Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Energy Systems
3 Energy Systems
Uploaded by
ulonggwapoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Exercise Physiology Course NotesDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course NotesAdam Linoby100% (16)
- Energy Systems PowerpointDocument27 pagesEnergy Systems PowerpointKellie Guest100% (1)
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- Analyze of 3 Different Energy Systems and Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports and ActivitiesDocument5 pagesAnalyze of 3 Different Energy Systems and Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports and Activitiesdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Energy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodDocument43 pagesEnergy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodApril Joy TicaoNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 OutlineDocument7 pagesHope 3 OutlinelynnNo ratings yet
- Nur Hannah BT HamzahDocument9 pagesNur Hannah BT HamzahNur Hannah Bt HamzahNo ratings yet
- ENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Document9 pagesENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Ben Jenkins100% (4)
- LO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & ActivitiesDocument6 pagesLO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & Activitiesnbeer93No ratings yet
- L.O.5. Energy SystemsDocument9 pagesL.O.5. Energy SystemsOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- ATP-PC System (Phosphogen System) - This System Is Used Only For Very ShortDocument1 pageATP-PC System (Phosphogen System) - This System Is Used Only For Very Shortfeilong82No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - BiochemistryDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Biochemistryizza ghafoorNo ratings yet
- Energy ConceptsDocument7 pagesEnergy Conceptsanon_965753265No ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Energy SystemDocument15 pagesLactic Acid Energy SystemroemriqwewqeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Energy SystemDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Energy SystemAyah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 XDocument8 pagesChapter 1 XMatt FNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy in Muscles: Why Can't I Sprint Forever?Document30 pagesWork and Energy in Muscles: Why Can't I Sprint Forever?Martín BiancalanaNo ratings yet
- Where Energy To Train Comes FromDocument12 pagesWhere Energy To Train Comes FromCanadaMikeNo ratings yet
- HOPE 4 Lesson 2 Energy SystemsDocument12 pagesHOPE 4 Lesson 2 Energy SystemsTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemDocument9 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemArmina ValdezNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Pathways - An Introduction To The Energy SystemsDocument33 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Pathways - An Introduction To The Energy SystemsMary Grace Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- My Script: 1. Aerobic Glycolysis (Slow Glycolysis) 2. Krebs Cycle (Also Known As The Citric Acid Cycle)Document6 pagesMy Script: 1. Aerobic Glycolysis (Slow Glycolysis) 2. Krebs Cycle (Also Known As The Citric Acid Cycle)Rico Yan CanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 PED001Document10 pagesLesson 7 PED001Marchille CosmianoNo ratings yet
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 pagesThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonNo ratings yet
- HOPE3 WorkSheet Week1Document8 pagesHOPE3 WorkSheet Week1Jerome CasilaoNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document7 pagesTask 4samantaNo ratings yet
- Hope3 Q1Document69 pagesHope3 Q1PatriciaNo ratings yet
- HOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Document10 pagesHOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Dary Jea ChingNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemDocument13 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemRhean100% (1)
- Muscle For This ImmediateDocument4 pagesMuscle For This ImmediateHAKDOGNo ratings yet
- H.O.P.E.-11: Exercise For FitnessDocument6 pagesH.O.P.E.-11: Exercise For FitnessJay ArNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning ObjectivesDocument79 pages3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning Objectiveszedy gullesNo ratings yet
- Core Two PDHPE NotesDocument17 pagesCore Two PDHPE Notesdarcym2604No ratings yet
- How Does Training Affect Performance Student HandoutDocument4 pagesHow Does Training Affect Performance Student HandoutSachitornadoNo ratings yet
- Energy SystemsDocument3 pagesEnergy Systemserica lamsen100% (1)
- Energy System NotesDocument3 pagesEnergy System Notesapi-267326015100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Human Energy TransferDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Human Energy TransferVidhisha Pai100% (1)
- CBR M Farhan 22Document11 pagesCBR M Farhan 22Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseArizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Aerobic SystemDocument7 pagesThe Aerobic SystemMohd Yusof JunsinNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document5 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Angelo Dela LlarteNo ratings yet
- Sintaxe RRC 01Document13 pagesSintaxe RRC 01weebmyphone11No ratings yet
- Energy Transfer During ExerciseDocument48 pagesEnergy Transfer During ExerciseHema Malini100% (1)
- Physical Education and Health-G12 Introduction To Dance: Not For SaleDocument13 pagesPhysical Education and Health-G12 Introduction To Dance: Not For SaleMaRlon Talactac OnofreNo ratings yet
- Pe 12 - SLHT 3 - January 18 To 22Document4 pagesPe 12 - SLHT 3 - January 18 To 22JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Week 3-4Document12 pagesWeek 3-4mariel balaguerNo ratings yet
- Explain The Energy SystemsDocument7 pagesExplain The Energy Systemswillbatcup100% (1)
- P.E.H 3 Module 1, Week 1Document5 pagesP.E.H 3 Module 1, Week 1erica lamsenNo ratings yet
- Hope 1 Energy SystemDocument27 pagesHope 1 Energy SystemJestoni MaravillasNo ratings yet
- PE - Final REPORTDocument20 pagesPE - Final REPORTRyan Abonales BagatuaNo ratings yet
- Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Document27 pagesEnergy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Josie JavierNo ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism in MuscleDocument19 pagesEnergy Metabolism in MuscleRidhaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Energy SystemsDocument9 pagesMetabolic Energy SystemsErwan Sha Habinullah100% (2)
- Lesson 2 HopeDocument26 pagesLesson 2 HopeCeline Joy Anipot RolaNo ratings yet
- PE and Health 11 First Sem Lesson 2Document12 pagesPE and Health 11 First Sem Lesson 2Eduardo ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Is Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonDocument4 pagesIs Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document8 pagesWeek 1 2Aliyah M.No ratings yet
- NISMAT Exercise Physiology1Document3 pagesNISMAT Exercise Physiology1sanalcrazyNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- The Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryFrom EverandThe Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ICT - 1A Achievement TestDocument2 pagesGrade 11 ICT - 1A Achievement Testulonggwapo100% (1)
- EpicDocument14 pagesEpiculonggwapoNo ratings yet
- TuwaangDocument2 pagesTuwaangulonggwapo100% (6)
- 40M+Business+Blueprint+v 3Document21 pages40M+Business+Blueprint+v 3ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- That Develop Problem Solving and Manipulative Play SkillsDocument1 pageThat Develop Problem Solving and Manipulative Play SkillsulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Teacher Assessment Form STUDENT # 747350969: Session #Document2 pagesTeacher Assessment Form STUDENT # 747350969: Session #ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 19Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 19ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 8: Approved: August 9, 1946Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 8: Approved: August 9, 1946ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 21Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 21ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 14Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 14ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- An Act To Amend Sections Five and Six of Commonwealth Act Numbered Six Hundred and Seventy-Two, Entitled "An Act ToDocument2 pagesAn Act To Amend Sections Five and Six of Commonwealth Act Numbered Six Hundred and Seventy-Two, Entitled "An Act ToulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 20Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 20ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 18Document3 pagesRepublic Act No. 18ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 10Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 10ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 16Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 16ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 7ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 2Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 2ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 11Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 11ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 1Document7 pagesRepublic Act No 1ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 9262Document19 pagesRepublic Act No 9262ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- The 2015 LEAP: CommitteeDocument3 pagesThe 2015 LEAP: CommitteeulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Mdam World AIDS Day 2015Document4 pagesMdam World AIDS Day 2015ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument3 pagesModule IIIulonggwapoNo ratings yet
3 Energy Systems
3 Energy Systems
Uploaded by
ulonggwapoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Energy Systems
3 Energy Systems
Uploaded by
ulonggwapoCopyright:
Available Formats
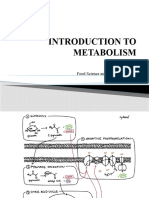
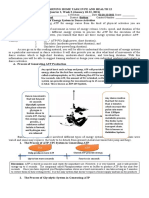
THE THREE METABOLIC ENERGY SYSTEMS 1. The first energy system is the ATP-PC Energy System.
This energy system is responsible for the High Power/Short Duration intensity of physical activity. ATP and phosphocreatine (PC) compose the ATP-PC system, also called the Phosphogen system. It is an anaerobic energy system. It is immediate and functions without oxygen. It allows for up to approximately 12 seconds of maximum effort. Examples are: a short sprint or lifting a heavy resistance for several repetitions, or a lawn tennis serve. 2. The second energy system is the the Glycolytic System. This energy system is responsible for the Moderate Power/Moderate Duration intensity of physical activity. The glycolytic system is the next in line tool after the ATP-PC system runs its course. Dietary carbohydrates supply glucose that circulates in the blood or is stored as glycogen in the muscles and the liver. Blood glucose and/or or stored glycogen is broken down to create ATP through the process of glycolysis. Like the ATP-PC system, oxygen is not required for the actual process of glycolysis (but it does play a role with the byproduct of glycolysis: pyruvic acid. After maximum power declines around 12 seconds, further intense activity up to approximately 30 seconds results in lactic acid accumulation, a decrease in power, and consequent muscle fatigue.This high, extended effort is labeled fast glycolysis. Exerting further effort up to approximately 50 seconds results in another drop in power due to the shift in dependence on the oxidative system. Bottom line: it is getting tougher. Example is an all-out sprint, to a slower jog, to an eventual walk. That is the progression of the three energy systems when going all-out. 3. The third energy system is the Oxidative System. This energy system is responsible for the Low Power/Long Duration intensity of physical activity. The maximal effort was fueled initially by the ATP-PC, but the performance declines. Continued effort results in further decline, either via fast glycolysis (quick decline) or slow glycolysis (slower decline). The human body is now entering the complex world of the low power but longer duration oxidative system. Examples are: 6-mile run, low-level manual labor on an eight-hour work shift, or a 5kilometer walk.
You might also like
- Exercise Physiology Course NotesDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course NotesAdam Linoby100% (16)
- Energy Systems PowerpointDocument27 pagesEnergy Systems PowerpointKellie Guest100% (1)
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- Analyze of 3 Different Energy Systems and Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports and ActivitiesDocument5 pagesAnalyze of 3 Different Energy Systems and Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports and Activitiesdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Energy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodDocument43 pagesEnergy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodApril Joy TicaoNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 OutlineDocument7 pagesHope 3 OutlinelynnNo ratings yet
- Nur Hannah BT HamzahDocument9 pagesNur Hannah BT HamzahNur Hannah Bt HamzahNo ratings yet
- ENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Document9 pagesENERGY SYSTEMS - Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems - 1.2Ben Jenkins100% (4)
- LO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & ActivitiesDocument6 pagesLO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & Activitiesnbeer93No ratings yet
- L.O.5. Energy SystemsDocument9 pagesL.O.5. Energy SystemsOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- ATP-PC System (Phosphogen System) - This System Is Used Only For Very ShortDocument1 pageATP-PC System (Phosphogen System) - This System Is Used Only For Very Shortfeilong82No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - BiochemistryDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Biochemistryizza ghafoorNo ratings yet
- Energy ConceptsDocument7 pagesEnergy Conceptsanon_965753265No ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Energy SystemDocument15 pagesLactic Acid Energy SystemroemriqwewqeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Energy SystemDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Energy SystemAyah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 XDocument8 pagesChapter 1 XMatt FNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy in Muscles: Why Can't I Sprint Forever?Document30 pagesWork and Energy in Muscles: Why Can't I Sprint Forever?Martín BiancalanaNo ratings yet
- Where Energy To Train Comes FromDocument12 pagesWhere Energy To Train Comes FromCanadaMikeNo ratings yet
- HOPE 4 Lesson 2 Energy SystemsDocument12 pagesHOPE 4 Lesson 2 Energy SystemsTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemDocument9 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemArmina ValdezNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Pathways - An Introduction To The Energy SystemsDocument33 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Pathways - An Introduction To The Energy SystemsMary Grace Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- My Script: 1. Aerobic Glycolysis (Slow Glycolysis) 2. Krebs Cycle (Also Known As The Citric Acid Cycle)Document6 pagesMy Script: 1. Aerobic Glycolysis (Slow Glycolysis) 2. Krebs Cycle (Also Known As The Citric Acid Cycle)Rico Yan CanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 PED001Document10 pagesLesson 7 PED001Marchille CosmianoNo ratings yet
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 pagesThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonNo ratings yet
- HOPE3 WorkSheet Week1Document8 pagesHOPE3 WorkSheet Week1Jerome CasilaoNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document7 pagesTask 4samantaNo ratings yet
- Hope3 Q1Document69 pagesHope3 Q1PatriciaNo ratings yet
- HOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Document10 pagesHOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Dary Jea ChingNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemDocument13 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemRhean100% (1)
- Muscle For This ImmediateDocument4 pagesMuscle For This ImmediateHAKDOGNo ratings yet
- H.O.P.E.-11: Exercise For FitnessDocument6 pagesH.O.P.E.-11: Exercise For FitnessJay ArNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning ObjectivesDocument79 pages3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning Objectiveszedy gullesNo ratings yet
- Core Two PDHPE NotesDocument17 pagesCore Two PDHPE Notesdarcym2604No ratings yet
- How Does Training Affect Performance Student HandoutDocument4 pagesHow Does Training Affect Performance Student HandoutSachitornadoNo ratings yet
- Energy SystemsDocument3 pagesEnergy Systemserica lamsen100% (1)
- Energy System NotesDocument3 pagesEnergy System Notesapi-267326015100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Human Energy TransferDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Human Energy TransferVidhisha Pai100% (1)
- CBR M Farhan 22Document11 pagesCBR M Farhan 22Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseArizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Aerobic SystemDocument7 pagesThe Aerobic SystemMohd Yusof JunsinNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document5 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Angelo Dela LlarteNo ratings yet
- Sintaxe RRC 01Document13 pagesSintaxe RRC 01weebmyphone11No ratings yet
- Energy Transfer During ExerciseDocument48 pagesEnergy Transfer During ExerciseHema Malini100% (1)
- Physical Education and Health-G12 Introduction To Dance: Not For SaleDocument13 pagesPhysical Education and Health-G12 Introduction To Dance: Not For SaleMaRlon Talactac OnofreNo ratings yet
- Pe 12 - SLHT 3 - January 18 To 22Document4 pagesPe 12 - SLHT 3 - January 18 To 22JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Week 3-4Document12 pagesWeek 3-4mariel balaguerNo ratings yet
- Explain The Energy SystemsDocument7 pagesExplain The Energy Systemswillbatcup100% (1)
- P.E.H 3 Module 1, Week 1Document5 pagesP.E.H 3 Module 1, Week 1erica lamsenNo ratings yet
- Hope 1 Energy SystemDocument27 pagesHope 1 Energy SystemJestoni MaravillasNo ratings yet
- PE - Final REPORTDocument20 pagesPE - Final REPORTRyan Abonales BagatuaNo ratings yet
- Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Document27 pagesEnergy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Josie JavierNo ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism in MuscleDocument19 pagesEnergy Metabolism in MuscleRidhaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Energy SystemsDocument9 pagesMetabolic Energy SystemsErwan Sha Habinullah100% (2)
- Lesson 2 HopeDocument26 pagesLesson 2 HopeCeline Joy Anipot RolaNo ratings yet
- PE and Health 11 First Sem Lesson 2Document12 pagesPE and Health 11 First Sem Lesson 2Eduardo ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Is Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonDocument4 pagesIs Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document8 pagesWeek 1 2Aliyah M.No ratings yet
- NISMAT Exercise Physiology1Document3 pagesNISMAT Exercise Physiology1sanalcrazyNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- The Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryFrom EverandThe Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ICT - 1A Achievement TestDocument2 pagesGrade 11 ICT - 1A Achievement Testulonggwapo100% (1)
- EpicDocument14 pagesEpiculonggwapoNo ratings yet
- TuwaangDocument2 pagesTuwaangulonggwapo100% (6)
- 40M+Business+Blueprint+v 3Document21 pages40M+Business+Blueprint+v 3ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- That Develop Problem Solving and Manipulative Play SkillsDocument1 pageThat Develop Problem Solving and Manipulative Play SkillsulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Teacher Assessment Form STUDENT # 747350969: Session #Document2 pagesTeacher Assessment Form STUDENT # 747350969: Session #ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 19Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 19ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 8: Approved: August 9, 1946Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 8: Approved: August 9, 1946ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 21Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 21ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 14Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 14ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- An Act To Amend Sections Five and Six of Commonwealth Act Numbered Six Hundred and Seventy-Two, Entitled "An Act ToDocument2 pagesAn Act To Amend Sections Five and Six of Commonwealth Act Numbered Six Hundred and Seventy-Two, Entitled "An Act ToulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 20Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 20ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 18Document3 pagesRepublic Act No. 18ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 10Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 10ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 16Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 16ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7Document2 pagesRepublic Act No. 7ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 2Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 2ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 11Document1 pageRepublic Act No. 11ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 1Document7 pagesRepublic Act No 1ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 9262Document19 pagesRepublic Act No 9262ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- The 2015 LEAP: CommitteeDocument3 pagesThe 2015 LEAP: CommitteeulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Mdam World AIDS Day 2015Document4 pagesMdam World AIDS Day 2015ulonggwapoNo ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument3 pagesModule IIIulonggwapoNo ratings yet