Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Uploaded by
monkeyriddleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology, 5th Edition - Robert WeaverDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology, 5th Edition - Robert WeaverTee Bee40% (5)
- Microbial GrowthDocument12 pagesMicrobial GrowthJosé MolinerosNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Document5 pagesLab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Ezad juferiNo ratings yet
- What Is Blotting ?Document31 pagesWhat Is Blotting ?sankarNo ratings yet
- Mining Sequence in Biological DataDocument89 pagesMining Sequence in Biological DataAbhinav BarikNo ratings yet
- Definition of AutoradiographyDocument1 pageDefinition of AutoradiographyRoshadahIqbalNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 4: Advance Molecular GeneticsDocument9 pagesAssignment No. 4: Advance Molecular GeneticshajraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code 2020Document20 pagesGenetic Code 2020PAVITHRA SNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology AssignmentDocument10 pagesMolecular Biology Assignmentbiya18No ratings yet
- Histological Techniques: A) Light Microscopy B) Fluorescent Microscopy C) Electron Microscopy D) AutoradiographyDocument17 pagesHistological Techniques: A) Light Microscopy B) Fluorescent Microscopy C) Electron Microscopy D) AutoradiographyJess LeungNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document4 pagesLab Report 1May Chan50% (2)
- BCH 226: Basic Molecular Biology (Jibril Liman) : Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ChromosomesDocument9 pagesBCH 226: Basic Molecular Biology (Jibril Liman) : Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ChromosomesSHALOM SULENo ratings yet
- Blotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemDocument33 pagesBlotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemPrasanna BabuNo ratings yet
- pyMOL ReportDocument11 pagespyMOL Reportkelvinkiplaa845No ratings yet
- Agarose Formaldehyde Ethidium Bromide Polyacrylamide UreaDocument3 pagesAgarose Formaldehyde Ethidium Bromide Polyacrylamide UreaSAMUELNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechniquesDocument33 pagesBlotting TechniquesAteef MarwatNo ratings yet
- By: Prabhat Khare: Asst. ProfessorDocument25 pagesBy: Prabhat Khare: Asst. ProfessorSUMIT KUMAR PANDITNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechDocument6 pagesBlotting Technitu85sethNo ratings yet
- Barry Schweitzer Et Al - Immunoassays With Rolling Circle DNA Amplification: A Versatile Platform For Ultrasensitive Antigen DetectionDocument7 pagesBarry Schweitzer Et Al - Immunoassays With Rolling Circle DNA Amplification: A Versatile Platform For Ultrasensitive Antigen DetectionGmso3No ratings yet
- Citation Lee20 /L 1033Document7 pagesCitation Lee20 /L 1033Garcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Document36 pagesAmplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Muhammad Achin YasinNo ratings yet
- Discover BiologyDocument63 pagesDiscover BiologyAndra Sabina ValeanuNo ratings yet
- Protein MicroarrayDocument5 pagesProtein Microarraysudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- Module IV-Screening of ClonesDocument14 pagesModule IV-Screening of ClonesAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Robert Morfin Et Al - Neurosteroids: Pregnenolone in Human Sciatic NervesDocument4 pagesRobert Morfin Et Al - Neurosteroids: Pregnenolone in Human Sciatic NervesLonkesNo ratings yet
- Protein Chip Protein MicroarrayDocument53 pagesProtein Chip Protein Microarrayfalcon274100% (1)
- 5.1 Blotting TechniquesDocument33 pages5.1 Blotting TechniquesAmir Al-Aiman100% (1)
- Westren and Northern BlottingDocument13 pagesWestren and Northern BlottingGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Clone Identification, Screening, SelectionDocument21 pagesClone Identification, Screening, SelectionPhytomenadione La Vitamine KNo ratings yet
- 5 - Orthogonal Genetic SystemsDocument18 pages5 - Orthogonal Genetic SystemsHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- SB251 - Genetic Code Oct512Document22 pagesSB251 - Genetic Code Oct512Siddharth Rajamohanan100% (1)
- (BIF 401) Current Solved Papers.Document16 pages(BIF 401) Current Solved Papers.Sagheer MalikNo ratings yet
- High Resolution Electrophoresis of Human Plasma Proteins: Two-DimensionalDocument5 pagesHigh Resolution Electrophoresis of Human Plasma Proteins: Two-DimensionalJheny LopezNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechniqueDocument34 pagesBlotting TechniqueUmair100% (2)
- 235 Recombinant DNA Technology BlottingDocument23 pages235 Recombinant DNA Technology BlottingAme Grace DubeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0006349518316114 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 S0006349518316114 MainDiego TulcanNo ratings yet
- AutoradiographyDocument12 pagesAutoradiographyMoner ManushNo ratings yet
- I) Using Isolated Organ / Tissues:: Ex.: Roots and Leaves For Study of Nicotiana and Datura, Petal Disc For StudyDocument22 pagesI) Using Isolated Organ / Tissues:: Ex.: Roots and Leaves For Study of Nicotiana and Datura, Petal Disc For Studypreetisingh17No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Verna Jean M. Magdayao 3/Bsbiology/ADocument56 pagesPrepared By: Verna Jean M. Magdayao 3/Bsbiology/AKathleya PeñaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Studying The Nervous System: OutlineDocument34 pagesMethods of Studying The Nervous System: OutlineMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics - Study ResourcesDocument2 pagesDiagnostics - Study Resourcesakankshapehlinov20No ratings yet
- Bioinfo Final PracticalDocument66 pagesBioinfo Final PracticalPolu ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- I. Determining Protein Amino Acid SequenceDocument4 pagesI. Determining Protein Amino Acid Sequenceganesh2gigNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequence of The Streptomycin-Producing MicroorganismDocument11 pagesGenome Sequence of The Streptomycin-Producing MicroorganismMatthew LareenNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument23 pagesDNA Sequencingrr48843100% (1)
- MBII - L9 - Gene Cloning 4 - Advanced Gene CloningDocument4 pagesMBII - L9 - Gene Cloning 4 - Advanced Gene CloningMiles NsgNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesBiotechnologyAnit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Bif 401 100% Solved Final Term Paper by Sulman AliDocument5 pagesBif 401 100% Solved Final Term Paper by Sulman AliArt TechNo ratings yet
- Nick Translation Primer Extension RNA Polymerase End Labelling Direct LabellingDocument3 pagesNick Translation Primer Extension RNA Polymerase End Labelling Direct LabellingShubha Rani SharmaNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 Session NotesDocument5 pagesPBL 3 Session NotesJon. . .No ratings yet
- Blotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Document31 pagesBlotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Amina ChNo ratings yet
- Molecular MethodsDocument8 pagesMolecular MethodspriyaNo ratings yet
- Dintzis ExerciseDocument5 pagesDintzis ExerciserichschurNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideDocument22 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211No ratings yet
- Continuation of GenetechnologyyDocument7 pagesContinuation of GenetechnologyySemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- BLOTTING TECHNIQUE p-1Document27 pagesBLOTTING TECHNIQUE p-1Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- BIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Document23 pagesBIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Awais BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Using Web Application of ProtParam, PeptideCutter, Compute Pi / MW, TMHMM, SignalPDocument24 pagesUsing Web Application of ProtParam, PeptideCutter, Compute Pi / MW, TMHMM, SignalPEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- Escherichia ColiDocument10 pagesEscherichia ColisurendrasrawanNo ratings yet
- Practical Laboratory Medicine: Gilles Cauet, Aurélien Daynès, Nevzat TemurokDocument7 pagesPractical Laboratory Medicine: Gilles Cauet, Aurélien Daynès, Nevzat TemurokFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Carotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975From EverandCarotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975B. C. L. WeedonNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: Making precision medicine possibleFrom EverandFast Facts: Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: Making precision medicine possibleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 5Document10 pagesQuarter 4 Module 5jiyuskie09No ratings yet
- (Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Document321 pages(Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Heruko Fatimah100% (1)
- Bioabsorption of MetalsDocument26 pagesBioabsorption of MetalsHamza NoorNo ratings yet
- Sathyanarayan Biochemistry 4epdfDocument35 pagesSathyanarayan Biochemistry 4epdfAbubakar SuleimanNo ratings yet
- MSC 1 Sem Bio Chemistry Advanced Enzymology CP 3 Jun 2016Document1 pageMSC 1 Sem Bio Chemistry Advanced Enzymology CP 3 Jun 2016Devashish SahasrabudheNo ratings yet
- DemyelinatingDocument78 pagesDemyelinatingaslan tonapaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd EditionDocument61 pagesGenetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd Editionjulia.swanson282100% (51)
- 9 BioDocument3 pages9 BioAnubhav jhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16 - 1 Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesLesson 16 - 1 Reading Comprehensionstorming25No ratings yet
- B Kon 2020 SouvenirDocument67 pagesB Kon 2020 SouvenirAmbaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis y MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis y MeiosisEdmundo Samaniego GuzmánNo ratings yet
- n094 NeuroscienceDocument74 pagesn094 NeuroscienceAnnaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionDocument25 pagesFrom Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionPUBG HackerNo ratings yet
- Discussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAINDocument4 pagesDiscussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAINKesha Gopal100% (4)
- 1 s2.0 S0006291X18325117 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0006291X18325117 Main PDFMerianaNo ratings yet
- Dasar-Dasar Biomolekuler Reproduksi Wanita: Rahmatina B. HermanDocument29 pagesDasar-Dasar Biomolekuler Reproduksi Wanita: Rahmatina B. HermansilmiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT Notes PDFDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT Notes PDFJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cell - Volumes1 and 2 David E. MetzlerDocument940 pagesBiochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cell - Volumes1 and 2 David E. Metzlerysmnsnmz100% (7)
- Bio Trial Paper SET 1Document8 pagesBio Trial Paper SET 1m-7319562No ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation V Inhibitors and UncouplersDocument15 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation V Inhibitors and UncouplersIffatnazNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Lysosome and Peroxisome: March 2017Document10 pagesDifference Between Lysosome and Peroxisome: March 2017HNZY IAFSNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Report 6 ActualDocument4 pagesBiology Lab Report 6 ActualMunachi Hugh MbaezueNo ratings yet
- Drug TargetsDocument34 pagesDrug TargetsmajedNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Regulation of Fermentation Processes PDFDocument12 pagesMetabolic Regulation of Fermentation Processes PDFqketzaNo ratings yet
- Reporting ScripttDocument4 pagesReporting Scripttnicole besarioNo ratings yet
- Ix-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupDocument3 pagesIx-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupTaroobaNo ratings yet
- Protein Estimation ReportDocument3 pagesProtein Estimation ReportSudip MajiNo ratings yet
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5Document34 pagesBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5SDO BSNL NALAGARHNo ratings yet
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Uploaded by
monkeyriddleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Auto Radiography and Science and Technology
Uploaded by
monkeyriddleCopyright:
Available Formats
Autoradiography:
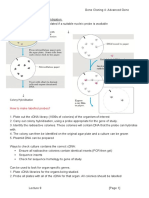
See Karp, chapter 18, section 18.4, pp. 730-731 Autoradiography is used to detect and to localize cell components (e.g., proteins; mRNA) based on their incorporation of radioactive precursor molecules. An alternative approach covalently links a radioactive tag to pre-existing macromolecules. Both techniques generate isotopically labeled macromolecules that can easily be detected by autoradiography against a negative background of unlabeled molecules and structures. The most commonly used isotopes for labeling biological material are: 14C amino acids; 3H amino acids; or 35S amino acids for labeling protein synthesis. 3H thymidine; or 32P - thymidine for labeling DNA synthesis 3H uridine or 32P uridine for labeling RNA synthesis Pre-existing proteins and other macromolecules with free NH2 groups can also be labeled by the Iodogen Reaction, which enzymatically links 125 Iodine or 131 Iodine to free amino groups. (carbohydrate and lipid synthesis can also be isotopically labeled by various means) Experimental protocol: 1. Expose live cells or tissues in culture, or inject live animals, with radioisotope precursor of choice. (e.g., 14C leucine to label proteins being synthesized) 2. After desired labeling interval (either continuous or pulse-chase), fix and section cell or tissue specimen and place on microscope slide. 3. Cover specimen with a photographic emulsion containing AgNO3 or cover with X-ray film. 4. Let specimen develop (beta emissions from isotope decay reduce Ag+ to Ago, creating a black spot or track of emissions). The number and intensity of the spots are proportional to the number of macromolecules that have incorporated the isotope. 5. Examine (usually by light or electron microscopy) specimen for black spots revealing the location of the protein, DNA, or RNA that was synthesized during the exposure to the labeled precursor. Note: autoradiography can also be performed on blots of proteins (western blots) or nucleic acids (southern and northern blots) after they have been resolved by electrophoresis.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology, 5th Edition - Robert WeaverDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology, 5th Edition - Robert WeaverTee Bee40% (5)
- Microbial GrowthDocument12 pagesMicrobial GrowthJosé MolinerosNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Document5 pagesLab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Ezad juferiNo ratings yet
- What Is Blotting ?Document31 pagesWhat Is Blotting ?sankarNo ratings yet
- Mining Sequence in Biological DataDocument89 pagesMining Sequence in Biological DataAbhinav BarikNo ratings yet
- Definition of AutoradiographyDocument1 pageDefinition of AutoradiographyRoshadahIqbalNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 4: Advance Molecular GeneticsDocument9 pagesAssignment No. 4: Advance Molecular GeneticshajraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code 2020Document20 pagesGenetic Code 2020PAVITHRA SNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology AssignmentDocument10 pagesMolecular Biology Assignmentbiya18No ratings yet
- Histological Techniques: A) Light Microscopy B) Fluorescent Microscopy C) Electron Microscopy D) AutoradiographyDocument17 pagesHistological Techniques: A) Light Microscopy B) Fluorescent Microscopy C) Electron Microscopy D) AutoradiographyJess LeungNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document4 pagesLab Report 1May Chan50% (2)
- BCH 226: Basic Molecular Biology (Jibril Liman) : Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ChromosomesDocument9 pagesBCH 226: Basic Molecular Biology (Jibril Liman) : Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ChromosomesSHALOM SULENo ratings yet
- Blotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemDocument33 pagesBlotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemPrasanna BabuNo ratings yet
- pyMOL ReportDocument11 pagespyMOL Reportkelvinkiplaa845No ratings yet
- Agarose Formaldehyde Ethidium Bromide Polyacrylamide UreaDocument3 pagesAgarose Formaldehyde Ethidium Bromide Polyacrylamide UreaSAMUELNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechniquesDocument33 pagesBlotting TechniquesAteef MarwatNo ratings yet
- By: Prabhat Khare: Asst. ProfessorDocument25 pagesBy: Prabhat Khare: Asst. ProfessorSUMIT KUMAR PANDITNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechDocument6 pagesBlotting Technitu85sethNo ratings yet
- Barry Schweitzer Et Al - Immunoassays With Rolling Circle DNA Amplification: A Versatile Platform For Ultrasensitive Antigen DetectionDocument7 pagesBarry Schweitzer Et Al - Immunoassays With Rolling Circle DNA Amplification: A Versatile Platform For Ultrasensitive Antigen DetectionGmso3No ratings yet
- Citation Lee20 /L 1033Document7 pagesCitation Lee20 /L 1033Garcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Document36 pagesAmplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (Aflp)Muhammad Achin YasinNo ratings yet
- Discover BiologyDocument63 pagesDiscover BiologyAndra Sabina ValeanuNo ratings yet
- Protein MicroarrayDocument5 pagesProtein Microarraysudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- Module IV-Screening of ClonesDocument14 pagesModule IV-Screening of ClonesAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Robert Morfin Et Al - Neurosteroids: Pregnenolone in Human Sciatic NervesDocument4 pagesRobert Morfin Et Al - Neurosteroids: Pregnenolone in Human Sciatic NervesLonkesNo ratings yet
- Protein Chip Protein MicroarrayDocument53 pagesProtein Chip Protein Microarrayfalcon274100% (1)
- 5.1 Blotting TechniquesDocument33 pages5.1 Blotting TechniquesAmir Al-Aiman100% (1)
- Westren and Northern BlottingDocument13 pagesWestren and Northern BlottingGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Clone Identification, Screening, SelectionDocument21 pagesClone Identification, Screening, SelectionPhytomenadione La Vitamine KNo ratings yet
- 5 - Orthogonal Genetic SystemsDocument18 pages5 - Orthogonal Genetic SystemsHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- SB251 - Genetic Code Oct512Document22 pagesSB251 - Genetic Code Oct512Siddharth Rajamohanan100% (1)
- (BIF 401) Current Solved Papers.Document16 pages(BIF 401) Current Solved Papers.Sagheer MalikNo ratings yet
- High Resolution Electrophoresis of Human Plasma Proteins: Two-DimensionalDocument5 pagesHigh Resolution Electrophoresis of Human Plasma Proteins: Two-DimensionalJheny LopezNo ratings yet
- Blotting TechniqueDocument34 pagesBlotting TechniqueUmair100% (2)
- 235 Recombinant DNA Technology BlottingDocument23 pages235 Recombinant DNA Technology BlottingAme Grace DubeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0006349518316114 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 S0006349518316114 MainDiego TulcanNo ratings yet
- AutoradiographyDocument12 pagesAutoradiographyMoner ManushNo ratings yet
- I) Using Isolated Organ / Tissues:: Ex.: Roots and Leaves For Study of Nicotiana and Datura, Petal Disc For StudyDocument22 pagesI) Using Isolated Organ / Tissues:: Ex.: Roots and Leaves For Study of Nicotiana and Datura, Petal Disc For Studypreetisingh17No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Verna Jean M. Magdayao 3/Bsbiology/ADocument56 pagesPrepared By: Verna Jean M. Magdayao 3/Bsbiology/AKathleya PeñaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Studying The Nervous System: OutlineDocument34 pagesMethods of Studying The Nervous System: OutlineMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics - Study ResourcesDocument2 pagesDiagnostics - Study Resourcesakankshapehlinov20No ratings yet
- Bioinfo Final PracticalDocument66 pagesBioinfo Final PracticalPolu ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- I. Determining Protein Amino Acid SequenceDocument4 pagesI. Determining Protein Amino Acid Sequenceganesh2gigNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequence of The Streptomycin-Producing MicroorganismDocument11 pagesGenome Sequence of The Streptomycin-Producing MicroorganismMatthew LareenNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument23 pagesDNA Sequencingrr48843100% (1)
- MBII - L9 - Gene Cloning 4 - Advanced Gene CloningDocument4 pagesMBII - L9 - Gene Cloning 4 - Advanced Gene CloningMiles NsgNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesBiotechnologyAnit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Bif 401 100% Solved Final Term Paper by Sulman AliDocument5 pagesBif 401 100% Solved Final Term Paper by Sulman AliArt TechNo ratings yet
- Nick Translation Primer Extension RNA Polymerase End Labelling Direct LabellingDocument3 pagesNick Translation Primer Extension RNA Polymerase End Labelling Direct LabellingShubha Rani SharmaNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 Session NotesDocument5 pagesPBL 3 Session NotesJon. . .No ratings yet
- Blotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Document31 pagesBlotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Amina ChNo ratings yet
- Molecular MethodsDocument8 pagesMolecular MethodspriyaNo ratings yet
- Dintzis ExerciseDocument5 pagesDintzis ExerciserichschurNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideDocument22 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211No ratings yet
- Continuation of GenetechnologyyDocument7 pagesContinuation of GenetechnologyySemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- BLOTTING TECHNIQUE p-1Document27 pagesBLOTTING TECHNIQUE p-1Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- BIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Document23 pagesBIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Awais BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Using Web Application of ProtParam, PeptideCutter, Compute Pi / MW, TMHMM, SignalPDocument24 pagesUsing Web Application of ProtParam, PeptideCutter, Compute Pi / MW, TMHMM, SignalPEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- Escherichia ColiDocument10 pagesEscherichia ColisurendrasrawanNo ratings yet
- Practical Laboratory Medicine: Gilles Cauet, Aurélien Daynès, Nevzat TemurokDocument7 pagesPractical Laboratory Medicine: Gilles Cauet, Aurélien Daynès, Nevzat TemurokFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Carotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975From EverandCarotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975B. C. L. WeedonNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: Making precision medicine possibleFrom EverandFast Facts: Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: Making precision medicine possibleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 5Document10 pagesQuarter 4 Module 5jiyuskie09No ratings yet
- (Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Document321 pages(Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Heruko Fatimah100% (1)
- Bioabsorption of MetalsDocument26 pagesBioabsorption of MetalsHamza NoorNo ratings yet
- Sathyanarayan Biochemistry 4epdfDocument35 pagesSathyanarayan Biochemistry 4epdfAbubakar SuleimanNo ratings yet
- MSC 1 Sem Bio Chemistry Advanced Enzymology CP 3 Jun 2016Document1 pageMSC 1 Sem Bio Chemistry Advanced Enzymology CP 3 Jun 2016Devashish SahasrabudheNo ratings yet
- DemyelinatingDocument78 pagesDemyelinatingaslan tonapaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd EditionDocument61 pagesGenetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd Editionjulia.swanson282100% (51)
- 9 BioDocument3 pages9 BioAnubhav jhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16 - 1 Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesLesson 16 - 1 Reading Comprehensionstorming25No ratings yet
- B Kon 2020 SouvenirDocument67 pagesB Kon 2020 SouvenirAmbaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis y MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis y MeiosisEdmundo Samaniego GuzmánNo ratings yet
- n094 NeuroscienceDocument74 pagesn094 NeuroscienceAnnaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionDocument25 pagesFrom Gene To Protein,: Cellular and Sub-Cellular Protein ExpressionPUBG HackerNo ratings yet
- Discussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAINDocument4 pagesDiscussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAINKesha Gopal100% (4)
- 1 s2.0 S0006291X18325117 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0006291X18325117 Main PDFMerianaNo ratings yet
- Dasar-Dasar Biomolekuler Reproduksi Wanita: Rahmatina B. HermanDocument29 pagesDasar-Dasar Biomolekuler Reproduksi Wanita: Rahmatina B. HermansilmiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT Notes PDFDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT Notes PDFJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cell - Volumes1 and 2 David E. MetzlerDocument940 pagesBiochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cell - Volumes1 and 2 David E. Metzlerysmnsnmz100% (7)
- Bio Trial Paper SET 1Document8 pagesBio Trial Paper SET 1m-7319562No ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation V Inhibitors and UncouplersDocument15 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation V Inhibitors and UncouplersIffatnazNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Lysosome and Peroxisome: March 2017Document10 pagesDifference Between Lysosome and Peroxisome: March 2017HNZY IAFSNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Report 6 ActualDocument4 pagesBiology Lab Report 6 ActualMunachi Hugh MbaezueNo ratings yet
- Drug TargetsDocument34 pagesDrug TargetsmajedNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Regulation of Fermentation Processes PDFDocument12 pagesMetabolic Regulation of Fermentation Processes PDFqketzaNo ratings yet
- Reporting ScripttDocument4 pagesReporting Scripttnicole besarioNo ratings yet
- Ix-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupDocument3 pagesIx-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupTaroobaNo ratings yet
- Protein Estimation ReportDocument3 pagesProtein Estimation ReportSudip MajiNo ratings yet
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5Document34 pagesBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5SDO BSNL NALAGARHNo ratings yet