Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mater
Mater
Uploaded by
Romneck RoveroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mater
Mater
Uploaded by
Romneck RoveroCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
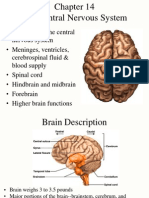
) DURA MATER the outmost layer grayish, though, thick, inelastic, fibrous layer 4 extensions of the dura o Falx Cerebi- separates the 2 hemisphere in a longitudinal plane. o Tentorium Cerebilli- an infolding of the dura that forms a membranous shelf - this supports the cerebral hemisphere s and separates it from the lower parts of the brain - displacement of this brought by increase ICP may cause Tentorial Herniation o Falx Cerebelli separates the cerebellar hemisphere o Diaphragm Sella provides a roof for the sella turnica, the area that houses the pituitary gland 2.) ARACHNOID MATER middle meningeal layer dorsally resembles a spider web appears white because it has no blood supply. contains fingerlike projection called Arachnoid Villi that reabsorbs CSF in a normal adult, about 500ml of CSF is produced / day but only 125- 150ml is reabsorbed when blood enters the system, the villi, may become obstructed and cause hydrocephalus ( increase size of ventricles ) between the dura and the arachnoid is the SUBDURAL SPACE, a potential space.
between the arachnoid and pia mater is the SUBARACHNOID SPACE which contains the CSF
between the skull and the dura in the cranium, to between the peristeum and the dura in the vertebral column is the EPIDURAL SPACE, a potential space. 3.) PIA MATER inner most layer clings tightly to the surface of the spinal cord. FLOW OF CSF Choroids Plexus Lateral Ventricle Foramen of Monroe (space bet. Lateral and 3rd ventricle) rd 3 ventricle Aqueduct of Sylvius th 4 Ventricle Foramen of Magendie (middle) and Luschka (L & R) -3 Subarachnoid space (space bet. arachnoidsd and pia mater) Arachnoid villi Dural sinuses
Venous system (internal jugular vein)
MAJOR NEUROTRANSMITTERS Usually Excitatory, Parasympathetic effort, sometimes inhibitory (stimulation of the heart by vagal nerve) Inhibitory, helps to control mood and sleep , inhibits pain pathways Usually inhibits affect behavior (attention, motion) Fine movement Usually excitatory, affects mood and over all activity
Acetylcholine (major transmitter of PNS)
Substantia Nigra and Basal Ganglia
Serotonin
Brain stem , hypothalamus, dorsal horn of the spinal cord
Dopamine
Many areas of the brain ANS
Norepinephrine ( major transmitter of SNS )
Brainstem , hypothalamus, postganglionic neurons of SNS Spinal cord, cerebellum, basal ganglia Nerve terminals in the spines, brainstem , thalamus and hypothalamus, pituitary gland
Gamma aminobutyric Acid
Excitatory
Enkephalins and Endorphins
Excitatory, pleasurable sensation, inhibitory pain transmission
You might also like
- Cns Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument25 pagesCns Anatomy & PhysiologyAgatha Terencia50% (2)
- Case Study FistulectomyDocument94 pagesCase Study FistulectomyQuolette Constante80% (5)
- Structure of Nervous System: BY Ms SabihaDocument87 pagesStructure of Nervous System: BY Ms SabihaHadia NoorNo ratings yet
- Presentation SHW 32oo, Isnin NiDocument23 pagesPresentation SHW 32oo, Isnin NiAmibella Amirah NabilahNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument49 pagesNeuro AnatomyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- BRAINDocument114 pagesBRAINJaravuy JaravuyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidDocument120 pagesAnatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem: - Located BTWN The Cerebrum and The SCDocument41 pagesBrain Stem: - Located BTWN The Cerebrum and The SCnkuligowskiNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument5 pagesThe BrainTanaya PujareNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument191 pagesNeuro Anatomysirima makuraNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem, Limbic System and Others: By: SufitniDocument42 pagesBrain Stem, Limbic System and Others: By: Sufitniasa0411 behiraNo ratings yet
- 1 Pituitary GlandDocument25 pages1 Pituitary Glandali msheikNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanDocument37 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanAnonymous xfBKTQfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument16 pagesChapter 2 NotesOfeliaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: by Sunil KumarDocument61 pagesCentral Nervous System: by Sunil KumarSUNIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous SystemDocument25 pages3.1 Nervous SystemHARNOOR KAURNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in NeuroanatomyDocument752 pagesLecture Notes in NeuroanatomyDenver NcubeNo ratings yet
- Meninges: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesMeninges: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Meninges &cerebrospinal FluidDocument40 pagesCerebral Meninges &cerebrospinal FluidНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Physio. Psych Structure-Of-The-Nervous-System-Fact-SheetDocument7 pagesPhysio. Psych Structure-Of-The-Nervous-System-Fact-SheetJustynmae JusainNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument11 pagesBrainBilal MashagebahNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: "CNS": Spinal Cord BrainDocument32 pagesCentral Nervous System: "CNS": Spinal Cord BrainAaysha NiyasNo ratings yet
- 11 CSFDocument25 pages11 CSFyadavaryan2004ccNo ratings yet
- Nervous System II: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument29 pagesNervous System II: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- 615d57d2d1f66a1941cfb64d-1633507463-CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument71 pages615d57d2d1f66a1941cfb64d-1633507463-CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEMJana Marie AngwaniNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Brain & Spinal CordDocument36 pagesCentral Nervous System: Brain & Spinal Cordthe_jokosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesDocument5 pagesChapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Curs 14. Sistemul Nervos CentralDocument90 pagesCurs 14. Sistemul Nervos CentralCiprian RataNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata: Mohsen Alenezi Fawaz AlreshedyDocument22 pagesMedulla Oblongata: Mohsen Alenezi Fawaz AlreshedyMhsnNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy - Dubbo 07Document54 pagesNeuro Anatomy - Dubbo 07Lemuel Pamaran del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cns LectureDocument10 pagesCns Lectureferg jeanNo ratings yet
- The Parts and Function of The Brain Presentation For Con ChemDocument45 pagesThe Parts and Function of The Brain Presentation For Con ChemArt MalakiNo ratings yet
- Brain FunctionDocument68 pagesBrain FunctionIdzhamReezaNo ratings yet
- Organization of Nervous System CNSDocument35 pagesOrganization of Nervous System CNSPayal MulaniNo ratings yet
- MENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterDocument34 pagesMENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterfidhavfathimaNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument28 pagesNeurological AssessmentAhmed MuflehNo ratings yet
- The Spinal CordDocument59 pagesThe Spinal CordbegeerizikNo ratings yet
- Crossman-book-summary-fullDocument53 pagesCrossman-book-summary-fullDaniele TomassiNo ratings yet
- Brain & Limbic SystemDocument63 pagesBrain & Limbic Systemgopscharan100% (1)
- 14 The Central Nervous SystemDocument61 pages14 The Central Nervous SystemvanderphysNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain: To Be Reported By: Cris Jaison Maquirang Froilan II PasarabaDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brain: To Be Reported By: Cris Jaison Maquirang Froilan II PasarabaMaquirang Cris JaisonNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument60 pagesSpinal CordPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Dr. Fitriani Lumongga Dr. Lita FeriyawatiDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Dr. Fitriani Lumongga Dr. Lita FeriyawatiWilan Dita NesyiaNo ratings yet
- Preskas Bedah IngDocument19 pagesPreskas Bedah Ingandriana wijayaNo ratings yet
- Physio Review Part 1Document96 pagesPhysio Review Part 1Edralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument26 pagesCerebrumsanthiyasandy100% (1)
- Brain AnatomyDocument30 pagesBrain AnatomyENN KAYNo ratings yet
- 2-Thyroid & Parathyroid GlandsDocument41 pages2-Thyroid & Parathyroid Glandsali msheikNo ratings yet
- PPT2Document47 pagesPPT2CBM UBJOM KALTIMNo ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 2 Meninges Group 1Document4 pagesNs1 Assignment 2 Meninges Group 1Roselle AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Termin SarafDocument26 pagesTermin SarafSyifa KaniaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument98 pagesNervous Systemsolomonchinagorom152No ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex 1Document39 pagesCerebral Cortex 1oluwaseun imoleayoNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psy LectureDocument125 pagesPhysiological Psy LectureKdrama SweetieNo ratings yet
- SPINAL CORD and TRACTSDocument38 pagesSPINAL CORD and TRACTSJames BastesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NOTES 4Document38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NOTES 4mike921goldNo ratings yet
- Meninges PPT NPDocument21 pagesMeninges PPT NPEmshellr RomeNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument28 pagesMeningesayesha rajputNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesUnit 10 - Nervous Systemlola.konjevicNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument17 pagesImmune SystemRomneck RoveroNo ratings yet
- Cancer Awareness: Jose Mari C. Castro, MD, MPH Medical Specialist I DSWD-NCR April 2010Document6 pagesCancer Awareness: Jose Mari C. Castro, MD, MPH Medical Specialist I DSWD-NCR April 2010Romneck RoveroNo ratings yet
- Etiology and PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesEtiology and PathophysiologyRomneck RoveroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To First Aid: Prepared By: Romneck R. Rovero, R.NDocument13 pagesIntroduction To First Aid: Prepared By: Romneck R. Rovero, R.NRomneck RoveroNo ratings yet
- LUIDocument2 pagesLUIRomneck RoveroNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument32 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- SAP Bracket Placement PDFDocument8 pagesSAP Bracket Placement PDFIsrael YumbayNo ratings yet
- New Neet 2020 - Watermarked PDFDocument11 pagesNew Neet 2020 - Watermarked PDFAnangsha DattaNo ratings yet
- Chest Xray PT 2Document41 pagesChest Xray PT 2pvs5155No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoDocument87 pagesCampbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoLawiswisNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Effects of Rapid Maxillary Expansion Followed by Fixed AppliancesDocument5 pagesLong-Term Effects of Rapid Maxillary Expansion Followed by Fixed AppliancesFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- A& P II Assignment 2Document5 pagesA& P II Assignment 2hepnandeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeadDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The HeadVina EmpialesNo ratings yet
- Case Study Typhoid FeverDocument15 pagesCase Study Typhoid FeverLesLie Joy100% (2)
- Techniques in Cognitive Neuroscience: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)Document33 pagesTechniques in Cognitive Neuroscience: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)ANTolaniNo ratings yet
- Gastric Secretion AND Motility: DR Shar Mariam Mohamed Human BiologyDocument45 pagesGastric Secretion AND Motility: DR Shar Mariam Mohamed Human BiologyWahida Amalin Ab RazakNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System HistologyDocument88 pagesLymphatic System Histologydajana212100% (1)
- Step 1 Study Schedule by Organ SystemDocument7 pagesStep 1 Study Schedule by Organ SystemfrabziNo ratings yet
- ArajhkbiDocument29 pagesArajhkbiAdrian NourNo ratings yet
- El Cateterismo Bilateral y Simultáneo de Los Senos Petrosos InferioresDocument8 pagesEl Cateterismo Bilateral y Simultáneo de Los Senos Petrosos InferioresPaoloNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On CholedocholithiasisDocument81 pagesA Case Study On Choledocholithiasischristelle6cadiente67% (9)
- IGCSE Human Biology Chapter 5 NotesDocument3 pagesIGCSE Human Biology Chapter 5 NotesMay Myat Thu0% (1)
- SUPPORTS OF UTERUS ShilpaDocument61 pagesSUPPORTS OF UTERUS ShilpaSreelasya83% (6)
- Thyroid Disorders 1Document53 pagesThyroid Disorders 1Abdulrahman AlshehriNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Anchorage For Orthopedic Correction of Growing Class III PatientsDocument14 pagesSkeletal Anchorage For Orthopedic Correction of Growing Class III PatientsIslam ShakerNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab ManualDocument104 pagesHistology Lab ManualBanyu علي تقويم Biru33% (3)
- KrugerDocument25 pagesKrugerfenimelaniNo ratings yet
- 6 - Unit 30aDocument104 pages6 - Unit 30aArmanda GjokaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueSarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- BSN - 4C: PresentorsDocument52 pagesBSN - 4C: PresentorsHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Gurrea Bruguera IJED 2014Document18 pagesGurrea Bruguera IJED 2014SitiKhadijahNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase Studyllyryc100% (1)
- Composition and Functions of BloodDocument8 pagesComposition and Functions of BloodArianne KimNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Traktus Gastrointestinal: Dr. Ety Sari H, M.KesDocument64 pagesAnatomi Traktus Gastrointestinal: Dr. Ety Sari H, M.KesHatta Diana TariganNo ratings yet