Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Uploaded by
api-237746849Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- International Business 14th Edition Daniels Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesInternational Business 14th Edition Daniels Test Bank DownloadChristina Walker100% (24)
- International Trade HWDocument6 pagesInternational Trade HWRei Diaz ApallaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage Are Both Concepts in International Trade That Help Explain The Reasons Behind Countries Specializing in Certain Goods and ServicesDocument2 pagesAbsolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage Are Both Concepts in International Trade That Help Explain The Reasons Behind Countries Specializing in Certain Goods and ServicesNaRgix AyObNo ratings yet
- Explanation:: Chapter 2 Study QuestionsDocument14 pagesExplanation:: Chapter 2 Study QuestionsChi Iuvianamo0% (1)
- Assignment: Absolute and Comparative Advantage: Labour Requirements Per Unit of OutputDocument1 pageAssignment: Absolute and Comparative Advantage: Labour Requirements Per Unit of OutputFareeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Law On Comparative AdvantageDocument33 pagesLaw On Comparative AdvantageEarl Louie MasacayanNo ratings yet
- MB0053 Why Is Comparative Cost Theory Considered As An Improvement Upon Absolute Cost Advantage Theory?Document22 pagesMB0053 Why Is Comparative Cost Theory Considered As An Improvement Upon Absolute Cost Advantage Theory?ajeetNo ratings yet
- Apply Concepts of Production and TradeDocument7 pagesApply Concepts of Production and TradeDaniel ChiarelliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Interdependence and Gains From Trade)Document5 pagesChapter 3 (Interdependence and Gains From Trade)Md Fahim Islam Antur 1931900643No ratings yet
- Comparative AdvantageDocument3 pagesComparative AdvantageARYEH YEHUDANo ratings yet
- Review of The Subject International Economics Intake 1 20232024 Edited 1Document8 pagesReview of The Subject International Economics Intake 1 20232024 Edited 1hhapanhNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomicsnorma johanna s. salamancaNo ratings yet
- Data For Exam Intro To ECODocument16 pagesData For Exam Intro To ECOLê Bá Thành PhúNo ratings yet
- Workshop in Export and Import PDFDocument11 pagesWorkshop in Export and Import PDFsemen.12qazNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Trade and Comparative AdvantageDocument48 pages4.1.2 Trade and Comparative AdvantageShazNo ratings yet
- International Business Environment BookDocument22 pagesInternational Business Environment BookSrikar ThalluriNo ratings yet
- Assignment For International Trade Agri Eco 3rdDocument3 pagesAssignment For International Trade Agri Eco 3rdgedisha katolaNo ratings yet
- A. Scarcity: The Nature of Economic Systems: Unit OneDocument25 pagesA. Scarcity: The Nature of Economic Systems: Unit OneShoniqua JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Remedial Take-Home Exam For Introduction To EconomicsDocument2 pagesRemedial Take-Home Exam For Introduction To EconomicsAgZawNo ratings yet
- Economics NSS F6 Exta Mock 4 MCDocument13 pagesEconomics NSS F6 Exta Mock 4 MCJerry LeeNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage Vs Comparative Advantage DifferencesDocument5 pagesAbsolute Advantage Vs Comparative Advantage DifferencesSyed InshanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Econ 101: Week 11 Practice ExercisesDocument3 pagesEcon 101: Week 11 Practice ExercisesManish MadishettyNo ratings yet
- What Is Absolute Advantage?Document9 pagesWhat Is Absolute Advantage?Ken ChepkwonyNo ratings yet
- W13 Topic 11 International TradeDocument30 pagesW13 Topic 11 International TradeCHZE CHZI CHUAHNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Assignment#1Document3 pagesBusiness Economics Assignment#1Ayesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Gains From TradeDocument26 pagesGains From TradeSaumya RaizadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To International TradeDocument30 pagesIntroduction To International TradeSudershan ThaibaNo ratings yet
- Gini CoefficientDocument41 pagesGini CoefficientKhagendra PoudelNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2: International Trade Submitted To: Dr. Zainab Jehan Submtted By: Tayyiba Ishaque Registration No: 2019-M-ECON-2-18Document9 pagesAssignment No 2: International Trade Submitted To: Dr. Zainab Jehan Submtted By: Tayyiba Ishaque Registration No: 2019-M-ECON-2-18zainabkhanNo ratings yet
- Trade Theories and Economic DevelopementDocument48 pagesTrade Theories and Economic DevelopementAhmed LoveNo ratings yet
- International Trade 1Document6 pagesInternational Trade 1Kunle OketoboNo ratings yet
- Student Number: (Enter On The Line Below) : HI5016 International Trade and Enterprise Final Assessment TRIMESTER T1, 2021Document8 pagesStudent Number: (Enter On The Line Below) : HI5016 International Trade and Enterprise Final Assessment TRIMESTER T1, 2021Muhammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage, Specialization and TradeDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics: Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage, Specialization and TradeLi ShiNo ratings yet
- Exim 2020-21Document4 pagesExim 2020-21Viraaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Theory of Absolute & Comparative AdvantagesDocument18 pagesSession 3 - Theory of Absolute & Comparative AdvantagesAnuj Goyal100% (1)
- MBA HR Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesMBA HR Managerial Economicskolli.99995891No ratings yet
- Describe How Do Factor Endowments Impact A CountryDocument5 pagesDescribe How Do Factor Endowments Impact A CountryNoor MughalNo ratings yet
- Economics 01Document2 pagesEconomics 01Ayesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Absolute and Comparative Advantage-Chapter 6Document3 pagesLecture Notes On Absolute and Comparative Advantage-Chapter 6Clebson CostaNo ratings yet
- English Auto Generated Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage With ExamplesDocument10 pagesEnglish Auto Generated Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage With Examplessabit.michelle0903No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Comparative Advantage and The Basis For TradeDocument3 pagesTopic 1: Comparative Advantage and The Basis For Tradefiren1388No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full International Economics 15th Edition Robert Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFDocument8 pagesDwnload Full International Economics 15th Edition Robert Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFtenjeichabac9100% (14)
- Week 3Document19 pagesWeek 3Raksa MaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage 1Document18 pagesAbsolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage 1Balpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics ExamDocument8 pagesMicroeconomics ExamBraceley & CoNo ratings yet
- Trade Theory, From Mercantilism To Free TradeDocument6 pagesTrade Theory, From Mercantilism To Free TradeMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 AnswerDocument16 pagesChapter 11 AnswerKathy WongNo ratings yet
- Theory of Absolute AdvantageDocument19 pagesTheory of Absolute AdvantageSaimuna YeasminNo ratings yet
- International Economics For Year 3Document306 pagesInternational Economics For Year 3Sovanda HokNo ratings yet
- Theory of Comparative AdvantageDocument3 pagesTheory of Comparative AdvantagePrime CartoonistNo ratings yet
- Case Study 27Document8 pagesCase Study 27Madhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Strategy: Third EditionDocument41 pagesManagerial Economics and Strategy: Third EditionRaeNo ratings yet
- BA 302 Lesson 3Document26 pagesBA 302 Lesson 3ピザンメルビンNo ratings yet
- Ibt 2Document9 pagesIbt 2Theingi Htike AungNo ratings yet
- Full Download International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manualcollicaepiphanys100% (45)
- Dwnload Full International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFtenjeichabac9100% (15)
- Money InternationalDocument7 pagesMoney Internationalofficialrrk06No ratings yet
- Micro Economics ProjectsDocument20 pagesMicro Economics ProjectsMd AshadNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Introduction Demand Supply Equilibrium ElasticityDocument203 pages1-2 Introduction Demand Supply Equilibrium Elasticitylemma4aNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy: in Law, The Fed Has A Dual Mandate: Monetary PolicyDocument1 pageMonetary Policy: in Law, The Fed Has A Dual Mandate: Monetary Policyapi-237746849No ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy: NameDocument1 pageFiscal Policy: Nameapi-237746849No ratings yet
- The Short-Run Macroeconomic Market and Business Cycle: SRAS Determinants 1. 2. 3. 4Document1 pageThe Short-Run Macroeconomic Market and Business Cycle: SRAS Determinants 1. 2. 3. 4api-237746849No ratings yet
- Central Banking, The Federal Reserve, and The Money Market: FunctionsDocument1 pageCentral Banking, The Federal Reserve, and The Money Market: Functionsapi-237746849No ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Check For Understanding! P/$ S PDocument1 pageThe Foreign Exchange Market: Check For Understanding! P/$ S Papi-237746849No ratings yet
- Morning Coffee: Chevy & AlbaDocument3 pagesMorning Coffee: Chevy & AlbaGà VipNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment S.Y. 2020-2021Document4 pagesHomeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment S.Y. 2020-2021Marnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- Abhinandan Updated CVDocument5 pagesAbhinandan Updated CVAbhinandan SenNo ratings yet
- Enb 12579 eDocument2 pagesEnb 12579 eadoptnegotiatorNo ratings yet
- Urban Green Spaces 2017Document202 pagesUrban Green Spaces 2017Diogo Guedes VidalNo ratings yet
- Incident Request Closeddate SepDocument315 pagesIncident Request Closeddate Sepأحمد أبوعرفهNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentAndrew MNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Secondary Brand KnowledgeDocument23 pagesLeveraging Secondary Brand KnowledgebappythegreatNo ratings yet
- Kajian Aktivitas Indeks Glikemik Brownies Kukus SuDocument13 pagesKajian Aktivitas Indeks Glikemik Brownies Kukus SuRippie RifdahNo ratings yet
- Trend Micro IWSS3.1 Master-Child and Shared DB 090205Document31 pagesTrend Micro IWSS3.1 Master-Child and Shared DB 090205Nitin JainNo ratings yet
- Phy Pract MockDocument9 pagesPhy Pract Mocksathvikpranavaug28No ratings yet
- Plato On Respect, and What "Belongs To" Oneself: Christopher J. RoweDocument16 pagesPlato On Respect, and What "Belongs To" Oneself: Christopher J. RoweOctavian DanNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Normal DistrributionDocument2 pagesQuiz On Normal Distrributiongulafshan100% (1)
- EMC Avamar 7.1 For SQL Server: User GuideDocument176 pagesEMC Avamar 7.1 For SQL Server: User GuideMohammed ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Mitkowski ResumeDocument1 pageMitkowski Resumeapi-381306663No ratings yet
- LECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanDocument30 pagesLECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanTJ BungayNo ratings yet
- Mealy and Moore Machine and Their Conversions (Http://smartclassacademy - Blogspot.pt/2012/11/mealy-And-Moore-Machine-And-Their - HTML)Document7 pagesMealy and Moore Machine and Their Conversions (Http://smartclassacademy - Blogspot.pt/2012/11/mealy-And-Moore-Machine-And-Their - HTML)brunoleriasNo ratings yet
- PRE DEMO TMDI LESSON PLAN Jay ForDocument8 pagesPRE DEMO TMDI LESSON PLAN Jay ForJayfor RabongNo ratings yet
- Best Increments For The Average Case of ShellsortDocument12 pagesBest Increments For The Average Case of Shellsortr4kemberNo ratings yet
- L1 Interferences and Psychological Factors in L2 Learning and AcquisitionDocument7 pagesL1 Interferences and Psychological Factors in L2 Learning and AcquisitionMa. Elena Abainza - ArambalaNo ratings yet
- Zoning in Processing Facilities 375003 7Document2 pagesZoning in Processing Facilities 375003 7TinnysumardiNo ratings yet
- CHN Lecture June 2012Document27 pagesCHN Lecture June 2012Jordan LlegoNo ratings yet
- 3U CompactPCI Spacewire DatasheetDocument2 pages3U CompactPCI Spacewire Datasheetprakasa88No ratings yet
- 7 Strategic Planning For PRDocument35 pages7 Strategic Planning For PRNsyazwani JUNo ratings yet
- Modern CryptographyDocument18 pagesModern CryptographyAmar SawriNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Assignment AnswersDocument2 pagesPLSQL Assignment Answersmadhav_kumarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Scores - ASSET ReportsDocument3 pagesSummary of Scores - ASSET ReportsCarterNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidDocument7 pagesAlkaloidMelinaNo ratings yet
- Cap1 - Engineering in TimeDocument12 pagesCap1 - Engineering in TimeHair Lopez100% (1)
- Arcuser Winter 2018 PDFDocument72 pagesArcuser Winter 2018 PDFNonnong MaguddayaoNo ratings yet
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Uploaded by
api-237746849Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Comparative Advantage: Fish Cars China 20 40 Japan 10 50
Uploaded by
api-237746849Copyright:
Available Formats
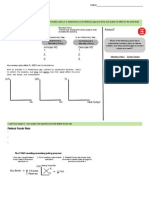
OTL 1.
Name__________________________________
Comparative Advantage
Learning Target 1: I can determine which country has an absolute advantage in the production of a good, using outputs and inputs
Absolute Advantage Outputs: when comparing two countries production possibilities, whichever country can make more of a particular good has an absolute advantage in that good Inputs: whichever country uses fewer inputs (cost, time) to make 1 of a good, that country has the absolute advantage Production Possibilities Fish 20 10
Fish China 20 or Japan 10
Cars 40 50
For outputs, Who has the absolute advantage in cars?
40
50
Cars
For inputs, who has the absolute advantage in cars?
Learning Target 2: I can determine which country has a comparative advantage in a product, for inputs and outputs, and explain what this means and its signicance for trade and production Comparative Advantage: The Basis for Trade 1. Calculate the opportunity cost to each country of producing one of each good 2. The country with the lowest opportunity cost in a good compared to the other country as a comparative advantage in that good 3. Whoever has a comparative advantage in a good should specialize in and make that good, and then trade for the other good
Calculating Opportunity Cost Outputs: Opp. Cost for 1 Good X = Good Y/Good X Inputs: Opp. Cost for 1 Good X = Good X/Good Y
Assess Yourself
The United States production possibilities are as follows: they can make 150 clothes or 100 software. Malaysia, on the other hand, can make 60 clothes or 20 software (fyi use the number 20, even though the video says 10 here). Show (calculating the opportunity cost) and explain which country has the comparative advantage in clothes, and in software.
Fish China 20 Japan 10
Cars 40 50
For outputs, which country has the comparative advantage in sh? Why?
For outputs, which country has the comparative advantage in cars? Why?
For inputs, which country has the comparative advantage in sh? Why?
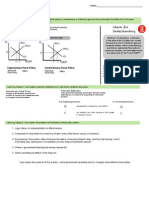
Learning Target 3: I can determine the mutually benecial terms of trade between countries
Mutually Benecial Terms of Trade If the countries decide to specialize and trade, what should the terms of trade be to where both countries benet? use United States and Malaysia example from above Mutually benecial terms (range) of trade The production possibilities for China and Japan are below. Suppose China and Japan decide to specialize in the good they have the comparative advantage in and then trade. Which of the following would be a mutually benecial term of
Finding the terms of trade (range) For 1 of Good X = a number in between the two opportunity costs of Good X in terms of Good Y
For 1 Clothes: For 1 Software:
a. 1 sh: 3 cars b. 1 car: 4 sh c. 1 car: 1/5 sh d. 1 sh: 1/3 cars e. 1 car: 1 sh
Learning Target 4: I can determine the consumption possibilities for a country given a term of trade
Consumption Possibilities - possible combination of goods a nation can consume - can consume more with specialization and trade than with self sufciency PPF and CPF for Malaysia Draw a PPF and consumption possibilities frontier for Japan assuming a mutually benecial term of trade is 1 car for 1/4 sh or 1 sh for 4 cars.
Clothes US 150 Malaysia 60
Software 100 20
Term of Trade 1 clothes for 1/2 software
What are Malaysias consumption possibilities with specialization and trade?
Malaysia had CA in clothes and US in software
Fish China 20 Japan 10
Cars 40 50
You might also like
- International Business 14th Edition Daniels Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesInternational Business 14th Edition Daniels Test Bank DownloadChristina Walker100% (24)
- International Trade HWDocument6 pagesInternational Trade HWRei Diaz ApallaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage Are Both Concepts in International Trade That Help Explain The Reasons Behind Countries Specializing in Certain Goods and ServicesDocument2 pagesAbsolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage Are Both Concepts in International Trade That Help Explain The Reasons Behind Countries Specializing in Certain Goods and ServicesNaRgix AyObNo ratings yet
- Explanation:: Chapter 2 Study QuestionsDocument14 pagesExplanation:: Chapter 2 Study QuestionsChi Iuvianamo0% (1)
- Assignment: Absolute and Comparative Advantage: Labour Requirements Per Unit of OutputDocument1 pageAssignment: Absolute and Comparative Advantage: Labour Requirements Per Unit of OutputFareeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Law On Comparative AdvantageDocument33 pagesLaw On Comparative AdvantageEarl Louie MasacayanNo ratings yet
- MB0053 Why Is Comparative Cost Theory Considered As An Improvement Upon Absolute Cost Advantage Theory?Document22 pagesMB0053 Why Is Comparative Cost Theory Considered As An Improvement Upon Absolute Cost Advantage Theory?ajeetNo ratings yet
- Apply Concepts of Production and TradeDocument7 pagesApply Concepts of Production and TradeDaniel ChiarelliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Interdependence and Gains From Trade)Document5 pagesChapter 3 (Interdependence and Gains From Trade)Md Fahim Islam Antur 1931900643No ratings yet
- Comparative AdvantageDocument3 pagesComparative AdvantageARYEH YEHUDANo ratings yet
- Review of The Subject International Economics Intake 1 20232024 Edited 1Document8 pagesReview of The Subject International Economics Intake 1 20232024 Edited 1hhapanhNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomicsnorma johanna s. salamancaNo ratings yet
- Data For Exam Intro To ECODocument16 pagesData For Exam Intro To ECOLê Bá Thành PhúNo ratings yet
- Workshop in Export and Import PDFDocument11 pagesWorkshop in Export and Import PDFsemen.12qazNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Trade and Comparative AdvantageDocument48 pages4.1.2 Trade and Comparative AdvantageShazNo ratings yet
- International Business Environment BookDocument22 pagesInternational Business Environment BookSrikar ThalluriNo ratings yet
- Assignment For International Trade Agri Eco 3rdDocument3 pagesAssignment For International Trade Agri Eco 3rdgedisha katolaNo ratings yet
- A. Scarcity: The Nature of Economic Systems: Unit OneDocument25 pagesA. Scarcity: The Nature of Economic Systems: Unit OneShoniqua JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Remedial Take-Home Exam For Introduction To EconomicsDocument2 pagesRemedial Take-Home Exam For Introduction To EconomicsAgZawNo ratings yet
- Economics NSS F6 Exta Mock 4 MCDocument13 pagesEconomics NSS F6 Exta Mock 4 MCJerry LeeNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage Vs Comparative Advantage DifferencesDocument5 pagesAbsolute Advantage Vs Comparative Advantage DifferencesSyed InshanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Econ 101: Week 11 Practice ExercisesDocument3 pagesEcon 101: Week 11 Practice ExercisesManish MadishettyNo ratings yet
- What Is Absolute Advantage?Document9 pagesWhat Is Absolute Advantage?Ken ChepkwonyNo ratings yet
- W13 Topic 11 International TradeDocument30 pagesW13 Topic 11 International TradeCHZE CHZI CHUAHNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Assignment#1Document3 pagesBusiness Economics Assignment#1Ayesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Gains From TradeDocument26 pagesGains From TradeSaumya RaizadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To International TradeDocument30 pagesIntroduction To International TradeSudershan ThaibaNo ratings yet
- Gini CoefficientDocument41 pagesGini CoefficientKhagendra PoudelNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2: International Trade Submitted To: Dr. Zainab Jehan Submtted By: Tayyiba Ishaque Registration No: 2019-M-ECON-2-18Document9 pagesAssignment No 2: International Trade Submitted To: Dr. Zainab Jehan Submtted By: Tayyiba Ishaque Registration No: 2019-M-ECON-2-18zainabkhanNo ratings yet
- Trade Theories and Economic DevelopementDocument48 pagesTrade Theories and Economic DevelopementAhmed LoveNo ratings yet
- International Trade 1Document6 pagesInternational Trade 1Kunle OketoboNo ratings yet
- Student Number: (Enter On The Line Below) : HI5016 International Trade and Enterprise Final Assessment TRIMESTER T1, 2021Document8 pagesStudent Number: (Enter On The Line Below) : HI5016 International Trade and Enterprise Final Assessment TRIMESTER T1, 2021Muhammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage, Specialization and TradeDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics: Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage, Specialization and TradeLi ShiNo ratings yet
- Exim 2020-21Document4 pagesExim 2020-21Viraaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Theory of Absolute & Comparative AdvantagesDocument18 pagesSession 3 - Theory of Absolute & Comparative AdvantagesAnuj Goyal100% (1)
- MBA HR Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesMBA HR Managerial Economicskolli.99995891No ratings yet
- Describe How Do Factor Endowments Impact A CountryDocument5 pagesDescribe How Do Factor Endowments Impact A CountryNoor MughalNo ratings yet
- Economics 01Document2 pagesEconomics 01Ayesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Absolute and Comparative Advantage-Chapter 6Document3 pagesLecture Notes On Absolute and Comparative Advantage-Chapter 6Clebson CostaNo ratings yet
- English Auto Generated Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage With ExamplesDocument10 pagesEnglish Auto Generated Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage With Examplessabit.michelle0903No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Comparative Advantage and The Basis For TradeDocument3 pagesTopic 1: Comparative Advantage and The Basis For Tradefiren1388No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full International Economics 15th Edition Robert Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFDocument8 pagesDwnload Full International Economics 15th Edition Robert Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFtenjeichabac9100% (14)
- Week 3Document19 pagesWeek 3Raksa MaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage 1Document18 pagesAbsolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage 1Balpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics ExamDocument8 pagesMicroeconomics ExamBraceley & CoNo ratings yet
- Trade Theory, From Mercantilism To Free TradeDocument6 pagesTrade Theory, From Mercantilism To Free TradeMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 AnswerDocument16 pagesChapter 11 AnswerKathy WongNo ratings yet
- Theory of Absolute AdvantageDocument19 pagesTheory of Absolute AdvantageSaimuna YeasminNo ratings yet
- International Economics For Year 3Document306 pagesInternational Economics For Year 3Sovanda HokNo ratings yet
- Theory of Comparative AdvantageDocument3 pagesTheory of Comparative AdvantagePrime CartoonistNo ratings yet
- Case Study 27Document8 pagesCase Study 27Madhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Strategy: Third EditionDocument41 pagesManagerial Economics and Strategy: Third EditionRaeNo ratings yet
- BA 302 Lesson 3Document26 pagesBA 302 Lesson 3ピザンメルビンNo ratings yet
- Ibt 2Document9 pagesIbt 2Theingi Htike AungNo ratings yet
- Full Download International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manualcollicaepiphanys100% (45)
- Dwnload Full International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full International Economics 17th Edition Carbaugh Solutions Manual PDFtenjeichabac9100% (15)
- Money InternationalDocument7 pagesMoney Internationalofficialrrk06No ratings yet
- Micro Economics ProjectsDocument20 pagesMicro Economics ProjectsMd AshadNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Introduction Demand Supply Equilibrium ElasticityDocument203 pages1-2 Introduction Demand Supply Equilibrium Elasticitylemma4aNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy: in Law, The Fed Has A Dual Mandate: Monetary PolicyDocument1 pageMonetary Policy: in Law, The Fed Has A Dual Mandate: Monetary Policyapi-237746849No ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy: NameDocument1 pageFiscal Policy: Nameapi-237746849No ratings yet
- The Short-Run Macroeconomic Market and Business Cycle: SRAS Determinants 1. 2. 3. 4Document1 pageThe Short-Run Macroeconomic Market and Business Cycle: SRAS Determinants 1. 2. 3. 4api-237746849No ratings yet
- Central Banking, The Federal Reserve, and The Money Market: FunctionsDocument1 pageCentral Banking, The Federal Reserve, and The Money Market: Functionsapi-237746849No ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Check For Understanding! P/$ S PDocument1 pageThe Foreign Exchange Market: Check For Understanding! P/$ S Papi-237746849No ratings yet
- Morning Coffee: Chevy & AlbaDocument3 pagesMorning Coffee: Chevy & AlbaGà VipNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment S.Y. 2020-2021Document4 pagesHomeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment S.Y. 2020-2021Marnellie Bautista-ValdezNo ratings yet
- Abhinandan Updated CVDocument5 pagesAbhinandan Updated CVAbhinandan SenNo ratings yet
- Enb 12579 eDocument2 pagesEnb 12579 eadoptnegotiatorNo ratings yet
- Urban Green Spaces 2017Document202 pagesUrban Green Spaces 2017Diogo Guedes VidalNo ratings yet
- Incident Request Closeddate SepDocument315 pagesIncident Request Closeddate Sepأحمد أبوعرفهNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentAndrew MNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Secondary Brand KnowledgeDocument23 pagesLeveraging Secondary Brand KnowledgebappythegreatNo ratings yet
- Kajian Aktivitas Indeks Glikemik Brownies Kukus SuDocument13 pagesKajian Aktivitas Indeks Glikemik Brownies Kukus SuRippie RifdahNo ratings yet
- Trend Micro IWSS3.1 Master-Child and Shared DB 090205Document31 pagesTrend Micro IWSS3.1 Master-Child and Shared DB 090205Nitin JainNo ratings yet
- Phy Pract MockDocument9 pagesPhy Pract Mocksathvikpranavaug28No ratings yet
- Plato On Respect, and What "Belongs To" Oneself: Christopher J. RoweDocument16 pagesPlato On Respect, and What "Belongs To" Oneself: Christopher J. RoweOctavian DanNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Normal DistrributionDocument2 pagesQuiz On Normal Distrributiongulafshan100% (1)
- EMC Avamar 7.1 For SQL Server: User GuideDocument176 pagesEMC Avamar 7.1 For SQL Server: User GuideMohammed ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Mitkowski ResumeDocument1 pageMitkowski Resumeapi-381306663No ratings yet
- LECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanDocument30 pagesLECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanTJ BungayNo ratings yet
- Mealy and Moore Machine and Their Conversions (Http://smartclassacademy - Blogspot.pt/2012/11/mealy-And-Moore-Machine-And-Their - HTML)Document7 pagesMealy and Moore Machine and Their Conversions (Http://smartclassacademy - Blogspot.pt/2012/11/mealy-And-Moore-Machine-And-Their - HTML)brunoleriasNo ratings yet
- PRE DEMO TMDI LESSON PLAN Jay ForDocument8 pagesPRE DEMO TMDI LESSON PLAN Jay ForJayfor RabongNo ratings yet
- Best Increments For The Average Case of ShellsortDocument12 pagesBest Increments For The Average Case of Shellsortr4kemberNo ratings yet
- L1 Interferences and Psychological Factors in L2 Learning and AcquisitionDocument7 pagesL1 Interferences and Psychological Factors in L2 Learning and AcquisitionMa. Elena Abainza - ArambalaNo ratings yet
- Zoning in Processing Facilities 375003 7Document2 pagesZoning in Processing Facilities 375003 7TinnysumardiNo ratings yet
- CHN Lecture June 2012Document27 pagesCHN Lecture June 2012Jordan LlegoNo ratings yet
- 3U CompactPCI Spacewire DatasheetDocument2 pages3U CompactPCI Spacewire Datasheetprakasa88No ratings yet
- 7 Strategic Planning For PRDocument35 pages7 Strategic Planning For PRNsyazwani JUNo ratings yet
- Modern CryptographyDocument18 pagesModern CryptographyAmar SawriNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Assignment AnswersDocument2 pagesPLSQL Assignment Answersmadhav_kumarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Scores - ASSET ReportsDocument3 pagesSummary of Scores - ASSET ReportsCarterNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidDocument7 pagesAlkaloidMelinaNo ratings yet
- Cap1 - Engineering in TimeDocument12 pagesCap1 - Engineering in TimeHair Lopez100% (1)
- Arcuser Winter 2018 PDFDocument72 pagesArcuser Winter 2018 PDFNonnong MaguddayaoNo ratings yet