Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Ortho
Drug Study Ortho
Uploaded by
Mc Crister SilangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Ortho
Drug Study Ortho
Uploaded by
Mc Crister SilangCopyright:
Available Formats
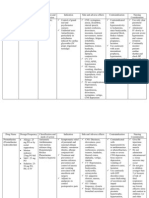
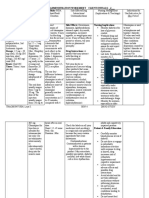
Drugs Name Penicillin-G
Classification Antibiotic
Indication Penicillin G procaine is indicated in the treatment of moderately severe infections in both adults and pediatric patients due to penicillinG-susceptible microorganis ms that are susceptible to the low and persistent serum levels common to this particular dosage form in the indications listed below. Therapy should be guided by bacteriological studies (including susceptibility tests) and by
Action Penicillin G exerts a bactericidal action against penicillinsusceptible microorganisms during the stage of active multiplication. It acts through the inhibition of biosynthesis of cellwall mucopeptide. It is not active against the penicillinaseproducing bacteria, which include many strains of staphylococci. Whilein vitro studies have demonstrated the susceptibility of most strains of the following organisms, clinical efficacy for infections other than those included in the indication and usage section has not been documented. Penicillin G exerts highin vitro activity against staphylococci (except penicillinase-
Contraindications / Precautions Contraindicated with a previous hypersensitivity reaction to any penicillin is a contraindication.
Adverse Reaction Allergic Reactions Penicillin is a substance of low toxicity but does possess a significant index of sensitization. The following hypersensitivity reactions associated with use of penicillin have been reported: Skin rashes, ranging from maculopapular eruptions to exfoliative dermatitis; urticaria; serum-sicknesslike reactions, including chills, fever, edema, arthralgia, and prostration. Severe and often fatal anaphylaxis has been reported. As with other treatments for syphilis, the JarischHerxheimer reaction has been reported. Gastrointestinal Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with the use
Patient/ Family Teaching
Penicillin should be used with caution in individuals with histories of significant allergies and/or asthma. Care should be taken to avoid intravenous or intra-arterial administration, or injection into or near major peripheral nerves or blood vessels, since such injections may produce neurovascular damage.
Instruct patient to take medication around the clock and to finish drug completely as directed, even if feeling better. Advise patient that sharing this medication may be dangerous. Advise patient to report signs of superinfection (black, furry overgrowth on tongue; vaginal itching or discharge; loose or foul-smelling stools) and allergy. Instruct patient to notify health care professional if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. Instruct patient to notify health care professional if symptoms do not
clinical response.
producing strains), streptococci (Groups A, C, G, H, L, and M), and pneumococci. Other organisms susceptible to penicillin G are Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Bacillus anthracis, Clostridiu m species, Actinomyc es bovis, Streptobacillus moniliformis,Listeria monocytogenes, and Leptospira specie s. Treponema pallidum is extremely susceptible to the bactericidal action of penicillin G.
of penicillin G. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment.
improve. Advise patient taking oral contraceptives to use an additional nonhormonal method of contraception during therapy with penicillin and until next menstrual period. Patient with an allergy to penicillin should be instructed to always carry an identification card with this information.
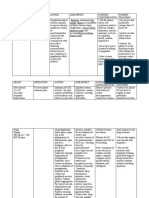
Drugs Name Cefazolin (ancef)
Classification Cephalosporins
Indication Treatment of variety of infections due to susceptible organisms including biliary tract infections, Staphylococcal e ndocarditis, endometritis (surgical infection prophylaxis at caesarean section), and peritonitis assoc iated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and surgical infections prophylaxis.
Action Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death. Active against many gram-positive cocci including: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci; Penicillinasproducing staphylococci.
Contraindications / Precautions Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity to cephalosphorins. Serious hypersensitivity to penicillin. Use Cautiously in: Renal impairment History of GI disease, especially colitis Geriatric patients (consider agerelated decrease in body mass, renal/hepatic/ cardiac function, concurrent medications and chronic disease states) Pregnancy or Lactation
Adverse Reaction CNS: headache, lethargy, confusion, hemiparesis, paresthesia, syncope, seizures CV: hypotension, palpitations, chest pain, vasodilation EENT: hearing loss GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, oral candidiasis, pseudome mbranous colitis GU: vaginal candidiasis, nephrotoxi city Hematologic: lymphocy tosis, eosinophilia, bleeding tendency, hemolytic anemia, hypoprothrombinemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, bone
Patient/ Family Teaching Tell patient to report reduced urinary output, persistent diarrhea, bruising, or bleeding. Instruct patient to take drug exactly as prescribed and to complete full course of therapy even when he feels better. As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, and behaviors mentioned above
marrow depression Hepatic: hepatic failure, hepatomegaly Musculoskeletal: arthra lgia Respiratory: dyspnea Skin: urticaria, maculopapular or erythematous rash Other: chills, fever, superinfection
Drugs Name Amikacin
Classification Aminoglycosi des
Indication Parenteral Uncomplicate d urinary tract infections Adult: 250 mg bid, given via IM, IV inj over 2-3 minutes or as IV infusion. Max Dosage: Renal impairment: D osage adjustments may be made by (a) normal doses at increased dosing intervals or (b) reduced doses at the usual intervals. For (a), dosing interval (in hr) can be calculated by multiplying the patient's serum creatinine (mg/100ml)
Action Amikacin binds to 30S ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria, thus inhibiting its protein synthesis. Distribution: Detecte d in body tissues and fluids after inj; crosses the placenta but does not readily penetrate the CSF. Significant amounts penetrate the bloodbrain barrier in children with meningitis. Excretion: Via the urine by glomerular filtration (within 24 hr); 2-3 hr (elimination half-life).
Contraindications / Precautions Contraindications Pregnancy, perforated ear drum, myasthenia gravis, hypersensitivity. Precautions Renal impairment; vertigo, tinnitus. Discontinue if signs of ototoxicity, neurotoxicity or hypersensitivity occurs; lactation. Safety has not been established for treatment period >14 days. Monitor renal function before and during treatment.
Adverse Reaction Tinnitus, vertigo; ataxia and overt deafness. Potentially Fatal: Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, neuromuscular blockade.
Patient/ Family Teaching Patient Teaching: Inform the patient this test can assist in monitoring for subtherapeutic, therapeutic, or toxic drug levels used in treatment of infection. Obtain a history of the patient's complaints, including a list of known allergens, especially allergies or sensitivities to latex. Obtain a history of the patient's immune system, symptoms, and results of previously performed
by 9. For (b), initiate at normal dose. Maintenance doses can be calculated by dividing the normal dose by the patient's serum creatinine. Parenteral Severe Gramnegative infections resistant to gentamicin and tobramycin Adult: 15 mg/kg daily in equally divided doses injected every 8 or 12 hr for 7-10 days. Max: Up to 500 mg every 8 hr in lifethreatening infections. Max cumulative
laboratory tests and diagnostic and surgical procedures. Nephrotoxicity is a risk associated with administration of aminoglycoside s. Obtain a history of the patient's genitourinary system, symptoms, and results of previously performed laboratory tests and diagnostic and surgical procedures. Ototoxicity is a risk associated with administration of aminoglycoside s. Obtain a history of the patient's known or suspected
dose: 15 g. Doses may be given via IM, slow IV inj over 2-3 minutes or IV infusion. Child: 15 mg/kg daily in equally divided doses injected every 8 or 12 hr for 7-10 days. Neonates: 10 mg/kg daily in 2 divided doses. Renal impairment: D osage adjustments may be made by (a) normal doses at increased dosing intervals or (b) reduced doses at the usual intervals. For (a), dosing interval (in hr) can be
hearing loss, including type and cause; ear conditions with treatment regimens; ear surgery; and other tests and procedures to assess and diagnose auditory deficit. Obtain a list of the patient's current medications, including herbs, nutritional supplements, and nutraceuticals (see Appendix F: Effects of Natural Products on Laboratory Values). Note the last time and dose of medication taken. Review the
calculated by multiplying the patient's serum creatinine (mg/100ml) by 9. For (b), initiate at normal dose. Maintenance doses can be calculated by dividing the normal dose by the patient's serum creatinine.
procedure with the patient. Inform the patient that specimen collection takes approximately 5 to 10 min. Address concerns about pain and explain that there may be some discomfort during the venipuncture. Obtain a culture, if ordered, before the first dose of aminoglycoside s. Sensitivity to social and cultural issues, as well as concern for modesty, is important in providing psychological support before,
during, and after the procedure. There are no food, fluid, or medication restrictions unless by medical direction.
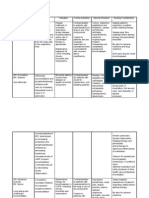
Drugs Name Celecoxib (celebrex)
Classification Nonsteroidal AntiInflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Indication Relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis. Relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
Action Physiologic Mechanism Decreased pain and inflammation caused by arthiritis Pharmacologic Mechanism Prevention of M Inhibits the enzyme COX-2. This enzyme is required for the synthesis of prostaglandins. Has analgesic, antiinflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
Contraindications / Precautions Contraindications :
Adverse Reaction
Patient/ Family Teaching Instruct patient to take celecoxib exactly as directed. Do not take more than prescribed dose. Increasing doses does not appear to increase effectiveness. Use lowest effective dose for shortest period of time Advise patient to notify health care professional promptly if sign or symptom of GI toxicity (abdominal pain, black stools), skin rash, unexplained weight gain, edema, or chest pain occurs. Patients should discontinue celecoxib and notify health care professional if signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, upper right quadrant tenderness, flu-like symptoms) occur Advise patient to notify
Anaphylactic reactions, acute renal failure. Hallucination, ageusia, anosmia, aseptic Hypersensitivity including those in meningitis, vasculitis, whom attacks of GI hemorrhage. Hepatitis, liver failure, angioedema, interstitial nephritis. rhinitis and Photosensitivity urticaria have reaction, exfoliative been dermatitis, erythema precipitated by multiforme, Stevensaspirin, NSAIDs or sulfonamides. Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal Severe hepatic necrolysis & menstrual impairment; disorder. Cerebral severe heart hemorrhage, fulminant failure; hepatitis, liver necrosis, inflammatory hyponatremia, bowel disease; conjunctivitis. peptic ulcer; renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min); pregnancy and lactation. Precautions: History of GI bleeding; renal/hepatic
insufficiency; asthma or allergic disorders; hypertension; monitor Hb or haematocrit levels for signs of anaemia. History of cerebrovascular disease or ischaemic heart disease (IHD).
health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected Advise patients with FAP to continue routine surveillance procedures
Drugs Name Tramadol
Classification Analgesics
Indication Moderate to moderately severe pain
Action Physiologic Mechanism Decreased pain. Pharmacologic Mechanism Binds to muopioid receptors. Inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS
Contraindications/ Precautions Abrupt discontinuation, ethanol intoxication, opiate agonist hypersensitivity, breast-feeding, children, driving or operating machinery, elderly, GI disease, head trauma, hepatic disease, increased intracranial pressure, labor, pregnancy, renal impairment, respiratory depression, seizure disorder, substance abuse
Adverse Reaction Dizziness or vertigo, Nausea and Vomiting, Constipation, Headache, Somnolence, Pruritus, central nervous system stimulation, Asthenia, Diaphoresis, Dyspepsia, Dry mouth, Diarrhea, Malaise, Vasodilatation, Anorexia, Flatulence, Rash, Visual disturbance, Urinary retention or frequency and menopausal symptoms
Patient/ Family Teaching May cause dependence. Avoid alcohol and over-thecounter medications. May cause drowsiness, dizziness, and blurred vision. Avoid tasks requiring alertness and motor skills until response to drug is established. Inform physician if severe constipation, difficulty in breathing, excessive sedation, seizures, muscle weakness, tremors, chest pain, and palpitations occur.
Drugs name Paracetamol
Classification Non-opiod analgesic and antipyretics
Indication Acute pain and fever
Action Through the produce analgesia by blocking pain impulse by inhibiting synthesis of prostaglandin in central nervous system that synthesize pain receptor to stimulation
Contraindication / precautions Anemia, cardiac & pulmonary disease. Hepatic or severe renal disease. Liver warning & disease. Other medicines containing paracetamol. Concomitant use of warfarin.
Adverse reaction Allergic reactions & gastro intestinal disturbances.
Patient/ family teaching Instruct patient to take with meals and have a plenty of water when taking this drug
Drugs Name Ranitidine
Classification Histamine Blocker
Indication Treatment and prevention of heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach.
Action Potent anti-ulcer drug that competitively and reversibly inhibits histamine action at H2-receptor sites on parietal cells, thus blocking gastric acid secretion. Indirectly reduces pepsin secretion but appears to have minimal effect on fasting and postprandial serum gastrin concentrations or secretion of gastric intrinsic factor or mucus.
Contraindications/ Precautions Contraindicated with allergy to ranitidine, lactation.
Adverse Reaction CNS: Confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, headache GI: Altered taste, black tongue, constipation, dark stools, diarrhea, nausea
Patient/ Family Teaching Take drug with meals and at bedtime. Therapy may continue for 4-6 weeks or longer. If you are using an antacid, take it exactly as prescribed. Have regular medical follow up care Report sore throat, fever, unusual bruising or bleeding, tarry stools, severe headache, muscle or joint pain.
Use cautiously with impaired renal or hepatic function and pregnancy.
Drugs Name Diclofenac
Classification Analgesic non-opiod antiinflammatory antipyretic
Indication Acute or long term treatment of mild to moderate pain, including dysmenorrhea Rheumatoid arthritis Acute treatmentof migraine headache with or without aura Osteoarthritis Ankylosing spondylitis Treatment of actinic keratosis in conjunction with the sun avoidance Topical treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains or contusions Ophthalmic:
Action
NSAIDs work by reducing the production of prostaglandins, chemicals that cause pain, fever and inflammation. NSAIDs block the enzyme that makes prostaglandins (cyclooxygenase), resulting in lower production of prostaglandins. As a consequence, inflammation, pain and fever are reduced. Since the response to different NSAIDs varies from patient to patient, it is not unusual for a doctor to try different NSAIDs for any given condition.
Contraindications / Precautions Contraindicated with allergy to NSAIDs, significant renal impairment, pregnancy and lactation
Adverse Reaction CNS: headache, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, fatigue, tiredness, tinnitus and ophthalmic effects.
Patient/ Family Teaching Take drug exactly as prescribed. Avoid hot environments while taking his
Dermatologic: rash, pruritus, sweating and dry mucous Use cautiously membrane, with impaired hearing, allergies, stomatatitis . hepatic, GI: nausea, dyspepsia, cardiovascular, GI conditions and GI pain, Diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, in elderly flatulence and GI patients. bleed. GU: dysurea and renal impairment. Hematologic: bleeding platelet inhibition with higher doses. Other : peripheral edema anaphylactoid reactions to fatal anaphylactic shock.
postoperative inflammation from cataract extraction
Drugs Name Metoclopra -mide
Classification
Indication
Action
Beta-blockers Gastrointestinal motility, nausea, vomiting of central and peripheral origin assoc. with surgery
Contraindications / Precautions Dopamine antagonist CONTRAINDICATthat acts by increasing IONS: receptor sensitivity GI hemorrhage, and response of upper epileptics, GIT tissues to hypersensitivity, acetylcholine lactation, patients with breast cancer PRECAUTION: Activities requiring mental alertness, elderly, lactation
Adverse Reaction Restlessness, drowsiness, fatigue, insomnia, headache, dizziness, nausea
Patient/ Family Teaching >give 30 mins before meals and at bed time> assess mental status during treatment >tell patient to avoid driving & other hazardous activities for at least 2 hrs >advice patient to avoid alcohol another CNS depressant that enhance sedating properties of this drug
You might also like
- HubSpot: Inbound Marketing and Web 2.0Document3 pagesHubSpot: Inbound Marketing and Web 2.0test100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - FractureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Fracturederic95% (20)
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- Wisdom From TD Jakes FREEDocument224 pagesWisdom From TD Jakes FREEayodeji78100% (3)
- Senior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteDocument7 pagesSenior High School: Emilio Aguinaldo College City of Dasmariñas, CaviteNicole De AsisNo ratings yet
- Time Chart 7:00-3:00 PM F Ineffective Individual Coping Related To SituationalDocument1 pageTime Chart 7:00-3:00 PM F Ineffective Individual Coping Related To SituationalAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Fdar PsycheDocument1 pageFdar PsycheAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document15 pagesDrug Study 1Czarina Isabela TuazonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyryanNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations: Delusion Is ADocument4 pagesHallucinations: Delusion Is AMari Ivy PradoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyjohnclement_dcNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drugs Generic Name: Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesDrug Study Name of Drugs Generic Name: Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesAlyssa Mae DumularNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument3 pagesDrugPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2Kirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- BRH Drug StudyDocument6 pagesBRH Drug StudyStephanie Dellera AgdanNo ratings yet
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JrodDocument8 pagesDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoNo ratings yet
- VII. Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVII. Drug StudyJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument3 pagesOlanzapineLeris Luigi VictorioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyDanian AntonioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease BleedDocument2 pagesCerebrovascular Disease BleedJogyBoyLunaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJoseph Dableo ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Fdar Psyche 3Document1 pageFdar Psyche 3Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone DipropionateDocument3 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Health Problem:: Carlatan, San Fernando City, La UnionDocument4 pagesPrioritization of Problems Health Problem:: Carlatan, San Fernando City, La UnionGabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac PI PDFDocument2 pagesKetorolac PI PDFintan kusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAlisse Sales De-PazNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument1 pageHaloperidol PDFAda AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Disorders NCPDocument7 pagesDisorders NCPFaye Dianne Damian-BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride Injection: Product MonographDocument18 pagesPotassium Chloride Injection: Product MonographMatthew ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDocument7 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Drug Study East AveDocument15 pagesDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMiCa VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJann Zaniel Allayne RiNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study FinalJazel OpinionNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinDocument51 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinfahmiNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessMaricon BautistaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug StudyDocument3 pagesEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolsleep whatNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilizers BookletDocument20 pagesMood Stabilizers Bookletrabiaa_48No ratings yet
- ENT Drug StudyDocument3 pagesENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline NasoclearDocument1 pageTerbutaline NasoclearSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia An OverviewDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia An OverviewEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AZITHROMYCINDocument2 pagesDrug Study AZITHROMYCINDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LCPDocument3 pagesDrug Study LCPalleen_viaNo ratings yet
- Course Description: 3. Communities (Community Service)Document35 pagesCourse Description: 3. Communities (Community Service)April Mae Magos LabradorNo ratings yet
- Pentabio PDFDocument7 pagesPentabio PDFDicky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyLeya ThaobunyuenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document5 pagesDrug Study 1Alen Alano100% (1)
- Therapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyMarc Louise DatoyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDocument2 pagesDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lorazepam (Ativan)Document1 pageLorazepam (Ativan)ENo ratings yet
- Lithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsDocument2 pagesLithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsgavinbuzzNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation 1Document34 pagesCase Presentation 1Joshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- What Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisVonn Bryan CalumiaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsgailannreyesNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsgailannreyesNo ratings yet
- Cholangiocarcinoma, Gallbladder Cancer, Common Bile Duct, Cystic Duct, Intrahepatic, PerihilarDocument25 pagesCholangiocarcinoma, Gallbladder Cancer, Common Bile Duct, Cystic Duct, Intrahepatic, PerihilarMc Crister Silang100% (1)
- Transition To IndependenceDocument14 pagesTransition To IndependenceMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- Normal ValuesDocument6 pagesNormal ValuesMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- In The Totality Paradigm Rosemarie ParseDocument2 pagesIn The Totality Paradigm Rosemarie ParseMc Crister Silang43% (7)
- Aku - To PrintDocument23 pagesAku - To PrintMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Skin PreparationDocument5 pagesPreoperative Skin PreparationMc Crister SilangNo ratings yet
- Shattered Reflections A Journey Beyond The MirrorDocument13 pagesShattered Reflections A Journey Beyond The MirrorSweetheart PrinceNo ratings yet
- LG+47ln5700 47ln570t 47ln570y 47ln5710 Chassis lb33bDocument119 pagesLG+47ln5700 47ln570t 47ln570y 47ln5710 Chassis lb33bmidominguez0% (1)
- Informe Sobre El Manejo de CostasDocument88 pagesInforme Sobre El Manejo de CostasMetro Puerto RicoNo ratings yet
- Dance As A CompetitionDocument3 pagesDance As A CompetitionJaymie NeriNo ratings yet
- Toward The Efficient Impact Frontier: FeaturesDocument6 pagesToward The Efficient Impact Frontier: Featuresguramios chukhrukidzeNo ratings yet
- AQU4518R4 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAQU4518R4 Datasheetcostin.bantoiuNo ratings yet
- Title: Relationship Between PH and Chemiluminescence of Luminol Author: Rolando Efraín Hernández RamírezDocument2 pagesTitle: Relationship Between PH and Chemiluminescence of Luminol Author: Rolando Efraín Hernández RamírezEfraínNo ratings yet
- Halimatus Islamiah Analisis Jurnal Internasional K3Document3 pagesHalimatus Islamiah Analisis Jurnal Internasional K3TussNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3 THESISDocument64 pagesChapter 1 3 THESISLyka Cartagena-Pandili Manalo-CabelloNo ratings yet
- GDPR ReportDocument84 pagesGDPR ReportKingPlaysNo ratings yet
- Federal University OtuokeDocument5 pagesFederal University OtuokeeteleruthNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab Dbms Lab: 23 March 202Document12 pagesDbms Lab Dbms Lab: 23 March 202LOVISH bansalNo ratings yet
- Inactive Volcanoes in The Philippine SDocument6 pagesInactive Volcanoes in The Philippine SChristian ParadoNo ratings yet
- Relatorio Mano JulioDocument7 pagesRelatorio Mano JulioProGeo Projetos AmbientaisNo ratings yet
- Applications Guide 2021 Covering LettersDocument8 pagesApplications Guide 2021 Covering LettersLALUKISNo ratings yet
- Marik ServitorsDocument20 pagesMarik ServitorsDWNloader100% (2)
- L550 19MY MB XC-EN V1j DX PDFDocument88 pagesL550 19MY MB XC-EN V1j DX PDFAnonymous gMgeQl1SndNo ratings yet
- 501-453 Universal Cable GalndsDocument1 page501-453 Universal Cable Galndsmeribout adelNo ratings yet
- Comfort ZoneDocument4 pagesComfort Zonesigal ardanNo ratings yet
- The Holy Spirit: A New LifeDocument2 pagesThe Holy Spirit: A New LifeKatu2010No ratings yet
- ContinueDocument3 pagesContinueJúÑi ØrNo ratings yet
- Padiernos vs. PeopleDocument22 pagesPadiernos vs. PeopleMariel ManingasNo ratings yet
- Tivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationDocument53 pagesTivoli Storage Manager Operational Reporting Installation, Configuration and CustomizationSABRINE KHNo ratings yet
- The Price of SilenceDocument9 pagesThe Price of Silencewamu885100% (1)
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch PaperHazirah AmniNo ratings yet
- Infosys-Broadcom E2E Continuous Testing Platform Business Process Automation SolutionDocument16 pagesInfosys-Broadcom E2E Continuous Testing Platform Business Process Automation Solutioncharu.hitechrobot2889No ratings yet
- CyberbullyingDocument8 pagesCyberbullyingapi-433558817No ratings yet