickel Based Superalloys UsesHeanjiaAlloysNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inKanwarlal KharolNo ratings yet
- Ship Building MaterialsDocument21 pagesShip Building Materialsimran5705074No ratings yet
- Steel AlloysDocument6 pagesSteel AlloysSanthosh LingappaNo ratings yet
- RTRTRTRTRDocument2 pagesRTRTRTRTRjanarthananNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolDocument56 pagesMaterial Science and Engineering Ch. 11 SolPatrick Gibson100% (1)
- AHSS RKuziakDocument16 pagesAHSS RKuziakJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Grade of Steel Is Used For ShipsDocument9 pagesWhat Grade of Steel Is Used For ShipsAbdallah AlbeityNo ratings yet
- 18-6 Theoretical PartsDocument11 pages18-6 Theoretical Partshayder1920No ratings yet
- Bed Plate Main Engine BedplateDocument52 pagesBed Plate Main Engine BedplateSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- Module - 2: Materials and Manufacturing & SystemsDocument15 pagesModule - 2: Materials and Manufacturing & SystemsKushal SinghNo ratings yet
- Materials: 6.1 Hull SteelDocument13 pagesMaterials: 6.1 Hull SteelJuan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Ball BearingDocument8 pagesCeramic Ball BearingSachin Kadwadkar100% (1)
- Application - Cast Iron RepairDocument16 pagesApplication - Cast Iron RepairAnonymous L0ChmPGNo ratings yet
- Steel Bars: For Automotive ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSteel Bars: For Automotive ApplicationsSunil AundhekarNo ratings yet
- Yousuf P ReportDocument91 pagesYousuf P ReportAnonymous l1dIwmHV5mNo ratings yet
- Cold-Rolled and Galvannealed (GA) High Strength Steel Sheets For Automotive Cabin StructureDocument9 pagesCold-Rolled and Galvannealed (GA) High Strength Steel Sheets For Automotive Cabin StructureAlexandre Lima LopesNo ratings yet
- Iml213 (2 Föy)Document65 pagesIml213 (2 Föy)HilalAldemirNo ratings yet
- Metals: Microstructural and Mechanical Assessment of Camshafts Produced by Ductile Cast Iron Low Alloyed With VanadiumDocument18 pagesMetals: Microstructural and Mechanical Assessment of Camshafts Produced by Ductile Cast Iron Low Alloyed With VanadiumJainer IbarraNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument30 pagesInstant Download PDF Civil Engineering Materials 1st Edition Sivakugan Solutions Manual Full Chapterbiadooluersa69100% (3)
- Physical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFDocument13 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFJose Merced Martinez VazquezNo ratings yet
- CrankshaftDocument11 pagesCrankshaftPankajBhamareNo ratings yet
- AK Hot Rolled Steel 062212 HSLA 60Document6 pagesAK Hot Rolled Steel 062212 HSLA 60Alexandre Lima LopesNo ratings yet
- 2 Welding On Rotors Welding On Rotors For Power Plant Turbo Sets Dr.-Ing. Wolfgang Janssen, Siemens AG, Power Generation, GermanyDocument13 pages2 Welding On Rotors Welding On Rotors For Power Plant Turbo Sets Dr.-Ing. Wolfgang Janssen, Siemens AG, Power Generation, GermanySumit RaiNo ratings yet
- 86 Weld Ability of Corten SteelsDocument1 page86 Weld Ability of Corten SteelsNattawat LeelapeerapongNo ratings yet
- (Welding) s7Document113 pages(Welding) s7Popo YuppyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Standard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsFrom EverandStandard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsNo ratings yet
- Higway, Bridge&AirportDocument7 pagesHigway, Bridge&AirportShaik Jhoir50% (2)
- Brazing ApplicationsDocument2 pagesBrazing ApplicationsLaw Hui HuangNo ratings yet
- Sample Drawings SU01, SU02 & SU03Document3 pagesSample Drawings SU01, SU02 & SU03Madan Pal SainiNo ratings yet
- HR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanyDocument55 pagesHR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanykevalNo ratings yet
- List of National Qualified FSTDs in Switzerland 110228Document1 pageList of National Qualified FSTDs in Switzerland 110228kanajuurikasNo ratings yet
- A06-90 Rock Bits CatalogDocument4 pagesA06-90 Rock Bits CatalogtifonNo ratings yet
- Istanbul High Streets 2015 enDocument14 pagesIstanbul High Streets 2015 enfbutteNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TradeDocument86 pagesUnit 6 TradeManoj SolankarNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics 101 - Mark Millar CILT HK 0212 FINAL CircDocument40 pagesReverse Logistics 101 - Mark Millar CILT HK 0212 FINAL CircfungeeeeNo ratings yet
- Explorer Hammerhead Classic: Instructions - Instructions - Gebrauchsanweisung - Instrucciones - InstructiesDocument60 pagesExplorer Hammerhead Classic: Instructions - Instructions - Gebrauchsanweisung - Instrucciones - InstructiesHerczku AnnamáriaNo ratings yet
- Gi Conduit LayingDocument5 pagesGi Conduit LayingPrasad PanchatsaramNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Crash Report NTSBDocument3 pagesHelicopter Crash Report NTSBABC15 NewsNo ratings yet
- Apron Safety-MBJ PDFDocument20 pagesApron Safety-MBJ PDFSankar CdmNo ratings yet
- ElevatorDocument10 pagesElevatorThömAs MédizàNo ratings yet
- Iron Steel GuideDocument160 pagesIron Steel GuideAtif Ahmad Khan100% (2)
- Dragon CementDocument8 pagesDragon CementPema WangdheeNo ratings yet
- Prerequisites For Diesel Generator DG Set InstallationsDocument6 pagesPrerequisites For Diesel Generator DG Set InstallationsTagel MarkosNo ratings yet
- Continuous Gas Carburising FurnaceDocument2 pagesContinuous Gas Carburising FurnaceEmba MadrasNo ratings yet
- BCA Project ListDocument7 pagesBCA Project ListPrashant BhushanNo ratings yet
- Space Syntax - Beijing CBD Case StudyDocument8 pagesSpace Syntax - Beijing CBD Case StudySpace Syntax Limited100% (1)
- Estimate Lesson 4 RSBDocument28 pagesEstimate Lesson 4 RSBBCXC LLAM100% (1)
- Astm A530Document2 pagesAstm A530Thiruvengadam75% (4)
- Stainless Steel Grade 904LDocument5 pagesStainless Steel Grade 904LMadan YadavNo ratings yet
- Survey PED-Standards 07-01-2013Document1 pageSurvey PED-Standards 07-01-2013Danut Rus100% (1)