Professional Documents
Culture Documents
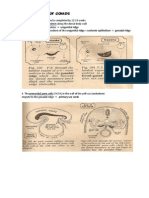
Suspected Case: Suspected Case
Suspected Case: Suspected Case
Uploaded by
ameerabestOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Suspected Case: Suspected Case
Suspected Case: Suspected Case
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright:
Available Formats
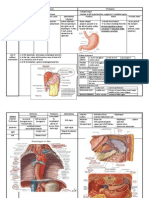
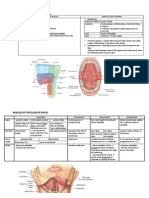
Differences of communicable diseases Tuberculosis Suspected case : *cough, expectoration >3w, fever, loss Wt, NIGHT sweating Confirmed
case : Pulmonary TB smear + 1. + sputum for AFB of direct ME 2 initial specimens 2. + sputum for AFB of direct ME 1 smear specimen + radio abnormal for active pulmonary TB 3. + sputum for AFB of direct ME + + culture for AFB Pulmonary TB smear 1. At least 3 sputum smear + radio abnormal for active pulmonary TB + decision to treat with full course anti TB 2. sputum + +culture Extra pulmonary TB 1. + culture + histological evidence with active extrapulmonary + decision to treat with full course anti TB. Worldwide *urban areas : slum dwellers, lower socioeconomic groups. Re-emerging reasons ** ** Meningitis Suspected case : SUDDEN onset fever, stiffness neck, altered consciousness, other meningeal signs/ peticheal rash Confirmed case : + culture CSF *complications : Deafness Blindness Otitis media Arthritis Influenza Fever Headache Sore throat Cough Coryza Myalagia Complications : Resp - pneumonia, acute bronchitis CNS encephalopathy, post influenza depression, transient peripheral neuritis 2 syndrome toxic shock syndrome, Reye syndrome Others - otitis media, MYOcarditis, exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions. Fatal kalau : Elderly, immunosup, debilitated. Worldwide, temperate and tropical countries. Hot dry regions : mid African countries Meningitis belt) Winter, spring Children, young adult Male Adult (crowded): military 3-4 days Pandemics, epid, localized outbreak and sporadic.
Standard case definition :
Place
Time Person
Winter, H1N1 (spring) Any age any sex
IP
Agent Reservoir
-Infection till 1ry lesion : 4-12 w -Infection till progressive pulmonary / extrapulmonary : 6-12m Mycobacterium TB Human : pulmonary TB with + sputum for AFB Bovine : infected cattle No treatment @ not fully treatment + sputum Unpasteurized milk (infected cattle). Nose and mouth (human) Udder of infected cattle (bovine) CONTACT DROPLET AIR BORN TRANSMISSION INGESTION UNPASTEURIZED MILK RARE : Contact contaminated articles. Nose and mouth Moderate : measured by 2nd attack rate.
1-3 days
NM gram diplococcic Major epid : A,C, lesser B Most common : carrier
Influenza A, B , C Man, Bird reservoir (turkey, duck, chicken),Mammalian (swine,horses) Discharge nose and mouth
SOI
Discharge nose and mouth
Exit MOT
Nose mouth DIRECT CONTACT- DROPLET INFECTION X indirect : delicate Nose mouth
Nose mouth DIRECT : CONTACT, DROPLETS INDIRECT : contaminated ARTICLES with discharge AIR BORN Nose mouth 3-5 days 1. Inactivated, LAV (diff of both)
Inlet Period communicable Vaccine BCG vaccine : type LAV**
Purified meningococcal POLYSAC No vaccine : group B NM
TETANUS (LOCK JAW) Standard case definition :
Adult type :
-abnormal rigidity - generalized spasm induced sensory stimuli. -painful muscular contraction 1.masseter, neck Ms 2.trunk Ms, Ms of face (risus sardonicus)
ANTHRAX Cutaneous : -Localised itching, Painless papulevesicularulcer black eschar -2ry vesicles, Hyperemia, Lymphadenopathy. -Fever, headache, malaise GIT : intestinal, pharyngeal forms. **shock, death Inhalation : mimic influenza -myalgia, fever, non prod cough, malaise, NV, URT rare -SEVERE (after2-3d) severe resp distress, cyanosis, diaphoresis, shock. May occur all : Hge meningitis Agricultural areas. Sporadic : US, Canada. INGESTION CONTAMINATED vegetation, water, soil 1. travelers endemic areas DIRECT INDIRECT with CARCASSES 2. people MAKE DRUMS CONTAMINATED HIDES. HOUSEHOLD drum making process. 3. WOOL sorters workers. 1-7 d BACILLUS anthracis gram + aerobic, SPORE, encapsule.
Neonatal :
Suspected case : any death 3rd-28th days of life. Confirmed case : -normal suck and cry 1st, 2nd -inability to suck 3rd-28th -episodes convulsions, stiffness Place Time Person World wide, sporadic Agricultural, underdeveloped Summer high humidity All ages esp <15y, agricultural : adult male. Newborn.
RABIES 100% FATALITY ACUTE FATAL ENCEPHALOMYELITIS Short prodrome : - Headache - Fever - Malaise - Indefinite sensory changes at site wound Paralysis : Ms of deglutition (hydrophobia) Resp Ms : resp paralysis- death
Developing USA : BAT AIR BORN transmission. ANY TIME all year At risk : MEN AND CHILDREN. LAB WORKER handling Vs VETERINARIANS DOG HANDLERS FIELD NATURALISTS
IP Agent
4-21 days : mean 10 d. Neonatal : 2d Clostridium tetani gram + anaerobic bacilli (neurotoxin). 2 items kill.** Soil and intestinal tract
4d-1y **5 factors Neurotropic Vs saliva, lymph, milk and urine infected animals. Street Vs (rabid animals), Fixed Vs (lab) Urban rabies : dog, cats, horses, camel. No HEALTHY CARRIER : DOGS Wild type : fox, jackals, raccoons, bats. HEALTHY CARRIER present. SALIVA OF infected animals MOUTH infected animals DIRECT CONTACT with INFECTED SALIVA thru BITE of INFECTED animals DIRECT CONTACT OF LAB WORKERS exposed to infected tissues skin abrasion, intact MM.
Reservoir
SOI Exit MOT
Soil, street dust contain SPORES Stool of animals esp horses. INJURY- CONTAMINATED WOUND with soil, street dust, animal faeces. ** UNHEALED UMBILICUS EAR PIERCING, CIRCUMCISION. Wound, puncture, burns, umbilicus stump
DIRECT CONTACT with infected animals, with contaminated products- CARCASSES, MEAT, HIDES, WOOL, DRUM. -Cutaneous : skin abrasion -GIT : Ingestion uncooked meat -Inhalational : inhalation spores.
Inlet Period communi cable Vaccine
Abraded skin, intact MM.
NON COMMUNICABLE
** TETANUS TOXOID
NON COMMUNICABLE
Cell free Vac bacterial Ag -Not recommended to travelers
NON COMMUNICABLE
HCDV prepared in culture of human diploid fibroblast cells.
Standard case definition :
PLAGUE Suspected case : Fever, chill, severe malaise, headache + bubonic : extreme painful swelling of lymph glands. pneumonic : cough, blood stained sputum, chest pain, diff breathing Confirmed : Isolation of YP from buboes, CSF, sputum Elevation Abs Complications : 2ry septicemic plague HIGH CASE FATALITY RATE : septicemic, pneumonic plague
YELLOW FEVER Suspected case : Acute fever Jaundice within 2wof onset of 1st ssx. Late dis : Hge manifest Confirmed case : Epidemiological criteria OR Lab criteria - Isolation of yellow fever Vs - Serology : detection of specific IgM, rising IgG - Positive post mortem liver pathology.
Place
Sylvatic @ wild rodent plague : many countries Urban @ human plague : controlled, endemic in some countries. FLEA breading, summer and autumn. ALL ages, sexes. Men hunting : in contact with rodents during hunting, cultivating, outdoor recreation. Movement people sea and land.
Time Person
Urban type : both sexes, all ages Jungle type : ADULT MALES (20-40y) exposed to the dis during HUNTING, WOOD CUTTING, VILLAGERS
IP Agent Reservoir
6d
Yersinia pestis. 6 kill. ** Bubonic plague : sylvatic plague WILD RODENTS PRE DOMESTIC RODENTS DOMESTIC RODENTS MAN : RABBITS, DOMESTIC CATS Pneumonic : MAN in the form of case of pneumonic plague. Bubonic plague : INFECTED RODENT FLEA (XENOPSYLLA CHEOPSIS) Pneumonic : RESP DISCHARGE of cases. Bubonic, 1ry septicemia plague : SKIN of RAT. Pneumonic : RESP discharge of Pt in Bubonic, 1ry septicemia plague : BITE OF INFECTED FLEAS (VECTOR biological propagative transmission) 1ry pneumonic plague : DROPLET CONTACT, AIR BORN ( DROPLET nuc) DIRECT : INFECTED tissues, fluids from handling sick, dead animals esp rodents, rabbits. Bubonic, 1ry septicemia plague : SKIN. 1ry pneumonic plague : RESP TRACT. Months Bubonic plague : NON COMMUNICABLE unless complicated with 2nd pneumonic plague. Pneumonic plague : HIGHLY
6d
Vs of yellow fever
Urban type : HUMAN Jungle type : MONKEY
SOI
Exit MOT
Urban type : infective FEMALE AEDES egypti mosquitos. Jungle type : FOREST MOSQUITOS (Aedes AFRICANS, SYMPSONI) Skin of mosquito bite. BITE OF INFECTIVE MOSQUITO (vector, biological, propagative transmission). TRANSOVARIAN
Inlet Period communic able
Skin of mosquito bite. Before onset of fever and first 3-5 days of illness.
COMMUNICABLE.
Vaccine 17 D strain, freeze dried LAV **
You might also like
- TB Skin Test FormDocument1 pageTB Skin Test Formapi-381635811No ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For TuberculosisDocument6 pagesDischarge Plan For Tuberculosisploy8No ratings yet
- Respi Micro WEEK 10 PDFDocument4 pagesRespi Micro WEEK 10 PDFalfonsojo002No ratings yet
- ViralDocument49 pagesViralأحمد خيريNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease BackgroundDocument6 pagesCommunicable Disease BackgroundmariaalmiramsaritaNo ratings yet
- Lec 15Document9 pagesLec 15surendradeora3628No ratings yet
- Reviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesDocument4 pagesReviewer - 1. Introduction To ZoonosesGeriel QuidesNo ratings yet
- Incidence:: Epidemiological DeterminantsDocument9 pagesIncidence:: Epidemiological DeterminantsGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis Rabies Pediculosis Bubonic Plague Anthrax HelminthesDocument92 pagesSchistosomiasis Rabies Pediculosis Bubonic Plague Anthrax Helminthesaltairejoshua.jalbayNo ratings yet
- Anthrax Icd-9 022 Icd-10 A22: Control Communicable Diseases ChinDocument5 pagesAnthrax Icd-9 022 Icd-10 A22: Control Communicable Diseases ChinSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseasesDocument7 pagesZoonotic DiseasesAzad SamiNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic Diseases Fact SheetDocument7 pagesZoonotic Diseases Fact SheetEightch PeasNo ratings yet
- Aljohn Patrick Gebrik GenverDocument33 pagesAljohn Patrick Gebrik GenverRionalynBalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Differences of Communicable Disease1Document4 pagesDifferences of Communicable Disease1ameerabest100% (1)
- Veterinary Large Animal MedicineDocument1,550 pagesVeterinary Large Animal Medicineburkadekamo5No ratings yet
- Vector-Borne Disease FleaDocument46 pagesVector-Borne Disease FleaSohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology: "Anthrax"Document9 pagesCommunicable Disease Epidemiology: "Anthrax"Eko PurwatiNo ratings yet
- ZOM, Anika (01) - Anthrax, TBDocument39 pagesZOM, Anika (01) - Anthrax, TBAnika Binte BelalNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument64 pagesCommunicable DiseaseMorris AngelaNo ratings yet
- Micr3011 NotesDocument3 pagesMicr3011 NotesKatherine WangNo ratings yet
- Anthrax and Ts PreventionDocument60 pagesAnthrax and Ts PreventionZahid Qamar100% (1)
- 8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)Document55 pages8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)ssatechies62No ratings yet
- Plaque Pest, Black Death, Pestilential Fever: Veterinary Medicine-UBDocument16 pagesPlaque Pest, Black Death, Pestilential Fever: Veterinary Medicine-UBmuhammadsugi23No ratings yet
- Antrax LectureDocument49 pagesAntrax LecturefraolNo ratings yet
- Major Animal DiseasesDocument47 pagesMajor Animal DiseasesADUGNA DEGEFENo ratings yet
- Preventive and Social MedicineDocument14 pagesPreventive and Social MedicineSuresh GuduruNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis PowerpointDocument32 pagesBacillus Anthracis PowerpointEnerose MagnoNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseaseDocument34 pagesZoonotic Diseasebajarangi_chaudhary100% (2)
- Fever Synonym:: Modes of TransmissionDocument6 pagesFever Synonym:: Modes of TransmissionEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Foot and Mouth DiseaseDocument93 pagesFoot and Mouth DiseaseVer Garcera Talosig100% (1)
- AnthraxDocument6 pagesAnthraxeutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Community in Tables AllTalabaDocument14 pagesCommunity in Tables AllTalabaAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Dermato Venerology ScienceDocument11 pagesDermato Venerology ScienceAQis AQishNo ratings yet
- Final Review - Microbio - paraDocument5 pagesFinal Review - Microbio - parajcarysuitos67% (3)
- Foot and Mouth DiseasesDocument9 pagesFoot and Mouth Diseaseseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Bovine Viral Diseases: 1: Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)Document17 pagesBovine Viral Diseases: 1: Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)chachaNo ratings yet
- Anthrax PDFDocument28 pagesAnthrax PDFMaryam IsmailNo ratings yet
- Clostridia and Bacillus Lecture SlideDocument37 pagesClostridia and Bacillus Lecture SlidePrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing The History of PandemicsDocument6 pagesVisualizing The History of PandemicsJerassimos MonokrousosNo ratings yet
- Large A.medicine 4th YearDocument285 pagesLarge A.medicine 4th YearAssefaTayachewNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium: Dr. Ella Amalia, M.Kes Bagian Mikrobiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaDocument41 pagesMycobacterium: Dr. Ella Amalia, M.Kes Bagian Mikrobiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaDeepy GmenNo ratings yet
- San Francisco Department of Public HealthDocument2 pagesSan Francisco Department of Public Healthjon elleNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria: Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesDiphtheria: Respiratory Systemprencess_jeny5006No ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument67 pagesTyphoidArnel L. SanicoNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis in Trinidad and Grenada, With Special Reference To The Mongoose 1972Document13 pagesLeptospirosis in Trinidad and Grenada, With Special Reference To The Mongoose 1972Hugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- Rodent Borne DiseaseDocument6 pagesRodent Borne DiseasecallmejusNo ratings yet
- Lam 2Document33 pagesLam 2bishal.ad.002No ratings yet
- Department of Infectious DiseasesDocument40 pagesDepartment of Infectious DiseasesPrerit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Tropical Medicine Lecture Edited-1Document96 pagesTropical Medicine Lecture Edited-1inspiredwriter617No ratings yet
- Introduction of MicroparasitoryDocument36 pagesIntroduction of MicroparasitoryEben Alameda-PalapuzNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers On COVID-19Document7 pagesQuestions and Answers On COVID-19Mubashir Hasan GilaniNo ratings yet
- HOST-PATHOGEN INTERACTIONS-2022-ppt-audioDocument48 pagesHOST-PATHOGEN INTERACTIONS-2022-ppt-audioFajar AnshoriNo ratings yet
- Public Health Pharmacy Notes-Semi Finals PPT3Document1 pagePublic Health Pharmacy Notes-Semi Finals PPT3Gizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology New NoteDocument44 pagesEpidemiology New NoteDIPENDRA CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- ZOONOSISDocument53 pagesZOONOSISBiManda Rizki NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis: Hirotaka Ishibashi Jennifer Jolivet Sean Patrick KellyDocument92 pagesBacillus Anthracis: Hirotaka Ishibashi Jennifer Jolivet Sean Patrick KellyReyza HasnyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Document26 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovNo ratings yet
- A Case HistoryDocument43 pagesA Case Historymel_pusagNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis A Re-Emerging DiseaseDocument4 pagesLeptospirosis A Re-Emerging DiseasemelshiyafNo ratings yet
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pages@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNo ratings yet
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 pagesCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestNo ratings yet
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pages@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 pagesSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)Document2 pagesExtracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)ameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 pagesGenital EmbryologyameerabestNo ratings yet
- #LungDocument1 page#LungameerabestNo ratings yet
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pages#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- #MediastinumDocument4 pages#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- Parotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandDocument5 pagesParotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandameerabestNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus & StomachDocument3 pagesOesophagus & StomachameerabestNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Mouth Cavity, Palate, TongueDocument8 pagesMouth Cavity, Palate, Tongueameerabest100% (1)
- Art 2Document14 pagesArt 2linda margaritaNo ratings yet
- Major Tropical Diseases-EditDocument50 pagesMajor Tropical Diseases-EditFitri TrianiNo ratings yet
- Blueprint For Global Heatlh ResilienceDocument27 pagesBlueprint For Global Heatlh ResiliencejuanNo ratings yet
- Project File On Human Health and Disease.Document21 pagesProject File On Human Health and Disease.Sanampreet89% (35)
- Radionics IntroductionDocument9 pagesRadionics IntroductiondheenadayalanNo ratings yet
- TB-Ordinance Draft v.2023Document11 pagesTB-Ordinance Draft v.2023DocJogy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Health Trends Issues and Concerns - GLOBAL LEVELS - T2Document12 pagesHealth Trends Issues and Concerns - GLOBAL LEVELS - T2Shanya DellosoNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Block 1 Unit 2 Healthcare PlanningDocument21 pagesIGNOU Block 1 Unit 2 Healthcare Planningerice.researchNo ratings yet
- 1992-2012 - The Center of The AO Foundation Network - Matter and PerrenDocument72 pages1992-2012 - The Center of The AO Foundation Network - Matter and PerrenAravind RaviNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Philippine Health SystemDocument10 pagesOverview of The Philippine Health SystemCaryl Ann RabanosNo ratings yet
- CIE-10 RIPS - Xls - 1Document547 pagesCIE-10 RIPS - Xls - 1john_trianaNo ratings yet
- Extrapulmonary TuberculosisDocument80 pagesExtrapulmonary TuberculosisYoursTruly FIBONNo ratings yet
- National Guidelines and Operational Manual For Tuberculosis Control PDFDocument90 pagesNational Guidelines and Operational Manual For Tuberculosis Control PDFFaisol KabirNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Document28 pagesSci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Mary Grace UntalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Resistant TuberculosisDocument94 pagesDrug Resistant Tuberculosistummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed University: Name of Investigator Budget Sr. Project No. Name of ProjectDocument38 pagesKrishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed University: Name of Investigator Budget Sr. Project No. Name of ProjectchahatpuriNo ratings yet
- InterOrient Maritime Enterprises, Inc. vs. Creer IIIDocument29 pagesInterOrient Maritime Enterprises, Inc. vs. Creer IIIAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Harrisons Reviewer 2Document59 pagesHarrisons Reviewer 2pluiedecielNo ratings yet
- Díptico Exposición TBTrabajo GrupalDocument2 pagesDíptico Exposición TBTrabajo GrupalPamela PerezNo ratings yet
- q3 - Week1 - Health 10 - Study ConceptDocument2 pagesq3 - Week1 - Health 10 - Study ConceptDhess Mulleda MantalaNo ratings yet
- Homework On Abstract & Tenses of The Verb - Homework 3Document2 pagesHomework On Abstract & Tenses of The Verb - Homework 3Ayra YayenNo ratings yet
- Cosh Module 8Document86 pagesCosh Module 8Montemayor, Diether D.No ratings yet
- Infliximab: Drug Treatment InformationDocument7 pagesInfliximab: Drug Treatment InformationAlin-Ionuț SălcianuNo ratings yet
- 28 - 04 RPS Pulmonologi TB SO, TB RO, TB Laten-1Document46 pages28 - 04 RPS Pulmonologi TB SO, TB RO, TB Laten-1ANISA SALAMAHNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Microbiology and Immunology - Side by SideDocument196 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Microbiology and Immunology - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff0% (1)
- CodeDocument88 pagesCodeGLADYSNo ratings yet
- Annual GAD Accomplishment Report 2014Document7 pagesAnnual GAD Accomplishment Report 2014jpllanesNo ratings yet
- Q3 PPT Health 8 Myths and Misconception of Communicable DiseasesDocument32 pagesQ3 PPT Health 8 Myths and Misconception of Communicable DiseasesJeal Amyrrh CaratiquitNo ratings yet