Professional Documents
Culture Documents
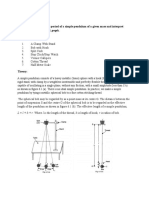
Simple Pendulum Experiment
Simple Pendulum Experiment
Uploaded by
rezzmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Pendulum Experiment
Simple Pendulum Experiment
Uploaded by
rezzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple pendulum
Using a simple pendulum,plot L-T and L-T2 graphs. Hence find the effective length of seconds Aim: pendulum using appropriate graph Apparatus: Simple pendulum, stop clock, vernier callipers, retort stand, split cork and meter scale Theory: The maximum displacement of the vibrating body from its equilibrium position is called its amplitude. The time for one oscillation of the vibrating body is called its period(T).The acceleration of a freely falling body due to earths attraction is called acceleration due to gravity (g). Formula:
T = (2 (l/g))1/2 L = T2g/42
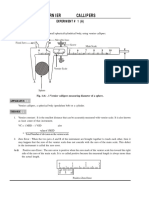
L = length of the pendulum Procedure : The diameter of the bob is determined 3 or 4 times using vernier callipers and its average radius is determined . Determine the diameter of bob(2r): Least count of vernier calipers = 1 main scale division (M.S.D)/No of divisions on the vernier scale = 1/10 =0.1 cm
S.NO
Main scale reading M.S.R(a)cm
Vernier coincidence,n
Fraction b=n*L.C cm
Total reading (a+b) cm
The distance (a) from the point of suspension (c) to the bottom of the bob is measured using scale . From it radius of bob (determined by using v.c) is substracted (a-r) and length of the pendulum (l =ar) it is adjusted to a convenient value (50 cm)
a l =a-r
Radius=r
The bob is drawn to a side giving a small amplitude and released. Then it begins to oscillate in the same vertical plane. After the first few swings, a stop clock is started as the bob passes a fixed mark in one direction and count as zero. When the string passes the fixed mark in the same direction it is count as one. At the end of 20 oscillations, the stop clock is stopped and the time for 20 oscillations is noted. The experiment is repeated twice and the mean time for 20 oscillations is determined. The mean time is divided by 20 to get the time taken for one oscillation or period (T). The value of L/T2 is calculated. The experiment is repeated for different lengths and in each case the value of L/T2 is calculated.
(1) L,T2 Graph : A graph is drawn between L on the X axis and T2 on the Y-axis.The graph is a straight line passing through the origin. From the graph the value of L/T2 is calculated.
T2 4
0 A L
L,T GRAPH: A graph is drawn between the value of L on the X-axis and the value of T on the Y-axis. The graph is a parabola.
Length of seconds Pendulum: For seconds pendulum T=2 and hence T2=4. At 4 on the Y-axis a line parallel to X-axis drawn to cut the graph at a point. From that point a line perpendicular to X-axis is drawn meet on X-axis at A. Then OA gives the length of seconds pendulum.
Determination of L/T2: S.No Length of the Pendulum L cm Time For 20 Oscillations Trial 1 Trial 2 Time period Mean(X) T=X/20 sec
T2
L/T2=constant
Average value of L/T2 =
g=42(L/T2)
Precautions:
cm/s2
1. Amplitude should be small. 2. The bob should not spin as it oscillates in the vertical plane 3. Vernier calipers should be used to find the radius of the bob. Result: The effective length of seconds pendulum =----------------------------------
You might also like
- Lab 13 Compound PendulumDocument4 pagesLab 13 Compound PendulumWaqas Muneer Khan100% (1)
- Experiment - 04 - Simple PendulumDocument12 pagesExperiment - 04 - Simple Pendulumadimegha33% (3)
- Compound PendulumDocument4 pagesCompound Pendulumamit100% (2)
- Simple PendulumDocument11 pagesSimple PendulumGNag R'Varma100% (1)
- Lab Report - Simple PendulumDocument12 pagesLab Report - Simple PendulumAnanyaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum LabDocument2 pagesThe Simple Pendulum LabMichael ComradeGeneral Chenko100% (2)
- Ib Physics ch12 PDFDocument2 pagesIb Physics ch12 PDFHansal Pravin KachharaNo ratings yet
- Torsional PendulumDocument12 pagesTorsional PendulumRichard Puni100% (4)
- The Simple Pendulum (Ver2)Document8 pagesThe Simple Pendulum (Ver2)Abigail ProctorNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4 - Bar Pendulum and Kater's PendulumDocument20 pagesExperiment - 4 - Bar Pendulum and Kater's PendulumDev HalvawalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveDocument2 pagesExperiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveReam MairNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple PendulumReshan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum ExperimentDocument3 pagesSimple Pendulum ExperimentSubesh ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Bar PendulumDocument5 pagesBar Pendulumradhakanta_phy8453No ratings yet
- Experiment 11 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 11 PDFHaroonNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS LAB REPORT NO.6 (Compound Pendulum)Document7 pagesPHYSICS LAB REPORT NO.6 (Compound Pendulum)Rajput JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Determine The Period of Simple Pendulum (Practical)Document1 pageDetermine The Period of Simple Pendulum (Practical)gdsutaNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument15 pagesSimple Pendulumvjpranesh7000100% (1)
- Lab Reports Mechanics, Heat & VibrationsDocument79 pagesLab Reports Mechanics, Heat & VibrationsNabeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design Measure List For Physics P5Document7 pagesDesign Measure List For Physics P5wasiqnisar100% (1)
- Simple Pendulum Lab WriteDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulum Lab WriterezzmanNo ratings yet
- To Measure The Length of A Rod With A Vernier CalipersDocument4 pagesTo Measure The Length of A Rod With A Vernier CalipersMahin SarkarNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument32 pagesSimple PendulumGnana Vishnu Varma PothuriNo ratings yet
- Experiment: To Determine The Value of G' by Kater's Pendulum. Apparatus Used: Theory: ProcedureDocument2 pagesExperiment: To Determine The Value of G' by Kater's Pendulum. Apparatus Used: Theory: Procedureamit75% (4)
- The Simple PendulumDocument8 pagesThe Simple PendulumInu Kag100% (2)
- Exp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationDocument5 pagesExp - 2 Simple Pendulam G DeterminationNahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Sextant by MR - CharisDocument4 pagesSextant by MR - CharisCharis Israel AnchaNo ratings yet
- Expt2 Simplependulum PDFDocument7 pagesExpt2 Simplependulum PDFSharifuddin RumanNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 1)Document10 pagesGroup 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 1)Shoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lab. ReportDocument10 pagesGeneral Physics Lab. ReportBa LamNo ratings yet
- Maxwell NeedleDocument2 pagesMaxwell NeedleKashifChaudhary50% (2)
- A2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017Document3 pagesA2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017AbhiKhanNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/msDocument16 pagesMultiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/mssliversniperNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Lab ReportDocument15 pagesPendulum Lab ReportasifNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Gravitation Worksheet ADocument5 pagesCBSE Class 11 Gravitation Worksheet APrajwal SinghNo ratings yet
- PhyI Assign&Answers 2011Document16 pagesPhyI Assign&Answers 2011Austin Phua Yun Hock100% (1)
- Nitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryDocument3 pagesNitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryVarun Kumar100% (1)
- Practical Physics (Part-I)Document84 pagesPractical Physics (Part-I)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2 Phy 433 1 1 PDFDocument18 pagesLab Report Experiment 2 Phy 433 1 1 PDFHANY NUR AQILAH YUSOFNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 The Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesLab Report 1 The Simple PendulumMohammedSalahNo ratings yet
- Notes For Paper 6Document25 pagesNotes For Paper 6RamY El NahasNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Conceptual QuestionsDocument1 pageVectors - Conceptual QuestionsMalaika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Walter Lewin NotesDocument4 pagesWalter Lewin NotesRomesor ApolNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Vibrating StringsDocument7 pagesExperiment 4 Vibrating StringsDonnaliza Delos Reyes0% (1)
- Worksheet 04 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 04 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForcesDocument19 pagesTurning Effect of ForcesFavaz TajwarNo ratings yet
- 11 SuperpositionDocument75 pages11 SuperpositionRonnie QuekNo ratings yet
- Practical 222Document4 pagesPractical 222Faris 2806100% (1)
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Kabir AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Pendulum LabDocument5 pagesPendulum Labmt9260100% (6)
- Experiment - 3 - Thermal Conductivity of Cu - Searle's ApparatusDocument8 pagesExperiment - 3 - Thermal Conductivity of Cu - Searle's ApparatussurajNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Lab RevisedDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Lab RevisedLeznan DayNo ratings yet
- Real and Apparent Expansion of Liquids Final Draft - Class 8 (HEAT - 2)Document3 pagesReal and Apparent Expansion of Liquids Final Draft - Class 8 (HEAT - 2)Sachin ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesPressure NotesVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- As Physics NotesDocument43 pagesAs Physics Notesleelakdd108100% (1)
- Compound Pendulum Lab ReportDocument11 pagesCompound Pendulum Lab ReportSyedlakhtehassan100% (1)
- Waves Revision MC TestDocument36 pagesWaves Revision MC Testlove_241No ratings yet
- Eee 102 - Exp-3 - 233001310Document6 pagesEee 102 - Exp-3 - 233001310nahianrahman0011No ratings yet
- D.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Bar PendulumDocument2 pagesD.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Bar PendulumVirender RanaNo ratings yet
- Chemidtry Practical Grade 11Document4 pagesChemidtry Practical Grade 11whatever whateverNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum Lab WriteDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulum Lab WriterezzmanNo ratings yet
- Solar Car Activity: David R. BrooksDocument13 pagesSolar Car Activity: David R. BrooksrezzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: RadioactivityDocument19 pagesChapter 5: RadioactivityrezzmanNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document4 pagesModul 1rezzmanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Understanding The Uses of The Cathode-Ray Oscilloscope (Document18 pages4.1 Understanding The Uses of The Cathode-Ray Oscilloscope (rezzmanNo ratings yet
- Copy of The Geography and Ecology Compendium - Disha Publication-ShashiDocument285 pagesCopy of The Geography and Ecology Compendium - Disha Publication-ShashiUsha SinghNo ratings yet
- Solar System KEY PDFDocument32 pagesSolar System KEY PDFAchmad FahrizaNo ratings yet
- Limits of Resolution The Rayleigh Criterion 5Document13 pagesLimits of Resolution The Rayleigh Criterion 5Kaique DantasNo ratings yet
- Refutation of Nilesh Oaks Astronomical DDocument15 pagesRefutation of Nilesh Oaks Astronomical DBharat NarrativesNo ratings yet
- Myths and Legends The Adventures of PerseusDocument4 pagesMyths and Legends The Adventures of PerseussddadhakNo ratings yet
- Ash Taka Varga CalculationDocument3 pagesAsh Taka Varga CalculationSrikanth DharmavaramNo ratings yet
- Science Entrance ExamDocument11 pagesScience Entrance ExamDan GregoriousNo ratings yet
- CPP Code Sun PositionDocument4 pagesCPP Code Sun Positionsiddharthpande777No ratings yet
- CosmologyDocument6 pagesCosmologyMelgeri Aubrey E. UngosNo ratings yet
- Planetary MotionDocument4 pagesPlanetary Motionapi-302899266No ratings yet
- Ncert Solution 11 FullDocument469 pagesNcert Solution 11 FullArkayan LahaNo ratings yet
- (SỐ 21-25) DE THI HSG ANH 9 CAP TINH +FILE NGHE+ DAP ANDocument35 pages(SỐ 21-25) DE THI HSG ANH 9 CAP TINH +FILE NGHE+ DAP ANVy 's Khánh50% (2)
- Earth Science Lesson Plan For Inner and Outer PlanetsDocument4 pagesEarth Science Lesson Plan For Inner and Outer PlanetslarissaNo ratings yet
- IEEE Latin American Robotics Competition For Student RULES OF SEK Category - 2015/2016Document12 pagesIEEE Latin American Robotics Competition For Student RULES OF SEK Category - 2015/2016Gorras New EraNo ratings yet
- Karthika Dass - From Somewhere Out ThereDocument154 pagesKarthika Dass - From Somewhere Out ThereAdina Elena Aruștei100% (1)
- Origin and Structure of The Earth Planet EarthDocument2 pagesOrigin and Structure of The Earth Planet EarthJoenell CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Black HoleDocument18 pagesBlack HoleHussain SarwarNo ratings yet
- The Little Liste: Lvashington, D.CDocument5 pagesThe Little Liste: Lvashington, D.CNur AgustinusNo ratings yet
- The Discovery of America An Out-Growth of The Conquest of The Moors by The Spaniards (1883)Document32 pagesThe Discovery of America An Out-Growth of The Conquest of The Moors by The Spaniards (1883)Tram Dickerson El100% (5)
- Making Graphic Organizers Using A Productivity Software Application2Document7 pagesMaking Graphic Organizers Using A Productivity Software Application2Be Mu NakamaNo ratings yet
- Juno - Pre - Phase A Case-Study PDFDocument34 pagesJuno - Pre - Phase A Case-Study PDFSriramNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Semiannual Report To Congress 1 July - 31 December 1967Document261 pagesEighteenth Semiannual Report To Congress 1 July - 31 December 1967Bob Andrepont100% (2)
- Albert Einstein BiographyDocument4 pagesAlbert Einstein BiographyJamirDiazMechanNo ratings yet
- NewSpace 2014 ProgramDocument47 pagesNewSpace 2014 ProgramSpace Frontier FoundationNo ratings yet
- Abirami Anthaathi, அபிராமி அந்தாதிDocument12 pagesAbirami Anthaathi, அபிராமி அந்தாதிKarthick N0% (1)
- Ramadan Mubarak and Happy EidDocument5 pagesRamadan Mubarak and Happy EidAnnur Childcare centre, DunedinNo ratings yet
- Your Human Design System Getting Started Guide: and Creator of Emergent Coaching and Divine DesignDocument17 pagesYour Human Design System Getting Started Guide: and Creator of Emergent Coaching and Divine DesignPaúl Olea IbarraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Icse ProjectDocument11 pagesTrigonometry Icse ProjectKrishna SenapatiNo ratings yet
- Questions-Senior - Sample 1Document2 pagesQuestions-Senior - Sample 1Ananya Mathur79% (14)
- Field Work No 9 SurveyingDocument17 pagesField Work No 9 SurveyingRalph GalvezNo ratings yet