Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Symbiotic Relationship
Symbiotic Relationship
Uploaded by
terezkiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Symbiotic Relationship
Symbiotic Relationship
Uploaded by
terezkiCopyright:
Available Formats
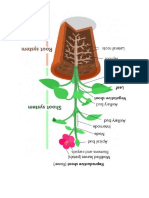
SYMBIOTIC RELATIONSHIP Mutualism 1.
An example of a mutualistic relationship is the cleaner fish that works with larger fish to remove parasites and diseased tissue from their scales, gills, or mouths. This cleaning may take place casually or at a cleaning station. The relationship may take place between species that are closely related, or more distantly related. One fish that act as cleaners when they are young is a hogfish, and another cleaner fish is a wrasse. 2. The bee and the flower. Bees fly from flower to flower gathering nectar, which they make into food, benefiting the bees. When they land in a flower, the bees get some pollen on their hairy bodies, and when they land in the next flower, some of the pollen from the first one rubs off, pollinating* the plant. This benefits the plants. In this mutualistic relationship, the bees get to eat, and the flowering plants get to reproduce. Commensalism 1. An example of commensalism is the relationship between the Anemone crab and an anemone. The Anemone crab lives in the protection of the anemones tentacles and catches its food without ever leaving the safety of the tentacles. However, the crab does not provide any service to the anemone. 2. The clownfish lives among the forest of tentacles of an anemone and is protected from potential predators. Parasitism 1. An example of a parasitic relationship is the Sacculina carcini, a barnacle that infests a host crab. This barnacle finds a hole in the exoskeleton of the crab, so microscopic hairs can penetrate the hole and the barnacle injects a few cells, and then appears as a slug on the underside of the crab. The barnacle absorbs nutrients from the crabs blood, but does not trigger any immune responses, so the crab continues with its daily life. The female Sacculina lays her eggs in the crabs brood pouch, and the instinct of the unsuspecting crab is to continue nurturing the contents of the pouch, and eventually aid in the dispersal of the barnacles eggs for future fertilization, which allows the parasite to continue on with its life cycle. 2. Tapeworms are segmented flatworms that attach themselves to the insides of the intestines of animals such as cows, pigs, and humans. They get food by eating the host's partly digested food, depriving the host of nutrients. Fleas harm their hosts, such as dogs, by biting their skin, sucking their blood, and causing them to itch. The fleas, in turn, get food and a warm home. Barnacles, which live on the bodies of whales, do not seriously harm their hosts, but they do itch and are annoying. Predation or prey-predator relationship 1. The fastest lions are able to catch food and eat, so they survive and reproduce, and gradually, faster lions make up more and more of the population. The fastest zebras are able to escape the lions, so they survive and reproduce, and gradually, faster zebras make up more and more of the population. An important thing to realize is that as both organisms become faster to adapt to their environments, their relationship remains the
same: because they are both getting faster, neither gets faster in relation to the other. This is true in all predator-prey relationships. 2. Another example of predator-prey evolution is that of the Galapagos tortoise. Galapagos tortoises eat the branches of the cactus plants that grow on the Galapagos islands. On one of the islands, where long-necked tortoises live, the branches are higher off the ground. On another island, where short-necked tortoises live, the branches are lower down. The cactuses, the prey, may have evolved high branches so that the tortoises, the predators, can't reach them. Amensalism 1. An example of .amensalism is the relationship between the bread mold Penicillium and a variety of bacteria. The secretion given off by the mold penicillin destroys many bacteria, hence its use in antibiotics. 2. Another example is the black walnut which secrets a chemical called juglone, which destroys most other plants in its root zone. A non-chemical example of amensalism is when trees' branches fall off. The branches falling to the ground cause damage to smaller plants beneath them Symbiosis 1. AFRICAN OXPECKERS African oxpeckers (Buphagus africanus and Buphagus erythrorhynchus) feed on the backs of zebra, elephants, hippopotamuses and other large African animals. Once thought to be friendly tick-eating helpers, theyre actually vampire birds, sucking blood out of open tick-wounds. This shows how the line between symbiotic assistant and parasite can be blurred. Oxpeckers do eat ticks as well, and some animals may be happy to sacrifice a bit of blood for this service. Oxpeckers may also be tolerated because they produce a hissing scream when startled like a personal danger alarm. 2. CELLS AND MITOCHONDRIA Over a billion years ago, one type of bacteria ate another or tried to. Surviving this ordeal, the prey became a permanent house guest in the wet, sheltered, food-rich environment of the predators body. Like an internal battery, the smaller bacteria adapted to turn food and oxygen into chemical energy for the larger one
You might also like
- Midpoints - Unleashing The POwer of The PlanetsDocument394 pagesMidpoints - Unleashing The POwer of The PlanetsAngela Gibson98% (104)
- Taste of Paradise Chapter 2Document16 pagesTaste of Paradise Chapter 2Gisele Ferreira33% (6)
- Symbiotic Relationships Worksheet: Name: - PerDocument2 pagesSymbiotic Relationships Worksheet: Name: - PerWyatt Huizenga100% (1)
- Good Buddies - Symbiotic RelationshipsDocument1 pageGood Buddies - Symbiotic Relationshipsapi-95178008No ratings yet
- Lab 05 Modeling of Mechanical Systems Using Simscap Multibody 2nd Generation Part 1Document19 pagesLab 05 Modeling of Mechanical Systems Using Simscap Multibody 2nd Generation Part 1Reem GheithNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy PresentationDocument92 pagesMatter and Energy Presentationapi-25442847475% (4)
- 26 Branches of BotanyDocument5 pages26 Branches of BotanyterezkiNo ratings yet
- Project Report PDFDocument41 pagesProject Report PDFAKRAMA HASANNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis A Relationship Where Two Organisms (Of Different Species) Live TogetherDocument5 pagesSymbiosis A Relationship Where Two Organisms (Of Different Species) Live TogetherJr MateoNo ratings yet
- SymbiosisDocument1 pageSymbiosisJonalvin KENo ratings yet
- BIO3207 Lecture 1Document33 pagesBIO3207 Lecture 1NGOGA NISINGIZWE NESTORNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument47 pagesSciencePinky Caina CabotajeNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Environmental Science Module 5 Lesson 1: MutualismDocument2 pagesAssignment - Environmental Science Module 5 Lesson 1: MutualismJhan RhayNo ratings yet
- Biology 2Document3 pagesBiology 2Cynthia Paola MelgarNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document8 pagesActivity 3Lawrence TamayoNo ratings yet
- B7 Species Interaction ReadingDocument3 pagesB7 Species Interaction ReadingMatt StromNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationships PracticeDocument2 pagesSymbiotic Relationships Practiceapi-264004571No ratings yet
- 11 Mutualism, Commensalism, ParasitismDocument10 pages11 Mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitismalv34nnnNo ratings yet
- Interaction of ParaSitism, Commensalism, and CompetitionDocument14 pagesInteraction of ParaSitism, Commensalism, and CompetitionMichelle LebosadaNo ratings yet
- Science Relationships hw123Document3 pagesScience Relationships hw123api-250941636No ratings yet
- BIO 111 NOTES (Autosaved) - 082311Document10 pagesBIO 111 NOTES (Autosaved) - 082311Borisade Tolulope VictorNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Science Notes - Interactions in A CommunityDocument2 pagesGrade 4 - Science Notes - Interactions in A Communitymarieanas trenchNo ratings yet
- Biotic InteractionDocument27 pagesBiotic InteractionMuhammad RamzanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Ecological Interactions and Their ExamplesDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Ecological Interactions and Their ExampleshannamNo ratings yet
- Science Presentation, Ecological RelationshipsDocument8 pagesScience Presentation, Ecological RelationshipsJustinne LacuestaNo ratings yet
- Interactions in EcosystemsDocument42 pagesInteractions in EcosystemsDeniel DenamarcaNo ratings yet
- CommensalismDocument20 pagesCommensalismotijNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 3 ProjectDocument21 pagesChapter 48 3 Projectapi-356810778No ratings yet
- AdvbioreportDocument6 pagesAdvbioreportapi-347823018No ratings yet
- Clownfish Fact SheetDocument2 pagesClownfish Fact SheetDuafarmNo ratings yet
- Commensalism: Commensalism, in Biology, A Relationship Between Individuals of Two Species inDocument3 pagesCommensalism: Commensalism, in Biology, A Relationship Between Individuals of Two Species inDaisuke InoueNo ratings yet
- Spectacular Science Symbiotic Relationships Practice PacketDocument3 pagesSpectacular Science Symbiotic Relationships Practice PacketnaremanNo ratings yet
- Mutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism, AdaptationDocument13 pagesMutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism, AdaptationA-04Maithili KarandeNo ratings yet
- MutualismDocument5 pagesMutualismamihaninternetshop aisNo ratings yet
- Predation, Mutualism, Commensalism, or ParasitismDocument25 pagesPredation, Mutualism, Commensalism, or ParasitismArisitica VinilescuNo ratings yet
- Tibaw Demo MaterialsDocument22 pagesTibaw Demo MaterialsMhermina MoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48.3 Project: By: Kam and MeganDocument19 pagesChapter 48.3 Project: By: Kam and MeganKamrin StevensonNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis PPT PresDocument28 pagesSymbiosis PPT PresNomer PacilanNo ratings yet
- Population InteractionDocument3 pagesPopulation Interactionrikitasingh2706No ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship Worksheet 2Document3 pagesSymbiotic Relationship Worksheet 2Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems & Material Cycles: Ecosystem Eco / System House / Made of Several PartsDocument19 pagesEcosystems & Material Cycles: Ecosystem Eco / System House / Made of Several PartsSarbani MallikNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship ScenariosDocument12 pagesSymbiotic Relationship Scenariosapi-262368188100% (1)
- Mutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism, and Adaptation: Name: Maithili Karande SRN No.: 202000140Document13 pagesMutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism, and Adaptation: Name: Maithili Karande SRN No.: 202000140A-04Maithili KarandeNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship Worksheet-4Document3 pagesSymbiotic Relationship Worksheet-4ah2504525No ratings yet
- Ecological RelationshipDocument7 pagesEcological RelationshipShadrack Ezra PublícoNo ratings yet
- Communities WorksheetDocument2 pagesCommunities WorksheetJamie MakrisNo ratings yet
- Interactions Among OrganismsDocument21 pagesInteractions Among OrganismsrismawatiNo ratings yet
- The Best Control For BatsDocument18 pagesThe Best Control For Batsflaviana17No ratings yet
- Interactions HomeworkDocument2 pagesInteractions HomeworkIselaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Proper in LPDocument4 pagesDiscussion Proper in LPJazzel Queny ZalduaNo ratings yet
- Interactions in Different EcosystemsDocument2 pagesInteractions in Different EcosystemsMahal TamondongNo ratings yet
- Pee M4 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPee M4 ReviewerAster GabbNo ratings yet
- Relationships Within The Ecosystem: MutualismDocument6 pagesRelationships Within The Ecosystem: MutualismLietOts KinseNo ratings yet
- AHMADDocument7 pagesAHMADSUNDAY MUSANo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Parasitology and Helminthology BernardDocument88 pagesGeneral Veterinary Parasitology and Helminthology Bernardprabha alphonsa50% (4)
- Summary BIO ReportingDocument16 pagesSummary BIO ReportingKristy Ann DalumpayNo ratings yet
- Parasite 1Document22 pagesParasite 1OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- BATS! The Only Flying Mammals | Bats for Kids | Children's Mammal BooksFrom EverandBATS! The Only Flying Mammals | Bats for Kids | Children's Mammal BooksNo ratings yet
- Q1.Define The Following Terms and Provide Example For Each. A) .CoevolutionDocument8 pagesQ1.Define The Following Terms and Provide Example For Each. A) .Coevolutionkathciri teroNo ratings yet
- Herps I 1ld0k49Document5 pagesHerps I 1ld0k49RajKumarNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis POWERPOINTDocument22 pagesSymbiosis POWERPOINTMs Abby GailNo ratings yet
- Ecological Relationship: Oppositional RelationshipsDocument7 pagesEcological Relationship: Oppositional Relationshipsjeanette PradesNo ratings yet
- Biological Associations, Succession and Pest ControlDocument13 pagesBiological Associations, Succession and Pest ControlAnselm Asafo-AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Unidad IV. - Trabajo Medicina Veterinaria Ingles InstrumentalDocument3 pagesUnidad IV. - Trabajo Medicina Veterinaria Ingles InstrumentalRicardo RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Species InteractionDocument4 pagesSpecies Interactionckhimmy_93No ratings yet
- Ecology 1Document7 pagesEcology 1terezkiNo ratings yet
- Ugnayang Sanhi at BungaDocument1 pageUgnayang Sanhi at BungaterezkiNo ratings yet
- Aleli Grace O. Macapugay Grade II-St. ClaireDocument2 pagesAleli Grace O. Macapugay Grade II-St. ClaireterezkiNo ratings yet
- Power Supply RepairDocument4 pagesPower Supply RepairterezkiNo ratings yet
- Pamulinawen LyricsDocument1 pagePamulinawen LyricsterezkiNo ratings yet
- Society Can Be Defined As A Group of People Who Share A Common EconomicDocument4 pagesSociety Can Be Defined As A Group of People Who Share A Common EconomicterezkiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Tools and EquipmentDocument3 pagesElectrical Tools and Equipmentterezki100% (2)
- Disbursement VoucherDocument2 pagesDisbursement VoucherterezkiNo ratings yet
- My PetDocument2 pagesMy PetterezkiNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety TipsDocument4 pagesFire Safety TipsterezkiNo ratings yet
- Browse Works by Mark TwainDocument5 pagesBrowse Works by Mark TwainterezkiNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument7 pagesFigure of SpeechterezkiNo ratings yet
- A A A A: Product RulesDocument6 pagesA A A A: Product RulesterezkiNo ratings yet
- Colanderdouble BolierDocument6 pagesColanderdouble BolierterezkiNo ratings yet
- Book Report in EnglishDocument5 pagesBook Report in EnglishterezkiNo ratings yet
- Care of The NoseDocument6 pagesCare of The NoseterezkiNo ratings yet
- Dancing Running: Locomotor MovementDocument2 pagesDancing Running: Locomotor MovementterezkiNo ratings yet
- Investigatoryproject 120912015750 Phpapp02.Docx QDocument10 pagesInvestigatoryproject 120912015750 Phpapp02.Docx Qterezki50% (2)
- National BookstoreDocument9 pagesNational BookstoreterezkiNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Accomplshement ReportDocument1 pageQuarterly Accomplshement ReportterezkiNo ratings yet
- Cat C32 ACERT Spec Sheet - Pleasure CraftDocument8 pagesCat C32 ACERT Spec Sheet - Pleasure CraftSteven Wong100% (1)
- HF Conventions: Marine VDocument21 pagesHF Conventions: Marine VHarun KınalıNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Construction CompanyDocument2 pagesHindustan Construction Companyakansha90No ratings yet
- DP086LA: Doosan Infracore Generator EngineDocument4 pagesDP086LA: Doosan Infracore Generator EnginehirararaNo ratings yet
- A Study of How Lighting Can Affect A Guests Dining ExperienceDocument133 pagesA Study of How Lighting Can Affect A Guests Dining ExperiencehattyuuNo ratings yet
- May 12, 1973 Oxal: Greetings in The Light, My Friends, I Am OxalDocument2 pagesMay 12, 1973 Oxal: Greetings in The Light, My Friends, I Am OxalBui QuaNo ratings yet
- Airport 170923125652Document46 pagesAirport 170923125652Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Little Baguio Building Rules and Regulations DraftDocument7 pagesLittle Baguio Building Rules and Regulations DraftJun Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Histology: Preparation of Tissue For Histology Dr. OkoloDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Histology: Preparation of Tissue For Histology Dr. OkoloAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- Marine and ShipyardDocument80 pagesMarine and Shipyardahlan zulfakhriNo ratings yet
- Airbus FBW Flight Control Laws: Abbreviated SummaryDocument5 pagesAirbus FBW Flight Control Laws: Abbreviated SummaryPiyushNo ratings yet
- Faiic 2016-05 Alpha Coy AssignmentDocument4 pagesFaiic 2016-05 Alpha Coy AssignmentVincent De VeraNo ratings yet
- MSDS Pentazocine Lactate Injection 101912 32-90761 1Document7 pagesMSDS Pentazocine Lactate Injection 101912 32-90761 1Andita ListyannisaNo ratings yet
- Taylor & Francis, LTD., Folklore Enterprises, Ltd. FolkloreDocument19 pagesTaylor & Francis, LTD., Folklore Enterprises, Ltd. FolkloreLobsang YeshiNo ratings yet
- Stem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalDocument91 pagesStem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalYonaNo ratings yet
- 20 K CatalogDocument126 pages20 K Catalogjchristoe2613No ratings yet
- China in 50 DishesDocument112 pagesChina in 50 Dishesdikstraa100% (1)
- ScienceSLM G7 Q3 M6 ElectricityDocument29 pagesScienceSLM G7 Q3 M6 ElectricityXemelle SuelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Respiration in OrganismsDocument13 pagesChapter - 10: Respiration in OrganismsCHINMAYA RANJAN SAHOONo ratings yet
- Fartlek - WikipediaDocument7 pagesFartlek - Wikipediamohan raoNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Transportation Risk-1Document7 pagesAssessment and Transportation Risk-1TanzeemNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure of Ionic LiquidsDocument3 pagesVapor Pressure of Ionic LiquidsAyoub ArrarNo ratings yet
- Swahili LanguageDocument14 pagesSwahili LanguagenedNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Drinking WaterDocument1 pageHealth Benefits of Drinking WaterailynaNo ratings yet
- Margo Lanagan - Sea Hearts (Extract)Document7 pagesMargo Lanagan - Sea Hearts (Extract)Allen & UnwinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument7 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International Educationigloo79No ratings yet