Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Uploaded by
kbhaskar66Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Board-Exam May2223242019Document11 pagesBoard-Exam May2223242019Jonnah Faye MojaresNo ratings yet
- ENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Document6 pagesENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Manel SashikalaNo ratings yet
- Bhagvan Kommadi - Learn Data Structures and Algorithms With Golang - Level Up Your Go Programming Skills To Develop Faster and More Efficient Code PDFDocument324 pagesBhagvan Kommadi - Learn Data Structures and Algorithms With Golang - Level Up Your Go Programming Skills To Develop Faster and More Efficient Code PDFLúar Mújica100% (2)
- PS Compilation For 2019Document10 pagesPS Compilation For 2019Nicole RamirezNo ratings yet
- Epf Pass Book Avula VaraprasadDocument1 pageEpf Pass Book Avula VaraprasadvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- TD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Document31 pagesTD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Narayanan Srinivasan100% (1)
- ETD Model IV QPDocument2 pagesETD Model IV QPtagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- 7157902Document62 pages7157902Red RedNo ratings yet
- Question Paper ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper ThermodynamicsThaanya sNo ratings yet
- MEC1405 - Thermodynamics I (2009Document3 pagesMEC1405 - Thermodynamics I (2009Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- Internal II Question Paper Etd Set IIDocument2 pagesInternal II Question Paper Etd Set IItagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesThermal Engineering - Department of Mechanical EngineeringPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Me 8301 EtdDocument3 pagesMe 8301 Etdsrinithims78No ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- ME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Document4 pagesME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007ARUNGREESMANo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesImportant Questionstamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Me8391 - EtdDocument3 pagesMe8391 - Etdsyed1188No ratings yet
- Ihw 2Document6 pagesIhw 2LogoNo ratings yet
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument5 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Guru PrakashNo ratings yet
- ETD Model 2024Document2 pagesETD Model 2024shivakeesNo ratings yet
- IES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002Document8 pagesIES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002aditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Me2202 PDFDocument15 pagesMe2202 PDFvis3012No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsDocument8 pagesMass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsIastraNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document7 pagesSheet 1Bahaa RaghebNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Ae 1201 - Aero Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesAe 1201 - Aero Engineering ThermodynamicsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER Previous PaperDocument8 pagesHEAT TRANSFER Previous PaperVibin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Kishore AtdDocument14 pagesKishore AtdKumar SamyanaikNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mechDocument2 pagesEtd 2mechgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocument16 pagesThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- ME2202 Question BankDocument5 pagesME2202 Question BankStanly ThomasNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 CalorDocument2 pagesTarea 4 CalorDenisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- (Ae8301)Document4 pages(Ae8301)aerochandru.87No ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document7 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234No ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringKarthik P MuraliNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- eNGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION PAPERDocument11 pageseNGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION PAPERAbubakkar Siddiq100% (3)
- Assignment 2 Second Law 2016Document7 pagesAssignment 2 Second Law 2016Mohit SInhaNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test SOMDocument7 pagesCycle Test SOMRyan GomezNo ratings yet
- 13A03302122016Document2 pages13A03302122016EhteshTubeNo ratings yet
- Che 320 ExamDocument3 pagesChe 320 ExamCharles Bailey100% (1)
- TDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IDocument11 pagesTDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IvinodNo ratings yet
- Tugas #1 OKDocument2 pagesTugas #1 OKfitriNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1Document2 pagesExercise No. 1Abe BenitoNo ratings yet
- Me 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)Document22 pagesMe 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)محمد تانزيم ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Homework BDocument28 pagesHomework BPravallika Kollipara0% (2)
- U15met303-Ii-B - AssignmentDocument8 pagesU15met303-Ii-B - AssignmentKumaran RNo ratings yet
- 2019 CPC Problem SheetDocument1 page2019 CPC Problem SheetjacksonNo ratings yet
- 8.assignment Tutorial QPDocument13 pages8.assignment Tutorial QPvsureshkannanmsecNo ratings yet
- MEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Document4 pagesMEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- T1 Ug 90Document6 pagesT1 Ug 90germangsilvaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialJayden ChanNo ratings yet
- Mech-Engg., Thermal EngineeringDocument8 pagesMech-Engg., Thermal Engineeringnims1964No ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document3 pagesTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Me2204 Nov Dec10Document3 pagesMe2204 Nov Dec10kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Nov Dec 2012 AEDocument3 pagesNov Dec 2012 AEkbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- At2255 Engine Performance and Emission Testing LabDocument4 pagesAt2255 Engine Performance and Emission Testing Labkbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Present 2002 Deer DecDocument0 pagesPresent 2002 Deer Deckbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire As A MaDocument8 pagesShort Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire As A MaNoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of The Setup Position of A Workpiece For Five-Axis Machining To Reduce Machining TimeDocument13 pagesOptimization of The Setup Position of A Workpiece For Five-Axis Machining To Reduce Machining TimeHungTranNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Tourism Development ProjectDocument4 pagesSustainable Tourism Development ProjectKularajah ThuthirajNo ratings yet
- Boyce ODEch 2 S 1 P 32Document1 pageBoyce ODEch 2 S 1 P 32Charbel KaddoumNo ratings yet
- 6469 4 Sun-Protection DigitalDocument2 pages6469 4 Sun-Protection DigitalMohammed sabatinNo ratings yet
- Entity Framework Net CoreDocument74 pagesEntity Framework Net Corerdslinkac100% (1)
- R Janardhana Rao Vs G Lingappa 12011999 SC1220s990785COM978453Document3 pagesR Janardhana Rao Vs G Lingappa 12011999 SC1220s990785COM978453A. L. JainNo ratings yet
- How To View and Interpret The Turnitin Similarity Score and Originality ReportsDocument5 pagesHow To View and Interpret The Turnitin Similarity Score and Originality ReportsRT LeeNo ratings yet
- Scope of SupplyDocument12 pagesScope of Supplyreza39No ratings yet
- Greer Citizen E-Edition 7.11.18Document16 pagesGreer Citizen E-Edition 7.11.18greercitizenNo ratings yet
- Funny Short StoriesDocument43 pagesFunny Short StorieschicankzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7,8Document4 pagesChapter 7,8zee412No ratings yet
- Changing HRM Practices With Firm Growth: Bernice Kotey and Alison SheridanDocument12 pagesChanging HRM Practices With Firm Growth: Bernice Kotey and Alison SheridanAhmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document34 pagesChapter 6Nguyễn Nhật SangNo ratings yet
- Catalog Sr10.1.1 Simeas R - R-Pmu - enDocument32 pagesCatalog Sr10.1.1 Simeas R - R-Pmu - enSuresh Kumar PariharNo ratings yet
- 9 - Napilas Integrated School Secondary - Rehabilitation of Ceiling Ivan PudaderaDocument14 pages9 - Napilas Integrated School Secondary - Rehabilitation of Ceiling Ivan PudaderaWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Amortization and Sinking FundDocument2 pagesAmortization and Sinking FundClariz Angelika EscocioNo ratings yet
- PLAN 423 - Module 3Document35 pagesPLAN 423 - Module 3ABCD EFGNo ratings yet
- Camshaft Opel Zafira-BDocument3 pagesCamshaft Opel Zafira-Bmr & mrsNo ratings yet
- Yogananda Sagar KDocument4 pagesYogananda Sagar KSagarNo ratings yet
- Construction Inc - QTN3255Document1 pageConstruction Inc - QTN3255denciopo61No ratings yet
- Air Flow Rate Calculation For Fire Smoke Exhaust System: Vietnam Nisshin Technomic Phase 2 ProjectDocument8 pagesAir Flow Rate Calculation For Fire Smoke Exhaust System: Vietnam Nisshin Technomic Phase 2 Projecttiger vuNo ratings yet
- Algeriavisa 2Document1 pageAlgeriavisa 2yaimara iimenezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Name: Satyarthsinh Gohil Regno: 16BCE1125 Course: Internet and Web Programming Faculty: Sandhya.P Slot: E2Document13 pagesAssignment 1: Name: Satyarthsinh Gohil Regno: 16BCE1125 Course: Internet and Web Programming Faculty: Sandhya.P Slot: E2ABHISHEK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Digest Admin-LawDocument50 pagesDigest Admin-LawCeslhee AngelesNo ratings yet
- S02 Rock Drill, Flushing HeadDocument28 pagesS02 Rock Drill, Flushing HeadrolandNo ratings yet
- Libehr List - New (Chennai MT)Document7 pagesLibehr List - New (Chennai MT)Krishna RajNo ratings yet
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Uploaded by
kbhaskar66Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.
Uploaded by
kbhaskar66Copyright:
Available Formats
Reg. No.
Question Paper Code :
53030
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2010 Third Semester Automobile Engineering
AT 2203 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (Regulation 2008) Time : Three hours
Answer ALL questions
PART A (10 2 = 20 Marks) 1.
Why does a bicycle pick up speed on a downhill road even when it is not pedaled? Does this violate the conservation of energy principle? A room is heated as a result of solar radiation coming in through the windows. Is this a heat or work interaction for the room? Is it possible for a heat engine to operate without rejecting any waste heat to a lower temperature reservoir? A system undergoes a process between two fixed states first in a reversible manner and then in an irreversible manner. For which case is the entropy change is greater? Why? What is the difference between triple point and critical point? Why is excessive moisture in steam undesirable in steam turbine? What is the highest moisture content allowed? Define mass and mole fractions. What does Joule Thomson coefficient represent?
2.
3.
4.
5. 6.
21 9
7. 8.
CENTRAL LIBRARY-SVCE, SRIPERUMBUDUR
21
(Use of standard thermodynamic tables, Mollier diagram, psychrometric chart and refrigerant tables permitted)
21 9
Maximum : 100 Marks
9. 10.
How do constant-enthalpy and constant wet bulb temperature lines compare on the psychrometric chart? How does humidity affect human comfort?
PART B (5 16 = 80 Marks) 11. (a)
A 50 kg iron block at 80C is dropped into an insulated tank that contains 0.5 m3 of liquid water at 25C. Determine the temperature when the thermal equilibrium is researched. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3. The specific heats of iron block and water are 0.45 kJ/kg K and 4.0187 kJ/kg K respectively. (16) Or
(b)
In rural areas, water is often extracted from underground by pumps. Consider an underground water source whose free surface is 60 m below ground level. The water is to be raised 5 m above the ground by the pump. The diameter of the pipe is 15 cm at the inlet and 20 cm at the exit. Neglecting any heat interaction with the surroundings and frictional heating effects, determine the power input to the pump required for the steady flow of water at the rate of 0.015 m3/s. (16) (i)
12.
(a)
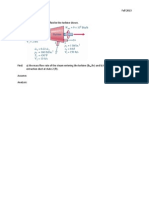
A rigid tank contains 5 kg of refrigerant initially at 20C and 140 kPa. The refrigerant is cooled while being stirred until its pressure drops to 100 kPa. Determine the entropy change of the refrigerant during this process. (8) Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 5 Mpa and 450C and leaves at a pressure of 1.4 MPa. Determine the work output of the turbine per unit mass steam flowing through the turbine if the process is reversible, with valid assumptions. (8) Or
(ii)
(b)
Steam enters a turbine steadily at 3 MPa and 450C at a rate of 8 kg/s and exits at 0.2 MPa and 150C. The steam is losing heat to the surrounding air at 100 kPa and 25C at a rate of 300 kW and the kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. Determine the actual power output, the maximum possible power output (the reversible power), the second law efficiency, the energy destroyed and the energy of the stream at the inlet conditions. (16) A piston cylinder device contains 0.1 m3 of liquid water and 0.9 m3 of water vapour in equilibrium at 800 kPa. Heat is transferred at a constant pressure until the temperature reaches 350C. What is the initial temperature of water? Determine the total mass of water, calculate the final volume and show the process on a P-V diagram with respect to saturation line. (16) Or 2
21 9
13. (a)
21 9
CENTRAL LIBRARY-SVCE, SRIPERUMBUDUR
21 9
53030
(b)
(i) (ii)
How do actual vapour power cycles differ from idealized one?
(4)
14.
(a)
(i)
The composition of moist air is given on a mole basis: 60 percent N2, 20 percent O2 and 2 percent water vapour. Determine the mass fractions of the constituents of air. (3) Using Daltons law, show that
k i =1
(ii)
Z m = Z yi Z i For a real gas mixture of k gases, where Z is the
compressibility factor Or (b) (i) (ii)
Describe the inversion line and maximum inversion temperature. (6)
15.
(a)
(i)
(ii)
The dry and wet-bulb temperature of atmospheric air at 95 kPa are 25 and 20C, respectively. Determine the specific humidity, relative humidity and the enthalpy of the air. (10) Or
(b)
(i) (ii)
At what states on the psychometric chart are the dry-bulb, wet-bulb and dew-point temperatures identical? (4) Two air streams are mixed steadily and adiabatically. The first stream enters at 32C and 40 percent relative humidity at the rate of 20 m3/min, while the second stream enters at 12C and 90 percent relative to humidity at a rate of 25 m3/min. Assuming that the mixing process occurs at a pressure of 1 atm, determine the specific humidity, the relative humidity, the dry-bulb temperature and the volume flow rate of the mixture. (12)
21 9
21
Explain how vapour pressure of the ambient air is determined when the temperature, total pressure and the relative humidity of the air are given. (6)
Using the Maxwells relations and the ideal-gas equation of state, S (10) determine a relation for for an ideal gas. V T
CENTRAL LIBRARY-SVCE, SRIPERUMBUDUR
21 9
(13)
A steam power plant operates on a simple Rankine cycle between the pressure limits of 3 Mpa and 50 kpa. The temperature of the steam at the turbine inlet is 400C and the mass flow rate of steam through cycle is 25 kg/s. Show the cycle on a T-s diagram with respect to saturation lines. Determine the thermal efficiency of the cycle and the net output of the power plant. (12)
53030
You might also like
- Board-Exam May2223242019Document11 pagesBoard-Exam May2223242019Jonnah Faye MojaresNo ratings yet
- ENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Document6 pagesENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Manel SashikalaNo ratings yet
- Bhagvan Kommadi - Learn Data Structures and Algorithms With Golang - Level Up Your Go Programming Skills To Develop Faster and More Efficient Code PDFDocument324 pagesBhagvan Kommadi - Learn Data Structures and Algorithms With Golang - Level Up Your Go Programming Skills To Develop Faster and More Efficient Code PDFLúar Mújica100% (2)
- PS Compilation For 2019Document10 pagesPS Compilation For 2019Nicole RamirezNo ratings yet
- Epf Pass Book Avula VaraprasadDocument1 pageEpf Pass Book Avula VaraprasadvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- TD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Document31 pagesTD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Narayanan Srinivasan100% (1)
- ETD Model IV QPDocument2 pagesETD Model IV QPtagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- 7157902Document62 pages7157902Red RedNo ratings yet
- Question Paper ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper ThermodynamicsThaanya sNo ratings yet
- MEC1405 - Thermodynamics I (2009Document3 pagesMEC1405 - Thermodynamics I (2009Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- Internal II Question Paper Etd Set IIDocument2 pagesInternal II Question Paper Etd Set IItagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesThermal Engineering - Department of Mechanical EngineeringPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Me 8301 EtdDocument3 pagesMe 8301 Etdsrinithims78No ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- ME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Document4 pagesME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007ARUNGREESMANo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesImportant Questionstamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Me8391 - EtdDocument3 pagesMe8391 - Etdsyed1188No ratings yet
- Ihw 2Document6 pagesIhw 2LogoNo ratings yet
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument5 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Guru PrakashNo ratings yet
- ETD Model 2024Document2 pagesETD Model 2024shivakeesNo ratings yet
- IES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002Document8 pagesIES-CONV-Mechanical Engineering-2002aditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Me2202 PDFDocument15 pagesMe2202 PDFvis3012No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsDocument8 pagesMass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsIastraNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document7 pagesSheet 1Bahaa RaghebNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Ae 1201 - Aero Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesAe 1201 - Aero Engineering ThermodynamicsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER Previous PaperDocument8 pagesHEAT TRANSFER Previous PaperVibin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Kishore AtdDocument14 pagesKishore AtdKumar SamyanaikNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mechDocument2 pagesEtd 2mechgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocument16 pagesThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- ME2202 Question BankDocument5 pagesME2202 Question BankStanly ThomasNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 CalorDocument2 pagesTarea 4 CalorDenisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- (Ae8301)Document4 pages(Ae8301)aerochandru.87No ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document7 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234No ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringKarthik P MuraliNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- eNGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION PAPERDocument11 pageseNGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS QUESTION PAPERAbubakkar Siddiq100% (3)
- Assignment 2 Second Law 2016Document7 pagesAssignment 2 Second Law 2016Mohit SInhaNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test SOMDocument7 pagesCycle Test SOMRyan GomezNo ratings yet
- 13A03302122016Document2 pages13A03302122016EhteshTubeNo ratings yet
- Che 320 ExamDocument3 pagesChe 320 ExamCharles Bailey100% (1)
- TDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IDocument11 pagesTDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IvinodNo ratings yet
- Tugas #1 OKDocument2 pagesTugas #1 OKfitriNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1Document2 pagesExercise No. 1Abe BenitoNo ratings yet
- Me 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)Document22 pagesMe 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)محمد تانزيم ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Homework BDocument28 pagesHomework BPravallika Kollipara0% (2)
- U15met303-Ii-B - AssignmentDocument8 pagesU15met303-Ii-B - AssignmentKumaran RNo ratings yet
- 2019 CPC Problem SheetDocument1 page2019 CPC Problem SheetjacksonNo ratings yet
- 8.assignment Tutorial QPDocument13 pages8.assignment Tutorial QPvsureshkannanmsecNo ratings yet
- MEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Document4 pagesMEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- T1 Ug 90Document6 pagesT1 Ug 90germangsilvaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialJayden ChanNo ratings yet
- Mech-Engg., Thermal EngineeringDocument8 pagesMech-Engg., Thermal Engineeringnims1964No ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document3 pagesTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Me2204 Nov Dec10Document3 pagesMe2204 Nov Dec10kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Nov Dec 2012 AEDocument3 pagesNov Dec 2012 AEkbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- At2255 Engine Performance and Emission Testing LabDocument4 pagesAt2255 Engine Performance and Emission Testing Labkbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Present 2002 Deer DecDocument0 pagesPresent 2002 Deer Deckbhaskar66No ratings yet
- Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire As A MaDocument8 pagesShort Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire As A MaNoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of The Setup Position of A Workpiece For Five-Axis Machining To Reduce Machining TimeDocument13 pagesOptimization of The Setup Position of A Workpiece For Five-Axis Machining To Reduce Machining TimeHungTranNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Tourism Development ProjectDocument4 pagesSustainable Tourism Development ProjectKularajah ThuthirajNo ratings yet
- Boyce ODEch 2 S 1 P 32Document1 pageBoyce ODEch 2 S 1 P 32Charbel KaddoumNo ratings yet
- 6469 4 Sun-Protection DigitalDocument2 pages6469 4 Sun-Protection DigitalMohammed sabatinNo ratings yet
- Entity Framework Net CoreDocument74 pagesEntity Framework Net Corerdslinkac100% (1)
- R Janardhana Rao Vs G Lingappa 12011999 SC1220s990785COM978453Document3 pagesR Janardhana Rao Vs G Lingappa 12011999 SC1220s990785COM978453A. L. JainNo ratings yet
- How To View and Interpret The Turnitin Similarity Score and Originality ReportsDocument5 pagesHow To View and Interpret The Turnitin Similarity Score and Originality ReportsRT LeeNo ratings yet
- Scope of SupplyDocument12 pagesScope of Supplyreza39No ratings yet
- Greer Citizen E-Edition 7.11.18Document16 pagesGreer Citizen E-Edition 7.11.18greercitizenNo ratings yet
- Funny Short StoriesDocument43 pagesFunny Short StorieschicankzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7,8Document4 pagesChapter 7,8zee412No ratings yet
- Changing HRM Practices With Firm Growth: Bernice Kotey and Alison SheridanDocument12 pagesChanging HRM Practices With Firm Growth: Bernice Kotey and Alison SheridanAhmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document34 pagesChapter 6Nguyễn Nhật SangNo ratings yet
- Catalog Sr10.1.1 Simeas R - R-Pmu - enDocument32 pagesCatalog Sr10.1.1 Simeas R - R-Pmu - enSuresh Kumar PariharNo ratings yet
- 9 - Napilas Integrated School Secondary - Rehabilitation of Ceiling Ivan PudaderaDocument14 pages9 - Napilas Integrated School Secondary - Rehabilitation of Ceiling Ivan PudaderaWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Amortization and Sinking FundDocument2 pagesAmortization and Sinking FundClariz Angelika EscocioNo ratings yet
- PLAN 423 - Module 3Document35 pagesPLAN 423 - Module 3ABCD EFGNo ratings yet
- Camshaft Opel Zafira-BDocument3 pagesCamshaft Opel Zafira-Bmr & mrsNo ratings yet
- Yogananda Sagar KDocument4 pagesYogananda Sagar KSagarNo ratings yet
- Construction Inc - QTN3255Document1 pageConstruction Inc - QTN3255denciopo61No ratings yet
- Air Flow Rate Calculation For Fire Smoke Exhaust System: Vietnam Nisshin Technomic Phase 2 ProjectDocument8 pagesAir Flow Rate Calculation For Fire Smoke Exhaust System: Vietnam Nisshin Technomic Phase 2 Projecttiger vuNo ratings yet
- Algeriavisa 2Document1 pageAlgeriavisa 2yaimara iimenezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Name: Satyarthsinh Gohil Regno: 16BCE1125 Course: Internet and Web Programming Faculty: Sandhya.P Slot: E2Document13 pagesAssignment 1: Name: Satyarthsinh Gohil Regno: 16BCE1125 Course: Internet and Web Programming Faculty: Sandhya.P Slot: E2ABHISHEK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Digest Admin-LawDocument50 pagesDigest Admin-LawCeslhee AngelesNo ratings yet
- S02 Rock Drill, Flushing HeadDocument28 pagesS02 Rock Drill, Flushing HeadrolandNo ratings yet
- Libehr List - New (Chennai MT)Document7 pagesLibehr List - New (Chennai MT)Krishna RajNo ratings yet