Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FOC UNIT 2 New
FOC UNIT 2 New
Uploaded by
Merlin GeorgeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FOC UNIT 2 New
FOC UNIT 2 New
Uploaded by
Merlin GeorgeCopyright:
Available Formats
185102FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING & PROGRAMMING UNIT II COMPUTER SOFTWARE Computer Software Types of Software Software Development Steps Internet
et Evolution Basic Internet Terminology Getting connected to Internet Applications. Software: Software is basically the set of instructions grouped into programs that make the computer to function in the desired way. It is a collection of programs which is responsible for controlling, integrating and managing the hardware components of a computer and to accomplish a specific task. Hardware: The term Hardware is applied to any of the physical equipments in the computer system, such as the machinery and equipments of itself usually containing electronic components and performing some kinds of functions in the information processing. Difference between Software and Hardware: S.No Software Hardware 1. It is a collection of program to bring It is the physical components of the the computer hardware system into computer system. operation. 2. It consists of numbers, alphabets, It consists of electronic components like alphanumeric symbols, identifies ICs, diodes, resistors, crystals, boards, keywords etc. insulators etc. 3. This should be prepared according to The design can be modified according to the the type of the software. capacity. 4. It will vary as per the computer and its It is almost construct for all types of built-in function and programming computer system. language. 5. It is designed and developed by a The hardware can understand only low-level experienced programmer in a high language or machine language. level language, which is readable by the human being. 6. It is represented in any high level The hardware works only on binary code as language such as BASIC, COBOL, C, 1s and 0s. C++etc 7. The Software is categorized as The hardware consists of Input, Output, operating systems, utilities, language Memory, ALU, Control unit etc. processor, application softwares etc.
Types of Software:
i.
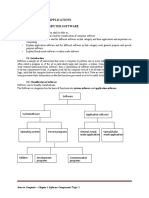
Software can be classified into two categories. They are: System Software and Application software. System Software: It is a set of programs to help the user to run the computer systems. It is more transparent and less noticed by the user since they interact with the hardware or the applications. Some examples of system software are: operating systems, device drivers, language translators and system utilities. Operating System: Operating System is the first layer of software loaded into main memory when it starts up. It acts as an interface between user and the hardware. Some of the functionalities of the operating system are: memory management, device management, CPU management etc. Device Drivers: They are system software which is responsible for proper functioning of devices. Whenever a device is connected to the computer system, the driver software has to be installed so that the device can function properly. A driver acts as a translator between device and the operating system. Language Translators: Computers can understand only binary language i.e. codes which consist of 0s and 1s. The users write instructions in high level language. The translators convert the high level instructions into machine code. There are 3 different types of language translators. They are: Compiler: The compiler translates the source code (high level language code) into object code (Binary form). Interpreter: An interpreter does the translation and executes the program line by line. Assembler: It translates the program written in assembly level language into machine code. COMPILERS AND INTERPRETERS S.No 1. 2. 3. COMPILERS It converts all the source code into machine code Compiler executes entire program at a time The compiler code runs faster INTERPRETERS It also converts all the source code into machine code Interpreter translates and then executes each line of the program, one line at a time The interpreter code runs slower than compiled code
System Utility: System utility programs perform day-to-day tasks related to the maintenance of the computer system. 2
ii.
They are used to support, enhance and secure existing programs and data in the computer system. Application Software: This is the most used software by the users. It is used to accomplish specific tasks. Application software consists of a single program (Ex. Notepad) or a collection of programs (Ex. Microsoft Office Suite). Some of the most commonly used application software are: (i)Word Processors: A word processor is software used to compose, format, edit and print electronic documents. Ex. Microsoft word. (ii)Spreadsheets: A spreadsheet application is a rectangular grid, which allows text, numbers and complex functions to be entered into a matrix of thousands of individual cells. Ex. Microsoft Excel. (iii)Image Editors: Image editor programs and designed specifically for capturing, creating, editing and manipulating images. The programs provide a variety of special features for creating and altering images. Ex. Adobe Photoshop. (iv)Database Management Systems: Database Management software is a collection of computer programs that allow storage, modification and extraction of information from a database in an efficient manner. It controls the security and integrity of the database from unauthorized access. Ex. Oracle. (v)Presentation Applications: A Presentation is a means of assessment, which requires presentation providers to present their work orally in the presence of an audience. It combines both visual and verbal elements. Presentation software allows the user to create presentations by producing slides for the presentation of projects. Ex. Microsoft PowerPoint. (vi)Desktop Publishing Software: The desktop publishing is a technique of using a personal computer to design images and pages, and assemble type and graphics, then using a printer to output the assembled pages onto paper. This software is used for creating magazines, books etc. Ex. Adobe PageMaker.
SOFTWARE TERMINOLOGIES: Some of the common terms used in the field of software are discussed below: 1. Public Domain Software:
It refers to any program that is not copyrighted. This software is free and can be used by anyone without restrictions. 2. Freeware: It is a copyrighted software but given away free by the developers of the software. The users do not have the right to modify the content of the software. There are different types of software. They are: i. Donationware: The authors of donationware ask that anyone using their software make a donation to the authors or to some third party such as charity. ii. Postcardware: The users of the software have to send the software provider a postcard as a form of payment. iii. Abadonware: It is commercial software that has not been sold for a long time or whose copyright holder is defunct; it has been abandoned. iv. Adware: It is distributed as freeware, but it requires the user to view advertisements to use the software. It is also called as spyware. 3. Shareware: Shareware is software which comes with permission for people to redistribute copies for a limited period. Anyone who continues to use a copy is required to pay a license fee. The free use of the software is usually limited to a period. 4. Commercial Software: Commercial software represents the software purchased from software publishers. This software comes pre-packaged, is available in software stores, and can be obtained through internet. 5. Open Source Software: It is created by generous programmers and released into the public domain for public use. The Source code is available to the users who can make modifications as per the needs. The software is distributed under an open source license General Public License (GPL). 6. Proprietary Software: It is owned exclusively by a single company or user. They guard knowledge about the technology or the products internal working. It is also called as closed source software. Example. Microsoft Windows operating system. 7. Firmware: It is a combination of software, permanently stored in the memory. It is a program or data that has been written onto ready only memory. Example. BIOS.
Installing and Uninstalling Software: Software which is purchased or acquired has to be installed on the computer so that it can be executed. During the installation process, files are copied to their appropriate locations and icons are added to the system menus. Definition: The process of copying software from CD-ROM to the hard disk and configuring it to work with the computer hardware is knows as the software installation. A special program known as installer does the installation process. The installer decompresses the required files within it, and places them in proper folders. Installation files usually have the extension .EXE or .ZIP. If the installation is of .EXE extension (ex. Setup.exe), double click the file and follow the instructions after that to install the software. If the installation is of .ZIP extension, the user has to decompress the compressed file and then install the software. Software Upgrade: It is a process by which a newer version of the existing software is installed. Software Update: It is a new release of software that is an error correction release and does not contain new functionality. Software Patch: It is a collection of one or more files that corrects flaws in the performance, reliability or security of a specific software product. Uninstall program completely removes all files of that program and all associated files in other directories. Properly uninstalling a program means deleting all the files and undoing any changes made to system files fully. Software Piracy: It is the unauthorized copying of an organizations internally developed software or the illegal duplication of commercially available software. While purchasing software, the user gets a license to use the application but it cannot be copied on other machines. A software license is a type of proprietary license, which acts as a memorandum of contract between the producer and user. It is also called as End User License Agreement (EULA). Starting a computer ( Booting) A Fundamental operation in computer is the booting process. This process is performed through a series of steps. They are: 1) The Computer is switch ON. 2) Computer loads data from ROM and checks whether all the major components like processor and hard disk are functioning properly. 3) Computer loads BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) from ROM to determine the machines fundamental configuration and environment. The information stored in ROM BIOS chip determines what peripherals the system can support.
4) Computer loads the operating system from the secondary storage (hard disk) into RAM. This allows the CPU to have immediate access to the operating system, which enhances the performance and functionality of the overall system. There are two types of Booting process. They are: 1. Warm Booting: Restarting the system by pressing the restart button or pressing Ctr+Alt+Del. 2.Cold Booting: Starting the computer by giving power supply and pressing the start button. SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT STEPS: The software development process passes through different phases, before a useable application emerges, thus there are secured way to progress through these phases, and each way is also called a software process. The phases of the software development steps are considered as the system development life cycle. The phases of software development steps a) Requirement Analysis b) Design c) Development d) Testing e) Implementation and Maintenance
Requirement Analysis
Design Development Testing Implementation & Maintenance
Requirement Analysis The objective of the requirement analysis is to identify and document the user requirements for the proposed system. It is also the process of understanding what is needed or wanted, and expressing the result in writing. This is the first and the most important step in the software development.
The main objective of the requirement analysis is to produce a document that properly specifies all requirements of the customer. That is called software requirement specification (SRS) document. Analysis is the process of understanding what is needed or wanted, and expressing the result in writing. Design Process The design phase is the process of designing exactly how the specifications are to be implemented. It defines specifically how the software is to be written including an object model with properties and method. Design phase could very expansive to solve in the later stage of the software development, so much care is taken during this phase. Development or coding The design must be translated into a machine readable form. The coding or development step performs this task. The development phase involves the actual coding of the entire application. Programming tools like compiler, interpreter, Debugger are used to generate the code. Different High level languages like C, C++, java COBOL etc. are used for writing programs. Depending upon the application, the right programming language is chosen. Testing Testing is the process of executing software with sample or test data put into regular use. Different testing methodologies are used for correcting the error. Different testing tools available for detect error and correct the error. Implementation and maintenance This involves installation and initial training and may involve hardware and network upgrades. Software will definitely undergo changes once it is delivered to the customer. Changes could happen because of some unexpected input values into the system. Changes in the system could directly affect the software operation The maintenance phase of the project is the last component and it continues as long as a. Requirement Analysis warranty, extended warranty or support contract is in place. Specifying what the applications must do? The phases of the Software Development Steps
b. Design Specifying, what the parts will be, and how will they fit together? c. Developing Writing Code d. Testing Executing the application with test data e. Implementation & Maintenance Repairing defects and adding capability
7
S. Stage No 1. Requirement Analysis: Preliminary Survey, Initial Investigation Feasibility Study: Evaluation of existing System & Procedures Analysis: Detailed Evaluation 2. Design: General design specification, detailed design specification Development: Writing Source code for the modules designed
Key Questions What is the Problem?
Results
3.
4. 5.
Testing: Unit Testing, Combined Module testing Implementaion & Is the system running at the User requirements met. Maintenance: Evaluation customers end? User standards met. maintenance, Enhancement Should the system be modified?
Statement of Scope & Objectives. Performance Criteria What are the Users needs? Technical, Cost Benefit Is the problem worth Analysis. solving? What must be done to solve Logical model of the the problem? system. How the problem to be Hardware specifications, solved? Cost estimates. What is the processing flow? What is the actual operation? Source code written for every module. Documentation of the operation of the system. Is the output correct? Formal System tests
INTERNET The internet is a worldwide, publicly accessible network of interconnected computer networks that transmit data using the standard Internet Protocol (IP). It is a network of networks. Evolution of Internet: During 1960s, US department of defence conducted an experiment where the computers were interconnected and they could still work even after a disaster like nuclear war. The network was called ARPANET (Advanced Research Project Agency Network).This experiment was the forerunner of todays Internet. During 1970s, ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) helped in the development of a new protocol knows as TCP/IP for transferring data between networks. In the 1980s, Usenet newsgroups and Electronic mail came into picture. Internet became popular in the 1990s after the development of the World Wide Web (WWW).
WWW permits access to information using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and the use of hypertext links to access information across the network. The Internet today is a repository of every consumable type of information.
Basic Internet Terms: Web page: The World Wide Web consists of files, called pages or web pages which contain information and links to resources throughout the Internet. A web page is an electronic document written in a computer language called HTML. These web pages are linked together by hyper links. The web pages are also knows as HTML documents. Website: A website is a set of related web pages published by an organization or an individual. Home page: A home page is a starting point or a doorway to the website. Home page provides an overview of what could be found at the website. Browser: A browser is a computer program that accesses web pages and displays them on the computer screen. Browser is needed to access the World Wide Web. Uniform Resource Locator (URL): Each web page has a unique address, called a URL that identifies the location of that page on the internet. The format of the URL consists of six parts: protocol, WWW, domain name, domain type, path and file name. Example: http://www.google.com Hypertext: It refers to the text or image that connects to other documents. It is also called as hypertext link, hotlink or link. A hyper link is used to jump to another part of the same page or to load a different web page. Hyperlinks are the foundation of the web and the operation of the web relies primarily on them as it is a means of information retrieval. Producing hypertext for the web is accomplished by creating documents with HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language). Internet Service Provider: An ISP is a company that provides access to the internet to individual or companies. The ISP provides the user software package, username, password and access phone number. Equipped with a modem, the user can then log on to the Internet and browse the web. Web Server: A server is a computer equipped with server software, which provides a specific kind of service to client software running on other computers. A web server is a computer that answers requests from users computers. It serves images and static content, such as web pages to fill the clients requests To view a website, the browser sends a request to the server. On receiving the request, the server sends the appropriate web page to the clients machine.
The clients machines receive the information in the form of HTML commands. The browser interprets the HTML, finds all the pictures and displays the information onto the users screens.
SERVER
Browser reads the text sent by screen
the server & web page is displayed on clients
1. Browser requests for information. 2. Server searches for the information and send it to the browser. Download & Upload: Download refers to the activity of moving or copying a document, program or other data from the internet or other interconnected computers to ones own computers. Upload refers to the activity of users moving or copying a document, program or other data from their computers to the Internet.
Online & Offline: Online is referred to as connected to the World Wide Web via Internet. Offline is referred to the actions performed when the user is not connected, via telecommunications, to another computer or a network like the internet. GETTING CONNECTED TO INTERNET: 10
The basic requirements for getting internet connections are: A TCP/IP enabled computer with a web browser. An account with ISP. A telephone line plugged to a suitable socket. A modem to connect the computer to the telephone line. TYPES OF INTERNET CONNECTION: There are six different types of Internet Connection available. They are: Dial-up: A dial-up connection is the access method that uses telephone lines to connect to the Internet. It is the most common way that individuals who use home computers connect to the Internet. To connect to the Internet by using dialup, the user needs to specify a user name, a password and a telephone number. After the connection is established, the user can start browsing sites on the Internet. ISDN: It stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. It is used in business and commercial use. ISDN involves the digitization of telephone network so that voice, graphics, text and other data can be provided to users from a single terminal over existing telephone wiring. Cable Modem: A cable modem connects the user to the Internet through a cable television line. A cable modem will typically have two connections, one to the television outlet and the other to the computer. Cable modems not only provide a faster internet access but they also give added interactivity to the television. Leased Line: This facility provides reliable, high speed internet access. A leased line connection is an affordable way to line two or more sites for fixed monthly charges. Leased line facility can be provided via fibre optic or copper lines. It provides a consistent amount of bandwidth and is an excellent way to provide data, voice and video links between sites. DSL: Digital subscriber line is provided through existing phone line, but it works differently than regular analog modem dial up access. It operates over normal telephone lines and it can be used simultaneously with the telephone. Broadband: This type of access is good for remote locations, where ISDN, cable or DSL are not available. 11
Satellite connection can be either a two-way service or a one-way service. In case of two-way satellite service, the data is transmitted via satellite to a dish antenna at the users house. In a one-way system, the user needs a conventional modem and telephone link to an ISP. INTERNET SERVICES The internet has become the biggest domain of information. An Internet user has access to a wide variety of services such as e-mail, WWW etc. Some of the important Internet services are given below: IRC, Chatting & Internet Messaging Telnet E-Mail
Mailing List INTERNET
Internet Telephony & Video Conferencing
File Transfer Protocol
News Groups
E-Commerce
World Wide Web: The World Wide Web is one of the most popular services available on internet. It is a subset if the Internet and it presents text, images, animation, video, sound and other multimedia in a single interface. The web is a part of the internet and it refers to a system of Internet servers that supports hypertext using a specific internet protocol called HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) on a single interface.
12
Electronic Mail (E-Mail): E-Mail is a fast, easy and inexpensive way to communicate with other Internet users around the world. Each user of e-mail has a mailbox address to which messages are sent and the mailbox can be accessed from anywhere and at anytime. E-mail can also be used to send documents, images, audio, video etc. as an attachment along with the mail. File Transfer Protocol (FTP): FTP or File Transfer Protocol is a set of rules that enables a user to log on to another computer and transfer information between it and his/her computer. FTP allows the users to get access to the files stored in the directory of a remote computer that is connected to the Internet. FTP sites can consist of hundred to thousands of files with information on books, music, software, images etc. Telnet: The word Telnet is derived from telecommunications and network and is a protocol that allows a user to long on to a remote computer. Once connected, the users computer emulates the remote computer. When the user types in commands, they are executed on the remote computer. The users computer, which initiates the connection, is referred to as the local computer or telnet client, and the machine being connected to, which accepts the connection is referred to as the remote computer or telnet server.
Telnet Server 1 OS TCP/IP
Telnet Server
TCP/IP 3 2
OS
Client Machine
INTERNET Reading the servers information Request to Server Request Received from client
13
Internet Relay Chat (IRC): IRC is a service on the internet that allows people to communicate in real-time and carry on conversations via the computer with one or more people. It provides the user with the facility to engage in simultaneous online conversations with other users from anywhere in the world. The user runs a program to connect to an IRC server. The server relays information to and from other servers on the same net. Chatting and Instant Messaging: Chat programs allow users on the Internet to communicate with each other by typing in real time. The Users log into chat rooms to exchange comments and information about the topics addressed on the site. Internet Telephony: Internet telephony is the use of Internet rather than traditional telephone company infrastructure to exchange spoken or other telephonic information. It consists of hardware and software that enable people to use the Internet as a transmission medium for telephone calls.
Video Conferencing: Video conferencing enables face-to-face communication across networks. A Video conferencing system has two or more parties in different locations, which have the ability to communicate using a combination of video, audio and data. The following five elements are needed for video conferencing: i. Camera ii. Visual Display iii. Audio System iv. Compression of Data both audio and video v. User Interface and control system Commerce through Internet: Today, business is taking place through electronic telecommunication media. Various organizations offer the facility of shopping online. This type of business model is known as electronic commerce or E-Commerce. E-Commerce refers to buying and selling goods and services online. It is end-to-end digital exchange of information needed to conduct business including Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT).
14
Newsgroups (Usenet): Newsgroups are international discussion groups that focus on a particular topic and help in gathering information about that topic. The topics discussed here cover all the fields such as politics, computers, technology etc. The information or articles that make up the news are written by people interested in a specific topic. Newsgroups provide a source of information and a medium through which users can ask questions from the Internet community. Mailing Lists (List server): The Internet is home to a large community of individuals who carry out active discussions organized around topic-oriented forums that are distributed via email. This method of internet communication is known as mailing list and it enables people with similar interests from all over the world to communicated and share information with each other.
15
You might also like
- History of SoftwareDocument8 pagesHistory of SoftwareASHLEY SUSANA URBINANo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Week 7 and 8 - Platform Technologies PDFDocument46 pagesModule 5 - Week 7 and 8 - Platform Technologies PDFRonald Bautista Rivera50% (4)
- EEC 112 Into To Computer SofwareDocument12 pagesEEC 112 Into To Computer SofwareorjimetitusterverNo ratings yet
- Software SystemDocument4 pagesSoftware SystemSaurabhSinghYadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BcomDocument8 pagesUnit 3 BcomMenaka PatilNo ratings yet
- Computer Software Jules 2023Document23 pagesComputer Software Jules 2023ameliakeza1No ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document7 pagesAssignment 8ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- Com Fun Lesson 2Document7 pagesCom Fun Lesson 2airamaymalicdem052No ratings yet
- Topic 6 - COMPUTER SOFTWAREDocument38 pagesTopic 6 - COMPUTER SOFTWARElibo benardNo ratings yet
- Computer Software ConceptsDocument10 pagesComputer Software ConceptsWAQAR FAYAZNo ratings yet
- Answer 1: (A) : Instructions Browser Operating SystemDocument26 pagesAnswer 1: (A) : Instructions Browser Operating SystemBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- CSC 407 Soft Eng Chapt 1 To 3Document22 pagesCSC 407 Soft Eng Chapt 1 To 3Emmanuel AbamsNo ratings yet
- FirstDocument85 pagesFirstTushar RajaNo ratings yet
- What Is Software ?: Software and Other Is To Prepare A New Program FromDocument8 pagesWhat Is Software ?: Software and Other Is To Prepare A New Program FromkamleshgyamlaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProgrammingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To ProgrammingVarun AroraNo ratings yet
- Juniors Computers SoftwareDocument14 pagesJuniors Computers SoftwareblessingNo ratings yet
- Software - Types of SoftwareDocument2 pagesSoftware - Types of Softwaresonysuyal24No ratings yet
- Лекция - 3Document27 pagesЛекция - 3Диана ЖдановаNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Computer SoftwareDocument11 pagesChapter 3 - Computer SoftwareKelvin mwaiNo ratings yet
- 5403 Ict 2Document18 pages5403 Ict 2ÂßdÛl KarÌmNo ratings yet
- Basics of SoftwareDocument7 pagesBasics of Softwaresaurav gautam singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document16 pagesLecture 4hafizaayeshasiddiqa816No ratings yet
- System SoftwareDocument7 pagesSystem SoftwareProgramming PotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - SoftwareDocument23 pagesChapter 4 - Softwareabobakerhassan2211No ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Classifications of Computer SoftwareDocument5 pagesLecture 2: Classifications of Computer SoftwareAntonio Doe AkokoNo ratings yet
- Web Browsers, Datebase, Enteprise Resource Planning, Word Processor. Windows OS, Mac OS, Chrome OS, Ubuntu, Android OS, OIS, Device DriversDocument3 pagesWeb Browsers, Datebase, Enteprise Resource Planning, Word Processor. Windows OS, Mac OS, Chrome OS, Ubuntu, Android OS, OIS, Device Drivers07310141No ratings yet
- Computer Software/Computer Intelligence: Instructions, Commands or Programs WhichDocument64 pagesComputer Software/Computer Intelligence: Instructions, Commands or Programs WhichDouglas MusinguziNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument48 pagesOperating Systemsdetel74956No ratings yet
- Computer Application PDFDocument16 pagesComputer Application PDFZohaib TariqNo ratings yet
- Software FinalDocument25 pagesSoftware FinalTina QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument25 pagesComputer SoftwaresanaullahbndgNo ratings yet
- Identification of Basic Software ClassificationDocument3 pagesIdentification of Basic Software ClassificationScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Software: Computer Software, or Just Software, Is The Collection of ComputerDocument10 pagesSoftware: Computer Software, or Just Software, Is The Collection of Computerakhtar_ali621No ratings yet
- System Software Is The Type of Software That Is The Interface Between Application Software and SystemDocument27 pagesSystem Software Is The Type of Software That Is The Interface Between Application Software and Systemimtiazahmedfahim87No ratings yet
- Software and Its TypesDocument4 pagesSoftware and Its TypesZafar Ullah Gharshin100% (1)
- Computer Software AssignmentDocument8 pagesComputer Software Assignmentimmu niaziNo ratings yet
- Computer Software: Types of Computer SoftwaresDocument3 pagesComputer Software: Types of Computer SoftwaresHaris ShahidNo ratings yet
- Hardware & SoftwareDocument8 pagesHardware & Softwarejanet.relatores17No ratings yet
- Introduction To System SoftwareDocument18 pagesIntroduction To System Softwareyani_06No ratings yet
- Computer Software1Document26 pagesComputer Software1Sophia FrueldaNo ratings yet
- ITDOCDocument26 pagesITDOCManav Chawla100% (1)
- Presentation of Software: Akademi Manajemen Informatika Dan Komputer Jakarta Teknologi Cipta 2021Document8 pagesPresentation of Software: Akademi Manajemen Informatika Dan Komputer Jakarta Teknologi Cipta 2021SonyacunNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProgrammingDocument22 pagesAssignment ProgrammingYoomif TubeNo ratings yet
- Diab Computer 4Document43 pagesDiab Computer 4RadNo ratings yet
- Computer Software Software Is A Program Commercially Prepared and Tested Code of Instructions by One or A GroupDocument6 pagesComputer Software Software Is A Program Commercially Prepared and Tested Code of Instructions by One or A GroupUSER PRONo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document4 pagesUnit 3Luis Norbert SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Applied Business Tools 2Document25 pagesApplied Business Tools 2Kirby Miranda100% (1)
- Hardware and SoftwareDocument23 pagesHardware and SoftwareHaidarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering EG2105CT Year SyllabusDocument12 pagesSoftware Engineering EG2105CT Year SyllabusDipen TamangNo ratings yet
- Operating System Notes 1Document9 pagesOperating System Notes 1Shivendra MishraNo ratings yet
- Software, or Simply Software, Is That Part of A: ComputerDocument10 pagesSoftware, or Simply Software, Is That Part of A: Computererica23No ratings yet
- CFA Unit Two AssignmentDocument4 pagesCFA Unit Two Assignmentvaiak076No ratings yet
- Software ConceptS Class XIDocument7 pagesSoftware ConceptS Class XIISHAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- M04 Install. SADocument22 pagesM04 Install. SAgetayewale7No ratings yet
- System Software ImpsDocument16 pagesSystem Software Impspp2121489No ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming With BasicDocument140 pagesIntroduction To Programming With BasicMalachy EziechinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Computer SoftwareDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Computer SoftwareshobaNo ratings yet
- International: UniversityDocument3 pagesInternational: UniversityTANZIN TANZINANo ratings yet
- Programming in C 1eDocument282 pagesProgramming in C 1eRK SinghNo ratings yet
- Software Suite: Revolutionizing Computer Vision with the Ultimate Software SuiteFrom EverandSoftware Suite: Revolutionizing Computer Vision with the Ultimate Software SuiteNo ratings yet
- Online Grading System Project in PHP With Source CodeDocument3 pagesOnline Grading System Project in PHP With Source Codeamaha alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Exchange Online Datasheet - FINALDocument2 pagesExchange Online Datasheet - FINALSha PlrNo ratings yet
- Forrester Consulting. Ecommerce Web Site Performance TodayDocument21 pagesForrester Consulting. Ecommerce Web Site Performance TodayNicolás BoettcherNo ratings yet
- VOC & CO - EnglishDocument50 pagesVOC & CO - EnglishAnandKumarPNo ratings yet
- RSNetWorx & RSNetWorx MD For DeviceNet, ControlNet, and EtherNet/IPDocument8 pagesRSNetWorx & RSNetWorx MD For DeviceNet, ControlNet, and EtherNet/IPOmarSNo ratings yet
- STEP 7 Professional V13 SP1 - Displaying Diagnostics Status and Comparison Status Using IconsDocument6 pagesSTEP 7 Professional V13 SP1 - Displaying Diagnostics Status and Comparison Status Using IconsHendra Faber CrezzNo ratings yet
- Consumer Education Blended SyllabusDocument11 pagesConsumer Education Blended SyllabusRemelyn RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Linkmatrix User ManualDocument37 pagesLinkmatrix User ManualGolivera OlovicNo ratings yet
- NASW Technology Standards 2017Document64 pagesNASW Technology Standards 2017Nikki HoseiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Psych 1A: Name: Marinette R. Parra Year & Section: BSE FILIPINO 1-2Document5 pagesUnderstanding The Self Psych 1A: Name: Marinette R. Parra Year & Section: BSE FILIPINO 1-2Marinette Parra100% (1)
- Module 2 EmTechDocument19 pagesModule 2 EmTechMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Student Management System and LibraryDocument16 pagesStudent Management System and LibraryNithin SikinamNo ratings yet
- Aspen Utilities: The Challenge: Reduction of Production CostsDocument6 pagesAspen Utilities: The Challenge: Reduction of Production CostsqjjonesNo ratings yet
- Teenager's Opinion About GameDocument10 pagesTeenager's Opinion About GameCesylia DealovaNo ratings yet
- Booking System Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesBooking System Literature Revieweyewhyvkg100% (1)
- Office Code ErrorsDocument3 pagesOffice Code ErrorsWe ShareNo ratings yet
- Directions: Write The LETTER of The Correct Answer. (NO Erasures)Document21 pagesDirections: Write The LETTER of The Correct Answer. (NO Erasures)Maria Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Python The Complete ReferenceDocument1 pagePython The Complete Referencepdkonline0% (1)
- The ICT Lounge: Section 7.7: Types of ProcessingDocument6 pagesThe ICT Lounge: Section 7.7: Types of ProcessingMahmoud A.RaoufNo ratings yet
- What's New - Retail Features in AX 2012 R3Document12 pagesWhat's New - Retail Features in AX 2012 R3Siva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Xyzmo Product OverviewDocument13 pagesXyzmo Product Overviewxyzmo SIGNificantNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project Report: "Factors Affecting The Trust of Customer in Online Shopping"Document25 pagesCapstone Project Report: "Factors Affecting The Trust of Customer in Online Shopping"Ekta Bansal50% (2)
- 40-Mainaustin Alcala Criminal ComplaintDocument39 pages40-Mainaustin Alcala Criminal ComplaintPatrick Howell O'NeillNo ratings yet
- ICT As: PlatformDocument40 pagesICT As: PlatformToga MarMarNo ratings yet
- UK Consumer Digital Index 2023Document82 pagesUK Consumer Digital Index 2023tamlqNo ratings yet
- Public Service Commission, West Bengal: 161A, S. P. Mukherjee Road, Kolkata-700026 Advertisement No. 19/2019Document3 pagesPublic Service Commission, West Bengal: 161A, S. P. Mukherjee Road, Kolkata-700026 Advertisement No. 19/2019alok dasNo ratings yet
- Ratnam College c2c 2022Document3 pagesRatnam College c2c 2022UPENDRA NISHADNo ratings yet
- Online System, Functions, and PlatformsDocument6 pagesOnline System, Functions, and PlatformsChristine Joy AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Siemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer's HandbookDocument58 pagesSiemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer's Handbooklemoresk100% (1)