Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analog & Digital (Microp)
Analog & Digital (Microp)
Uploaded by
Bharath ChOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analog & Digital (Microp)
Analog & Digital (Microp)
Uploaded by
Bharath ChCopyright:
Available Formats
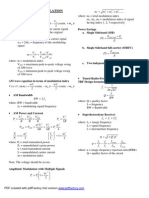
A&D ,p 1
Decoder Encode De-MUX Multiplexer
n X m m 2 ; one o/p line will enable for diff i/p n X m n 2 ; at time one i/p line only encoded. 1 X m m= 2 ; E is no.of enable pins. n X 1 n= 2 ; E is no.of enable pins. F = AB I 0 + AB I 1 + AB I 2 + AB I 3
JK FF Q(t) 0 0 1 X J 0 0 1 1 K 0 1 0 1 Q(t+1) Q(t) 0 1 Q(t)* Q(t+1)=TQ+TQ Q(t+1)=D T FF (toggle) T 0 1 Q(t+1) Q(t) Q(t) D FF (dela y) MOSFET - NAND for +ve logic Emitter coupled logic (ECL) NOR for +ve logic D 0 1 Q(t+1) 0 1 Adv:as the load is realised by the MOSFET itself the package density . Fanout bcoz high i/p resistance. a)Open collector TTL: Adv: used to drive LEDs, Lamps Used in commen bus system Dis adv:over all speed is less b) Toten pole TTL:adv: swiching speed is high,bcoz =RC is reduced, emitter follwer o/p resistance(R) is Differential Amplifier: (high i/p R, low o/p R) One transister will draw more ct.(power disipation Ct mode logic: No swiching cts less disipation. Adv:both NOR, OR gate are available. Wired OR logic, swiching speed .Fanout Dis.adv:power disipation as the transistors are always in active region. Poor noice margin. Dis adv: Swiching speed c) Tristate TTL:adv: tristate (0, 1, high impedence state), in high impedence state power disipation is 0.
E E m
CMOS INVERTER for +ve logic Diode Transistor Logic (DTL)-NAND for +ve logic Transistor transistor logic (TTL) NAND for +ve logic
SR FF S 0 0 1 1 R 0 1 0 1
T depends on previous sta te
O/p = i/p
Q(t+1)=S+RQ(t)
Q(t+1)=JQ+KQ
Ri ng Counter f/N As table Mul ti Vibra tor Squa re wa ve genera tor
Johnson f/2N Bi s table Multi vibra tor
Ri pple f/2n Mono s table Pulse genera tor
Modules f/N Schmi tt tri gger Squa ring ckt, flip flop
1 bi t memory element(flip flop)
Res olution/step si ze = VR/2N Bi na ry wei ghted Resis ter DAC R-2R ladder DAC
DAC N No.of s teps (n)= [2 -1] N Full s cale o/p=[2 -1] x(S) :. (S) is Step size %Resolution = (S)/F s cale o/p=1/[2N -1]x100 Dis adv: If the si ze of DAC size of Resistance value become la rge Adv: Better linea rty, It requi res onl y two diff types of resis wi th R, 2R ADC Converti on time= [2N-1] x T Where T is Clock period Dis adv: In the s teady s tate i f the i/p Vt , i t cant tra ck the i/p In above ADC repla ce counter wi th updown counter Replace counter with Succssi ve approxima tion Dis adv: for N-bit flash type ADC no.of requi red compera tors 2N-1 More accurate
Res olution/step si ze = V/(2N-1); V is range of i /p vol ta ge eg:-V/2 to V/2 Counter type ADC Tra cking type ADC Succssi ve approxi mati on ADC Convertion ti me= N x T Flash type ADC (pa rallel ADC) Fastest ADC Dual slope ADC (Integra ting ADC)
DTL TTL ECL MOS CMOS Fan out 8 10 25 20 >50 Prop.delay (nsec) 30 10 4 300 70 Power dissipation(mw) 8 10 40 0.2 1 0.01 Noise margin (mV) 700 400 200 150 300 HTL(high Tr eshold logic)--noise margin ,use near Industries tristate logic have 3 states 0, 1, high impedance state. NMOS is faster than PMOS
Adv: less power consumption. More fanout.
A&D ,p 2 Mi cro prossor: 8085 16 add.lines (A0-A15 8 da ta lines(D 0 - D 7) f= 3.072 Mhz clock period T =1/f =320nsec 8-bi t regis ter--7 16-bi t register--3 B BC C D DE E H HL L ACC PSW=ACC8+Fla g.Reg 8(prog s tatusword) AC X P X Ins truction Types : 1.Da ta transfer 2.Arthemeti c 3.logi c 4.M/C Related I/O 5.Additi onal
Fla g Register S Z
Cy
Set Interrupt Mask (SIM) SOD SDE X Priori ty Hi gh Least
R 7.5
MSE
M 7.5
M 6.5 Masking NMI Maskable Maskable Maskable Maskable
M 5.5
TRAP RST 7.5 RST 6.5 RST 5.5 INTR
Vector Add 0024 H 003C H 0034 H 002C H NVI ( Non-vector int )
Rea d Interrupt Mask SID I7 I6 Source R, R.P
I5
I.E
I 7.5
I 6.5
I 5.5
1.Regis ter
Des tina tion R, R.P
2.Di rect 3.Reg Indi rect 4.Immediate 5.Impli cit
R/M
M/R
8/16 bi t add Acc
R, R.P, Memory Acc
Example MOV C,A ADD R XCHG HL,DE LDA 5000 LHLD 8250 LDAX B BCA MVI C,32 32C LXI B,1111 1111BC DAR, RLC, RAC, CMA
A&D ,p 3
BJT (bipolar jection Transister) 1.Bipolar 2. High power 3.Low speed(w.r.toperating freq) High Speed(w.r.t Swithching i/p) 4. Noice margin 5. Fanout 6.Fanin 7.package densty 8. gain 9. BW Diode [+, -] V/Vt I = I S [e -1] I S -Reverse sat Ct VT - 26mv = KT/q non-identity const, no dimention
FET (Field effect Transistor) 1.uniploar 2. Low power 3. High speed Low Speed 4. Noice margin 5. Fanout 6.Fanin 7.package densty 8. gain 9. BW FET [G, D, S] 2 I D = IDS [1-(VGS/VP)] I D VGS Vt controlled
BJT [B, E, C] I C = I B + (1+) I CB Ic I B Ct Controlled
Ri Ro AI AV = AI x (Ro/Ri) Phase shift b/w i/p&o/p Vt Applications
CB Low (100 High 450 K = I C/I E 1 Low High >1500 0 or 360 High freq. Ckts RF = /* +1+
CE Medium750 Medium45K = I C/I B High (50-500) Medium 500 180 For Audio freq. = /*1 - +
CC High (750 K) Low (25 ) =I E/IB High (51-501) Low <1 0 or 360 For impdance matching = +1 = 1/1 -
Ideal op-amp cha racteris ti cs 1. i/p i mp = o/p i mp =0 hence vol ta ge a mplifier 2.gain = - 3. BW = 4. slew ra te = 5. CMRR (common mode rejection ra tio =A d/Ac) should be high = Schmi tt tri gger (a special type of bistable MV) Squa ring ckt:(any a rbi ta ry w/f converted into an uns ym squa re wa ve) Sili con Transistor (N-P-N) V = 0.5 V VBE(act) = 0.6 V VBE(sat) = 0.6 V Germanium Transistor (N-P-N) V = 0.1 V VBE(act) = 0.2 V VBE(sat) = 0.3 V
You might also like
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Programmable Quad Bipolar Operational Amplifier: LM146 LM246 LM346Document6 pagesProgrammable Quad Bipolar Operational Amplifier: LM146 LM246 LM346Alejandro Borrego DominguezNo ratings yet
- El T I III Electronics III: - Power Dissipation in CMOS Digital Circuits - Optimization of Chain of InvertersDocument23 pagesEl T I III Electronics III: - Power Dissipation in CMOS Digital Circuits - Optimization of Chain of InvertersSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- STPR1020CB/CG/CT/CF/CFP/CR: Ultra-Fast Recovery Rectifier DiodesDocument11 pagesSTPR1020CB/CG/CT/CF/CFP/CR: Ultra-Fast Recovery Rectifier DiodesMiloud ChouguiNo ratings yet
- 4 X 45W Quad Bridge Car Radio Amplifier Plus HSD: Multipower BCD TechnologyDocument11 pages4 X 45W Quad Bridge Car Radio Amplifier Plus HSD: Multipower BCD TechnologysanlugoNo ratings yet
- Transistor MPSH10 PDFDocument14 pagesTransistor MPSH10 PDFJohnJairoArangoQuinteroNo ratings yet
- Lecture37&38 - Power Analysis: Jagannadha Naidu KDocument22 pagesLecture37&38 - Power Analysis: Jagannadha Naidu Ksophieee19No ratings yet
- CD8227GPDocument8 pagesCD8227GPAlfredo Valencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual in PDFDocument56 pagesCs Lab Manual in PDFvasukonetiNo ratings yet
- PWM Off-Line Switching Regulator Ics: Str-A6000H SeriesDocument13 pagesPWM Off-Line Switching Regulator Ics: Str-A6000H SeriesAnonymous Lfgk6vygNo ratings yet
- CN0350Document7 pagesCN0350Narayan ApteNo ratings yet
- Ha 13563Document18 pagesHa 13563Danh ProNo ratings yet
- Tda 7439Document17 pagesTda 7439Arwana ChipmunksNo ratings yet
- Receiving Properties of AntennasDocument20 pagesReceiving Properties of AntennasAtiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Icl 8038 DataDocument10 pagesIcl 8038 DataTushar Kanti BeraNo ratings yet
- Ta 0104 ADocument18 pagesTa 0104 AJump DownNo ratings yet
- U3761mb TelefonoDocument23 pagesU3761mb Telefonogabriel6276No ratings yet
- TDA7442Document16 pagesTDA7442gaston30-3@No ratings yet
- Tda 7438Document18 pagesTda 7438sontuyet82No ratings yet
- Tda 7293Document16 pagesTda 7293Gerson FelipeNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab Manual: V Semester B.E (E & C)Document43 pagesCommunication Lab Manual: V Semester B.E (E & C)HacraloNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument12 pagesDatasheetebertecnicoNo ratings yet
- Tda 7440Document17 pagesTda 7440Albert ThomasNo ratings yet
- HT9200A/HT9200B DTMF Generators: FeaturesDocument14 pagesHT9200A/HT9200B DTMF Generators: FeaturesNOTIS64No ratings yet
- TDA7440D: Tone Control Digitally Controlled Audio ProcessorDocument17 pagesTDA7440D: Tone Control Digitally Controlled Audio ProcessorJimmy R. Calderon GualeNo ratings yet
- Elettronica II Lezione 10-11-12-13 LTSPICEDocument34 pagesElettronica II Lezione 10-11-12-13 LTSPICEVito NotoNo ratings yet
- Datasheet L6229Document25 pagesDatasheet L6229Raul Sense MejiaNo ratings yet
- 3 V To 5 V Single Supply, 200 KSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC AD7858/AD7858LDocument36 pages3 V To 5 V Single Supply, 200 KSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC AD7858/AD7858Ljnax101No ratings yet
- Tutorial-1 Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) Design: by Rashad.M.Ramzan Rashad@isy - Liu.se ObjectiveDocument18 pagesTutorial-1 Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) Design: by Rashad.M.Ramzan Rashad@isy - Liu.se ObjectiveRakesh Rt100% (1)
- Tda 2005Document20 pagesTda 2005Cris VMNo ratings yet
- Tda 2005Document21 pagesTda 2005Vamsi Mani Deep ElapakurtyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document10 pagesTutorial 5bayman66No ratings yet
- TDA7442 TDA7442D: Tone Control and Surround Digitally Controlled Audio ProcessorDocument17 pagesTDA7442 TDA7442D: Tone Control and Surround Digitally Controlled Audio ProcessormochuraNo ratings yet
- LTC1799 DatasheetDocument13 pagesLTC1799 Datasheetkonan_heriNo ratings yet
- Ring OscillatorDocument12 pagesRing OscillatorCmeLiv InmyHart NpaynoRentNo ratings yet
- MF10-N Universal Monolithic Dual Switched Capacitor Filter: Features DescriptionDocument35 pagesMF10-N Universal Monolithic Dual Switched Capacitor Filter: Features DescriptionAlbeiro Yr TrancerNo ratings yet
- STK4132IIDocument8 pagesSTK4132IIAttila SzelelkiNo ratings yet
- AFT05MP075NDocument21 pagesAFT05MP075NjeremyAW2SNo ratings yet
- Irf7811Avpbf Irf7811Avpbf: Absolute Maximum RatingsDocument6 pagesIrf7811Avpbf Irf7811Avpbf: Absolute Maximum RatingsnewmailsNo ratings yet
- Tda 7313Document14 pagesTda 7313ClaudiuMaxmiucNo ratings yet
- Tda 7497Document8 pagesTda 7497Madein ChinaNo ratings yet
- DAC0808 DatasheetDocument12 pagesDAC0808 DatasheetRicky CoxNo ratings yet
- XR 8038aDocument16 pagesXR 8038akeyboard2014No ratings yet
- 3 V To 5 V Single Supply, 200 KSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC AD7858/AD7858LDocument32 pages3 V To 5 V Single Supply, 200 KSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC AD7858/AD7858LJodelCamarinNo ratings yet
- STR W6753 DatasheetDocument8 pagesSTR W6753 DatasheetjgerabmNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- DatasheetDocument4 pagesDatasheetDenendra Pro-AudioNo ratings yet
- Irfp 250 NDocument9 pagesIrfp 250 NjozzemarNo ratings yet
- Example Verilog Unit 5Document8 pagesExample Verilog Unit 5Priyanka JainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VLSI DesignDocument19 pagesIntroduction To VLSI DesignFariyad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Irs 2103Document14 pagesIrs 2103Việt LêNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Questions-2Document8 pagesVlsi Questions-2Chinu SoodNo ratings yet
- 051790D0.sch-1 - Fri Jun 14 09:35:13 2002Document19 pages051790D0.sch-1 - Fri Jun 14 09:35:13 2002Italo BocattuNo ratings yet
- Q 1.an NMOS Has A Substrate Impurity Doping Concen...Document4 pagesQ 1.an NMOS Has A Substrate Impurity Doping Concen...Zulqarnain KhanNo ratings yet
- Advanced TopCon Solar Cells Processing - RENA - RenaDocument2 pagesAdvanced TopCon Solar Cells Processing - RENA - Renaxaxinev359No ratings yet
- Arun Kumar-White PaperDocument1 pageArun Kumar-White PaperAmitNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDocument12 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- A - Semiconductores PDFDocument19 pagesA - Semiconductores PDFAndres GarciaNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument4 pagesSilicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationSebastian ChaileNo ratings yet
- VLSI Assignment 3Document2 pagesVLSI Assignment 3RIONA RACHEL JACOBNo ratings yet
- ملخص يشرح القلابات PDFDocument15 pagesملخص يشرح القلابات PDFZaki Zàkiï Zacharias100% (1)
- Nte 382Document2 pagesNte 382Abel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PhotodiodeDocument4 pagesPhotodiodejullianagabriel1103No ratings yet
- VLSI Problems of Chapter 3Document5 pagesVLSI Problems of Chapter 3Ahsan MoinNo ratings yet
- Linearity and Speed Optimization in SOI LDMOS Using Gate EngineeringDocument22 pagesLinearity and Speed Optimization in SOI LDMOS Using Gate EngineeringMamidala Jagadesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document23 pagesChapter 13Shibin Kuthirummal KNo ratings yet
- 16 Mosfet I-V and C-VDocument22 pages16 Mosfet I-V and C-VAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Ece2034 Flexible-Electronics-And-Sensors TH 1.0 55 Ece2034 PDFDocument2 pagesEce2034 Flexible-Electronics-And-Sensors TH 1.0 55 Ece2034 PDFRithyshNo ratings yet
- 34 Top Electronic Device and Circuits Lab Viva Questions and Answers Electronic Device and Circuits Lab Viva QuestionsDocument7 pages34 Top Electronic Device and Circuits Lab Viva Questions and Answers Electronic Device and Circuits Lab Viva QuestionsDINESHNo ratings yet
- Triac bt137 600Document674 pagesTriac bt137 600Mauricio Garcia50% (2)
- 5 NMDocument4 pages5 NMPiyush AmbulgekarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document45 pagesLesson 3 Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Chacko MathewNo ratings yet
- Schott KyDocument1 pageSchott KyDelos Santos JojoNo ratings yet
- Advanced VLSI Architecture: MEL G624Document16 pagesAdvanced VLSI Architecture: MEL G624Udai ValluruNo ratings yet
- Transition CapacitanceDocument3 pagesTransition CapacitanceVikas Chandra100% (4)
- Experiment No. 1 DC (BJTS)Document13 pagesExperiment No. 1 DC (BJTS)Lawrence Neil PimentelNo ratings yet