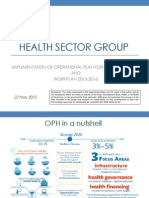
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept of Planning
Concept of Planning
Uploaded by
Peter AbikoyeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept of Planning
Concept of Planning
Uploaded by
Peter AbikoyeCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction Planning for VISION2020 is around a disease control strategy The priorities are of specific disease control but
t you develop a Comprehensive Eye Care (CEC) programme CEC includes community-based rehabilitation which identifies blind people in the community and takes the treatable e.g. cataract to the hospital CEC also includes rehabilitation of the incurable blind: mobility training, vocational placement, social adaptation Spiral Cycle of Planning Define Aim Aim: a direction; not necessarily achievable. Its the big picture Eradication; Elimination; Control VISION 2020 Aim: Elimination of avoidable blindness Elimination of cataract blindness in Kaduna Set Objectives Do not over-plan Setting SMART objectives enables one to have commitment and focus Take advantage of opportunities as they arise Try to recognise your communitys perspective and craft a solution that wins for both sides; creating a longer-term model of success Objectives are SMART SMART Objectives S specific M measurable A achievable, at the tip of your reach; requires effort R realistic T time-bound Example VISION 2020 Aim: Global elimination of avoidable blindness
Its general objective is to reduce global blindness to 0.3% by 2020 It has a time-frame and it is measurable Set Priorities of disease control based on 1.Magnitude: Burden of disease
Expected number of blind years 2.Feasibility of control: can you do something about it? Available skills (the know-how) Available resources 3.Cost-effectiveness: economic rate of return 4.Consider geographical spread of the disease Develop Strategy: The How Outlining strategies ensures success and completion
The best strategy is often not the optimal one, but the one that is easiest to implement Centered around specific objectives Activity-based Develop a Comprehensive Eye-Care Programme Develop an Eye-Care plan based on the principles I SEE I- Integration S- Sustainability E- Equity E- Excellence On the foundation of Community Participation A plan must include Activity: What? Target: When? Personnel: Who? Strategy: How? Cost: How much? Cataract The proposed 5-year plan Aim: To eliminate cataract blindness in Maiduguri by the year 2020
Objectives: 1.To achieve a CSR of 2000 by the next 5 years (OUTPUT) 2.To monitor and ensure the quality of surgery in order to achieve a good uncorrected visual outcome in at least 80% of operated cases by the next 5 years (OUTCOME) 3.To make cataract surgery more affordable and cost-effective in order to achieve selfsustainability by the next 5 years (OUTLAY) Strategies to increase output (CSR) How Many? Gradually increase number of surgeries done over 5 years Efficient service: Improve work culture and management Create Demand HRD: Enhance training of surgeons, nurses and supporting staff Strategies to ensure good outcome How good? WHO guidelines for monitoring VA outcomes Appropriate technology Build and maintain surgical skills Surgical technique: ECCE + PC IOL or SICS + PC IOL Pre-op IOL power calculation Post-op refraction Implement monitoring Develop system of follow-up in the community Strategies to make surgery affordable How much? Consider subsidy monitor patient paying capacity Cost-containment; Cost-sharing; Cost-recovery; value for money Income generation Childhood Blindness This should be in the plan as a service for: 1.Teaching institution/Tertiary/Referral centre 2.V. poor rural area with malnutrition 3.Blind school responsibility as an eye-care provider for the school Childhood Blindness
Aim: To eliminate childhood blindness due to cataract and (VAD)
vitamin A deficiency
Objectives: (related to 1 3 above) 1.To have a child eye-care centre dealing with cataract, glaucoma and optical/low vision services in children 2.A survey for assessment of VAD and control measures 3.To examine all blind school children and determine those who could be helped Strategy for child eye-care centre Teach/educate workers on VAD Vitamin A supplementation with measles immunization Ante-natal vitamin A supplementation Nutrition education for mothers Trachoma Trachoma is a focal disease Targets are set in relation to the magnitude of the disease in the community.
Aim: To eliminate trachoma blindness by 2020
Objectives: 1.To reduce the number of people with TT from 200/1000 to 20/1000 population in the next 5 years. Note:The Ultimate Intervention Goal (UIG) is to reduce number of people with TT to 1/1000 population 2.To reduce the prevalence of TF/TI from 10% to <5% in 1-10 year-olds in the next 5 years Strategy for control of trachoma blindness S Surgery: Bilamellar tarsal rotation by ophthalmic nurses in the community A Antibiotics: Use azithromycin, one dose/year, mass treatment F Face washing/Facial cleanliness: A Health Promotion E Environmental control: Water, sanitation, economy (e.g. micro-credit scheme). It is a Developmental goal Glaucoma Situational analysis is done to estimate the number of people at risk number with glaucoma number blind from glaucoma
Aim: To eliminate glaucoma blindness by 2020
Objectives: 1.To find the late imminently blind glaucoma patient (case-detection) 2.To achieve a glaucoma surgical rate (GSR) of 200 eyes/million population/year in the next 5 years. Strategy: How do we find the glaucoma patient? 1.VA screening in the community and referral of all those with VA<6/60 for diagnosis 2.Fundoscopy and IOP measurement of referred cases done by ophthalmic nurses. Specific examination by ophthalmologist for patients if vertical cup/disc ratio (VCDR) >0.6; IOP > 21mmHg 3.If more resources are available, can check VCDR in all >40 year-olds 4.Outline exact mode of fundoscopy 5.Outline exact method of IOP measurement: Shiotz, hand-held e.g. Perkins or tono-pen, etc. Strategy: Increase GSR 1.Trabeculectomy (with antimetabolites) to all diagnosed patients 2.Surgery done at the ?secondary level 3.Use a cataract programme to promote glaucoma intervention 4.Improve public health awareness and Create demand Diabetic Retinopathy Developed countries and the urban populations of developing countries In 1m population: 30-50,000 diabetics (3-5%) Of which 6-10,000 have diabetic retinopathy (20%) Of which 500 have diabetic maculopathy and proliferative disease (500 per million per year incidence) Plan for Control of Diabetic Retinopathy? How do we find the patient with diabetic retinopathy? Need to know diabetics Hospital-based register What is the treatment strategy? LASER for the retinopathy Vitreo-retinal surgery for advanced disease Issues: Available equipment and maintenance Trained personnel
Screening? Adult screening for diabetes not feasible, not cost-effective Screening of diabetics for diabetic retinopathy Have LASER available before embarking on screening programme Summary 1.The AIM is to implement VISION 2020 2.The objectives are planned around major causes of blindness in the community: cataract, childhood blindness, refractive error, trachoma, etc; depending on your priorities 3.Other objectives are around human resource development (HRD), infrastructural development (ISD) and the context in which you do that 4.The Strategy: is the HOW to achieve each objective/target 5.Phase in project years (PY). Make a 12 year plan, go year by year: remember, the more we do, the more we dilute our resources 6.Plan for a million population. Even if doing for 3 5 million, replicate the plan in the next million population Summary 7. Plan activity along budget-lines. Include operational costs and inflation. 8.The programme should be sustainable in 3-5 years. Generate income to cover costs. 9.Integrate the programme within the existing healthcare system/structure. 10.Is eyecare a priority in the picture of HIV, malaria, TB, etc? Selling point: do do-able programmes with minimal resources, giving a positive impact.
You might also like
- The Body Transformation Blueprint 271 Pages - Sean NalewanyjDocument271 pagesThe Body Transformation Blueprint 271 Pages - Sean NalewanyjAdam Khoo92% (39)
- Clinic DFD Context DiagramDocument37 pagesClinic DFD Context Diagramமனிதம்83% (23)
- CVS Essay QuestionsDocument3 pagesCVS Essay QuestionsPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesEndocrinology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye0% (1)
- 48 Vision 2020Document20 pages48 Vision 2020Ngurah DwiNo ratings yet
- Navya Krishna-National Programme For Control of BlindnessDocument41 pagesNavya Krishna-National Programme For Control of BlindnessAnmol KudalNo ratings yet
- Tamalika de - Bo 505.ca2Document4 pagesTamalika de - Bo 505.ca2Santanu SautyaNo ratings yet
- BLINDNESSDocument24 pagesBLINDNESSpriyagerardNo ratings yet
- Blindness 130303005645 Phpapp01 PDFDocument25 pagesBlindness 130303005645 Phpapp01 PDFnehaNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of Blindness: - Jayashree Iyer Roll No. 43Document12 pagesNational Programme For Control of Blindness: - Jayashree Iyer Roll No. 43Jayashree Iyer0% (1)
- Serv MarkDocument13 pagesServ MarkRaghu SandraNo ratings yet
- Blindness ProgramDocument12 pagesBlindness ProgramRakersh PatidarNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Medcene and Health Scince Department of OptometryDocument50 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Medcene and Health Scince Department of OptometryHenok BirukNo ratings yet
- BlindnessDocument26 pagesBlindnessdrmeenaxiNo ratings yet
- Blindness Control Program: Riza R. Dacalos RN, MPH Hepo Ii Program CoordinatorDocument9 pagesBlindness Control Program: Riza R. Dacalos RN, MPH Hepo Ii Program CoordinatorAmandoron Dash AdevaNo ratings yet
- The ADB Health Sector: Implementation of The OPH and Workplan by Susann RothDocument5 pagesThe ADB Health Sector: Implementation of The OPH and Workplan by Susann RothADB Health Sector GroupNo ratings yet
- C11 P08 NPCBDocument20 pagesC11 P08 NPCBChandana KrishnaNo ratings yet
- National Blindness Control ProgrammeDocument34 pagesNational Blindness Control ProgrammeSneha Gopalkrishnan100% (2)
- NPCBDocument21 pagesNPCBtarunNo ratings yet
- VIP Documentary Script Revised+n Edits RevisedDocument4 pagesVIP Documentary Script Revised+n Edits RevisedRael GibendiNo ratings yet
- Sightfirst Grant ApplicationDocument13 pagesSightfirst Grant ApplicationGeorge SitanayaNo ratings yet
- IIVM College of OptometryDocument5 pagesIIVM College of OptometryiivmcoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To M&EDocument133 pagesIntroduction To M&EChisowa100% (1)
- Community OphthalmologyDocument33 pagesCommunity OphthalmologyVarun BoddulaNo ratings yet
- Optician Vision of Eyesight Vector PowerPoint Templates StandardDocument39 pagesOptician Vision of Eyesight Vector PowerPoint Templates Standardtahirabeer50No ratings yet
- National Programme For BlindnessDocument6 pagesNational Programme For BlindnessMANISH MAMIDINo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of Blindness: Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH ChandigarhDocument23 pagesNational Programme For Control of Blindness: Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH ChandigarhSumon SarkarNo ratings yet
- Nlep 2019Document58 pagesNlep 2019PreethiNo ratings yet
- Combine Majpr TopicsDocument86 pagesCombine Majpr TopicsDr. Pooja DubeyNo ratings yet
- Woundcare Just StartedDocument40 pagesWoundcare Just StartedMaizatul Akmar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Solving The Blind SpotDocument16 pagesCase 2 Solving The Blind SpotHans Markson TanNo ratings yet
- ToRs SHM Zvandiri Endline EvaluationDocument6 pagesToRs SHM Zvandiri Endline Evaluationraymondkaridza5No ratings yet
- 2.2.3 Develop Economic PlanDocument47 pages2.2.3 Develop Economic PlanChuru iddyNo ratings yet
- Community Surge PresentationDocument23 pagesCommunity Surge PresentationTheresia Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Planning To Reach Every CommunityDocument37 pagesPlanning To Reach Every Communityzedregga2No ratings yet
- Blindness Control ProgrammeDocument6 pagesBlindness Control Programmearunjv1234No ratings yet
- Basic EPI Training Course For Raiders: June 27 - 30, 2016 Naga Regent Hotel, Naga CityDocument16 pagesBasic EPI Training Course For Raiders: June 27 - 30, 2016 Naga Regent Hotel, Naga Citypaul arvie violetaNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of Blindness - Ananda YncDocument52 pagesNational Programme For Control of Blindness - Ananda YncAnand gowdaNo ratings yet
- 2017-19 Strategic PlanDocument10 pages2017-19 Strategic PlanMadhumitaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Pooja Kharbanda PPT 64th DOS Annual Conference, Appreciation Award PaperDocument36 pagesDr. Pooja Kharbanda PPT 64th DOS Annual Conference, Appreciation Award PaperdrpoojakharbandaNo ratings yet
- Health Tourism Presentation IBMDocument65 pagesHealth Tourism Presentation IBMMd. Ashraf Hossain SarkerNo ratings yet
- Nikoletta Mavroeidi MediPIETDocument24 pagesNikoletta Mavroeidi MediPIETtsiko111No ratings yet
- Doh Updated Prog M-RDocument49 pagesDoh Updated Prog M-Rdeeday echavezNo ratings yet
- Why OptometryDocument30 pagesWhy OptometrysandiNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of BlindnessDocument18 pagesNational Programme For Control of BlindnessS P DigitalNo ratings yet
- Overview of GP Confederation Contracts 2020-21 July 2020Document82 pagesOverview of GP Confederation Contracts 2020-21 July 2020Confederation ContractsNo ratings yet
- Overview of Confed Contracts 2020-21 July 2020Document82 pagesOverview of Confed Contracts 2020-21 July 2020Confederation ContractsNo ratings yet
- Oig Gfoig10007audituzbekistan Report enDocument112 pagesOig Gfoig10007audituzbekistan Report encismercNo ratings yet
- Eye Disease Intervention FoDocument20 pagesEye Disease Intervention FononawitaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Consumer Behavior Pattern For Select Eye-Care Facilities in Vashi and Koparkhairne, Navi MumbaiDocument14 pagesA Study of Consumer Behavior Pattern For Select Eye-Care Facilities in Vashi and Koparkhairne, Navi MumbaiBESTJournalsNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of BlindnessDocument2 pagesNational Programme For Control of BlindnessPintu KumarNo ratings yet
- Aravind Eye Care SystemDocument5 pagesAravind Eye Care SystemArpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Model of Community PrEP Distribution USAID Key Populations Activity Dec 1, 2020Document16 pagesModel of Community PrEP Distribution USAID Key Populations Activity Dec 1, 2020Eneyew BirhanNo ratings yet
- 2020 3 Year Strategic PlanDocument10 pages2020 3 Year Strategic PlanAbebayehu AmaniyasNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing ManagementDocument26 pagesStrategic Marketing ManagementadralovesmichaNo ratings yet
- Risk and OpportunitiesDocument44 pagesRisk and OpportunitiesDina LacsonNo ratings yet
- Eye Care ReportDocument20 pagesEye Care ReportJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Eye - & - Vision - Care - Toolkit - HOW-TO-GUIDEDocument16 pages1.1. Eye - & - Vision - Care - Toolkit - HOW-TO-GUIDECynthia Jaramillo MachucaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Study ProposalDocument4 pagesGlaucoma Study Proposaljasb1980100% (1)
- Case Study KenyaDocument18 pagesCase Study KenyaIsaac BundiNo ratings yet
- Global Initiatives For Prevention of Blindness: By: Mohammed Seid (BSC, MSC)Document34 pagesGlobal Initiatives For Prevention of Blindness: By: Mohammed Seid (BSC, MSC)Henok BirukNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Overview of DM & DRDocument27 pagesModule 1 - Overview of DM & DRkhairulfatinNo ratings yet
- Upsc Monthly Current Affairs Jan 2021 e 89Document145 pagesUpsc Monthly Current Affairs Jan 2021 e 89ShaamalanNo ratings yet
- Asian Development Bank Knowledge Management Action Plan 2021–2025: Knowledge for a Prosperous, Inclusive, Resilient, and Sustainable Asia and the PacificFrom EverandAsian Development Bank Knowledge Management Action Plan 2021–2025: Knowledge for a Prosperous, Inclusive, Resilient, and Sustainable Asia and the PacificRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- OphthalmologyDocument6 pagesOphthalmologyPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Situational Analysis: Assessing Needs and Resources For VISION2020 Service Delivery and Identifying GAPSDocument11 pagesSituational Analysis: Assessing Needs and Resources For VISION2020 Service Delivery and Identifying GAPSPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument1 pageRich Text Editor FilePeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- GIT Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesGIT Essay QuestionsPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Forensics Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesForensics Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (3)
- Snake Bite: Families of Venomous SnakesDocument4 pagesSnake Bite: Families of Venomous SnakesPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument1 pageRich Text Editor FilePeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Urology Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesUrology Essay QuestionsPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesDermatology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (1)
- Neurology Essay QuestionsDocument3 pagesNeurology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (3)
- Airway Assessment MeDocument46 pagesAirway Assessment MePeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Technology Guidelines For A District Eye Care Programme: July 2006Document53 pagesTechnology Guidelines For A District Eye Care Programme: July 2006Peter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- Management of Ocular BurnsDocument53 pagesManagement of Ocular BurnsPeter AbikoyeNo ratings yet
- A. BDRRM Plan Template - EnglishDocument48 pagesA. BDRRM Plan Template - EnglishPaul Christian AsayNo ratings yet
- Luknis - Nursing ResumeDocument1 pageLuknis - Nursing Resumeapi-737863984No ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Thuja OrientalisDocument9 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Thuja OrientalisMădălina FrunzeteNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy: AdvantagesDocument9 pagesIV Therapy: AdvantagesKaren HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Proposal - Technology Innovation Sandbox PDFDocument25 pagesProposal - Technology Innovation Sandbox PDFhadyan hafizhNo ratings yet
- YOGA - Yoga at Home 100 Yoga PosesDocument55 pagesYOGA - Yoga at Home 100 Yoga PosesBlanca Rios MartinNo ratings yet
- Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Tuljapur Campus: Final Reflexive Journal SubmissionDocument50 pagesTata Institute of Social Sciences, Tuljapur Campus: Final Reflexive Journal SubmissionDISHANT D. RATHODNo ratings yet
- Work LifeDocument15 pagesWork LifeanashussainNo ratings yet
- Brachycephalization in Japan Has CeasedDocument9 pagesBrachycephalization in Japan Has CeasedangellisimalNo ratings yet
- Murmurs Made Easy Epomedicine 2Document1 pageMurmurs Made Easy Epomedicine 2KC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 6Document13 pagesModule 2 Lesson 6Chlea Marie Tañedo Abucejo100% (2)
- Tone AbnormalitiesDocument32 pagesTone AbnormalitiespuchioNo ratings yet
- 1212 PDF PDFDocument5 pages1212 PDF PDFarleneNo ratings yet
- Farmer Type Ion Chambers, NE2571 and NE2581Document2 pagesFarmer Type Ion Chambers, NE2571 and NE2581Russell ClarkNo ratings yet
- DLP P. E. Week ADocument21 pagesDLP P. E. Week AjoelNo ratings yet
- Stroke Awareness EducationDocument7 pagesStroke Awareness EducationIneke Putri100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Doctor TomatoNo ratings yet
- Hurt and Grievous HurtDocument31 pagesHurt and Grievous HurtBig RED100% (1)
- Fdar Charting and Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesFdar Charting and Discharge PlanningFaine Angela Caones100% (1)
- Funda Rle PrelimsDocument13 pagesFunda Rle PrelimsIvan MaximusNo ratings yet
- Neuro FibromaDocument2 pagesNeuro FibromaRara ChanNo ratings yet
- RESUME Mark Reardon PHDDocument3 pagesRESUME Mark Reardon PHDMark Reardon, PhDNo ratings yet
- Mineral Metabolism: General FunctionsDocument12 pagesMineral Metabolism: General FunctionsibntauhidNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus in Guidance and Counseling For Children With Special Needs 1Document6 pagesCourse Syllabus in Guidance and Counseling For Children With Special Needs 1Jansel S ArongNo ratings yet
- NCSBN - Pharmacology and ParenteralDocument36 pagesNCSBN - Pharmacology and ParenteralKarissa May Cortez92% (12)
- Vaccine TextDocument2,739 pagesVaccine TextMark Mast0% (2)
- Kepatuhan 5 Momen Hand Hygiene Pada Petugas Di Laboratorium Klinik Cito YogyakartaDocument9 pagesKepatuhan 5 Momen Hand Hygiene Pada Petugas Di Laboratorium Klinik Cito YogyakartaDwi KristantoNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Infographic A2Document1 pageSepsis Infographic A2Nuril AnwarNo ratings yet