Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Catia Rectangular Beam Analysis
Catia Rectangular Beam Analysis
Uploaded by
UNsha bee komOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Catia Rectangular Beam Analysis
Catia Rectangular Beam Analysis
Uploaded by
UNsha bee komCopyright:
Available Formats
CAD/CAM/CAE example
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
CAD-CAM-CAE example
example title: example number: example level: CAx system: Related material part with TMOP Job Description: Fem analysis of a cantilever beam which is fixed at one end E-A15 basic - medium - advanced CATIA V5 CAD, FEM Build a cantilever beam model which is fixed at one end and make Finite element analysis with CATIA s Generative Structural Analysis module
1.
The task
Determine the deflection of the captured cantilever beam. The cantilever beams material is steel. See below the main parameters. F=1000N a=100mm b=80mm l=1000mm E=210000
F drawned fiber
compressioned fiber l
-h max
CAD/CAM/CAE example 2. The solution steps 2.1. Build the model
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
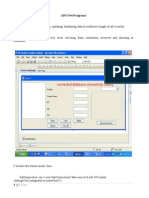
First we build the model of cantilever beam. Draw a sketch with this dimension, and use the pad command and enter 1000 mm in the Length field.
This picture show the sketch. 2.2. Material Properties
In the case no material has been previously assigned to the part, before entering the Generative Structural Analysis workbench, you should proceed as follows: Select the part in the specification tree. Click Apply Material icon. The Material library appears. Select a Metal material family, then select the desired material from the displayed list, select the Steel then click OK. The material is applied.
CAD/CAM/CAE example
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
You can visualize the material properties and its analysis characteristics by selecting the material in the specification tree and using Edit > Properties > Analysis. If you have special material enter the properties here. 3. 3.1. Finite Element Analysis Enter Generative Structural Analysis Workbench. Select Start > Analysis & Simulation > Generative Structural Analysis.
The New Analysis Case dialog box appears with Static Analysis as default option. Static Analysis means that you require a linear static computation by referencing restraints and loads. In this particular case, also keep Static Analysis type selected. Click OK. The CATAnalysis document now opens. It is named Analysis1. You will now perform different operations in this document. A link exist is between the CATPart and the CATAnalysis document.
CAD/CAM/CAE example 3.2. Restraint
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
Click Clamp in the Restraints toolbar. Clamps are restraints applied to surface or curve geometries, for which all points are to be blocked in the subsequent analysis. The Clamp dialog box appears. Select the face at the end of body.
3.3.
Loads
Click Distributed Force in the Loads toolbar. The Distributed Force dialog box appears. Select the supports on which you want to apply a distributed force. Select the face at the end of body opposite clamp side. Enter the -1000 N value in the Z field of Force Vector section.
CAD/CAM/CAE example
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
3.4.
Modify of the Mesh size
Select the mesh part in the specification tree which you want to modify. Click twice on the OCTREE Tetrahedron Mesh.1 : Part1 in the specification tree on the right side of screen. The OCTREE Tetrahedron Mesh dialog box appears.
Change global parameters in the Global tab. Enter 5mm in the Size field. Enter 1mm in the Absolute sage field. Click OK in the OCTREE Tetrahedron Mesh dialog box.
3.5.
Calculation
Click Compute icon. Computing a mesh will enable the analysis of any object of Restraints, Loads and Masses type, without requiring the computation of a solution. The Compute dialog box appears. Select All from the list then click OK. Both the Computation Status dialog box and the Computing... progress bar appear. The progress bar provides a series of status messages (Meshing, Factorization, Solution) that inform you of the degree of advancement of the computation process. 5
CAD/CAM/CAE example
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
3.6
Results Visualization in the Image toolbar. The image is also visualized.
Click Deformation
Click Von Mises Stress in the Image toolbar. The Von Mises stress image is displayed, and a Von Mises Stress (nodal value).1 image appears in the specification tree under the active static case solution. The Von Mises stress distribution on the part is visualized in Isovalue mode, along with a colour palette. You can visualize the Von Mises stress image in different ways by modifying the custom view modes. To do this, select View > Render Style > Customize View. When the mouse cursor is passing over finite elements of the mesh, the values of the Von Mises stress are visualized at each of their nodes.
Click Displacement in the Image toolbar. The translational displacement vector distribution on the part is visualized in arrow symbol mode, along with a colour palette.
CAD/CAM/CAE example
TMOP 4-1-2-08-2-A-KMR-2009-0029
A Translational displacement vector.1 image also appears in the specification tree under Static Case Solution.1. When the mouse cursor is passing over vector arrow symbols, their components with respect to the global reference frame are visualized.
You might also like
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gas Cutting Pressure Tip Chart PDFDocument2 pagesGas Cutting Pressure Tip Chart PDFChozha RajanNo ratings yet
- Blue Book Edition 13-Excerpt PDFDocument257 pagesBlue Book Edition 13-Excerpt PDFMas Ahmad Safwan Masbah100% (4)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- Infrastructure Setup For RPADocument4 pagesInfrastructure Setup For RPAsandeepNo ratings yet
- SAP2000-Example Moving LoadDocument22 pagesSAP2000-Example Moving Loadgustic1100% (2)
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Rexroth Rho 4.1 Rexroth Rho 4.1/IPC300 Connectivity ManualDocument131 pagesRexroth Rho 4.1 Rexroth Rho 4.1/IPC300 Connectivity ManualJohn Forbes NashNo ratings yet
- FRAC W01 ThreePointDocument11 pagesFRAC W01 ThreePointavenashaNo ratings yet
- Me 266 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Virtual Tensile Test Tutorial 1 Problem DescriptionDocument9 pagesMe 266 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Virtual Tensile Test Tutorial 1 Problem DescriptionDeva RajNo ratings yet
- 2d TrussDocument19 pages2d Trussbapu28No ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Pipe Flow Ass 2 Adv Fluid Mech 1Document18 pagesModeling and Simulation of Pipe Flow Ass 2 Adv Fluid Mech 1Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- SAP2000-Example 3D Steel TrussDocument21 pagesSAP2000-Example 3D Steel Trussandyoreta633289% (9)
- Verification Example Preprocessing Solution Postprocessing Command Line Bicycle Example Preprocessing Solution Postprocessing Command LineDocument26 pagesVerification Example Preprocessing Solution Postprocessing Command Line Bicycle Example Preprocessing Solution Postprocessing Command Lineapi-3833671No ratings yet
- SAP2000 Example 3D Steel Truss PDFDocument21 pagesSAP2000 Example 3D Steel Truss PDFkelly maribelNo ratings yet
- Application of Distributed LoadsDocument7 pagesApplication of Distributed LoadsNafees ImitazNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of 3D Steel Truss Using SAP2000Document21 pagesAnalysis and Design of 3D Steel Truss Using SAP2000arjunjonNo ratings yet
- Distributed LoadingDocument6 pagesDistributed LoadingJean David ChanNo ratings yet
- PSG College OFDocument14 pagesPSG College OFKarthic EaswarNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil and Combat Engineering D.E.C DebrezietDocument18 pagesDepartment of Civil and Combat Engineering D.E.C DebrezietHaftom GebreegziabiherNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Using Pro ENGINEER and ANSYSDocument11 pagesFinite Element Method Using Pro ENGINEER and ANSYSsunil481No ratings yet
- ABI UNIT11 W11 LoadCasesDocument11 pagesABI UNIT11 W11 LoadCasesTuanNguễnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1-2 ElasticCantilever V4Document29 pagesTutorial1-2 ElasticCantilever V4abuumayrNo ratings yet
- Basic - Bicycle Space FrameDocument17 pagesBasic - Bicycle Space Framegustavo5150No ratings yet
- TP 19 - Distributed LoadingDocument7 pagesTP 19 - Distributed LoadingFatima FatimaNo ratings yet
- Vps 2008 Educ Example 1Document28 pagesVps 2008 Educ Example 1Charan KumarNo ratings yet
- Application of Distributed LoadsDocument7 pagesApplication of Distributed Loadsakroma123No ratings yet
- Defining A Linear Static AnalysisDocument4 pagesDefining A Linear Static AnalysisPraveen SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To Abaqus/ CaeDocument9 pagesQuick Guide To Abaqus/ CaeginejonathanNo ratings yet
- Abaqus GuideDocument9 pagesAbaqus GuidePravin AwalkondeNo ratings yet
- Sap2000 BeamDocument21 pagesSap2000 BeamRicardo Rabelo75% (4)
- QA-CAD Software Installation Beginners GuideDocument42 pagesQA-CAD Software Installation Beginners GuideDorivalNo ratings yet
- Non Linear AnalysisDocument53 pagesNon Linear AnalysisdpksobsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Star-Ccm+: FeaturesDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Star-Ccm+: Featuresintro3873No ratings yet
- Tyler Wing Section TuturialDocument6 pagesTyler Wing Section TuturialbenjiworldNo ratings yet
- Asce 7Document20 pagesAsce 7Anonymous tBhJoH5wgMNo ratings yet
- U of A ANSYS Tutorials - NonLinear MaterialsDocument8 pagesU of A ANSYS Tutorials - NonLinear Materialskiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- 2 - Design OptimizationDocument14 pages2 - Design OptimizationBaljinder SinghNo ratings yet
- 1Document25 pages1Idehen KelvinNo ratings yet
- SaP NoteDocument6 pagesSaP NoteGautam KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Workshop 7 Abaqus XFEM Pressure VesselDocument13 pagesWorkshop 7 Abaqus XFEM Pressure VesselMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Iaba Unit02 w02 LoadcasesDocument10 pagesIaba Unit02 w02 LoadcasesHemanthMunuNo ratings yet
- 2D Analysis of Cantilver Beam Subjected To Point LoadDocument14 pages2D Analysis of Cantilver Beam Subjected To Point LoadNEELIMANo ratings yet
- SAP2000 Example Prestress BeamDocument28 pagesSAP2000 Example Prestress BeamHugoStiglic100% (4)
- Ansys ExperimentsDocument10 pagesAnsys ExperimentsASIST MechNo ratings yet
- SAP2000-Example 2D Steel TowerDocument23 pagesSAP2000-Example 2D Steel Towerandyoreta6332100% (4)
- Prewhitening With SPSSDocument4 pagesPrewhitening With SPSSSylvia CheungNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Getting Start Cae 2Document10 pagesLecture 1 Getting Start Cae 2CKNo ratings yet
- NonLinear MaterialsDocument12 pagesNonLinear MaterialsNafees ImitazNo ratings yet
- Design OptimizationDocument15 pagesDesign Optimizationakroma123No ratings yet
- Application of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleDocument6 pagesApplication of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A Titlesilverknights007No ratings yet
- 156 - Understanding Dynamic Random AnalysesDocument20 pages156 - Understanding Dynamic Random AnalysesSameOldHatNo ratings yet
- Analyse and Design of Truss by STADProDocument18 pagesAnalyse and Design of Truss by STADProSuvajit BisaiNo ratings yet
- ProCAST20091 TutorialsDocument213 pagesProCAST20091 TutorialsKmilo Giraldo100% (1)
- TIME SERIES FORECASTING. ARIMAX, ARCH AND GARCH MODELS FOR UNIVARIATE TIME SERIES ANALYSIS. Examples with MatlabFrom EverandTIME SERIES FORECASTING. ARIMAX, ARCH AND GARCH MODELS FOR UNIVARIATE TIME SERIES ANALYSIS. Examples with MatlabNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision Graph Cuts: Exploring Graph Cuts in Computer VisionFrom EverandComputer Vision Graph Cuts: Exploring Graph Cuts in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements for Truss and Frame Structures: An Introduction Based on the Computer Algebra System MaximaFrom EverandFinite Elements for Truss and Frame Structures: An Introduction Based on the Computer Algebra System MaximaNo ratings yet
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingFrom EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements Using Maxima: Theory and Routines for Rods and BeamsFrom EverandFinite Elements Using Maxima: Theory and Routines for Rods and BeamsNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ship Design EngineeringDocument69 pagesIntroduction Ship Design EngineeringUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- NavyDocument74 pagesNavyUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Design of A 4-SeatDocument46 pagesDesign of A 4-SeatUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Parametric 3dDocument131 pagesAircraft Parametric 3dUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Aero 7sem Ae2404lmDocument35 pagesAero 7sem Ae2404lmUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- FULLTEXT01Document117 pagesFULLTEXT01UNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Project-1 of Fighter byDocument82 pagesAircraft Design Project-1 of Fighter byUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Darrin Willis Masters Thesis Corrected FinalDocument167 pagesDarrin Willis Masters Thesis Corrected FinalUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- 63 B 3Document4 pages63 B 3UNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy FULLTEXT01Document99 pagesWind Energy FULLTEXT01UNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Turbine Hill Dig Thesis PDFDocument210 pagesKaplan Turbine Hill Dig Thesis PDFUNsha bee kom100% (2)
- Impact Assessment Case Studies From Southern Africa: SaieaDocument14 pagesImpact Assessment Case Studies From Southern Africa: SaieaUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- R&D Planning and Governance: Ronald P. Evens and Joel CovinskyDocument34 pagesR&D Planning and Governance: Ronald P. Evens and Joel CovinskyUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis: Analyzing Pressure Vessels Using Fea in CatiaDocument6 pagesFinite Element Analysis: Analyzing Pressure Vessels Using Fea in CatiaUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Cycloidal TrajectorysimulinkDocument8 pagesCycloidal TrajectorysimulinkUNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionDocument51 pagesChapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionUNsha bee kom100% (1)
- Aircraft Equations of Motion - 2Document26 pagesAircraft Equations of Motion - 2UNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Ado.NetDocument58 pagesAdo.NetShailendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- HD9 1.1.x DICOM Conformance StatementDocument121 pagesHD9 1.1.x DICOM Conformance Statementotrupon melliNo ratings yet
- t000004112 Filename2 Barauni TechDocument251 pagest000004112 Filename2 Barauni TechNikhil KarkeraNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Setup - Kali - Metasploitable - Live AttackDocument10 pagesLab 2 - Setup - Kali - Metasploitable - Live Attackmira7122002No ratings yet
- m120 PartsDocument6 pagesm120 PartsParamedico GuadalajaraNo ratings yet
- Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 - Lab GuideDocument5 pagesInterconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 - Lab GuideDenis AparicioNo ratings yet
- Sap 4/hanaDocument13 pagesSap 4/hanaTchordach2020No ratings yet
- Idrac9 6xx RacadmDocument176 pagesIdrac9 6xx RacadmCatalin GabrielNo ratings yet
- Coding GuidelinesDocument14 pagesCoding GuidelinesEddie ScarpaNo ratings yet
- TAC+Xenta+527+NPR FeatureBlastDocument3 pagesTAC+Xenta+527+NPR FeatureBlastMihai ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- README InstallerDocument3 pagesREADME InstallerDaniel PachecoNo ratings yet
- Cityzen Research PaperDocument8 pagesCityzen Research PaperDolly MehraNo ratings yet
- 15,16 2 Mark SEQADocument32 pages15,16 2 Mark SEQAbhuvi2312No ratings yet
- Razer Ouroboros & Synapse 2 PDFDocument14 pagesRazer Ouroboros & Synapse 2 PDFBruno LubeNo ratings yet
- Practice For JavascriptDocument19 pagesPractice For JavascriptMr. BossNo ratings yet
- Check WASSCE Result Check WASSCE Result Online Online: You May Like This - You May Like ThisDocument1 pageCheck WASSCE Result Check WASSCE Result Online Online: You May Like This - You May Like Thishardi HuseinNo ratings yet
- MSN MSGRDocument892 pagesMSN MSGRHammad TariqNo ratings yet
- CMS SM1281 RMS DOC V3 1 enDocument43 pagesCMS SM1281 RMS DOC V3 1 enRARBG TOP 10 MOVIES DIRECT LINKNo ratings yet
- LVM Version 2.0 Volume Groups in HP-UX 11i v3Document31 pagesLVM Version 2.0 Volume Groups in HP-UX 11i v3robinNo ratings yet
- TV Led M2252D-PS LGDocument36 pagesTV Led M2252D-PS LGMaurilio CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Surveillance Camera WithDocument12 pagesBuild Your Own Surveillance Camera WithibnuramadhanNo ratings yet
- Autocad Architecture: Admec Multimedia InstituteDocument15 pagesAutocad Architecture: Admec Multimedia Institutebluesky_1976No ratings yet
- API Code For Truss OptimizerDocument3 pagesAPI Code For Truss OptimizerarazNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Graphql in Action 1St Edition Samer Buna Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Graphql in Action 1St Edition Samer Buna Online Ebook All Chapter PDFnatalie.oconnor713100% (9)
- 75 Target Controlled Infusions in Anaesthetic PracticeDocument10 pages75 Target Controlled Infusions in Anaesthetic PracticeadamkurniawandanaNo ratings yet
- Vuejs Design Patterns Best PracticesDocument418 pagesVuejs Design Patterns Best Practicesmarcos100% (1)
- Module-3-E.Tech Part 2Document5 pagesModule-3-E.Tech Part 2Lalaine Cababa Opsima-JoveNo ratings yet