Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Short-Circuits
Introduction To Short-Circuits
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Short-Circuits
Introduction To Short-Circuits
Uploaded by
sunny_nsecCopyright:
Available Formats
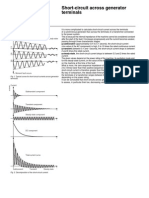
Short-circuit currents
Introduction to short-circuits
Symmetrical components
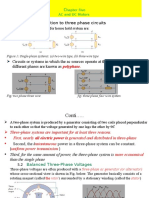
During normal, balanced symmetrical operation, analysis of three-phase systems is similar to that of an equivalent single-phase system, characterized by the phase-toneutral voltages, phase currents and power system impedances (called cyclical impedances). As soon as a significant dissymmetry appears in the configuration or in power system operation, simplification is no longer possible. It is not possible to establish simple electrical relations in the conductors, using the cyclical impedances. In this case, the symmetrical-components method is used, which consists of expressing the real system as a superposition of three independent, single-phase power systems, called: b positive sequence (designated by a subscript 1, e.g. V1), b negative sequence (designated by a subscript 2, e.g. V2), b zero-sequence (designated by a subscript 0, e.g. V0). For each system (positive-, negative- and zero-sequence respectively), voltages V1, V2, V0 and currents I1, I2, I0 are related by the impedances Z1, Z2, Z0 of the same system. The symmetrical impedances are a function of the real impedances, notably the mutual inductances. The notion of symmetrical components is also applicable to power. V1 = V 1 + V 2 + V 0 V2 = a 2 V 1 + a V 2 + V 0 V3 = a V 1 + a 2 V 2 + V 0 where a = e
2 j -----3
1 - ( V1 + a V2 + a 2 V3 ) V 1 = -3 1 - ( V1 + a 2 V2 + a V3 ) V 2 = -3 1 - ( V1 + V2 + V3 ) V 0 = -3 where a = e
2 j -----3
Positive sequence
DE55214EN
Negative sequence V2 2
V31 V3 V1 V2 t V21 V11 V1 2
Zero sequence V10 V20 V30 t
V3 2
Decomposition of a three-phase system into symmetrical components.
Decomposition into symmetrical components is not simply a mathematical technique, it corresponds to the physical reality of the phenomena. It is possible to directly measure the symmetrical components (voltages, currents, impedances) of an unbalanced system. The positive-, negative- and zero-sequence impedances of an element in the power system are the impedances of the element subjected to voltage systems that are, respectively, positive three-phase, negative three-phase and phase-to-earth on three parallel phases. Generators produce the positive-sequence component and faults may produce the negative and zero-sequence components. In the case of motors, the positive-sequence component creates the useful rotating field, whereas the negative-sequence component creates a braking rotating field. For transformers, an earth fault creates a zero-sequence component that produces a zero-sequence field passing through the tank.
13
You might also like
- (English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Document58 pages(English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Sveta EnglishNo ratings yet
- Ybus Matrix With Regulating Transformer - Self Study TopicDocument21 pagesYbus Matrix With Regulating Transformer - Self Study TopicSankar MuthuswamyNo ratings yet
- Tanabe Air Compressor ManualDocument4 pagesTanabe Air Compressor ManualMeta Beta50% (2)
- Symmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsDocument26 pagesSymmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsRTNo ratings yet
- EEE. 2mark and 16 Marks Quest-With AnswerDocument21 pagesEEE. 2mark and 16 Marks Quest-With AnswerPrasanth Govindaraj100% (1)
- Unsymetrical Power Faults2-1Document6 pagesUnsymetrical Power Faults2-1dominique fortierNo ratings yet
- Zero Sequence ImpedanceDocument11 pagesZero Sequence ImpedanceBharat100% (1)
- Oliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 3Document7 pagesOliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 3TheNinjaDragon gamingNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2Document52 pagesModule 5.2Loreto CorderoNo ratings yet
- Power System Fault LabDocument13 pagesPower System Fault LabShubham DwivediNo ratings yet
- Electrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence Impedance - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesElectrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence Impedance - Electrical4ukondareddy0% (1)
- All Lectures Power System IIDocument89 pagesAll Lectures Power System IIعبد الله حمديNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Lecture NoteDocument20 pages3 Phase Lecture NoteMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- Electrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceDocument8 pagesElectrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceMehrdad Nirui100% (1)
- Active Filters With Control Based On The P-Q TheoryDocument8 pagesActive Filters With Control Based On The P-Q TheoryradhathotaNo ratings yet
- Sequence Impedance of ALTERNATORDocument10 pagesSequence Impedance of ALTERNATORkumarchaturvedula75% (4)
- Symmetrical Components PDFDocument21 pagesSymmetrical Components PDFAhmed Fawad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Lec 16 Symmetrical NumericalsDocument10 pagesLec 16 Symmetrical NumericalsQurat Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Three-Phase SystemDocument30 pagesLecture 2: Three-Phase SystemAddi KhattakNo ratings yet
- Lec 2.1Document33 pagesLec 2.1Chamod DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Power in Terms of Symmetrical ComponentsDocument6 pagesPower in Terms of Symmetrical ComponentsKlint TomenaNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis of Three-Phase Power SystemsDocument35 pagesTransient Analysis of Three-Phase Power SystemsBerly NoviantoniNo ratings yet
- Balanced GeneratorDocument6 pagesBalanced GeneratorAbdurrahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Fault Analysis - Part 2Document17 pagesIntro To Fault Analysis - Part 2ChRis dE LeonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Mashood NasirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Symmetrical ComponentsDocument55 pagesLecture 5 - Symmetrical ComponentsGuruvulu BhagamNo ratings yet
- Sequence Impedances of An AlternatorDocument8 pagesSequence Impedances of An AlternatorBhanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document67 pagesChapter 4idris ghousNo ratings yet
- 4 Symmetrical ComponentsDocument4 pages4 Symmetrical ComponentsvirenpandyaNo ratings yet
- 6 +ok+MEASURE+MENT+OF+SEQUENCE+REACTANCES+OF+SALIENT+POLE+SYNCHRONOUS+MACHINEDocument3 pages6 +ok+MEASURE+MENT+OF+SEQUENCE+REACTANCES+OF+SALIENT+POLE+SYNCHRONOUS+MACHINEaissmsNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis of Ac Power System: TH Z VTHDocument7 pagesFault Analysis of Ac Power System: TH Z VTHVibin NivasNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument15 pagesUnsymmetrical Fault Analysiszeemred085100% (1)
- Sequence Impedances of Alternator Aim: Apparatus RequiredDocument10 pagesSequence Impedances of Alternator Aim: Apparatus RequiredLeela KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tests of 3-Phase SystemsDocument26 pagesTests of 3-Phase SystemsNgô KiệtNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis Objective Type QuestionsDocument7 pagesShort Circuit Analysis Objective Type Questionsjiguparmar1516No ratings yet
- Propogation of Unbalance in Electrical Power SystemsDocument5 pagesPropogation of Unbalance in Electrical Power SystemsNeethu EappanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2mesfin snowNo ratings yet
- Lec09 Three PhaseDocument84 pagesLec09 Three Phasebiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- L-L FaultsDocument4 pagesL-L FaultsEngr Saleh AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase AnalysisDocument44 pages3 Phase AnalysisMuruganantham ChandrappanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - Symmetrical Components Unbalanced FaultDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 10 - Symmetrical Components Unbalanced FaultMohd A IshakNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components PDFDocument24 pagesSymmetrical Components PDFtanayspatel100% (1)
- Chapter 8 3 Phase AC CircuitsDocument47 pagesChapter 8 3 Phase AC CircuitsKì Hyö JüngNo ratings yet
- Psa Unit 4Document21 pagesPsa Unit 4Aish KrishNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Systems: M. I - ElsaidDocument25 pagesThree-Phase Systems: M. I - ElsaidعبداللهأحمدNo ratings yet
- 3 Unsymmetrical Faults Eet308 Updated SVDocument74 pages3 Unsymmetrical Faults Eet308 Updated SVAMar RidhwanNo ratings yet
- Three Phase System: Prepared by Mr. Lim Cheng Siong Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument46 pagesThree Phase System: Prepared by Mr. Lim Cheng Siong Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaKenneth ChawNo ratings yet
- Fault Calculation - Symmetrical Components: Basic Symmetrical Component TheoryDocument3 pagesFault Calculation - Symmetrical Components: Basic Symmetrical Component TheoryadauNo ratings yet
- Sequence ComponentsDocument9 pagesSequence Componentsindula123No ratings yet
- Symmetricalfault PPTDocument22 pagesSymmetricalfault PPTpriyanshum230825eeNo ratings yet
- Basic Elec Chapter 5Document19 pagesBasic Elec Chapter 5Nebiyou KorraNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument42 pagesPower System Analysismedanite ashebirNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current RelationshipDocument6 pagesVoltage and Current RelationshipJOHN LLOYD PEREZNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase CircuitsDocument69 pagesThree-Phase CircuitsZhong Kiat TehNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intoduction To Three Phase SystemDocument20 pagesModule 1 - Intoduction To Three Phase SystemEarl Jenn AbellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - 3phase PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 03 - 3phase PDFNguyễn Anh TàiNo ratings yet
- آلات طيران المحاضرة الثامنةDocument46 pagesآلات طيران المحاضرة الثامنةomarjoker808No ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentsDocument61 pagesSymmetrical ComponentsAlcibiades MaytaNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Aer 534 QCDocument48 pagesAer 534 QCsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Industrial and Logistics Light GuideDocument14 pagesIndustrial and Logistics Light Guidesunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case StudyDocument4 pagesLED Lighting at Truck Rest Area: Case Studysunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 9sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 10sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- TGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1Document1 pageTGD 031 Amendments To The M E D 005 For Post Primary Schools 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Stylus Plus Pricelist 2012-13Document2 pagesStylus Plus Pricelist 2012-13sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 1sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 2sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 8sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 6sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 11Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 11sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 4sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 5Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 5sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Pbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3Document1 pagePbu TGD 026 Addendum 1 3sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- NOWA Price ListDocument2 pagesNOWA Price Listsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- H 3-Phase Online Ups Technical SpecificationDocument9 pagesH 3-Phase Online Ups Technical Specificationsunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 24Document1 pageCg0021en 24sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 18Document1 pageCg0021en 18sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Phase-Current Sensors (CT)Document1 pagePhase-Current Sensors (CT)sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Cg0021en 19Document1 pageCg0021en 19sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Short-Circuit Across Generator TerminalsDocument1 pageShort-Circuit Across Generator Terminalssunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Greaves Cotton Ar 2018 1 PDFDocument168 pagesGreaves Cotton Ar 2018 1 PDFanand_parchureNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 8601Document18 pagesAssignment No 1 8601Sobia AtifNo ratings yet
- Impact of AIS On OE of AC in Alabang Muntinlupa PROPER 2Document39 pagesImpact of AIS On OE of AC in Alabang Muntinlupa PROPER 2Kyle Baladad50% (2)
- CME355 MATERIAL HANDLING AND SOLID PROCESSING EQUIPMENT SyallabusDocument1 pageCME355 MATERIAL HANDLING AND SOLID PROCESSING EQUIPMENT SyallabusGanapathiappan VelukumarNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Examination: Physical Activity and The Stages of Behavior Change ModelDocument8 pagesMid Term Examination: Physical Activity and The Stages of Behavior Change Modelapi-457299309No ratings yet
- Twisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical FiberDocument34 pagesTwisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical Fiber7t854s6wd2No ratings yet
- People CodeDocument44 pagesPeople CodehardanuNo ratings yet
- Inductive Deductive QuizDocument1 pageInductive Deductive Quizkimbeerlyn doromasNo ratings yet
- Ma Muse M'Abuse Article - Odd Meters On The Drumset (9/16)Document10 pagesMa Muse M'Abuse Article - Odd Meters On The Drumset (9/16)Jarrod CagwinNo ratings yet
- BhramariDocument4 pagesBhramariRitu TyagiNo ratings yet
- Myth of Hades and PersephoneDocument4 pagesMyth of Hades and PersephoneTikvahNo ratings yet
- Drone pg1Document1 pageDrone pg1kokiuaNo ratings yet
- Verification and Certification of Non-Forum ShoppingDocument13 pagesVerification and Certification of Non-Forum Shoppingromeo luis villonco100% (1)
- Funda Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesFunda Finals Reviewerchloepaxton030No ratings yet
- (J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFDocument259 pages(J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFPaco FernándezNo ratings yet
- Journal Pmed 1003501Document28 pagesJournal Pmed 1003501Abi HinojosaNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSAmanda100% (1)
- LESSON - PLANS Group 6 ACID BASEDocument6 pagesLESSON - PLANS Group 6 ACID BASEindah sinagaNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument2 pagesHRMHariom BhatiNo ratings yet
- An Overview On The Validation Approach For Steam Sterilization - Part II, Madalina Brindusa Boca Et. Al.Document9 pagesAn Overview On The Validation Approach For Steam Sterilization - Part II, Madalina Brindusa Boca Et. Al.bocam100% (1)
- Aviat ODU 600 Product BriefingDocument6 pagesAviat ODU 600 Product BriefingSihejiNo ratings yet
- Requirements DefinitionDocument242 pagesRequirements DefinitionMohsin NazirNo ratings yet
- Camo Paint ManualDocument182 pagesCamo Paint Manualwhsprz100% (1)
- Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreDocument15 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreJoselyn Vallejo PizanánNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementDocument45 pagesMood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementFikatu HugoronNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid and Folates Vitamins and Hormones Volume 79Document443 pagesFolic Acid and Folates Vitamins and Hormones Volume 79Stefania Nicu100% (1)
- ACK NAK EnhancementDocument15 pagesACK NAK Enhancementbasit_engineerNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ekonomi SyariahDocument5 pagesJurnal Ekonomi Syariahjubaidahnurhayati100% (1)