Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resume Xerostomia
Resume Xerostomia
Uploaded by
Gieh SyafitriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resume Xerostomia
Resume Xerostomia
Uploaded by
Gieh SyafitriCopyright:
Available Formats
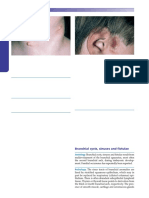
ABSCESS AND PHLEGMON An abscess is a localized collection of pus often caused by bacteria such as staphyloccus aureus.
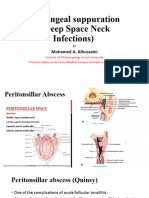
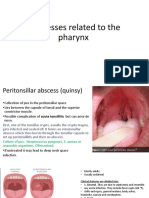
Foreign material, fibrin, and blood clot (bekuan darah) may predispose. There is severe (parah) inflammation with masses of neutrophils, living and dead, necrotic tissue debris, and formation of granulation tissue at the periphery to wall off the abscess. Leukocytes gather in the infected area and produce proteases that degrade dead tissue and convert (mengubah) it into pus. This process is termed liquefactive necrosis. The pus may discharge (dibuang) to the surface or if resolution occurs, there is healing with scar formation. CLINCAL ASPECTS: A common site for abscess in the head and neck area is the peritonsillar space. A peritonsillar abscess is also known as a quinsy. Bacteria spread from an acute infection of the palatine tonsil to the potential space between the tonsil and the adjacent muscle with the resultant development of an abscess. A large abscess may literally dissect the tonsil from its bed but more commonly the abscess is less advanced. In the healing process, a marked fibrotic reaction results in dense scar that may make dissection difficult should the patient later undergo tonsillectomy. Untreated, a peritonsillar abscess usually ruptures into the pharynx spontaneously, or slowly resolves. In rare instances, an untreated patient may develop a life-threatening situation should the peritonsillar abscess obstruct the airway, rupture with aspiration of pus, or extend into the parapharyngeal space and superior mediastinum (carotid rupture), or travel along the carotid sheath and reach the intracranial cavity resulting in cerebritis/meningitis. Thyroglossal cysts and branchial cysts commonly develop intermittent infections with abscess formation and there are a multitude of other conditions about the head and neck predisposing to abscess. CLINCAL ASPEK: Sebuah situs umum untuk abses di kepala dan leher adalah ruang peritonsillar. Abses peritonsillar juga dikenal sebagai "quinsy." Bakteri menyebar dari suatu infeksi akut pada tonsil palatina ke ruang potensial antara amandel dan otot yang berdekatan dengan perkembangan yang dihasilkan dari abses. Abses besar harfiah dapat membedah tonsil dari tempat tidur, tetapi lebih sering abses kurang canggih. Dalam proses penyembuhan, sebuah hasil reaksi ditandai fibrosis di bekas luka padat yang dapat membuat sulit diseksi harus pasien kemudian menjalani operasi amandel. Tidak diobati, abses peritonsillar biasanya pecah ke dalam faring spontan, atau perlahan-lahan sembuh. Dalam kasus yang jarang, pasien yang tidak diobati dapat mengembangkan situasi yang mengancam jiwa harus abses peritonsillar menghalangi jalan napas, pecah dengan aspirasi nanah, atau memperpanjang ke dalam ruang parafaringeal dan mediastinum superior (karotis pecah), atau perjalanan sepanjang selubung karotis dan mencapai rongga intrakranial mengakibatkan cerebritis / meningitis. Kista tiroglosus dan kista branchial umumnya mengalami infeksi intermiten dengan pembentukan abses dan ada banyak kondisi lain mengenai kepala dan leher predisposisi abses.
A phlegmon results when an acute infection is not confined as in the case of abscess. Instead the infection spreads along tissue planes and between muscle fibers. Ludwigs angina is a phlegmon of the neck. In that condition, infection (usually streptococcal) comes from a mandibular tooth and produces brawny induration of the neck that may extend from mandible to clavicle and be life-threatening.
Sebuah hasil phlegmon saat infeksi akut tidak terbatas seperti dalam kasus abses. Sebaliknya infeksi menyebar di sepanjang pesawat jaringan dan antara serat otot. Angina Ludwig adalah phlegmon leher. Dalam kondisi itu, infeksi (biasanya streptokokus) berasal dari gigi rahang bawah dan menghasilkan indurasi berotot leher yang dapat memperpanjang dari mandibula untuk klavikula dan mengancam nyawa.
You might also like
- TonsilitisDocument23 pagesTonsilitisatai-phin-4632100% (4)
- Bscess AND Hlegmon: Tlas OF EAD AND ECK Athology Bscess AND LegmonDocument4 pagesBscess AND Hlegmon: Tlas OF EAD AND ECK Athology Bscess AND LegmonDanis Diba Sabatillah YaminNo ratings yet
- Abscess, Lud Wig AnginaDocument64 pagesAbscess, Lud Wig Anginafahim ahamedNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Area of FaceDocument1 pageDangerous Area of FaceDianPresarioNo ratings yet
- EmpyemaDocument52 pagesEmpyemaDivara Syauta100% (3)
- Neuroscience - The Brain and Spiral CordDocument4 pagesNeuroscience - The Brain and Spiral CordAnn MutisyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Tuberculosis (TB) : Saja Al-MarshadDocument21 pagesTypes of Tuberculosis (TB) : Saja Al-MarshadsajaNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument12 pagesUntitled PresentationFasihaNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Kepala Dan LeherDocument17 pagesKelainan Kepala Dan LeherSoraya HumairaNo ratings yet
- Purulent Exudates (Pus), Facilitating The Spread of Infection. These Spaces' AreDocument4 pagesPurulent Exudates (Pus), Facilitating The Spread of Infection. These Spaces' ArehappymeluckymeNo ratings yet
- Kongenitalne Ciste I Fistule VrataDocument2 pagesKongenitalne Ciste I Fistule VrataRoppeNo ratings yet
- Systemic Infection Is An Infection That Is in The BloodstreamDocument4 pagesSystemic Infection Is An Infection That Is in The BloodstreamninaNo ratings yet
- Abses SubmandibularDocument17 pagesAbses Submandibularhoney_hannieNo ratings yet
- Fascial Space InfectionDocument19 pagesFascial Space Infectiondion leonardoNo ratings yet
- 28-Clin Head & NeckDocument42 pages28-Clin Head & NeckKHAIRUN NISA MOHD ZAIDANNo ratings yet
- Deep Neck Infections: ProblemDocument14 pagesDeep Neck Infections: ProblemAmy KochNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial - Infection - Dari KikiDrDocument20 pagesMaxillofacial - Infection - Dari KikiDrmashitadyahNo ratings yet
- 3,2 - Spread of InflamationDocument14 pages3,2 - Spread of Inflamationحمزة تلاحمةNo ratings yet
- Definition of Operation Performed Tonsillectomy (ton-sih-LEK-tuh-mee) Is The Surgical Removal of The Tonsils, Two Oval-Shaped Pads ofDocument3 pagesDefinition of Operation Performed Tonsillectomy (ton-sih-LEK-tuh-mee) Is The Surgical Removal of The Tonsils, Two Oval-Shaped Pads ofcaligean_827936No ratings yet
- Neck MassesDocument24 pagesNeck MassesIstiklal SurgeryNo ratings yet
- LP Abses SerebriDocument29 pagesLP Abses SerebriMarinaLestariNo ratings yet
- Gambar Makros Mikros RadangDocument41 pagesGambar Makros Mikros RadangBevi Ayu Kumala WardaniNo ratings yet
- Ent PPT On Pharyngeal AbscessDocument20 pagesEnt PPT On Pharyngeal AbscessDocwocNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Space Infections: Parotid AbscessDocument7 pagesHead and Neck Space Infections: Parotid AbscessFara Nindya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Spread of InflamationDocument14 pagesSpread of InflamationShadeeBreijiehNo ratings yet
- Case of The Week: Professor Yasser MetwallyDocument9 pagesCase of The Week: Professor Yasser MetwallyNinaNo ratings yet
- Spread of Oral InfectionDocument4 pagesSpread of Oral InfectionBhaveshNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disease, Any of The Diseases and Disorders That Affect HumanDocument26 pagesRespiratory Disease, Any of The Diseases and Disorders That Affect HumanAryan RajNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Urogenital: Urología Dr. Francisco Cruz López Universidad Veracruzana Javier Evaristo Hernández OrdazDocument80 pagesTuberculosis Urogenital: Urología Dr. Francisco Cruz López Universidad Veracruzana Javier Evaristo Hernández OrdazJavier EvaristoNo ratings yet
- 2 RHINOLOGY SinusDocument87 pages2 RHINOLOGY SinusWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Abscess 2Document4 pagesAbscess 2SANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Exposicion FinishDocument13 pagesExposicion FinishFernanda ChNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal SuppurationDocument29 pagesPharyngeal SuppurationMazen HossamNo ratings yet
- Deep Neck Spaces: Skull BaseDocument17 pagesDeep Neck Spaces: Skull BaseRaja Ahmad Rusdan MusyawirNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDocument49 pagesMaxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDentist Dina SamyNo ratings yet
- Ent CsomDocument18 pagesEnt CsomtarunNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Bleb: On This PageDocument6 pagesPulmonary Bleb: On This PageYaumul RobbiNo ratings yet
- Wo MSKK Week 5Document7 pagesWo MSKK Week 5GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Tromboza Sinus Cavernos in Engleza F OkDocument4 pagesTromboza Sinus Cavernos in Engleza F OkCocosul Cocosului CocosaruluiNo ratings yet
- 6.lung AbscessDocument13 pages6.lung AbscessManushi HenadeeraNo ratings yet
- ENT DefinationDocument22 pagesENT Definationيدا واحدةNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Patterns of InfectionDocument4 pagesTuberculosis: Patterns of InfectionvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: Dr. Kapil Rastogi MPT (Cardiopulmonary) Assistant ProfessorDocument18 pagesBronchiectasis: Dr. Kapil Rastogi MPT (Cardiopulmonary) Assistant ProfessorKavya MittalNo ratings yet
- TB MeningitisDocument10 pagesTB MeningitisEveline YuniartiNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument6 pagesMeningitisرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Dr. K Tarun Rao PG in Dept of Orthopedics Caims, KarimnagarDocument163 pagesDr. K Tarun Rao PG in Dept of Orthopedics Caims, KarimnagarShravani ShagapuramNo ratings yet
- 0019 2A Ful-Orr-gegeszet AngolDocument4 pages0019 2A Ful-Orr-gegeszet AngolagusNo ratings yet
- Case Report Jurnal EnglishDocument5 pagesCase Report Jurnal EnglishAhmad AbrorNo ratings yet
- Drugs RespiratoryDocument15 pagesDrugs RespiratoryLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Acute Lung Abscesses. Definition of The Idea. Classification. Etiology and Pathogenesis. Clinical Picture. Diagnosis.Document6 pagesAcute Lung Abscesses. Definition of The Idea. Classification. Etiology and Pathogenesis. Clinical Picture. Diagnosis.Lucas Victor AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesDocument102 pagesRespiratory Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesMirza SullivanNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Document16 pagesTuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Usman MirzaNo ratings yet
- 135 Infections of The External EarDocument12 pages135 Infections of The External EarDickyJuliandaNo ratings yet
- Retropharyngeal AbscessDocument17 pagesRetropharyngeal AbscessLisa MoyoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tuberculosis IandIIDocument59 pagesSpinal Tuberculosis IandIIagisagitaNo ratings yet
- Deep Neck Space InfectionsDocument43 pagesDeep Neck Space InfectionsmariscaclaudiaaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and EpistaxisDocument17 pagesTonsillitis and EpistaxisAllaine Grace CanoNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: State The Possible Sites & Varied Clinical Presentations of Extra-Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument15 pagesTuberculosis: State The Possible Sites & Varied Clinical Presentations of Extra-Pulmonary TuberculosisDila MananNo ratings yet
- Abscesses Related To The PharynxDocument22 pagesAbscesses Related To The PharynxhamsNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Deema Alshammery and Hanan AlghmadiDocument2 pagesCase Report: Deema Alshammery and Hanan AlghmadiGieh SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Post RetentionDocument7 pagesPost RetentionGieh SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Obat Kumur Asli Indonesia Terhadap Kuman StreptococcusDocument7 pagesPengaruh Obat Kumur Asli Indonesia Terhadap Kuman StreptococcusGieh SyafitriNo ratings yet
- What Is A MucoceleDocument2 pagesWhat Is A MucoceleGieh SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Laporan Komuda Blok 10 Tumbuh Kembang Anak Penyuluhan Dan Pemeriksaan Gigi Pada AnakDocument5 pagesLaporan Komuda Blok 10 Tumbuh Kembang Anak Penyuluhan Dan Pemeriksaan Gigi Pada AnakGieh SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in Infants and ChildrenDocument29 pagesTuberculosis in Infants and ChildrenAnisah TifaniNo ratings yet
- Pas Xi Ganjil-MorristDocument8 pagesPas Xi Ganjil-MorristZefanya YizreelNo ratings yet
- Periodic Breathing in Infants Can Lead To Sids by Ms. NolascoDocument4 pagesPeriodic Breathing in Infants Can Lead To Sids by Ms. NolascoDARREN EDMARKNo ratings yet
- SCLCDocument66 pagesSCLCPavan JonnadaNo ratings yet
- Fanny Chin Medicare PCP DirectoryDocument217 pagesFanny Chin Medicare PCP Directoryclaudia4321No ratings yet
- Ida Jean Orlando'S Nursing Process Theory Prepared By:1. Tigist G/Maryam (BSCN) 2. Tiruye Menshaw (BSCN) Adviser: Gebre YitayihDocument70 pagesIda Jean Orlando'S Nursing Process Theory Prepared By:1. Tigist G/Maryam (BSCN) 2. Tiruye Menshaw (BSCN) Adviser: Gebre YitayihHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Clinical Epidemiology of Heart Failure: Arend Mosterd, Arno W HoesDocument11 pagesClinical Epidemiology of Heart Failure: Arend Mosterd, Arno W HoesCAMILO ANDRES TOVAR DAZANo ratings yet
- Hospital Guide Better Being ThailandDocument7 pagesHospital Guide Better Being ThailandNenad PavlovićNo ratings yet
- Aids & Cancer Disease Hindu MantraDocument3 pagesAids & Cancer Disease Hindu MantralalagopegapangamdassNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Acute Low Back Pain - American Family PhysicianDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Acute Low Back Pain - American Family Physicianmagdalena novianaNo ratings yet
- Programa Fundazione Dolor InglesDocument14 pagesPrograma Fundazione Dolor InglesKaryn Olascuaga-CastilloNo ratings yet
- Case Report Amalgam TattooDocument3 pagesCase Report Amalgam TattooAyu SawitriNo ratings yet
- Child Health Program: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of IndiaDocument19 pagesChild Health Program: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of IndiaPrsh BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Listening Is Therapy: Patient Interviewing From A Pain Science PerspectiveDocument12 pagesListening Is Therapy: Patient Interviewing From A Pain Science PerspectiveGilbert ThierryNo ratings yet
- Oncology BulletsDocument11 pagesOncology BulletsDonaJeanNo ratings yet
- Apexification and ApexogenesisDocument32 pagesApexification and ApexogenesisRajneesh JindalNo ratings yet
- Contoh Pico Terbaru-Blok EndokrinDocument3 pagesContoh Pico Terbaru-Blok EndokrinIndra ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pharmacology For Canadian Health Care Practice 2nd Edition LilleyDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology For Canadian Health Care Practice 2nd Edition Lilleymoneyedcoronal1ah2y100% (28)
- FinalDocument36 pagesFinalNirali GalaNo ratings yet
- Hahnemann's Three Rules Concerning The Rank of Symptoms.Document5 pagesHahnemann's Three Rules Concerning The Rank of Symptoms.karavi schiniasNo ratings yet
- Hazard Report Form-Checklist 4 - Covid-19 - 16252 - Rebeca RaducuDocument3 pagesHazard Report Form-Checklist 4 - Covid-19 - 16252 - Rebeca RaducuRebeca RaducuNo ratings yet
- Stress Among Charge NursesDocument10 pagesStress Among Charge NursesRey AllanNo ratings yet
- Kuesioner DiabetesDocument5 pagesKuesioner DiabetesEk MerepNo ratings yet
- Management of Intractable AspirationDocument49 pagesManagement of Intractable Aspirationekaefka50% (2)
- School Implementation Plan: Department of EducationDocument15 pagesSchool Implementation Plan: Department of EducationimajaynaryNo ratings yet
- Ebola Virus DiseaseDocument41 pagesEbola Virus DiseaseAbshame T.No ratings yet
- INFECTION CONTROL 2nd YearDocument12 pagesINFECTION CONTROL 2nd YearAmy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- Sports Medicine Meets Musculoskeletal MeDocument3 pagesSports Medicine Meets Musculoskeletal MeMotea IoanaNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Sovereign Birth - 2021Document6 pagesPractical Guide To Sovereign Birth - 2021Eva TuáNo ratings yet
- Medical Officer (AYUSH)Document5 pagesMedical Officer (AYUSH)Kirankumar MutnaliNo ratings yet