Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron Arrangement
Hydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron Arrangement
Uploaded by
car_yiiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron Arrangement
Hydrogen Atom: Duplet Electron Arrangement
Uploaded by
car_yiiCopyright:
Available Formats
The formation of ionic bonds in sodium chloride, NaCl is explained as follows: The electron arrangement of a sodium atom is 2.8.1.
. Sodium atom releases one valence electron to form sodium ion, Na+ Na Na+ + e The electron arrangement of sodium ion is 2.8. Sodium ion achieves a stable octet electron arrangement. The electron arrangement of a chlorine atom is 2.8.7. Chlorine atom receives one electron to form chloride ion, ClCl + e Cl The electron arrangement of chloride ion is 2.8. Chloride ion achieves a stable octet electron arrangement. Strong electrostatic force pulls the sodium ion and chloride ion together. An ionic bond is formed. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound.
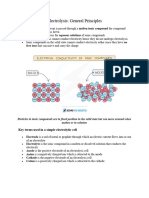
Formation of hydrogen chloride molecule, HCl ( covalent compound) The formation of covalent bonds in hydrogen chloride molecule is explained as follows: Each hydrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 1. The outermost shell needs one electron in order to achieve a stable duplet electron arrangement. Clorine atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.7. The outermost shell needs one electron in order to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement. Clorine atom contributes one valence electron while hydrogen atom contributes one valence electron for sharing. A single covalent bond is formed.
Remarks: The electrons must be drawn in the overlap of two shells. Students may use Lewis structure in drawing the formation of covalent compound. ( Lewis structure only show the valence electrons)
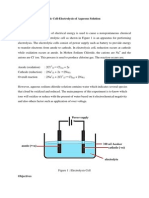
Electrolysis of aqueous solution
1. Electrolysis of potassium nitrate solution, KNO3 using carbon electrodes. Anode (+) NO-3, OH4OH- 2H2O + O2 +4e Colourless gas bubbles are released Oxygen gas Cathode (-) K+, H+ 2H+ + 2e H2 Colourless gas bubbles are released Hydrogen gas
Ion presents Half equation Observation Product
2. Electrolysis of silver nitrate solution, AgNO3 using carbon electrodes. Anode (+) NO-3, OH4OH- 2H2O + O2 +4e Colourless gas bubbles are released Oxygen gas Cathode (-) Ag+, H+ Ag+ + e Ag A grey solid is formed Silver metal
Ion presents Half equation Observation Product
3. Electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution, CuSO4 using carbon electrodes. Anode (+) SO2-4, OH4OH- 2H2O + O2 +4e Colourless gas bubbles are released Oxygen gas Cathode (-) Cu2+, H+ Cu2+ + 2e Cu Brown solid is formed Copper metal
Ion presents Half equation Observation Product
4. Electrolysis of concentrated potassium chloride solution, KCl using carbon electrodes. Anode (+) Cl- , OHCl- Cl2 + 2e Greenish-yellow gas bubbles are released Chlorine gas Cathode (-) K+, H+ 2H+ + 2e H2 Colourless gas bubbles are released Hydrogen gas
Ion presents Half equation Observation Product
5. Electrolysis of silver sulphate solution, Ag2SO4 using silver electrode as anode and carbon electrode as cathode. Anode (+) Ag Ag+ +e Silver electrode corrodes and become thinner Silver ion Cathode (-) Ag+ + e Ag A grey solid is deposited and electrode becomes thicker. Silver metal
Ion presents Half equation Observation
Product
6. Electrolysis of copper(II) nitrate solution, Cu(NO3)2 using copper electrode as anode and carbon electrode as cathode. Anode (+) Cu Cu2+ +2e Copper electrode corrodes and become thinner Copper(II) ion Cathode (-) Cu2+ + 2e Cu Brown solid is deposited and electrode becomes thicker. Copper metal
Ion presents Half equation Observation
Product
You might also like
- Mollier Chart WaterDocument1 pageMollier Chart Waterchouchou575% (8)
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (35)
- 14 Dehydrogenase in YeastDocument4 pages14 Dehydrogenase in Yeastsung_kei_pin100% (1)
- Science IIIDocument3 pagesScience IIIMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Absorber Design FinalDocument27 pagesAbsorber Design FinalTamara NwaserNo ratings yet
- CSI Model 5100Document7 pagesCSI Model 5100SreekanthMylavarapuNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Molten Sodium ChlorideDocument2 pagesElectrolysis Molten Sodium ChlorideHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesDocument20 pagesElectricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6Elynn TanNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3Document6 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3aikubing100% (1)
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesElectrolysisbilldanit4fitzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: ConductivityDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: Conductivityapi-181176018No ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry ElectrolysisdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson23 (Electrochemistry3)Document23 pagesChemistry Lesson23 (Electrochemistry3)Siang DanielNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetDocument83 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetbhargavintnaiduNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Text SolnDocument38 pagesElectrolysis Text Solnhemanth PNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Document33 pagesELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- 8th Clemicl Bond-1Document19 pages8th Clemicl Bond-1Nischal Reddy SareddyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument24 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Metals and Non-Metalsshaistudy1No ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- CHAPTER 6 ElctrochemistryDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 6 ElctrochemistryMohd Nazri Mat JaridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Electrochemistry SPMDocument62 pagesChapter 6 Electrochemistry SPMhanifzainol100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument83 pagesElectrolysismoizbadri100% (3)
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis HLDocument34 pagesElectrolysis HLRyan BoukaaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument9 pagesElectricity and ChemistryFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Esis 2Document35 pagesEsis 2Amir Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument8 pagesExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionNad Sng90% (21)
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsDocument2 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsSunnyNo ratings yet
- New Electrolysis 1Document18 pagesNew Electrolysis 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Notes 5 - Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesNotes 5 - Chemical Bondingochiengjoseph122No ratings yet
- Electrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode DischargeDocument28 pagesElectrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode Dischargeanwar9602020100% (1)
- Electrolysis 1Document14 pagesElectrolysis 1cleohambiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahDocument3 pagesChemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahAdaugo UbahNo ratings yet
- CHEM SS2 NoteDocument6 pagesCHEM SS2 NoteEli yunanaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument24 pagesElectrolysisstudent purposesNo ratings yet
- IGCSE-ELECTROLYSIS KimDocument13 pagesIGCSE-ELECTROLYSIS KimEssie KutisariNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Ionic Bonding & Structure: Mrs. Page IB Chem. 2015-2016Document38 pages4.1 Ionic Bonding & Structure: Mrs. Page IB Chem. 2015-2016api-546066323No ratings yet
- Preferential Discharge TheoryDocument4 pagesPreferential Discharge TheoryRitesh Mittra33% (3)
- REDOX REACTIONS STDocument11 pagesREDOX REACTIONS STirehan.saiyedNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Crysttal BindingDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Crysttal Bindingkorna2No ratings yet
- 584 6 Electrometallurgy Solid: State Example Type of ConductivityDocument2 pages584 6 Electrometallurgy Solid: State Example Type of ConductivityAshish KotwalNo ratings yet
- L2Chemical Bonding PDFDocument17 pagesL2Chemical Bonding PDFswarabenkar08No ratings yet
- C2 Topic 2 NotesDocument4 pagesC2 Topic 2 NotesfractoremNo ratings yet
- CH 19H NotesDocument40 pagesCH 19H NotesHello HelloNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Magnesium Oxide MagnesiumDocument11 pagesCarbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Magnesium Oxide MagnesiumelizabethNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compounds: Jons J. Berzelius 1779-1848Document24 pagesChemical Compounds: Jons J. Berzelius 1779-1848ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Te-Metals and Non Metal Final Revisor (2022-23)Document85 pagesTe-Metals and Non Metal Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Reflection: 1. Lengkapkan Jadual Di Bawah. Objek Imej Penerangan Pantulan A) P P'Document2 pagesReflection: 1. Lengkapkan Jadual Di Bawah. Objek Imej Penerangan Pantulan A) P P'car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Write Down Reflection Before Leave The Laboratory.: Exist CardDocument1 pageWrite Down Reflection Before Leave The Laboratory.: Exist Cardcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- PLC ExerciseDocument1 pagePLC Exercisecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Borang Markah KK 2015Document4 pagesBorang Markah KK 2015car_yiiNo ratings yet
- 10 SepDocument6 pages10 Sepcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- The Data Shows The Time Spent For Revision of 30 Students of Class 2 PurpleDocument1 pageThe Data Shows The Time Spent For Revision of 30 Students of Class 2 Purplecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Program Dasar 60:40 Sains (Tingkatan 1)Document1 pageProgram Dasar 60:40 Sains (Tingkatan 1)car_yiiNo ratings yet
- 11 JuneDocument5 pages11 Junecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Amali Tahunan 2o15Document5 pagesRancangan Amali Tahunan 2o15car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Human Body Word ScrambleDocument2 pagesHuman Body Word Scramblecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Investigate How Surface Area Affects The Rate of CoolingDocument1 pageInvestigate How Surface Area Affects The Rate of Coolingcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Space Word Search: Human Body Word ScrambleDocument2 pagesSpace Word Search: Human Body Word Scramblecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Name: Class: NO Topic/Title Homework Checked Date RemarkDocument1 pageChemistry: Name: Class: NO Topic/Title Homework Checked Date Remarkcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Quantities Word SearchDocument1 pageChemical Quantities Word Searchcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Book 11Document4 pagesBook 11car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 4Document2 pagesTopical Test 4car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Perubahan Yang Positif Dalam PDPDocument1 pagePerubahan Yang Positif Dalam PDPcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Planning Experiment: Form 4Document9 pagesPlanning Experiment: Form 4car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Analisis SPMDocument2 pagesAnalisis SPMcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- CosmeticEmulsions PDFDocument119 pagesCosmeticEmulsions PDFMai Lâm100% (4)
- ASTM International - BOS Volume 09.01 - 2017 ContentsDocument8 pagesASTM International - BOS Volume 09.01 - 2017 Contentspedro serranoNo ratings yet
- 9701 w15 Ms 22 PDFDocument7 pages9701 w15 Ms 22 PDFAl BeruniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Document9 pagesLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria ICE SolutionsDocument15 pagesChemical Equilibria ICE SolutionsAmirah Alhabshi0% (1)
- A'Takamul International School: Grade 11 - Chemistry I CH 7 & 8 WorksheetDocument3 pagesA'Takamul International School: Grade 11 - Chemistry I CH 7 & 8 WorksheetRami ChaoulNo ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2013 09 29 077Document3 pagesIjaiem 2013 09 29 077Asok AyyappanNo ratings yet
- Perry 02Document2 pagesPerry 02Thaly MejiaNo ratings yet
- Bwa Flocon 260 Gpi - WF 4Document10 pagesBwa Flocon 260 Gpi - WF 4dalton2004No ratings yet
- 13.12.2020 - JR Iit Co - Super Chaina - N120 - Adv - 2016 - P1 - (Wta) Model QP PDFDocument14 pages13.12.2020 - JR Iit Co - Super Chaina - N120 - Adv - 2016 - P1 - (Wta) Model QP PDFYugandher BadanaNo ratings yet
- Eutectic SolventsDocument128 pagesEutectic Solventsjenan h.albayatiiNo ratings yet
- Equipment SizingDocument5 pagesEquipment SizingPandu RockingNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Co2FeAl Heusler Alloy NanoparticleDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Co2FeAl Heusler Alloy Nanoparticlekarthik kaonNo ratings yet
- KITCHEN Roster 2018Document28 pagesKITCHEN Roster 2018Anonymous Wb2VvAC5No ratings yet
- Surface Temperature: C T 0 A MaxDocument2 pagesSurface Temperature: C T 0 A MaxjameeloNo ratings yet
- Rubber MaterialDocument5 pagesRubber MaterialJavier Alejandro Rodriguez MelgozaNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument10 pagesFINALSMirasol EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - PsychrometryDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - PsychrometryamdevaNo ratings yet
- Team0 Sampleb Project1 FinalReport PDFDocument196 pagesTeam0 Sampleb Project1 FinalReport PDFGlacier RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemistry Homework Worksheets Without Answer LinesDocument12 pagesQuantitative Chemistry Homework Worksheets Without Answer Linesdaley.miaaNo ratings yet
- Mec 672 Advanced Heat and Mass TransferDocument11 pagesMec 672 Advanced Heat and Mass TransferShivam VermaNo ratings yet
- Nyb U4 Acids Bases Part 1Document67 pagesNyb U4 Acids Bases Part 1Aindrila KaziNo ratings yet
- 4 ChimneyDocument4 pages4 ChimneyyanyanNo ratings yet
- Tds 0000249Document2 pagesTds 0000249Dodi SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Fick's Law of Diffusion: Imaicela Gloria, Calderón Luis, Romero Henry, Criollo Erick, Trujillo WillamDocument5 pagesFick's Law of Diffusion: Imaicela Gloria, Calderón Luis, Romero Henry, Criollo Erick, Trujillo WillamLuis Calderon SalasNo ratings yet