Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sound Waves Physics Lab
Sound Waves Physics Lab
Uploaded by
Arius ArandiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sound Waves Physics Lab
Sound Waves Physics Lab
Uploaded by
Arius ArandiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Sound waves longitudinal, mechanical wave, exists as variations of pressure in a medium.
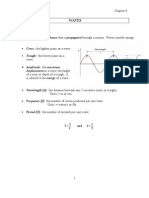
. Can be created by vibration of an object which causes the surround air to vibrate. 3 characteristics to describe sound waves: 1.) Wavelength () crest of one wave to the next. 2.) Frequency (f) no. of waves that pass a point per second. 3.) Amplitude (a) measure of amount of energy. Crest highest point of the wave. Trough lowest point of the wave. Transverse wave Direction of particle is up/down while the direction of the wave is horizontal. Direction is perpendicular to the particle. Longitudinal wave sound direction of particle is parallel to the direction of the wave. Compression = Crest Rarefaction = Trough
Amplitude modulation = longer , lower f Frequency modulation = higher f, shorter
Where; V=velocity of sound wave f=frequency =wavelength Closed-pipe = 4L Open-pipe= 2L Grad cylinder: =4[L+0.3D] L=length of air column D=diameter Sound and temperature: V = 331m/s + 0.6 T
You might also like
- Introduction Coursework STPMDocument4 pagesIntroduction Coursework STPMSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves Lecture PPT (Wave Motion Part 2)Document37 pagesSound Waves Lecture PPT (Wave Motion Part 2)Leilani Manalaysay100% (1)
- Edexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointDocument92 pagesEdexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointAnonymous tlSLEPRRe92% (12)
- The Nature and Properties of WavesDocument24 pagesThe Nature and Properties of WavesMeryl PalenciaNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument65 pagesWAVESArman Leal Bernardo100% (1)
- WavesDocument34 pagesWavesBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Lecture 1Document32 pagesAcoustics Lecture 1Sonisha Aryal100% (1)
- The Nature and Properties of WavesDocument19 pagesThe Nature and Properties of Waves7-SAL 2022No ratings yet
- Sound WaveDocument4 pagesSound WaveFS21EC011No ratings yet
- Sounds and AcousticsDocument11 pagesSounds and AcousticsSikari LocoNo ratings yet
- Sound Class 9Document7 pagesSound Class 9sohan.gspatilNo ratings yet
- HKPhO - 13vbnvbnvbnv BNV BNVBNDocument28 pagesHKPhO - 13vbnvbnvbnv BNV BNVBNSumihar SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Waves - Lecture 1Document45 pagesWaves - Lecture 1Hisham MohamedNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Types of WavesDocument5 pagesThere Are Two Types of WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17.1-3Document34 pagesChapter 17.1-3Cielo PerdomoNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 10533Document13 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 10533Vinayak RamdhunNo ratings yet
- Idebe Physics 4 1Document147 pagesIdebe Physics 4 1May Nang'onde75% (8)
- WavesDocument36 pagesWavesjomelleann.pasolNo ratings yet
- What Does Hooke's Law Mean?Document15 pagesWhat Does Hooke's Law Mean?Bassem KhalidNo ratings yet
- AccousticsDocument62 pagesAccousticsSahil MistryNo ratings yet
- 9 Science TP 12 1Document5 pages9 Science TP 12 1SaurabhNo ratings yet
- 9780 - Week 2 - Sound WavesDocument3 pages9780 - Week 2 - Sound Wavesvivianada683No ratings yet
- Wave 7Document2 pagesWave 7Ma. Bernadette EballeNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties: Secondary 3 PhysicsDocument13 pagesGeneral Wave Properties: Secondary 3 PhysicsShakil MalikNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument65 pagesWavesMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A WaveDocument28 pagesAnatomy of A WaveAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument21 pagesSoundhardik singh cheemaNo ratings yet
- ch11 2Document90 pagesch11 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Ch-12 SoundDocument21 pagesCh-12 SoundManthan MudgalNo ratings yet
- Waves: Physical Science 1Document7 pagesWaves: Physical Science 1SivaramaKrishnanNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesIfrah ZiaNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument42 pagesVibrations and WavesAdal GanisNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 w4Document2 pagesLas Science 7 w4Darven CinchezNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal WaveDocument5 pagesLongitudinal WaveChristineNo ratings yet
- 10 WavesDocument36 pages10 Wavesfitrifisika07No ratings yet
- Form 2 18 WavesDocument19 pagesForm 2 18 WavesMAGDALENE MWANGANGINo ratings yet
- 8.1a Properties - of - WavesDocument31 pages8.1a Properties - of - WavesNoel John UmallaNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument21 pagesSOUNDdav borlNo ratings yet
- The World Communicates James SaraDocument11 pagesThe World Communicates James SaraJames coleNo ratings yet
- Waves Study MAterialDocument16 pagesWaves Study MAterialSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes - Waves Part 1Document3 pagesPhysics Notes - Waves Part 1ankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument37 pagesWavesmohammed issaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument53 pagesSoundlvsaruNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument5 pagesWavesGedeon PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Building Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Document97 pagesBuilding Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Mahamud MusaNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound: Younes SinaDocument30 pagesWaves and Sound: Younes SinayounessinaNo ratings yet
- 18 Arc 74 AcousticsDocument25 pages18 Arc 74 Acousticssuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- Physics - WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics - WavesMemory SitambuliNo ratings yet
- Unit-I (INTRODUTION)Document30 pagesUnit-I (INTRODUTION)GokulNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument21 pagesSounduma mishraNo ratings yet
- WAVESjsjDocument4 pagesWAVESjsjtinotaku58No ratings yet
- Waves GOODDocument92 pagesWaves GOODSuriani DharmaNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- Phy CHAPTER 4Document5 pagesPhy CHAPTER 4Krystal KagamiNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Velocity of SoundDocument23 pagesExpt. 7 Velocity of SoundKatMV100% (1)
- UT Level IIDocument170 pagesUT Level IIhabayeb165No ratings yet
- 1.1 Wave and VibrationDocument24 pages1.1 Wave and VibrationHanif HussinNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet