Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Some Red Rashes in Children
Some Red Rashes in Children
Uploaded by
Meidy RuthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Some Red Rashes in Children
Some Red Rashes in Children
Uploaded by
Meidy RuthCopyright:
Available Formats
Some red rashes in children.
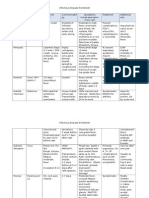
(Current Pediatrics 20th) Condition Incubation Prodrome Period (d) Adenovirus 45 URI; cough; fever Morbilliform (may Normal; may see be petechial) leukopenia or lymphocytosis Upper or lower respiratory symptoms are prominent. No Koplik spots. No desquamation. Drug allergy None, or fever alone, or with myalgia, pruritus Enterovirus 27 Variable fever, chills, throat Usually macular, maculopapular on soles; vesicles or Variable; PCR Macular, maculopapular, urticarial, or erythroderma Leukopenia, eosinophilia Rash variable. Severe reactions may resemble measles, scarlet fever; Kawasaki disease; marked toxicity possible. Varied rashes may resemble those of many other infections. Pharyngeal or hand-footRash Laboratory Tests Comments, Other Diagnostic Features
myalgia, sore trunk or palms,
petechiae also seen Ehrlichiosis (monocytic) 521 Fever; headache; flulike; myalgia; GI symptoms Variable; maculopapular, petechial, scarlatiniform, vasculitic Leukopenia, abnormal liver function. Serology for diagnosis; morulae in monocytes Erythema multiforme Usually none Discrete, red or related to maculopapular underlying cause lesions; symmetrical, distal, palms and soles; target lesions classic Infectious 3060 Fever, Macular, Atypical Normal or eosinophilia
mouth vesicles may occur.
Geographic distribution is exposure; rash present in only 45%.
thrombocytopenia, a clue; seasonal; tick
Reaction to drugs (especially sulfonamides), or infectious agents (Mycoplasma; herpes simplex virus). Urticaria, arthralgia also seen.
Pharyngitis,
mononucleosis (EBV infection)
malaise
scarlatiniform, or urticarial in 5% to are on penicillins and related drugs (not a penicillin allergy)
lymphocytosis; heterophil specific antibodies in an acute pattern EBV; abnormal liver function tests Increases inflammatory leukocytosis; thrombocytosis
lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly.
almost 100% who antibodies; EBV-
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (systemic; Still diseases)
High fever, malaise
Evanescent salmon-pink in pressure areas (prominent when fever is present)
Oligo- or polyarticular arthritis; asymptomatic anterior uveitis.
macules, especially markers;
Kawasaki disease
Unknown
Fever, cervical irritability
Polymorphous (may be trunk and
Leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, reactive protein;
Swollen hands, feet; prolonged illness; uveitis; response to antibiotics.
adenopathy, erythroderma) on
elevated ESR or C- aseptic meningitis; no
extremities; red palms and soles, conjunctiva, lips, tongue, pharynx.
pyuria; decreased albumin; negative cultures and streptococcal
Vasculitis and aneurysms of coronary and other arteries occur (cardiac ultrasound).
Late desquamation serology; resting is common. Some tachycardia of these findings may be absent with atypical disease Leptospirosis 419 Fever (biphasic), myalgia, chills Measles 914 Cough, rhinitis, Maculopapular; Variable erythroderma Leukocytosis; hematuria, proteinuria; Conjunctivitis; hepatitis, aseptic meningitis may be seen. Rodent, dog
hyperbilirubinemia contact. Leukopenia; antiToxic. Bright red rash becomes confluent, may desquamate. Fever falls
face to trunk; lasts measles IgM
conjunctivitis 710 d; Koplik
spots in mouth
after rash appears. Inadequate measles vaccination.
Parvovirus (erythema infectiosum)
1017 (rash)
Mild (flulike) Maculopapular on IgM-EIA; PCR cheeks ("slapped cheek"), forehead, chin; then down limbs, trunk, buttocks; may fade and reappear for several weeks
Purpuric stocking-glove rash is rare, but distinctive; aplastic crisis in patients with chronic hemolytic anemia. May cause arthritis or arthralgia.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
312
Headache (retroorbital); toxic; GI symptoms; high fever;
Onset 26 d after fever; palpable palms, soles, extremities, with spread centrally;
Leukopenia;
Eastern seaboard and States; AprilSeptember; tick exposure.
thrombocytopenia; southeastern United function; CSF pleocytosis; serology positive at
maculopapular on abnormal liver
flulike
petechial
710 d of rash; biopsy will give earlier diagnosis
Roseola (exanthem subitum) (HHV-6)
1014
Fever (34 d) Pink, macular rash Normal occurs at the end of febrile period; transient
Fever often high; disappears when rash develops; child appears well. Usually occurs in children 6 mo3 y of age. Seizures may complicate.
Rubella
1421
Usually none Mild maculopapular; rapid spread face to extremities; gone by day 4
Normal or leukopenia
Postauricular, occipital adenopathy common. Polyarthralgia in some older girls. Mild clinical illness. Inadequate rubella vaccination.
Staphylococcal Variable scalded skin
Irritability, absent to
Painful erythroderma,
Normal if only colonized by
Normal pharynx. Look for focal staphylococcal
low fever
followed in 12 d by cracking around eyes, mouth; bullae form with friction (Nikolsky sign)
staphylococci; leukocytosis and sometimes bacteremia if infected
infection. Usually occurs in infants.
Staphylococcal 17 scarlet fever
Variable fever
Diffuse erythroderma; resembles streptococcal scarlet fever except eyes may be hyperemic, no "strawberry" tongue, pharynx
Leukocytosis is common because of infected focus
Focal infection usually present.
spared StevensJohnson syndrome Pharyngitis, fever, malaise Bullous erythema slough in large areas; hemorrhagic lips; purulent conjunctivitis Leukocytosis Classic precipitants are drugs (especially sulfonamides);
conjunctivitis, multiforme; may
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
and herpes simplex infections. Pneumonitis and urethritis also seen.
Streptococcal scarlet fever
17
Fever, abdominal pain, headache, sore throat
Diffuse erythema, "sandpaper" texture; neck, axillae, inguinal areas; spreads to rest of body; d; eyes not red
Leukocytosis; positive group A
Strawberry tongue, red pharynx with or without exudate. Eyes, perioral palms, and soles spared. Pastia lines. Cervical adenopathy. Usually occurs in children 210 y of age.
Streptococcus
wound; positive streptococcal pharynx
culture of throat or and periorbital area,
desquamates 714 antigen test in
Toxic shock syndrome
Variable
Fever, myalgia, headache, diarrhea, vomiting
Nontender
Leukocytosis;
Staphylococcus aureus
infection; toxin-mediated multiorgan involvement. Swollen hands, feet. Hypotension or shock.
erythroderma; red abnormal liver eyes, palms, soles, enzymes and pharynx, lips coagulation tests; proteinuria
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; EIA, enzyme immunoassay; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; GI, gastrointestinal; HHV-6, human herpesvirus 6; IFA, immunofluorescent assay; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; URI, upper respiratory infection.
You might also like
- Measles Differential DiagnosisDocument1 pageMeasles Differential Diagnosistobechi86No ratings yet
- Differentials: Less Common InfectionsDocument6 pagesDifferentials: Less Common InfectionsTaeyomiNo ratings yet
- Morbid Viral DiseasesDocument31 pagesMorbid Viral DiseasesWael Magdi MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Manifestations of GIT and Liver DiseasesDocument48 pagesCutaneous Manifestations of GIT and Liver DiseasesSippy Iqbal MemonNo ratings yet
- Clues To Case-Based Questions-1Document4 pagesClues To Case-Based Questions-1Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- Fever and RashDocument14 pagesFever and RashSelvi Puspa SariNo ratings yet
- Bullets CDDocument2 pagesBullets CDAlexander Ruiz QueddengNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Disease What Is Kawasaki Disease?Document6 pagesKawasaki Disease What Is Kawasaki Disease?Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Disease FitzpatrickDocument2 pagesKawasaki Disease FitzpatrickIka ArdyantiNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument25 pagesPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (13)
- Fever and Rash: Djatnika SetiabudiDocument50 pagesFever and Rash: Djatnika SetiabudiNur OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Share Inflammatory ArthritisDocument122 pagesShare Inflammatory ArthritisDrAnkur BorahNo ratings yet
- #Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeDocument5 pages#Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeameerabestNo ratings yet
- Fever With RashDocument48 pagesFever With RashAnand VermaNo ratings yet
- Allergic and Immunologic DiseaseDocument50 pagesAllergic and Immunologic DiseaseRajkumari Sriraman100% (1)
- Spot Diagnosis Medicine OspeDocument212 pagesSpot Diagnosis Medicine OspeMahnoor TariqNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Approach: Fayza RayesDocument108 pagesDermatology Approach: Fayza RayesMinghan Shi100% (2)
- Fever and Rash by DR Djatnika (2 September 2014)Document67 pagesFever and Rash by DR Djatnika (2 September 2014)DimasHariAgungNo ratings yet
- LeptospirosisDocument7 pagesLeptospirosisFarah Nadia MoksinNo ratings yet
- Case of LeptospirosisDocument60 pagesCase of LeptospirosisNoreen Cala-MayubayNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument140 pagesInfectious DiseasesSamah IzzNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 3Document15 pagesPemicu 3iche_lovemeNo ratings yet
- Diseases Study Guide 2007Document6 pagesDiseases Study Guide 2007Bahaa Ibrahim HelmiNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease: Measles (Rubeola)Document5 pagesInfectious Disease: Measles (Rubeola)spoorthi shelomethNo ratings yet
- Red EyesDocument86 pagesRed Eyesarnol3090No ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy 4th YearDocument57 pagesLymphadenopathy 4th Yearanas barakahNo ratings yet
- DDs of Fever With RashDocument18 pagesDDs of Fever With RashEBNo ratings yet
- Lymph Ad en Op A ThyDocument24 pagesLymph Ad en Op A ThyAlyaa El SayedNo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionDocument2 pagesPathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionMauliza Resky NisaNo ratings yet
- M13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5Document6 pagesM13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5medipro clinicNo ratings yet
- RKK Insip 2019Document14 pagesRKK Insip 2019dimas ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionDocument36 pagesViral InfectionHani El-asferNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis:: Dr. Francisco Eizayaga, MD PHDDocument18 pagesAtopic Dermatitis:: Dr. Francisco Eizayaga, MD PHDAngelaNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis: Dr. Doni Priambodo Wijisaksono, Sppd-KptiDocument33 pagesLeptospirosis: Dr. Doni Priambodo Wijisaksono, Sppd-KptialbaazaNo ratings yet
- Toacs 6Document159 pagesToacs 6Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)
- Https://ar - scribd.com/document/391648283/OET Future Land Full Book Final Edition July 2018Document52 pagesHttps://ar - scribd.com/document/391648283/OET Future Land Full Book Final Edition July 2018Qutaiba ShdaifatNo ratings yet
- Swine 3&4Document73 pagesSwine 3&4Keegan McElroyNo ratings yet
- Approach To Fever With RashDocument35 pagesApproach To Fever With RashSenthilnathan ANo ratings yet
- Dengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andDocument5 pagesDengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andFrance John Evangelista TorresNo ratings yet
- Buzz WordsDocument67 pagesBuzz Wordsmb167204No ratings yet
- Oral Cavity LesionsDocument106 pagesOral Cavity LesionsFrederick Mars Untalan100% (1)
- Fever WHODocument80 pagesFever WHOSanti PadmasariNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases PhilippinesDocument11 pagesCommunicable Diseases Philippinessisjing88510No ratings yet
- RNA VirusesDocument10 pagesRNA VirusesMafie BarreiroNo ratings yet
- Vesiculobullous LesionsDocument130 pagesVesiculobullous LesionsRobins DhakalNo ratings yet
- Nail Changes: III-A '07 - Derma MegatableDocument21 pagesNail Changes: III-A '07 - Derma MegatableAileen Peña100% (2)
- Epidemiology.: Aegypti, A Daytime Biting Mosquito, Is The Principal Vector, and All Four Virus TypesDocument12 pagesEpidemiology.: Aegypti, A Daytime Biting Mosquito, Is The Principal Vector, and All Four Virus TypesMuhammad NazliNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease WorksheetDocument4 pagesInfectious Disease WorksheetBrittanyMarieNo ratings yet
- PATHOGNOMONIC SIGNS From Mam Della CruzDocument2 pagesPATHOGNOMONIC SIGNS From Mam Della CruzCiao AtienzaNo ratings yet
- StomatitisDocument118 pagesStomatitisUrwa NaveedNo ratings yet
- Henoch Scholein PurpuraDocument15 pagesHenoch Scholein PurpurapkpowerhouseNo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic Signs of Communicable DiseasesDocument2 pagesPathognomonic Signs of Communicable DiseasesErjohn Vincent Lim0% (1)
- RashDocument3 pagesRashNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Poultry Health ManagementDocument32 pagesPoultry Health Managementdawn100% (2)
- 2.papulosquamous DiseasesDocument65 pages2.papulosquamous DiseasesThesa TagalogNo ratings yet
- Paeds PresentationDocument28 pagesPaeds PresentationSantiyaa Selvamalar SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Approach in Lymphadenopathy in ChildrenDocument14 pagesApproach in Lymphadenopathy in Childrennahiry100% (1)
- Hema Lesson ADocument31 pagesHema Lesson AEbiNo ratings yet
- Health Dept - Training NeedsDocument72 pagesHealth Dept - Training NeedsSunil Kumar MalikNo ratings yet
- Use of Simulation Based Medical Education For AdvaDocument4 pagesUse of Simulation Based Medical Education For AdvaLê Huy HoàngNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxant Mind MapsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle Relaxant Mind MapsHello PBJNo ratings yet
- UWorld Notes Step 2 CKDocument11 pagesUWorld Notes Step 2 CKSamah Khan67% (3)
- Assessment of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument13 pagesAssessment of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusBaso AgusofyangNo ratings yet
- Neurotrauma Rural Guidelines 2edDocument27 pagesNeurotrauma Rural Guidelines 2edAldion ZericoNo ratings yet
- Phosphate BinderDocument51 pagesPhosphate BinderbedestySNo ratings yet
- Effective Educational and Clinical SupervisionDocument19 pagesEffective Educational and Clinical SupervisionMohammad Sutami100% (1)
- Acid Base PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAcid Base PhysiologyrajivprasanthNo ratings yet
- Rapid Trance Formations Advanced ManualDocument45 pagesRapid Trance Formations Advanced Manualmihail100% (3)
- Respiratory Therapist InterviewDocument8 pagesRespiratory Therapist Interviewapi-532603306No ratings yet
- RevitalVision™ - Scientific BackgroundDocument5 pagesRevitalVision™ - Scientific BackgroundEmil MoldoveanuNo ratings yet
- Identification Data of PatientDocument12 pagesIdentification Data of PatientJyoti100% (6)
- Glukoma (Prevention)Document36 pagesGlukoma (Prevention)Bagus Nur Eko PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Coombs TestDocument5 pagesCoombs TestMima Fatimah LuthfieNo ratings yet
- Folfiri Beva Gi Col PDocument12 pagesFolfiri Beva Gi Col Pvera docNo ratings yet
- Abdulsalam Mohammed Yakasai Physiotherapy Intervention in Children With EpiDocument17 pagesAbdulsalam Mohammed Yakasai Physiotherapy Intervention in Children With Epinaveen chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Objectives of The SystemDocument4 pagesObjectives of The Systemvivekanand_bonalNo ratings yet
- Cranial Release Technique - Free ReportDocument4 pagesCranial Release Technique - Free ReportchirotrelNo ratings yet
- Listen To A Conversation Between A Nurse and A Patient. Choose The Correct AnswersDocument5 pagesListen To A Conversation Between A Nurse and A Patient. Choose The Correct Answersmiy500_542116704No ratings yet
- CaseStudy HLTENN042 Task2 Student 220301Document9 pagesCaseStudy HLTENN042 Task2 Student 220301royroyalasadiNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Ibuprofen: Effects, Risks, and AlternativesDocument6 pagesAsthma and Ibuprofen: Effects, Risks, and AlternativesYasIsaNo ratings yet
- Level of Breast Cancer Awareness On Fourth-Year FemaleDocument28 pagesLevel of Breast Cancer Awareness On Fourth-Year FemaleLafayette Kirsi NoelNo ratings yet
- Indian Heart Journal: Narendra Kumar Arya, Kamlesh Singh, Anushree Malik, Rahul MehrotraDocument6 pagesIndian Heart Journal: Narendra Kumar Arya, Kamlesh Singh, Anushree Malik, Rahul MehrotraPAULSELVINo ratings yet
- Neet PG Preparation GuideDocument4 pagesNeet PG Preparation GuideGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- My TCM Diagnosis.Document64 pagesMy TCM Diagnosis.Omer Binmahfooz100% (2)
- OIG 2015 Work PlanDocument90 pagesOIG 2015 Work PlanThe Fox Group, LLCNo ratings yet
- CB Insights Digital Healthcare WebinarDocument80 pagesCB Insights Digital Healthcare WebinarMohammed KhairyNo ratings yet
- Brief Note On Child HealthDocument6 pagesBrief Note On Child HealthSivakumar Reddy JeevanNo ratings yet
- Proximity of Magnesium Exposure To Delivery and Neonatal Outcomes 2016 American Journal of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument6 pagesProximity of Magnesium Exposure To Delivery and Neonatal Outcomes 2016 American Journal of Obstetrics and GynecologyFarin MauliaNo ratings yet