Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Controlled Rectifier DC Drives
4 Controlled Rectifier DC Drives
Uploaded by
shonmlrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Controlled Rectifier DC Drives
4 Controlled Rectifier DC Drives
Uploaded by
shonmlrCopyright:
Available Formats
Controlled Rectifier DC Drives
By
Dr. Ungku Anisa Ungku Amirulddin
Department of Electrical Power Engineering
College of Engineering
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 1 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
Outline
Power Electronics Converters for DC Drives
Controlled Rectifier Fed DC Drives
Single Phase
Two-quadrant
Four-quadrant
Three Phase
Two-quadrant
Four-quadrant
References
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 2
Power Electronic Converters
for DC Drives
Speed Control Strategy:
below base speed: V
a
control
above base speed: flux control via V
f
control
Power electronics converters are used to obtain variable
voltage
Highly efficient
Ideally lossless
Type of converter used is depending on voltage source :
AC voltage source Controlled Rectifiers
Fixed DC voltage source DC-DC converters
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 3
Controlled Rectifier Fed DC Drives
To obtain variable DC voltage from fixed AC source
DC current flows in only 1 direction
Example of a drive system
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 4
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Two-quadrant drive
Limited to applications up to 15 kW
Regeneration (Q4) only be achieved with loads that can drive
the motor in reverse (-ve e)
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 5 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Two-quadrant drive
For continuous current:
Armature voltage
where V
m
= peak voltage
Armature current
Field voltage
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 6
a
m
a
V
V o
t
cos
2
=
f
m
f
V
V o
t
cos
2
=
a
a a
a
R
E V
I
=
90
o
180
o
t
m
V 2
t
m
V 2
o
Single-
phase
supply
+
V
a
i
a
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Two-quadrant drive
For Quadrant 1 operation:
e positive E
a
and V
a
positive
o
a
s 90
I
a
positive
Rectifier delivers power to motor,
i.e. forward motoring.
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 7
a
m
a
V
V o
t
cos
2
=
90
o
180
o
t
m
V 2
t
m
V 2
o
Single-
phase
supply
+
V
a
i
a
+
E
a
e
Q1
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Two-quadrant drive
For Quadrant 4 operation:
e negative E
a
negative
o
a
> 90 V
a
negative
I
a
positive (still in same direction)
Rectifier takes power from motor,
i.e. regenerative braking.
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 8
a
m
a
V
V o
t
cos
2
=
90
o
180
o
t
m
V 2
t
m
V 2
o
Single-
phase
supply
V
a
+
i
a
E
a
+
e
Q4
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Four-quadrant drive
Converter 1 for operation in 1
st
and 4
th
quadrant
Converter 2 for operation in 2
nd
and 3
rd
quadrant
Limited to applications up to 15 kW
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 9 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
Converter 1 Converter 2
Single-
phase
supply
Single-
phase
supply
+
V
a
i
a
Two rectifiers
connected in anti-
parallel across
motor armature
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Single-phase DC Drives
Four-quadrant drive
For continuous current:
Both converters are operated to produce the same dc voltage across the
terminal, i.e.:
where and
(V
m
= peak supply voltage)
Hence, firing angles of both converters must satisfy the following:
Armature current
Field voltage
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 10 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
1 1
cos
2
a
m
V
V o
t
=
f
m
f
V
V o
t
cos
2
=
a
a a
a
R
E V
I
=
t o o = +
2 1 a a
0
2 1
= +V V
2 2
cos
2
a
m
V
V o
t
=
+
V
1
Converter 1 Converter 2
V
2
+
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
Two-quadrant drive
Limited to applications up to 1500 kW
Regeneration (Q4) only be achieved with loads that can
drive the motor in reverse (-ve e)
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 11 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
For continuous current:
Armature voltage
where V
L-L, m
= peak line-to-line voltage
Armature current
Field voltage
(assuming a three-phase supply is used for
field excitation)
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 12
a
m
a
V
V o
t
cos
3
L, - L
=
f
m
f
V
V o
t
cos
3
L, - L
=
a
a a
a
R
E V
I
=
90
o
t
m
V
L, - L
3
t
m
V
L, - L
3
180
o
o
3-phase
supply
+
V
a
i
a
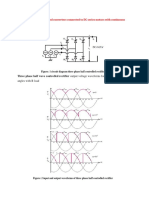
Three-phase Controlled Rectifier
2Q DC Drive Example
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 13
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
Four-quadrant drive
Converter 1 for operation in 1
st
and 4
th
quadrant
Converter 2 for operation in 2
nd
and 3
rd
quadrant
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 14 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
Converter 1 Converter 2
3-phase
supply
3-phase
supply
+
V
a
i
a
Two rectifiers
connected in anti-
parallel across
motor armature
I
a
+ve,
V
a
+ve or -ve
I
a
-ve,
V
a
+ve or -ve
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
Four-quadrant drive
For continuous current:
where V
L-L, m
= peak line-to-line voltage.
Similar to single-phase drive:
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 15 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
Converter 1 Converter 2
+
V
a
i
a
Converter 1:
I
a
+ve,
V
a
+ve
Converter 2:
I
a
-ve,
V
a
+ve
1 2
1
90 0
a a
a
o t o
o
=
< <
Converter 1:
I
a
+ve,
V
a
-ve
1 2
1
180 90
a a
a
o t o
o
=
< <
2 1
2
180 90
a a
a
o t o
o
=
< <
Converter 2:
I
a
-ve,
V
a
-ve
2 1
2
90 0
a a
a
o t o
o
=
< <
a
m
a
V
V o
t
cos
3
, L L
=
t o o = +
2 1 a a
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
For continuous current:
Armature current
Field voltage
Disadvantages:
Circulating current
Inductors L
1
and L
2
added to reduce
circulating currents
Slow response
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 16 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
+
V
a
Converter 1 Converter 2
i
a
L
1
L
2
f
m
f
V
V o
t
cos
3
L, - L
=
a
a a
a
R
E V
I
=
Three-phase Controlled Rectifier
4Q DC Drive Example
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 17
Controlled Rectifier Fed
Three-phase DC Drives
Four-quadrant drive
One controlled rectifier with 2 pairs of contactors
M1 and M2 closed for operation in 1
st
and 4
th
quadrant
R1 and R2 closed for operation in 2
nd
and 3
rd
quadrant
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 18 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
T
Q1 Q2
Q3 Q4
e
M1
M2
R1
R2
+ V
a
-
3-phase
supply
i
a
i
a
Rectifier Fed DC Drives Problems
1. Distortion of Supply
Controlled rectifier introduces harmonics to supply currents
and voltages which cause:
heating and torque pulsations in motor
resonance in power system network interaction between rectifier
RL with capacitor banks in system
Solution - eliminate most dominant harmonics by:
install LC filters at input of converters tuned to absorb most
dominant harmonics (i.e. 5
th
and 7
th
harmonics)
Use 12-pulse converter consists of two 6-pulse controlled rectifiers
connected in parallel
Selective switching of supply input using self-commutating devices
(eg. GTOs, IGBTs) in the converter
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 19
Rectifier Fed DC Drives Problems
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 20
12-pulse converter consists of two 6-pulse controlled rectifiers
connected in parallel
Rectifier Fed DC Drives Problems
2. Low supply power factor
Power factor related to firing angle o of rectifier
Low power factor especially during low speed operations
Solution:
Employ pulse-width modulated (PWM) rectifiers using GTOs,
IGBTs
High power factor
Low harmonic supply currents
Low efficiency - high switching losses (disadvantage)
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 21
Rectifier Fed DC Drives Problems
3. Effect on motor
Ripple in motor current harmonics present (most dominant
is 6
th
harmonic)
causes torque ripple, heating and derating of motor
solution: extra inductance added in series with L
a
Slow response
Discontinuous current may occur if
L
a
not large enough
Motor is lightly loaded
Effect of discontinuous current
Rectifier output voltage increases motor speed increases
(poor speed regulation under open-loop operation)
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 EEEB443 - Control & Drives 22
References
Rashid, M.H, Power Electronics: Circuit, Devices and
Applictions, 3
rd
ed., Pearson, New-Jersey, 2004.
Dubey, G.K., Fundamentals of Electric Drives, 2
nd
ed., Alpha
Science Int. Ltd., UK, 2001.
Krishnan, R., Electric Motor Drives: Modeling, Analysis and
Control, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 2001.
Nik Idris, N. R., Short Course Notes on Electrical Drives,
UNITEN/UTM, 2008.
Ahmad Azli, N., Short Course Notes on Electrical Drives,
UNITEN/UTM, 2008.
Dr. Ungku Anisa, July 2008 23 EEEB443 - Control & Drives
11/4/2013 EEL 4242 by Dr. M.H. Rashid 24
Three-Phase Full-Converter
Figure 10.5
Reference:
Rashid, M.H, Power Electronics: Circuit, Devices and
Applictions, 3
rd
ed., Pearson, New-Jersey, 2004
11/4/2013 EEL 4242 by Dr. M.H. Rashid 25
Waveforms and Conduction Times
/ 2
( )
/ 6
/ 2
/ 6
3
3
3 sin
6
3 3
cos
o dc ab
m
m
V v d
V d
V
t o
t o
t o
t o
u
t
t
u u
t
o
t
+
+
+
+
= =
| |
= +
|
\ .
=
}
}
Figure 10.5
/ 2
2 2
( )
/ 6
3
3 sin
6
1 3 3
3 cos 2
2 4
o rms m
m
V V d
V
t o
t o
t
u u
t
o
t
+
+
| |
= +
|
\ .
= +
}
Reference:
Rashid, M.H, Power Electronics:
Circuit, Devices and Applictions,
3
rd
ed., Pearson, New-Jersey, 2004
You might also like
- Series and Parallel Connection of SCRDocument21 pagesSeries and Parallel Connection of SCRDeepika BairagiNo ratings yet
- Nexygen Plus 41 User Manual Issue 10Document107 pagesNexygen Plus 41 User Manual Issue 10MARY CARMEN NAVARRETE GUILENNo ratings yet
- Parameters Which Effect Real and Reactive Power Flow: I I E X+ZDocument12 pagesParameters Which Effect Real and Reactive Power Flow: I I E X+ZvenkatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled RectifiersDocument38 pagesChapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled Rectifiersyemane gebremichal100% (2)
- The Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemDocument10 pagesThe Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemsantoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Cs1802 Visual Programming: Unit I: Windows ProgrammingDocument47 pagesCs1802 Visual Programming: Unit I: Windows ProgrammingSuneel Kumar GoudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part1Document46 pagesChapter 1 DC Drives Part1Mohammad MunzirNo ratings yet
- EE2351Document27 pagesEE2351Anonymous TJRX7C100% (1)
- Chapter - 2 DC & AC BridgesDocument18 pagesChapter - 2 DC & AC Bridgesvnyshreyas100% (2)
- Assignment-I (Power System Stability and Control EE16103)Document2 pagesAssignment-I (Power System Stability and Control EE16103)Prasenjit Dey50% (2)
- Alternators Connected To Infinite Bus BarDocument9 pagesAlternators Connected To Infinite Bus Barbharatk100% (1)
- Unit - I Economic Load DispatchDocument36 pagesUnit - I Economic Load DispatchRoopa Reddy100% (1)
- Single Phase Semi and Full Converter DC Separately Excited MotorDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Semi and Full Converter DC Separately Excited MotorHeliosAlaricNo ratings yet
- 4 (B) - IM Drives - AC Voltage ControllersDocument71 pages4 (B) - IM Drives - AC Voltage ControllersimdadamuNo ratings yet
- Auto TransformerDocument20 pagesAuto TransformerDawa PenjorNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lab PDFDocument54 pagesPower Systems Lab PDFBhanu BkvNo ratings yet
- On AC Voltage ControllersDocument25 pagesOn AC Voltage ControllersSahil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit V Design of Controllers For Drives: 3.1transfer Function For DC MotorDocument12 pagesUnit V Design of Controllers For Drives: 3.1transfer Function For DC Motormanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- CH2Document55 pagesCH2Shantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersDocument18 pagesPower Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersMaruti MohiteNo ratings yet
- Steps To Solve Power Flow Analysis For DummiesDocument6 pagesSteps To Solve Power Flow Analysis For DummiesAhmad Fateh Mohamad NorNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Voltage Control of Single-Phase InvertersDocument17 pagesVoltage Control of Single-Phase Invertersmailmanugs100% (1)
- Power System Stability - Unit 4 PSOCDocument57 pagesPower System Stability - Unit 4 PSOChareesh.makesuNo ratings yet
- SSSC PPT (Autosaved)Document14 pagesSSSC PPT (Autosaved)shubham bansalNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controllers: AC To Ac ConvertersDocument25 pagesAC Voltage Controllers: AC To Ac ConvertersPhạm Hữu Kỳ0% (1)
- Sources and Sinks of Reactive PowerDocument2 pagesSources and Sinks of Reactive Powershukla dhavalNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Discontinuous Mode)Document5 pagesFull-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Discontinuous Mode)hamza abdo mohamoud50% (4)
- Subject Code/name: EE 2306-Flexible AC Transmission Systems: Facts 8 Kce/Eee/Qb/Ivyr/FactsDocument26 pagesSubject Code/name: EE 2306-Flexible AC Transmission Systems: Facts 8 Kce/Eee/Qb/Ivyr/FactssivakumarsarvananNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Chopper Fed-Dc MotorDocument1 pageBlock Diagram of Chopper Fed-Dc MotorMohammed Saad100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Voltage ControlDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Voltage ControlNaveen Reddy100% (2)
- Capítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsDocument49 pagesCapítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsPaulinha BezerraNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 6 Pulse ConverterDocument27 pagesAnalysis of 6 Pulse ConverterSowjanya BhamidipatiNo ratings yet
- All Classroom Class ExamplesDocument51 pagesAll Classroom Class ExamplesAhmed Sabri0% (1)
- Emf Equation of AlternatorDocument2 pagesEmf Equation of AlternatorThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- 1.voltage Distribution Across String of InsulatorsDocument3 pages1.voltage Distribution Across String of Insulatorsarjuna4306No ratings yet
- Experiment.3. Load Characteristics of D.C Shunt GeneratorDocument2 pagesExperiment.3. Load Characteristics of D.C Shunt Generatorمحمد الحدي100% (1)
- Unit-V: Power Flow ControllersDocument11 pagesUnit-V: Power Flow Controllersgjk1236596No ratings yet
- J 10 KG-M: Problems Unit I Electric Drives (EEC3110) 1. A Drive Has Following ParametersDocument5 pagesJ 10 KG-M: Problems Unit I Electric Drives (EEC3110) 1. A Drive Has Following ParametersTan ThangNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)Document27 pagesUnified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)mksamy2021No ratings yet
- Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument14 pagesRepresentation of Power System ComponentsRume EmujekarohwoNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Op-Amp ApplicationDocument52 pagesCH 2 - Op-Amp Applicationknighthood4all100% (3)
- 2-Charge Formation in Clouds-1Document26 pages2-Charge Formation in Clouds-1Gokulraja GokulNo ratings yet
- Graetz Bridge LCCDocument42 pagesGraetz Bridge LCCKaran Singhania100% (3)
- BrakingDocument19 pagesBrakingMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 Noc18 Ee44 61Document4 pagesAssignment-4 Noc18 Ee44 61Sudip Mondal100% (1)
- Ee3008 Ps-II Lab Manual 2Document25 pagesEe3008 Ps-II Lab Manual 2Swapnil Gade007No ratings yet
- DC Motor Three Phase Half & Full Controlled DrivesDocument5 pagesDC Motor Three Phase Half & Full Controlled DrivesUjjal Dey0% (1)
- Unit-2-Converter and HVDC System ControlDocument13 pagesUnit-2-Converter and HVDC System Controlravikumar_ranganNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment - Introduction To Switch Mode Power SupplyDocument9 pagesLab Experiment - Introduction To Switch Mode Power SupplyChris ManahanNo ratings yet
- 180 Degree ConductionDocument27 pages180 Degree Conductionsathishsutharsan87No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Document29 pagesPower System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Jishnuraj KubandrarajNo ratings yet
- Steady-State Analysis of DC MotorsDocument24 pagesSteady-State Analysis of DC MotorsUsama RaoNo ratings yet
- Exp 1: OC and SC Test Along With Direct Load Test On A Single Phase TransformerDocument7 pagesExp 1: OC and SC Test Along With Direct Load Test On A Single Phase TransformerSumit KatreNo ratings yet
- Shunt Compensators: T.S.L.V.AyyaraoDocument9 pagesShunt Compensators: T.S.L.V.Ayyaraokrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Turbine, Generator and Governing SystemDocument21 pagesModeling of Turbine, Generator and Governing SystemdanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Unit CommitmentDocument31 pagesUnit 4 Unit Commitmentbrain420100% (1)
- 6 Chopper Controlled DC DrivesDocument24 pages6 Chopper Controlled DC DrivesMohamad Tauffik KamalullailNo ratings yet
- 2 Modeling of DC MachinesDocument23 pages2 Modeling of DC MachinessubhasishpodderNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - Modeling of DC MachinesDocument23 pagesLecture - 4 - Modeling of DC Machinesstubborn002No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Z Source Inverters WWWDocument5 pagesZ Source Inverters WWWshonmlrNo ratings yet
- Simulation of 8/6 and 8/14 Switched Reluctance Motor Based On Matlab/Simulink EnvironmentDocument5 pagesSimulation of 8/6 and 8/14 Switched Reluctance Motor Based On Matlab/Simulink EnvironmentshonmlrNo ratings yet
- S1&2-Basic Electrical Engineering: MGU B.TECH SyllabusDocument1 pageS1&2-Basic Electrical Engineering: MGU B.TECH SyllabusshonmlrNo ratings yet
- Oc and SC TransDocument9 pagesOc and SC TransshonmlrNo ratings yet
- Oc and SC TransDocument9 pagesOc and SC TransshonmlrNo ratings yet
- Rbead 600Document5 pagesRbead 600Rodrigo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Computer - Grade 9 - ClassTestDocument7 pagesComputer - Grade 9 - ClassTestfarzinahammedNo ratings yet
- Catalog Sommerkamp 2010Document20 pagesCatalog Sommerkamp 2010yu3zaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OS-Introduction-and-Hardware-Review Print VersionDocument6 pagesChapter 1 OS-Introduction-and-Hardware-Review Print VersionIonut GrozaNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Exercise 5.5 With SolutionDocument12 pagesLaplace Transform Exercise 5.5 With SolutionKiran ShakeelNo ratings yet
- LifeHacker - How To Set Up Your Own Private Cloud Storage Service in Five Minutes With OwncloudDocument5 pagesLifeHacker - How To Set Up Your Own Private Cloud Storage Service in Five Minutes With OwncloudrepakulakishoreNo ratings yet
- MQ RPGDocument579 pagesMQ RPGAnkit Kumar0% (1)
- Pipenet Vision Standard Module User and Reference Manual: © 2016 Sunrise Systems LimitedDocument27 pagesPipenet Vision Standard Module User and Reference Manual: © 2016 Sunrise Systems LimitedNitesh KirnakeNo ratings yet
- Oracle 10g R3 EnterpriseDocument224 pagesOracle 10g R3 Enterprisealasad parvezNo ratings yet
- AN-D26 High Voltage Isolated MOSFET Driver: FeaturesDocument6 pagesAN-D26 High Voltage Isolated MOSFET Driver: Featuresjulio meloNo ratings yet
- SSC9500 Application Note (Ver. 0.1) : Sanken Electric Co., LTDDocument19 pagesSSC9500 Application Note (Ver. 0.1) : Sanken Electric Co., LTDzhlikhonNo ratings yet
- Site Save of CodeSlinger - Co.uk - GameBoy Emulator Programming in C++ - MemoryDocument3 pagesSite Save of CodeSlinger - Co.uk - GameBoy Emulator Programming in C++ - MemoryRyanNo ratings yet
- Readme - Intel (R) Wireless Display 6.0 PV Build 6 0 60 0 PDFDocument33 pagesReadme - Intel (R) Wireless Display 6.0 PV Build 6 0 60 0 PDFMatias Alejandro GajardoNo ratings yet
- Exploiting Additional Actuators and Sensors For Nano-Positioning Robust Motion ControlDocument7 pagesExploiting Additional Actuators and Sensors For Nano-Positioning Robust Motion ControlEdward KikkenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ESE246 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 1 ESE246 PDFMuhamad AmmarNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education Lesson Log: Homeroom GuidanceDocument3 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Lesson Log: Homeroom GuidanceGem Lam SenNo ratings yet
- IPL Logic FlowDocument40 pagesIPL Logic FlowPriya Ekambaram100% (1)
- Developing Applications For The Java EE Platform (FJ-310-EE5)Document2 pagesDeveloping Applications For The Java EE Platform (FJ-310-EE5)nuricanNo ratings yet
- D Scope2Document2 pagesD Scope2dsimovicNo ratings yet
- 1:1 Digital Interface Transceiver With PLL: Description FeaturesDocument66 pages1:1 Digital Interface Transceiver With PLL: Description FeaturesAENo ratings yet
- Shiny::: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesShiny::: Cheat SheetFelipe Balboa PolancoNo ratings yet
- Questions About MicrocontrollerDocument8 pagesQuestions About MicrocontrollernolawitNo ratings yet
- 8998-19657-100 Power Tips For Fpga Designers2-1Document130 pages8998-19657-100 Power Tips For Fpga Designers2-1Yokoyoko YokoyokoNo ratings yet
- Building Recreational Flight Simulators - Mike's Flight DeckDocument78 pagesBuilding Recreational Flight Simulators - Mike's Flight DeckJúlio César MachadoNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing (EE-394) : Practical Work BookDocument13 pagesDigital Signal Processing (EE-394) : Practical Work BookHermain Fayyaz KarimNo ratings yet
- User Customer ExitsDocument16 pagesUser Customer ExitsShyam JaganathNo ratings yet
- Ptz-Box 5.0 - e - 098-002-001 - 2019-11Document4 pagesPtz-Box 5.0 - e - 098-002-001 - 2019-11Nurdeny Hidayanto PribadiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3: 8051 Programming in C: Microcontroller Notes:18EE52Document62 pagesMODULE 3: 8051 Programming in C: Microcontroller Notes:18EE52Supritha100% (1)