Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Uploaded by
biestavelCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Backup and Recovery PolicyDocument17 pagesBackup and Recovery PolicyJasminBesic100% (2)
- Information Security Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesInformation Security Policy Templategfb0% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery PlanDocument6 pagesIT Disaster Recovery PlanCentaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan PolicyDocument3 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan Policyrozeny2kNo ratings yet
- IT Disaster RecoveryDocument7 pagesIT Disaster RecoveryVarun AhujaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan SampleDocument17 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan SampleJosé Pedro Neves100% (2)
- Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument30 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan TemplateVenkatraman Krishnamoorthy100% (4)
- IT Operations - User Access Management PoliciesDocument8 pagesIT Operations - User Access Management PoliciesChokchai AunhavichaiNo ratings yet
- IT Security PoliciesDocument10 pagesIT Security Policiesapexauditsystem67% (3)
- Backup Policy TemplateDocument6 pagesBackup Policy TemplateRamdani DDS100% (1)
- It Disaster Recovery Workbook and TemplateDocument37 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Workbook and Templateata_rehman70100% (4)
- CNV 03 BDocument4 pagesCNV 03 BMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery PlanningDocument14 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Planningtarnav86% (7)
- Disaster Recovery Plan Template 02Document34 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan Template 02ryandini fadhilah100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery PolicyDocument21 pagesDisaster Recovery PolicyLavhonte Antonio Davis50% (2)
- IT Security Policy Word TemplateDocument29 pagesIT Security Policy Word Templateapi-373663686% (7)
- It Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateARCO EXPORTNo ratings yet
- IT Security Incident ManagementDocument3 pagesIT Security Incident ManagementBrianEarlNo ratings yet
- Information Security Policy DocumentDocument84 pagesInformation Security Policy DocumentbendahlNo ratings yet
- Sample Disaster Recovery PlanDocument24 pagesSample Disaster Recovery PlantalhaniazNo ratings yet
- It Security GuidelinesDocument143 pagesIt Security GuidelinesTeam LeaderNo ratings yet
- Business Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesBusiness Impact AnalysisvipermyNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument14 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanAnis GharbiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery Planprabhu0487100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery and Bussines Continuity PlanDocument7 pagesDisaster Recovery and Bussines Continuity Plankumar100% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery Action PlanDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Action Plancrissdemon100% (2)
- DR BCP Guidebook PDFDocument17 pagesDR BCP Guidebook PDFhaji5No ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery Plan PDFDocument74 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Plan PDFJay Zetroc100% (2)
- IT Policies-Asset Classification and Control PolicyDocument5 pagesIT Policies-Asset Classification and Control Policyrajagopalansankar0% (1)
- Disaster Recovery DrillDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery DrillApoorv Bishnoi100% (3)
- Backup PolicyDocument3 pagesBackup PolicypeacebabatundeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan 2018Document7 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan 2018Anonymous ZsAYr5WAa100% (1)
- Business Continutity Plan Slides V1.1Document34 pagesBusiness Continutity Plan Slides V1.1Akmal GafarNo ratings yet
- Data Backup ProceduresDocument5 pagesData Backup ProceduresAzuchukwuene Chikeluba Dominic100% (2)
- Lecture#5: IT Service Continuity ManagementDocument58 pagesLecture#5: IT Service Continuity Managementzolfa mohammedNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument24 pagesInformation SecurityHumera GullNo ratings yet
- Information Security Patch Management ProcedureDocument5 pagesInformation Security Patch Management ProcedureSyed Zeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- MBCF BIA Template FinalDocument20 pagesMBCF BIA Template FinaldanirodigicomNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Planning Template RevisedDocument36 pagesDisaster Recovery Planning Template RevisedSatria Ardi Perdana100% (1)
- IT Policies, Procedures and Standards v1Document176 pagesIT Policies, Procedures and Standards v1Jimmy UkoboNo ratings yet
- SAMA Cyber Security Framework 1.0Document56 pagesSAMA Cyber Security Framework 1.0iawanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument16 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanPab Ronald Rafanan CalanocNo ratings yet
- DRP REVISED Final VersionDocument15 pagesDRP REVISED Final Versionfawas hamdiNo ratings yet
- DRP TemplateDocument13 pagesDRP Templatemiloja99No ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument8 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan TemplateSandsw3ptNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanUthpala Pahalavithaƞa100% (2)
- Security Incident Response Plan HLDocument6 pagesSecurity Incident Response Plan HLnicolasv100% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery Plan Template: ContentsDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Plan Template: ContentsUriel TijerinoNo ratings yet
- BCP Testing PDFDocument16 pagesBCP Testing PDFOmeni Phil AceNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity and Disaster RecoveryDocument38 pagesBusiness Continuity and Disaster Recoverymadunix100% (1)
- Business Continuity Management and IT Disaster RecoveryDocument4 pagesBusiness Continuity Management and IT Disaster RecoveryKeith Parker100% (3)
- IT Security PolicyDocument13 pagesIT Security PolicyMohammad Farooq100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery Plan LastDocument13 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan LastMary Ařmĥølīc Yøja100% (1)
- Network Security and ManagementDocument4 pagesNetwork Security and Managementrashid1986No ratings yet
- Business Continuity Planning BCP Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandBusiness Continuity Planning BCP Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- IT Disaster Recovery Plan - Ready - GovDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Plan - Ready - Govtarun7787No ratings yet
- Title of The Project:: Revenue Collection SystemDocument29 pagesTitle of The Project:: Revenue Collection Systemsrinibashb5546No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1JayaJayashNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument7 pagesData ProcessingOlapade BabatundeNo ratings yet
- ISCL Case Study 1Document3 pagesISCL Case Study 1Sandeep ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog: Machine Type: Vip Iii 46 / Vip Iii 47 Gaming Platform: Various Game Software: VariousDocument14 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: Machine Type: Vip Iii 46 / Vip Iii 47 Gaming Platform: Various Game Software: VariousDumitru ScurtuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: CPU Scheduling: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2009 Operating System Concepts - 8 EditionDocument61 pagesChapter 5: CPU Scheduling: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2009 Operating System Concepts - 8 Editionmervat anwarNo ratings yet
- System App Anr@1601924853309Document51 pagesSystem App Anr@1601924853309lozano palominoNo ratings yet
- Foc Theory Unit 2Document96 pagesFoc Theory Unit 2dhruv shahNo ratings yet
- LC MeterDocument10 pagesLC MeterYenidir TeknoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #1 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial #1 PDFHilal HuseyinliNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx XC7A200T-1FBG676CDocument12 pagesWhat Is Xilinx XC7A200T-1FBG676CjackNo ratings yet
- GE Energy Mark Ve Control: I/O Communication (PMVE) Module DescriptionDocument142 pagesGE Energy Mark Ve Control: I/O Communication (PMVE) Module DescriptionJorge Contreras100% (1)
- Canon FB1210U Service ManualDocument102 pagesCanon FB1210U Service ManualDuplessisNo ratings yet
- DRAM PresentationDocument11 pagesDRAM PresentationVani SallyNo ratings yet
- Asus P6 WS Pro ManualDocument194 pagesAsus P6 WS Pro ManualNeilKumar100% (1)
- 12-23-14-New-Long - Dealers Price PDFDocument2 pages12-23-14-New-Long - Dealers Price PDFJhon Ray CagampangNo ratings yet
- Memory and StorageDocument2 pagesMemory and Storagefahmi rizaldiNo ratings yet
- Intel Scalable Io Virtualization Technical SpecificationDocument29 pagesIntel Scalable Io Virtualization Technical SpecificationDJSNo ratings yet
- Embedded Controls IntroDocument25 pagesEmbedded Controls IntroEgy SangajiNo ratings yet
- Leica DFC420 DFC420C Brochure enDocument4 pagesLeica DFC420 DFC420C Brochure enCsaba GibártiNo ratings yet
- Data Computing Appliance Version 3Document150 pagesData Computing Appliance Version 3Derek YuenNo ratings yet
- Dpc2535a Error Code ListDocument7 pagesDpc2535a Error Code List黃義翔No ratings yet
- CSEN702-Week2 24539Document24 pagesCSEN702-Week2 24539Mohamed ElzareiNo ratings yet
- FUJITSU Call Center System CCRM-1 - Product DescriptionDocument29 pagesFUJITSU Call Center System CCRM-1 - Product Descriptiontsegab bekeleNo ratings yet
- Eduzone A Complete Campus Management SystemDocument3 pagesEduzone A Complete Campus Management Systemsiji_mtNo ratings yet
- Lab GPDocument15 pagesLab GPpremNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNote FileList of B1400CEAE 2009 X64 V2.01A LDocument7 pagesReleaseNote FileList of B1400CEAE 2009 X64 V2.01A LMorosan AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Intel WiFi 6E AX210 Extended Temp Industrial Module - Product Brief - 0622Document3 pagesIntel WiFi 6E AX210 Extended Temp Industrial Module - Product Brief - 0622Nhân Huỳnh ThiệnNo ratings yet
- All-In-One Guide (Number 1)Document346 pagesAll-In-One Guide (Number 1)Jayapal Errabelli67% (3)
- Class 5Document59 pagesClass 5Mandil Bhandari100% (1)
- Networker 9.X Archive Downloads For Customers and Partners: You Start!Document2 pagesNetworker 9.X Archive Downloads For Customers and Partners: You Start!Zuhaib ShafiNo ratings yet
- Sewing SunstarDocument1 pageSewing Sunstarsongdongemdem28No ratings yet
- Password Recovery Procedure Overview - 3650Document3 pagesPassword Recovery Procedure Overview - 3650tuananh0788No ratings yet
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Uploaded by
biestavelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Uploaded by
biestavelCopyright:
Available Formats
IT Disaster Recovery Plan
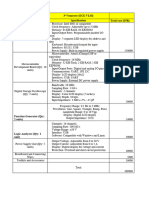
Businesses use information technology to quickly and effectively process information. Employees use electronic mail and Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP) telephone systems to communicate. Electronic data interchange (E I) is used to transmit data including orders and payments from one company to another. !ervers process information and store large amounts of data. esktop computers" laptops and #ireless devices are used $y employees to create" process" manage and communicate information. %hat do you #hen your information technology stops #orking& 'n information technology disaster recovery plan (I( )P) should $e developed in con*unction #ith the $usiness continuity plan. Priorities and recovery time o$*ectives for information technology should $e developed during the $usiness impact analysis. (echnology recovery strategies should $e developed to restore hard#are" applications and data in time to meet the needs of the $usiness recovery. Businesses large and small create and manage large volumes of electronic information or data. +uch of that data is important. !ome data is vital to the survival and continued operation of the $usiness. (he impact of data loss or corruption from hard#are failure" human error" hacking or mal#are could $e significant. ' plan for data $ackup and restoration of electronic information is essential. )ecovery strategies should $e developed for Information technology (I() systems" applications and data. (his includes net#orks" servers" desktops" laptops" #ireless devices" data and connectivity. Priorities for I( recovery should $e consistent #ith the priorities for recovery of $usiness functions and processes that #ere developed during the $usiness impact analysis. I( resources required to support time,sensitive $usiness functions and processes should also $e identified. (he recovery time for an I( resource should match the recovery time o$*ective for the $usiness function or process that depends on the I( resource. Information technology systems require hard#are" soft#are" data and connectivity. %ithout one component of the -system". the system may not run. (herefore" recovery strategies should $e developed to anticipate the loss of one or more of the follo#ing system components/
0omputer room environment (secure computer room #ith climate control" conditioned and $ackup po#er supply" etc.) 1ard#are (net#orks" servers" desktop and laptop computers" #ireless devices and peripherals) 0onnectivity to a service provider (fi$er" ca$le" #ireless" etc.) !oft#are applications (electronic data interchange" electronic mail" enterprise resource management" office productivity" etc.) ata and restoration
!ome $usiness applications cannot tolerate any do#ntime. (hey utili2e dual data centers capa$le of handling all data processing needs" #hich run in parallel #ith data mirrored or synchroni2ed $et#een the t#o centers. (his is a very e3pensive solution that only larger companies can afford. 1o#ever" there are other solutions availa$le for small to medium si2ed $usinesses #ith critical $usiness applications and data to protect.
Internal Recovery Strategies
+any $usinesses have access to more than one facility. 1ard#are at an alternate facility can $e configured to run similar hard#are and soft#are applications #hen needed. 'ssuming data is $acked up off,site or data is mirrored $et#een the t#o sites" data can $e restored at the alternate site and processing can continue.
Vendor Supported Recovery Strategies
(here are vendors that can provide -hot sites. for I( disaster recovery. (hese sites are fully configured data centers #ith commonly used hard#are and soft#are products. !u$scri$ers may provide unique equipment or soft#are either at the time of disaster or store it at the hot site ready for use. ata streams" data security services and applications can $e hosted and managed $y vendors. (his information can $e accessed at the primary $usiness site or any alternate site using a #e$ $ro#ser. If an outage is detected at the client site $y the vendor" the vendor automatically holds data until the client4s system is restored. (hese vendors can also provide data filtering and detection of mal#are threats" #hich enhance cy$er security.
Developing an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Businesses should develop an I( disaster recovery plan. It $egins $y compiling an inventory of hard#are (e.g. servers" desktops" laptops and #ireless devices)" soft#are applications and data. (he plan should include a strategy to ensure that all critical information is $acked up. Identify critical soft#are applications and data and the hard#are required to run them. 5sing standardi2ed hard#are #ill help to replicate and reimage ne# hard#are. Ensure that copies of program soft#are are availa$le to ena$le re,installation on replacement equipment. Prioriti2e hard#are and soft#are restoration. ocument the I( disaster recovery plan as part of the $usiness continuity plan. (est the plan periodically to make sure that it #orks.
You might also like
- Backup and Recovery PolicyDocument17 pagesBackup and Recovery PolicyJasminBesic100% (2)
- Information Security Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesInformation Security Policy Templategfb0% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery PlanDocument6 pagesIT Disaster Recovery PlanCentaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan PolicyDocument3 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan Policyrozeny2kNo ratings yet
- IT Disaster RecoveryDocument7 pagesIT Disaster RecoveryVarun AhujaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan SampleDocument17 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan SampleJosé Pedro Neves100% (2)
- Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument30 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan TemplateVenkatraman Krishnamoorthy100% (4)
- IT Operations - User Access Management PoliciesDocument8 pagesIT Operations - User Access Management PoliciesChokchai AunhavichaiNo ratings yet
- IT Security PoliciesDocument10 pagesIT Security Policiesapexauditsystem67% (3)
- Backup Policy TemplateDocument6 pagesBackup Policy TemplateRamdani DDS100% (1)
- It Disaster Recovery Workbook and TemplateDocument37 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Workbook and Templateata_rehman70100% (4)
- CNV 03 BDocument4 pagesCNV 03 BMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery PlanningDocument14 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Planningtarnav86% (7)
- Disaster Recovery Plan Template 02Document34 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan Template 02ryandini fadhilah100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery PolicyDocument21 pagesDisaster Recovery PolicyLavhonte Antonio Davis50% (2)
- IT Security Policy Word TemplateDocument29 pagesIT Security Policy Word Templateapi-373663686% (7)
- It Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateARCO EXPORTNo ratings yet
- IT Security Incident ManagementDocument3 pagesIT Security Incident ManagementBrianEarlNo ratings yet
- Information Security Policy DocumentDocument84 pagesInformation Security Policy DocumentbendahlNo ratings yet
- Sample Disaster Recovery PlanDocument24 pagesSample Disaster Recovery PlantalhaniazNo ratings yet
- It Security GuidelinesDocument143 pagesIt Security GuidelinesTeam LeaderNo ratings yet
- Business Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesBusiness Impact AnalysisvipermyNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument14 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanAnis GharbiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery Planprabhu0487100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery and Bussines Continuity PlanDocument7 pagesDisaster Recovery and Bussines Continuity Plankumar100% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery Action PlanDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Action Plancrissdemon100% (2)
- DR BCP Guidebook PDFDocument17 pagesDR BCP Guidebook PDFhaji5No ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery Plan PDFDocument74 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Plan PDFJay Zetroc100% (2)
- IT Policies-Asset Classification and Control PolicyDocument5 pagesIT Policies-Asset Classification and Control Policyrajagopalansankar0% (1)
- Disaster Recovery DrillDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery DrillApoorv Bishnoi100% (3)
- Backup PolicyDocument3 pagesBackup PolicypeacebabatundeNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan 2018Document7 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan 2018Anonymous ZsAYr5WAa100% (1)
- Business Continutity Plan Slides V1.1Document34 pagesBusiness Continutity Plan Slides V1.1Akmal GafarNo ratings yet
- Data Backup ProceduresDocument5 pagesData Backup ProceduresAzuchukwuene Chikeluba Dominic100% (2)
- Lecture#5: IT Service Continuity ManagementDocument58 pagesLecture#5: IT Service Continuity Managementzolfa mohammedNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument24 pagesInformation SecurityHumera GullNo ratings yet
- Information Security Patch Management ProcedureDocument5 pagesInformation Security Patch Management ProcedureSyed Zeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- MBCF BIA Template FinalDocument20 pagesMBCF BIA Template FinaldanirodigicomNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Planning Template RevisedDocument36 pagesDisaster Recovery Planning Template RevisedSatria Ardi Perdana100% (1)
- IT Policies, Procedures and Standards v1Document176 pagesIT Policies, Procedures and Standards v1Jimmy UkoboNo ratings yet
- SAMA Cyber Security Framework 1.0Document56 pagesSAMA Cyber Security Framework 1.0iawanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument16 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanPab Ronald Rafanan CalanocNo ratings yet
- DRP REVISED Final VersionDocument15 pagesDRP REVISED Final Versionfawas hamdiNo ratings yet
- DRP TemplateDocument13 pagesDRP Templatemiloja99No ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument8 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan TemplateSandsw3ptNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery PlanDocument12 pagesDisaster Recovery PlanUthpala Pahalavithaƞa100% (2)
- Security Incident Response Plan HLDocument6 pagesSecurity Incident Response Plan HLnicolasv100% (1)
- IT Disaster Recovery Plan Template: ContentsDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Plan Template: ContentsUriel TijerinoNo ratings yet
- BCP Testing PDFDocument16 pagesBCP Testing PDFOmeni Phil AceNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity and Disaster RecoveryDocument38 pagesBusiness Continuity and Disaster Recoverymadunix100% (1)
- Business Continuity Management and IT Disaster RecoveryDocument4 pagesBusiness Continuity Management and IT Disaster RecoveryKeith Parker100% (3)
- IT Security PolicyDocument13 pagesIT Security PolicyMohammad Farooq100% (1)
- Disaster Recovery Plan LastDocument13 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan LastMary Ařmĥølīc Yøja100% (1)
- Network Security and ManagementDocument4 pagesNetwork Security and Managementrashid1986No ratings yet
- Business Continuity Planning BCP Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandBusiness Continuity Planning BCP Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- IT Disaster Recovery Plan - Ready - GovDocument7 pagesIT Disaster Recovery Plan - Ready - Govtarun7787No ratings yet
- Title of The Project:: Revenue Collection SystemDocument29 pagesTitle of The Project:: Revenue Collection Systemsrinibashb5546No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1JayaJayashNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument7 pagesData ProcessingOlapade BabatundeNo ratings yet
- ISCL Case Study 1Document3 pagesISCL Case Study 1Sandeep ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog: Machine Type: Vip Iii 46 / Vip Iii 47 Gaming Platform: Various Game Software: VariousDocument14 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: Machine Type: Vip Iii 46 / Vip Iii 47 Gaming Platform: Various Game Software: VariousDumitru ScurtuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: CPU Scheduling: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2009 Operating System Concepts - 8 EditionDocument61 pagesChapter 5: CPU Scheduling: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2009 Operating System Concepts - 8 Editionmervat anwarNo ratings yet
- System App Anr@1601924853309Document51 pagesSystem App Anr@1601924853309lozano palominoNo ratings yet
- Foc Theory Unit 2Document96 pagesFoc Theory Unit 2dhruv shahNo ratings yet
- LC MeterDocument10 pagesLC MeterYenidir TeknoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #1 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial #1 PDFHilal HuseyinliNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx XC7A200T-1FBG676CDocument12 pagesWhat Is Xilinx XC7A200T-1FBG676CjackNo ratings yet
- GE Energy Mark Ve Control: I/O Communication (PMVE) Module DescriptionDocument142 pagesGE Energy Mark Ve Control: I/O Communication (PMVE) Module DescriptionJorge Contreras100% (1)
- Canon FB1210U Service ManualDocument102 pagesCanon FB1210U Service ManualDuplessisNo ratings yet
- DRAM PresentationDocument11 pagesDRAM PresentationVani SallyNo ratings yet
- Asus P6 WS Pro ManualDocument194 pagesAsus P6 WS Pro ManualNeilKumar100% (1)
- 12-23-14-New-Long - Dealers Price PDFDocument2 pages12-23-14-New-Long - Dealers Price PDFJhon Ray CagampangNo ratings yet
- Memory and StorageDocument2 pagesMemory and Storagefahmi rizaldiNo ratings yet
- Intel Scalable Io Virtualization Technical SpecificationDocument29 pagesIntel Scalable Io Virtualization Technical SpecificationDJSNo ratings yet
- Embedded Controls IntroDocument25 pagesEmbedded Controls IntroEgy SangajiNo ratings yet
- Leica DFC420 DFC420C Brochure enDocument4 pagesLeica DFC420 DFC420C Brochure enCsaba GibártiNo ratings yet
- Data Computing Appliance Version 3Document150 pagesData Computing Appliance Version 3Derek YuenNo ratings yet
- Dpc2535a Error Code ListDocument7 pagesDpc2535a Error Code List黃義翔No ratings yet
- CSEN702-Week2 24539Document24 pagesCSEN702-Week2 24539Mohamed ElzareiNo ratings yet
- FUJITSU Call Center System CCRM-1 - Product DescriptionDocument29 pagesFUJITSU Call Center System CCRM-1 - Product Descriptiontsegab bekeleNo ratings yet
- Eduzone A Complete Campus Management SystemDocument3 pagesEduzone A Complete Campus Management Systemsiji_mtNo ratings yet
- Lab GPDocument15 pagesLab GPpremNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNote FileList of B1400CEAE 2009 X64 V2.01A LDocument7 pagesReleaseNote FileList of B1400CEAE 2009 X64 V2.01A LMorosan AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Intel WiFi 6E AX210 Extended Temp Industrial Module - Product Brief - 0622Document3 pagesIntel WiFi 6E AX210 Extended Temp Industrial Module - Product Brief - 0622Nhân Huỳnh ThiệnNo ratings yet
- All-In-One Guide (Number 1)Document346 pagesAll-In-One Guide (Number 1)Jayapal Errabelli67% (3)
- Class 5Document59 pagesClass 5Mandil Bhandari100% (1)
- Networker 9.X Archive Downloads For Customers and Partners: You Start!Document2 pagesNetworker 9.X Archive Downloads For Customers and Partners: You Start!Zuhaib ShafiNo ratings yet
- Sewing SunstarDocument1 pageSewing Sunstarsongdongemdem28No ratings yet
- Password Recovery Procedure Overview - 3650Document3 pagesPassword Recovery Procedure Overview - 3650tuananh0788No ratings yet