Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Observations
Observations
Uploaded by
Kumar PraveenkumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Observations
Observations
Uploaded by
Kumar PraveenkumarCopyright:
Available Formats
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE Ex.
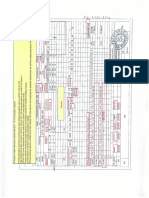
No:01 Date: AIM: To determine the input & output characteristics of BJT in CE configuration and to find the h-parameters for the same. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 RPS Ammeter Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor Transistor Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-100) mA (0-500)A (0-10) V (0-1) V 1K BC107 -Quantity 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 -
Characteristics Of BJT In CE Configuration
FORMULE REQUIRED: VBE 1.Input impedance, hie+= IB IC 2.Output admittance, hoe= VCE
VCE=Constant.
IB=Constant.
VBE 3.Voltage gain, hre= VCE IB=Constant.
IC 4.Current gain, hfe= IB VCE=Constant.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
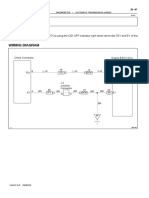
PROCEDURE: INPUT CHARACTERISTICS: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2. At first VCE is kept constant at any non-zero value. 3.The base current variation with VBE is noted. 4.The readings are tabulated and graph is drawn by taking VBE along X-axis and IB along Y-axis. 5.The values of hfe and hie were calculated. OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.At first IB is kept constant at any non-zero current value. 3.The voltage VCE is varied by varying the regulated power supply. 4.The collector current variations with VCE is noted. 4.The readings are tabulated and the graph is drawn. 5.The values of hoe&hfe were calculated.
RESULT Thus the static characteristics of transistor under CE configuration of hybrid parameter was determined, 1.Input Impedance, hie= 2.Output Admittance hoe= 3.Voltage gain, hre= 4.Current gain, hfe=
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Ex.No:02 Date: AIM:
Characteristics Of BJT In CC Configuration
To determine the input & output characteristics of BJT in CC configuration and to find the h-parameters for the same. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 RPS Ammeter Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor Transistor Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-10) mA (0-1)A (0-10) V (0-30) V 68K BC107 -Quantity 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 -
FORMULE REQUIRED: VBE 1.Input impedance, hie+= IB IC 2.Output admittance, hoe= VCE
VCE=Constant.
IB=Constant.
VBE 3.Voltage gain, hre= VCE IB=Constant.
IC 4.Current gain, hfe= VCE=Constant.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE IB PROCEDURE: INPUT CHARACTERISTICS: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2. At first VEC is kept constant at any non-zero value 2.The base current variation with VBC is noted. 3.The readings are tabulated and graph is drawn by taking VBC along X-axis and IB along Y-axis. 4.The values of hfe and hie were calculated. OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.At first IB is kept constant at any non-zero current value. 3.The voltage VCE is varied by varying the regulated power supply. 4.The emitter current variations with VCE are noted. 4.The readings are tabulated and the graph is drawn. 5.The values of hoe&hfe were calculated.
RESULT Thus the static characteristics of transistor under CE configuration of hybrid parameter was determined, 1.Input Impedance, hie= 2.Output Admittance hoe= 3.Voltage gain, hre= 4.Current gain, hfe=
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Ex.No:03 Date: AIM:
Characteristics Of BJT In CB Configuration
To determine the input & output characteristics of BJT in CB configuration and to find the h-parameters. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor Transistor Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-10) mA (0-30) V (0-1) V 1K BC107 -Quantity 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 -
FORMULE REQUIRED: VBE 1.Input impedance, hib= IE IC 2.Output admittance, hob= VCB VBE 3.Reverse Voltage gain, hrb= VCB IC 4.ForwardCurrent gain, hfb= IE
VCB=Constant.
IE=Constant.
IE=Constant.
VCB=Constant.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
PROCEDURE: INPUT CHARACTERISTICS: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2. At first VCB is kept constant at any non-zero value. 3.Note the emitter current by varying VBE. 4.The readings are tabulated and graph is drawn by taking VBE along X-axis and IE along Y-axis. 5.The values of hfb and hib were calculated. OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.At first IE is kept constant at any non-zero current value. 3.The voltage VCB is varied by varying the regulated power supply and note down the collector current variations with VCB is noted. 4.The readings are tabulated and the graph is drawn. 5.The values of hob & hfb were calculated.
RESULT Thus the static characteristics of transistor under CB configuration of hybrid parameter was determined, PARAMETERS 1.Input Impedance, hib 2.Output Admittance hob 3. Reverse Voltage gain, hrb 4. Forward Current gain, hfb PRACTICAL READINGS
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Ex.No:04 Date:
STATIC CHARACTERISTICS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF JFET
AIM: To determine the static characteristics of JFET. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor JFET Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-100) mA (0-10) V (0-30) V 1K BFW10 -Quantity 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 -
FORMULE REQUIRED: VDS 1.Drain resistance, rD= ID . VDS2-VDS1 ID2-ID1
VGS=Constant. ID VDS=Constant.
2.Transcondutace, gm==
VGS
ID2-ID1 VGS2-VGS1 3.Amplification factor =gm X rD
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
PROCEDURE: DRAIN CHARACTERISTICS: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.For drain characteristics the gate source is kept constant. 3.The VDS is varied by the regulated power supply and the corresponding values of drain current to be noted. 4.The same procedure is repeated for different values of VDS. 5.The graph is plotted between VDS&ID. 6.The drain resistance is calculated from the graph by the formula, VDS rp= ID TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.For transfer characteristics the drain source voltage is kept constant. 3.The VGS is varied by the regulated power supply and the corresponding values of drain current to be noted. 4.The same procedure is repeated for different values of VGS. 5.The graph is plotted between VGS &ID. 6.The drain resistance is calculated from the graph by the formula, ID gm= VDS=Constant. VGS 7.Amplification factor =gmXrD. RESULT Thus the static characteristics and parameter of JFET was verified, 1.Drain resistance (rD)= 2.Transconductance (gm)= VGS=Constant.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE 3.Amplification factor ()= Ex.No:05 Date: V-I CHARACTERISTICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE
AIM To determine the reverse saturation current and dynamic resistance of the diode from its V-I characteristics. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor PN Junction DIODE Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-10) mA (0-1) V (0-30) V 2.2K IN4007 -Quantity 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 -
FORMULE REQUIRED: 1.PN junction for forward bias, rf=
Vf If Vr
2.PN junction for reverse bias, rr= Ir PROCEDURE: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.The supply voltage is increased gradually in step by using regulated power supply. 3.At each step the readings are tabulated for both forward and reverse bias conditions. 4.The graph is drawn with voltage on X-axis and current on Y-axis for forward and reverse bias conditions. RESULT Thus the static characteristics of semiconductor DIODE was verified,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE 1.Semiconductor diode for forward bias Dynamic resistance= 2. Semiconductor diode for reverse bias Dynamic resistance Ex.No:06 Date: AIM To study and determine V-I characteristics of the ZENER diode in forward and reverse biased conditions. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Resistor ZENER DIODE Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-100) mA (0-15) V 220 FZ9.1 -Quantity 1 1 1 1 1 V-I CHARACTERISTICS OF ZENER DIODE
FORMULE REQUIRED: Vf 1. Forward bias, rf= If Vr 2. Reverse bias, rr= Ir PROCEDURE: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.The supply voltage is increased gradually in step by using regulated power supply. 3.At each step the readings are tabulated for both forward and reverse bias conditions. 4.The graph is drawn with voltage on X-axis and current on Y-axis for forward and reverse bias conditions. RESULT Thus the static characteristics of ZENER DIODE was verified,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE 1.Zener diode for forward bias = 2. Zener diode for reverse bias = Ex.No:07 Date: V-I CHARACTERISTICS OF UJT
AIM To study and determine V-I characteristics of the UJT and to plot the graph. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor UJT Bread Board Connecting Wires Range (0-30) V (0-30) mA (0-10) V (0-30) V 1K 2N2646 -Quantity 1 1 1 1 1 1 -
PROCEDURE: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.Set VBB=10V as constant. 3.Vary VEE and note down the readings of IE from various values of VEB. 4.Plot the graph VEB, IE for a constant VBB. 5.Determine the stand off ratio. = Vp-Vv/VBB
RESULT Thus the V-I characteristics of UJT was verified,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE Intrinsic stand off ratio =
Ex.No:08 Date: AIM
ZENER DIODE AS VOLTAGE REGULATOR
To determine the voltage regulation for zener diode. COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 RPS Ammeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Resistor Zener diode Potentiometer Bread Board Connecting Wires
Range (0-30) V (0-100)A (0-30) V (0-1) V 1K FZ6.2 2.2K ---
Quantity 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -
PROCEDURE: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.The input voltage varied the line regulation was obtained in each step out put voltage was noted. 3.By varying potentiometer the load regulation obtained, the out put voltage noted down. 4. At each step the readings are tabulated and required graphs drawn.
RESULT Thus the voltage regulator for zener diode was determined and the readings for line and load regulation was tabulated and graph was drawn.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Ex.No:09 Date:
Frequency Response Of Common Emitter Amplifier
AIM: To determine the frequency response of CE amplifiers and to draw the frequency response curve.
COMPONENTS REQUIRED: S.no Components 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Function generator Capacitor Resistor Transistor Bread Board Connecting Wires Resistors RPS Range -0.1F 1.2K, 5.2K BC107 -100K, 320K Quantity 1 1 1,1 11,1 1
PROCEDURE: 1.Connections are given as per the circuit diagram. 2.The input frequency varied gain was obtained in each step out put voltage was noted. 3. At each step the readings are tabulated and required graphs drawn. RESULT Thus the frequency response of common emitter amplifier was determined and the graph was drawn. Band width= KHz.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Corrective Math Common ProblemsDocument6 pagesCorrective Math Common ProblemsmissfhNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ramniranjan Jhunjhunwala College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous)Document1 pageRamniranjan Jhunjhunwala College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous)Angelina JoyNo ratings yet
- ALS-R User's Manual: Amplified Spontaneous Emission Light SourceDocument16 pagesALS-R User's Manual: Amplified Spontaneous Emission Light SourceAnonymous 60esBJZIjNo ratings yet
- As 3566.2-2002 Self-Drilling Screws For The Building and Construction Industries Corrosion Resistance RequireDocument7 pagesAs 3566.2-2002 Self-Drilling Screws For The Building and Construction Industries Corrosion Resistance RequireSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- How To Teach English Harmer, Jeremy-133-138Document6 pagesHow To Teach English Harmer, Jeremy-133-138Elin Afi NajwaNo ratings yet
- Sasa Yoga Ke: Louis XIVDocument1 pageSasa Yoga Ke: Louis XIVNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 9.08 Solving Systems With Cramer's RuleDocument10 pages9.08 Solving Systems With Cramer's RuleRhea Jane DugadugaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Negotiation Style in IndiaDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Negotiation Style in IndiaChariNo ratings yet
- DSA With Java - Unit4Document12 pagesDSA With Java - Unit4Sabin MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Der DirectoryDocument262 pagesDer DirectoryBenNo ratings yet
- Sublime VocabularyDocument6 pagesSublime VocabularyHum Nath BaralNo ratings yet
- Sizing of The Buffer Tank in Chilled Water Distribution A C Systems - PUBLISHED VERSIONDocument31 pagesSizing of The Buffer Tank in Chilled Water Distribution A C Systems - PUBLISHED VERSIONHai PhanNo ratings yet
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Dictation As Writing ExercisesDocument6 pagesAdvantages & Disadvantages of Dictation As Writing ExercisesAfiq AzmanNo ratings yet
- Paintng Works U#3 Boiler Turbine Area: DuplicateDocument1 pagePaintng Works U#3 Boiler Turbine Area: DuplicatevenkateshbitraNo ratings yet
- Ozone - Depletion PackDocument33 pagesOzone - Depletion PackMEHDI MAICHOUFNo ratings yet
- A Short Monograph On Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : T R Pgp-DsbaDocument44 pagesA Short Monograph On Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : T R Pgp-DsbarajatNo ratings yet
- Cirrus: Illustrated Parts Catalog Model Sr20Document4 pagesCirrus: Illustrated Parts Catalog Model Sr20enriqueNo ratings yet
- Value of G at Different Locations On EarthDocument4 pagesValue of G at Different Locations On EarthDannyRaoNo ratings yet
- Traditional Methods For Performance Appraisal 1 LATESTDocument38 pagesTraditional Methods For Performance Appraisal 1 LATESTSheev Kumar RamdoyalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Auditory SystemDocument47 pagesPhysiology of The Auditory Systemmkct111No ratings yet
- After Review Sig Sixma UR65 Standoff Vision Improvement IrinaDocument41 pagesAfter Review Sig Sixma UR65 Standoff Vision Improvement IrinaBetty RosalinaNo ratings yet
- Love in The Cornhusks Formalist CritiqueDocument2 pagesLove in The Cornhusks Formalist CritiqueKarma AkabaneNo ratings yet
- CR, Cri, CRN, CRT ATEX-approved Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument18 pagesCR, Cri, CRN, CRT ATEX-approved Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsXuan Man NguyenNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document10 pagesProject 1rashmi patilNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Power SupplyDocument7 pagesLab 1 Power SupplyKatherine YenNo ratings yet
- MTC 17022021063931Document1 pageMTC 17022021063931Ahmed LepdaNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics FinalDocument10 pagesMnemonics Finalapi-285415466No ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Plc DVP-PLC PM en 20140804Document749 pagesDelta Ia-Plc DVP-PLC PM en 20140804Ali PadaryamNo ratings yet
- TE1 Terminal CircuitDocument2 pagesTE1 Terminal Circuitcelestino tuliaoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument15 pagesConservation of EnergySreemanth C ReddyNo ratings yet