Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Uploaded by
Kenny RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Condmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideDocument238 pagesCondmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideKenny Ruiz67% (6)
- RESEARCH GCS AdecDocument62 pagesRESEARCH GCS Adec07 FARAH ATHIRAH BINTI MOH FUZINo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Waste Heat Boiler, HRSGDocument13 pagesEfficiency of Waste Heat Boiler, HRSGHasan Ahmed100% (1)
- FAD Calculation For CompressorDocument2 pagesFAD Calculation For CompressorDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- ESP Sizing Calculation (240315)Document4 pagesESP Sizing Calculation (240315)Amlan SahaNo ratings yet
- FD Fan Efficiency CalculationDocument6 pagesFD Fan Efficiency CalculationPraveen VaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument145 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasHime_ChiakiNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors - Gas IndustryDocument2 pagesConversion Factors - Gas IndustryKailas Nimbalkar100% (3)
- Overall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Document8 pagesOverall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Tamer FathyNo ratings yet
- Cooler CalculationDocument3 pagesCooler Calculationmohanprocess24No ratings yet
- H&M CalculationsDocument14 pagesH&M CalculationsNITINNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsDocument2 pagesConversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsvvijaybhanNo ratings yet
- Id Fan Size CalcDocument1 pageId Fan Size CalculhatolkargmailcomNo ratings yet
- Material Balance ADocument8 pagesMaterial Balance ATheepa SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Eff FormulaDocument59 pagesEff FormulaVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Calculations - WHRSDocument10 pagesThermal Calculations - WHRSshani5573No ratings yet
- Combustion CalcsDocument8 pagesCombustion Calcs31331311313No ratings yet
- 4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1Document1 page4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1rinabiswasNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat BalanceDocument4 pages1 Heat BalanceKiran Veerubhotla100% (1)
- Line III Heat BalanceDocument65 pagesLine III Heat Balancehmaza shakeelNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance CalculationsDocument29 pagesHeat Balance CalculationsGuillermo Càceres100% (1)
- Gas Flow CalculationDocument59 pagesGas Flow CalculationOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Hot AirDocument6 pagesHot AirElancheran RengaNo ratings yet
- 18 Roots Blower I ToDocument31 pages18 Roots Blower I ToBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Is 14164 2008Document45 pagesIs 14164 2008Pukhraj DagaNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling System CalculationDocument4 pagesAsh Handling System CalculationAndi HarsoNo ratings yet
- Verification of Capacity of Secondary Air Fan For Bagasse Fired BoilerDocument2 pagesVerification of Capacity of Secondary Air Fan For Bagasse Fired BoilerAu TagolimotNo ratings yet
- Kiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationDocument4 pagesKiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationVijay Bhan75% (4)
- Result: Economizer Heating Surface and Outlet Flue Gas Temperature CalculationDocument2 pagesResult: Economizer Heating Surface and Outlet Flue Gas Temperature CalculationjagjitNo ratings yet
- Heat Rate Calc in ExcelDocument13 pagesHeat Rate Calc in ExcelMukesh VadaliaNo ratings yet
- Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow RateDocument25 pagesNormal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow RateChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- ATEC Preheater Data Sheet - Old EnglDocument2 pagesATEC Preheater Data Sheet - Old Englayaskant751001100% (1)
- Cooler BalanceDocument16 pagesCooler BalanceIrfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Dryer EBDocument4 pagesDryer EBOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Steam Cost Calculations 2020Document3 pagesSteam Cost Calculations 2020Malwadkar P.B.0% (1)
- Burner Calculation OCLDocument4 pagesBurner Calculation OCLayaskant751001100% (1)
- Coal CombustionDocument3 pagesCoal CombustionRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- WHR Kcal Per HR Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesWHR Kcal Per HR Calculation SheetirfanNo ratings yet
- 1X 66 Mwkohinoor Power Pvt. Ltd. CNT 5110122 Stack Height SizingDocument4 pages1X 66 Mwkohinoor Power Pvt. Ltd. CNT 5110122 Stack Height SizingPriyanathan ThayalanNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Calc VisaDocument4 pagesStoichiometric Calc Visamkchy12No ratings yet
- Cooler Air Flow Vs Kiln FeedDocument2 pagesCooler Air Flow Vs Kiln FeedBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Cement Kiln Pyro BalanceDocument44 pagesCement Kiln Pyro BalanceirfanNo ratings yet
- Heat Rate Calculation - JITPLDocument8 pagesHeat Rate Calculation - JITPLbnswain1No ratings yet
- Heat & Mass BalanceDocument2 pagesHeat & Mass Balancesneha_21100% (1)
- Coal Drying (Dry Basis)Document9 pagesCoal Drying (Dry Basis)billyNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance Programme0Document18 pagesHeat Balance Programme0Mohamed SelimNo ratings yet
- Boiler CalculationDocument4 pagesBoiler Calculationmohsin husen BargirNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDocument50 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDilip MishraNo ratings yet
- Chimney Height CalculationDocument3 pagesChimney Height CalculationDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine EfficiencyDocument71 pagesSteam Turbine EfficiencyAnonymous LjE1R12CasNo ratings yet
- Application Procedure - Phoscast 60Document2 pagesApplication Procedure - Phoscast 60RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cost Per Hour CalculationDocument1 pageBoiler Cost Per Hour Calculationsreelu100% (2)
- Desalination Plant Feed Water ArrangementsDocument11 pagesDesalination Plant Feed Water ArrangementsSooraj Surendran SugathaNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Chemical Analysis of CementDocument1 pageFormulas of Chemical Analysis of CementFahadullah Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Chimney Draft CalculationsDocument4 pagesChimney Draft CalculationsTushar KhannaNo ratings yet
- Pump Calculation Data Sheet: Wilmar Id Engineering Amd Construction Management Flourmills Greenfield PelintungDocument11 pagesPump Calculation Data Sheet: Wilmar Id Engineering Amd Construction Management Flourmills Greenfield PelintungcitramuaraNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsDocument7 pagesHeat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsmanojNo ratings yet
- Air Receivers Volume CalculationDocument19 pagesAir Receivers Volume CalculationKenny Ruiz100% (4)
- MMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - ProblemDocument13 pagesMMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - Problemyasin kocaboğaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanic and Turbines IDocument45 pagesFluid Mechanic and Turbines IAbdulrazzak AmanNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal CompressorsDocument40 pagesReciprocal CompressorsSathish KasilingamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Part 8Document9 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics Part 8Amanullah RafiNo ratings yet
- SketchsDocument1 pageSketchsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Successful Solution: To The Challenge ofDocument2 pagesSuccessful Solution: To The Challenge ofKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Solar CellsDocument8 pagesElectrical Properties of Solar CellsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC417Document4 pagesMba ZC417Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Book-I Chapter 1: Input DataDocument3 pagesBook-I Chapter 1: Input DataKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Fly AcDocument7 pagesFly AcKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Test Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaDocument6 pagesTest Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Partial Report - RawanDocument23 pagesPartial Report - RawanKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- VB 29 - 10Document5 pagesVB 29 - 10Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Annexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeDocument3 pagesAnnexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- WE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelDocument1 pageWE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- List of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameDocument2 pagesList of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- cdk1 Coal B-EDocument1 pagecdk1 Coal B-EKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Equipment Dossier R0Document50 pagesEquipment Dossier R0Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 139 FPDocument7 pages139 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 142 EaDocument3 pages142 EaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 148 FPDocument2 pages148 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialDocument4 pagesIIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)Document43 pagesChapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)kjw 2No ratings yet
- McDonald & Dominos Entry in IndiaDocument24 pagesMcDonald & Dominos Entry in IndiaRaj Paroha83% (6)
- Complexometric Titrations by Gunja ChaturvediDocument16 pagesComplexometric Titrations by Gunja ChaturvediGunja Chaturvedi100% (3)
- Eppendorf Centrifuge 5415D and 5415R DatasheetDocument4 pagesEppendorf Centrifuge 5415D and 5415R DatasheetGeorgyNo ratings yet
- Ashridge Business School, UK: Scientist-PractitionerDocument1 pageAshridge Business School, UK: Scientist-PractitionerSharma ShikhaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Document Star Health Insurance Hospital MOUDocument9 pagesHospital Document Star Health Insurance Hospital MOUSanket Sahare100% (1)
- Enviroline 199+ds+eng PDFDocument4 pagesEnviroline 199+ds+eng PDFMohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- Warrenton Horse Show Program 2016Document36 pagesWarrenton Horse Show Program 2016Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz 300sd 1993 Operators ManualDocument10 pagesMercedes Benz 300sd 1993 Operators Manualvirginia100% (55)
- PriceSmart FoodsDocument12 pagesPriceSmart FoodsPraneet BatwarNo ratings yet
- Sample Application For NCH Nomination On Province Reserved Seats 2017Document2 pagesSample Application For NCH Nomination On Province Reserved Seats 2017Tabib Afzaal Ahmad Virk100% (1)
- Vartes Io-A2 Final VersionDocument94 pagesVartes Io-A2 Final VersionAlex CastelNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Purpose of The Unit: 8 Design of Distillation ColumnDocument16 pages8.1 Purpose of The Unit: 8 Design of Distillation Columnsami ullahNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Portfolio: Jhon Carlo Cera CatindoyDocument22 pagesWork Immersion Portfolio: Jhon Carlo Cera CatindoyJoel DufaleNo ratings yet
- English File Intermediate Third Edition-Pages-5-8Document4 pagesEnglish File Intermediate Third Edition-Pages-5-8akbal13No ratings yet
- Fall Arrest SystemDocument16 pagesFall Arrest SystemDragos VerdesNo ratings yet
- Hop Swimming Pool & Fire Water Tank Method of StatementDocument5 pagesHop Swimming Pool & Fire Water Tank Method of StatementRichard DumaogNo ratings yet
- CBT 210Document1 pageCBT 210Carlos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Perspective: The Integrative Human Microbiome ProjectDocument8 pagesPerspective: The Integrative Human Microbiome Projectdainsyah dainNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa - MechanismsDocument22 pagesAntibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa - MechanismsValentina RondonNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Control Circuits MC34063A: DescriptionDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter Control Circuits MC34063A: Descriptionfarhood ranjbarkhanghahNo ratings yet
- Kingspan Bluemaster PRO PDFDocument2 pagesKingspan Bluemaster PRO PDFDiego Felipe Gavilán RetamalesNo ratings yet
- Solubility Equilibria Tutorial Answers OHTDocument4 pagesSolubility Equilibria Tutorial Answers OHTDomNo ratings yet
- CA1 Online Class 2Document13 pagesCA1 Online Class 2kemerutNo ratings yet
- LP No 11 BMPDocument11 pagesLP No 11 BMPVikasNo ratings yet
- 718Document19 pages718shankerahulNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drainage SystemDocument7 pagesArchitectural Drainage SystemReuben ValencinasNo ratings yet
- HIRA of Batching Plant Erection.Document3 pagesHIRA of Batching Plant Erection.Gyanendra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- XC975 EV 英语译文Document2 pagesXC975 EV 英语译文abangNo ratings yet
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Uploaded by
Kenny RuizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow Rate
Uploaded by
Kenny RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
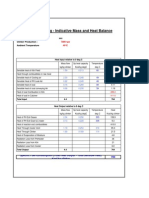
1.- Normal flow rate to real flow rate Normal flow rate data Vn = Pn = Tn = 7.53 273.
15 Nm3/h K Operation absolute pressure Pop = Patm_loc + Pop Patm_loc = Pop = Pop = Pop = Local atmospheric pressure Patm_loc = 80 kPa Operating conditions Pop = 600 top = 10 80 600 680.00 680,000 kPa kPa (g) kPa Pa Real flow rate data V= Pop = top =
2.- Real
101,325 Pa
Real volumetric flow rate (Pn/Pop) * (Top/Tn) * Vn V= Pn = 101,325 273.15 680,000 283.15 7.53 1.16 Pa K Pa C Nm3/h m3/h Tn = Pop = Top = Vn = V=
Local atmospheric pressure Patm_loc = Normal conditions Pn = Tn =
kPa (g) C
Operation absolute temperature Top = top + 273.15 top = Top = 10 283.15 C K
Operation absolute temperatu Top = top = Top =
Rev. cjc 26.02.2013
3.- Normal flow rate to real flow rate Normal flow rate data Nm3/h Vn = 7.53 top = Hloc = Pop_g = 10 1949 600.0 C m.a.s.l. kPa (g)
Patm_oc = f(H)
4.- Real flow rat Real flow rate data V= top = Hloc = Pop_g =
Operation conditions Pop = 680,000 Top = 283
Pa K
Normal conditions Pn = 101,325 Tn = 273.15
Pa K H= Patm_loc =
Patm_Loc = 101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588
Patm_Loc = 101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,
H= Patm_loc =
1949 80.00
m.a.s.l. kPa (abs) Real volumetric flow rate (Pn/Pop) * (Top/Tn) * Vn V= Pn = Tn = Pop = Top = Vn = V= 101,325 273 680,000 283.15 7.53 1.16 Pa K Pa C Nm3/h m /h
3
Operation pressure Pop = Pop_g + Patm_loc Pop_g = Patm_loc = Pop = Pop = 600.00 80.00 680.00 kPa (g) kPa kPa
Operation pressure Pop = Pop_g = Patm_loc = Pop = Pop =
680,000 Pa
Operation absolute temperature Top = top +273.15 top = 10 C
Operation absolute temperatu Top = top =
Top =
283.15
Top =
Rev. cjc. 01.08.2013
2.- Real flow rate to normal flow rate Operation absolute pressure Pop = Patm_loc + Pop m3/h kPa (g) C Patm_loc = Pop = Pop = Pop = 80 600 680 680,000 kPa kPa (g) kPa Pa
Real flow rate data 1.16 600 10
Local atmospheric pressure 80 kPa
Normal volumetric flow rate (Pop/Pn) * (Tn/Top) * V Vn = Pop = 680,000 101,325 273.15 283.15 1.2 7.53 Pa Pa K C m3/h Nm3/h Pn = Tn = Top = V= Vn =
Normal conditions 101,325 273.15 Pa K
Operation absolute temperature top + 273.15 10 283.15 C K
4.- Real flow rate to normal flow rate
Ploc = f(H)
Real flow rate data 1.2 10 1949 600
m3/h C m.a.s.l. kPa (g)
Operation conditions Pop = 680,000 Top = 283.15
Pa K
Normal conditions Pn = 101,325 Tn = 273.15
Pa K
atm_Loc
= 101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588
1949 80.00
m.a.s.l. kPa (abs)
Normal volumetric flow rate (Pop/Pn) * (Tn/Top) * V Vn = Pop = Pn = Tn = Top = V= Vn = 679,999.9 Pa 101,325 273.15 283.15 1.2 7.53 Pa K C m3/h Nm3/h
Operation pressure Pop_g + Patm_loc 600.00 80.00 680.00 680,000 kPa (g) kPa kPa Pa
Operation absolute temperature top +273.15 10 C
283.15
FAD volume flow rate Free air delivery (FAD) is the volume of air delivered under the conditions of temperature and pressure existing at the compressor's intake (state 2). V2 = V1 * (P1 - RH1 * Psat.water_1) / (P2 - RH2 * Psat.water_2) * (T2 / T1)
1.- Normal flow rate (state 1) to FAD flow rate (state 2) Normal air conditions (State 1) V1 = 480 Nm3/h P1 = RH1 = t1= T1 = Psat.water_1 = Psat.water_1 = 101,325 0 0 273 f(T1) 609.6 Pa C K Pa
FAD conditions (State 2)) P2 = 73,400 RH2 = 0.42 t2= Psat.water_2 = Psat.water_2 = T2 = V2 = 22 f(T2) 2645.1 295 726.99
Pa C Pa K
m3/h (FAD)
Rev. cjc 26.02.2013
Psat.water1 = t1= T1 = Psat.water1 =
100000 * EXP(153.5411 + 0.066953 *(D36) - 0.0000505796 * (D36)^ 2 + 0.00000002183911 * (D36) ^ 3 0 273 609.6 C K Pa
Free air delivered (FAD) Free air delivery is the volume of air delivered under the conditions of temperature and pressure existing at the compressor`s intake (state 2).
To obtain the volume flow rate at the intake conditions (2), knowing the volume flowrate at the standard conditions (1), one applicates Boyle-Mariot law between both cases. Since we want a value of dry air, Boyle-Mariot is to be applied to the dry air. Thus, dry air partial pressures are to be used. - Since normal air is a dry air (da), the total air pressure at this conditions is the same as the partial dry air pressure Pda_1 = P1 - Pw_1 with an air without water vapor Pw_1 = 0 thus Pda_1 = P1
- The partial pressure of the dry air (da) in the ambient air (2) is Pda_2 = P2 - Pw_2 P2 : Total pressure of ambient air (state 2) Pw_2 : Partial pressure of water vapor in sate 2 where the water vapor pressure is calculated as Pw_2 = f2 * Psat.water_2 with f2 : Psat.water_2 = Relative humidity of ambient air (Also, indicated as RH) Pressure of saturated water vapor at ambient temperatute "t2"
Thus, Boyle-Mariot is applied as
Determination of dry air flowrate (V2) that is to be sucked at the compressor's intake to obtain the desired volume flowrate (V1) V1 = 480 Nm3/h Intake or local conditions (2) t2 = 22 C T2 = P2 = RH2 =
Psat.water_2 =
Normal conditions (1) t1 = 0 T1 = P1 = RH1 =
Psat.water_1 =
C K Pa Pa
273.15 101,325 0 609.6
295 73,400 0.42 2645.1
K Pa Pa
V2 = V1 = P1 =
V1 * (P1 - RH1 * Psat.water_1) / (P2 - RH2 * Psat.water_2) * (T2 / T1) 480 Nm3/h 101,325 Pa
RH1 = t1= Psat.wate1 = P2= RH2 = t2= Psat.wate_2 = T2 = T1 = V2 =
0 0 609.6 73,400 0.42 22 2645.1 295 273
C Pa Pa C Pa K K
726.99 m3/h (FAD)
Saturation pressure of water Valid 0 for C < t < 100 C t= 0 C Psat= 609.6 Pa
Psat = 100000 * Exp(153.5411 + 0.066953 *(C3+273.15) - 0.0000505796 * (C3+273.15)^ 2 + 0.00000002183911 * (C3+273.15) ^ 3 - 8990.134 * (C3+273.
V1 =
V2 * (P2 - RH2 * Psat.water_2) / (P1 - RH1 * Psat.water_1) * (T1 / T2)
2.- FAD flow rate (state 2) to Normal flow rate (state 1) FAD conditions (State 2)) V2 = 726.99 P2 = RH2 = t2= Psat.water_2 = Psat.water_2 = T2 = 73,400 0.42 22 f(T2) 2645.1 295
m3/h (FAD)
Pa C Pa K
Normal air conditions (State 1) P1 = 101,325 Pa RH1 = t1= T1 = Psat.water_1 = Psat.water_1 = V1 = 0 0 273 f(T1) 609.6 C K Pa 480 m3/h
0.00000002183911 * (D36) ^ 3 - 8990.134 * (D36) ^ -1 - 25.07797 * LN((D17+273.15)))
Water vapor pressure P1 y P2 son presiones absolutas totales de la mezcla de aire y vapor de agua
La presin parcial del aire seco es Pa_1 La temperatura normal es t1 = 0C La presin parcial del vapor de agua a la temperatura normal es Pw_1 La humedad relativa del aire seco es RH1 = 0 Air at normal conditions (state "1") (Pw_2 / Psat.water_2) * Psat.water_2 Pw_1 = (Pw_1 / Psat.water_1) = f with "f" : air Relative Humidity (RH) Pw_1 = f1 * Psat.water_1 Pw_1 = RH1 = t1 = Pw_1= RH1 * Psat_1 0 0 609.6 C Pa
Air at ambient conditions (estado "2") (Pw_2 / Psat.water_2) * Psat.water_2 Pw_2 = (Pw_2 / Psat.water_2) = f with "f" : air Relative Humidity (RH) Pw_2 = f2 * Psat.water_2 RH2 * Psat_2 Pw_2 = RH2 = t2 = Pw_2= 0.42 22 2645.1 C Pa
FAD volume flowrate V2 = V1 * (P1 - RH1 * Psat.water_1) / (P2 - RH2 * Psat.water_2) * (T2 / T1) V1 = P1 = 480 101,325 Nm3/h Pa State 1: Normal air conditions
RH1 = t1= Psat.wate1 = P2= RH2 = t2= Psat.wate_2 = T2 = T1 = V2 =
0 0 609.6 73,400 0.42 22 2645.1 295 273 726.99
C Pa Pa C Pa K K
m3/h (FAD)
State 2: Local ambient air conditions and also compressor intake conditions Free air delivery (FAD) is the volume of air delivered under the conditions of temperature and pressure existing at the compressor's intake (state 2).
(C3+273.15) ^ 3 - 8990.134 * (C3+273.15) ^ -1 - 25.07797 * Ln((C3+273.15)))
Air density and mass flow rates Air constant R=
287.0
J/(kg*K)
1.-Normal flow rate to mass flow rate. SI
3.- Mass flow rate imperial to Normal flow rate. SI m= m= m= Vn = 0.792 0.359 1293.2 m / rn 1,293.2 1.29 1,000
Vn = Mass flowrate m= Vn = rn = m= m=
1,000
Nm3/h
Vn * rn 1000 1.29 1293 0.3592 Nm3/h kg/Nm kg/h kg/s
3
m= rn = Vn =
2.- Mass flow rate to Normal flow rate. SI m= m= Vn = m= rn = Vn = 0.3592 1293.2 m / rn 1,293.2 1.29 1,000 kg/h kg/Nm3 Nm3/h kg/s kg/h
4.- Normal flow rate to mass flow rate imperial Vn = Mass flowrate m= Vn = rn = m= m= m= 1000 Vn * rn 1000 1.29 1293 0.3592 0.792
Normal density rn = p / ( R * T) p= 101,325 R= 287.0 T= 273 rn = 1.29
Pa J/(kg*K) K kg/Nm3
1 kg = m= m=
2.20 0.3592 0.7920
flow rate imperial to Normal
5.- Actual density tact = 10 450.0 1730 C kPa (g) m.a.s.l.
Air constant R= Rg = MM = R=
lb/s kg/s kg/h
Pact_g = H= patm_loc = patm_loc =
101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588
Nitrogen constant R= Rg = MM =
82.20 tact + 273.15 10 283.15
kPa
kg/h kg/Nm3 Nm3/h
T= tact = T= P= Pact_g = patm_loc =
C K
R= Molecular masses from [1]
al flow rate to mass flow
Pact_g + Patm_loc 450.0 82.20 532.2 532,197 p / ( R * T) 532,197 287.0 283 6.55 Pa J/(kg*K) K kg/m3
Rev. cjc. 30.05.2013
kPa (g) kPa kPa Pa
Nm3/h
P= P= ract =
3
Nm3/h kg/Nm kg/h kg/s lb/s
p= R= T= ract =
lb kg/s lb/s
Rg / MM 8314.41 28.97 287.0
[ J / (kmol*K)] kg/kmol J/(kg*K)
Nitrogen constant Rg / MM 8314.41 28.0134 296.8 Molecular masses from [1] [ J / (kmol*K)] kg/kmol J/(kg*K)
Nitrogen density and mass flow rates Nitrogen constant R= 296.8
J/(kg*K)
1.-Normal flow rate to mass flow rate. SI
3.- Mass flow rate imperial to Normal flow rate. SI m= m= m= Vn = 0.766 0.347 1250.5 m / rn 1,250.5 1.25 1,000
Vn = Mass flowrate m= Vn = rn = m= m=
1,000
Nm3/h
Vn * rn 1000 1.25 1251 0.3474 Nm3/h kg/Nm kg/h kg/s
3
m= rn = Vn =
2.- Mass flow rate to Normal flow rate. SI m= m= Vn = m= rn = Vn = 0.3474 1250.5 m / rn 1,250.5 1.25 1,000 kg/h kg/Nm3 Nm3/h kg/s kg/h
4.- Normal flow rate to mass flow rate imperial Vn = Mass flowrate m= Vn = rn = m= m= m= 1000 Vn * rn 1000 1.25 1251 0.3474 0.766
Normal density rn = p / ( R * T) p= 101,325 R= 296.8 T= 273 rn = 1.25
Pa J/(kg*K) K kg/Nm3
1 kg = m= m=
2.20 0.3474 0.7658
flow rate imperial to Normal
5.- Actual density tact = 10 450.0 1730 C kPa (g) m.a.s.l.
Air constant R= Rg = MM = R=
lb/s kg/s kg/h
Pact_g = H= patm_loc = patm_loc =
101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588
Nitrogen constant R= Rg = MM =
82.20 tact + 273.15 10 283.15
kPa
kg/h kg/Nm3 Nm3/h
T= tact = T= P= Pact_g = patm_loc =
C K
R= Molecular masses from [1]
al flow rate to mass flow
Pact_g + Patm_loc 450.0 82.20 532.2 532,197 p / ( R * T) 532,197 296.8 283 6.33 Pa J/(kg*K) K kg/m3
Rev. cjc. 03.07.2013
kPa (g) kPa kPa Pa
Nm3/h
P= P= ract =
3
Nm3/h kg/Nm kg/h kg/s lb/s
p= R= T= ract =
lb kg/s lb/s
Rg / MM 8314.41 28.97 287.0
[ J / (kmol*K)] kg/kmol J/(kg*K)
Nitrogen constant Rg / MM 8314.41 28.0134 296.8 Molecular masses from [1] [ J / (kmol*K)] kg/kmol J/(kg*K)
Imperial standard flow rate to Normal flow rate Imperial standard flow rate data VS = 1.0 Sm3/h Normal absolute pressure PN = 101,325
Pa
Normal absolute temperature TN = 273.15 K Standard volumetric flow rate to Normal volumetric flow rate VS * (PS/Pn) * (Tn/TS) Vn = PS = Pn = Tn = 101,325 101,325 273.15 288.71 1.0 0.9461 Pa Pa K C m3/h Nm3/h
Imperial standard temperature tS = 60 F tS = 15.56 C Imperial standard pressure PS = 101,325 kPa
Standard conditions (Imperial) PS = 101,325 Pa TS = 288.71 K
TS = VS = Vn =
Sm3/h
0.9461
Nm3/h
Nm3/h
1.057
Sm3/h
Approximate method Aproximate equation for calculating the atmospheric pressure as a function of the height above sea level p= H= p= 101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588 1730 m 82.20 kPa
The Engineering Toolbox
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/air-altitude-pressure-d_462.html
Esta ecuacin es una simplificacin de la frmula hipsomtrica [2], en la que la temperatura ambiente se toma con un valor aproximado de 15,2 C Esta ecuacin aproximada produce un error mximo de 0.1% cuando se aplica en le rango de alturas 0 m.sn.m. <= H <= 6000 m.s.n.m.
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/molecular-weight-gas-vapor-d_1156.html
Molecular Weight - Gases and Vapors
Molecular mass of common gases and vapors
The molecular weight of a substance, also called molecular mass, is the mass of one molecule of that substance, relative to the unified atomic mass unit u equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12. Gas or Vapor Acetylene, C2H2 Air Ammonia (R-717) Argon, Ar Benzene N-Butane, C4H10 Iso-Butane (2-Metyl propane) Butadiene 1-Butene cis -2-Butene trans-2-Butene Isobutene Carbon Dioxide, CO2 Carbon Disulphide Carbon Monoxide, CO Chlorine Cyclohexane Deuterium Ethane, C2H6 Ethyl Alcohol Ethyl Chloride Ethylene, C2H4 Fluorine Helium, He N-Heptane Hexane Hydrochloric Acid Molecular Weight kg/kmol 26.04 28.966 17.02 39.948 78.11 58.12 58.12 54.09 56.108 56.108 56.108 56.108 44.01 76.13 28.011 70.906 84.16 2.014 30.07 46.07 64.515 28.054 37.996 4.02 100.2 86.17 36.47 Gas or Vapor Hydrogen, H2 Hydrogen Chloride Hydrogen Sulfide Hydroxyl, OH Krypton Methane, CH4 Methyl Alcohol Methyl Butane Methyl Chloride Natural Gas Neon, Ne Nitric Oxide, NO2 Nitrogen, N2 Nitrous Oxide N-Octane Oxygen, O2 Ozone N-Pentane Iso-Pentane Propane, C3H8 Propylene Molecular Weight kg/kmol 2.016 36.461 34.076 17.01 83.8 16.044 32.04 72.15 50.488 19 20.179 30.006 28.0134 44.012 114.22 31.9988 47.998 72.15 72.15 44.097 42.08
Gas or Vapor R-11 R-12 R-22 R-114 R-123 R-134a R-611 Sulfur Sulfur Dioxide Sulfuric Oxide Toluene Xenon Water Vapor Steam, H2O
Molecular Weight kg/kmol 137.37 120.92 86.48 170.93 152.93 102.03 60.05 32.02 64.06 48.1 92.13 131.3 18.02
[1]
The Engineering Toolbox
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/air-altitude-pressure-d_462.html
also www.piping-tools.net Atmospheric_temperature_pressure_and_density_as_function_of_the_height_above_sea
the_height_above_sea_level.xlsm
You might also like
- Condmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideDocument238 pagesCondmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideKenny Ruiz67% (6)
- RESEARCH GCS AdecDocument62 pagesRESEARCH GCS Adec07 FARAH ATHIRAH BINTI MOH FUZINo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Waste Heat Boiler, HRSGDocument13 pagesEfficiency of Waste Heat Boiler, HRSGHasan Ahmed100% (1)
- FAD Calculation For CompressorDocument2 pagesFAD Calculation For CompressorDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- ESP Sizing Calculation (240315)Document4 pagesESP Sizing Calculation (240315)Amlan SahaNo ratings yet
- FD Fan Efficiency CalculationDocument6 pagesFD Fan Efficiency CalculationPraveen VaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument145 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasHime_ChiakiNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors - Gas IndustryDocument2 pagesConversion Factors - Gas IndustryKailas Nimbalkar100% (3)
- Overall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Document8 pagesOverall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Tamer FathyNo ratings yet
- Cooler CalculationDocument3 pagesCooler Calculationmohanprocess24No ratings yet
- H&M CalculationsDocument14 pagesH&M CalculationsNITINNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsDocument2 pagesConversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsvvijaybhanNo ratings yet
- Id Fan Size CalcDocument1 pageId Fan Size CalculhatolkargmailcomNo ratings yet
- Material Balance ADocument8 pagesMaterial Balance ATheepa SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Eff FormulaDocument59 pagesEff FormulaVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Calculations - WHRSDocument10 pagesThermal Calculations - WHRSshani5573No ratings yet
- Combustion CalcsDocument8 pagesCombustion Calcs31331311313No ratings yet
- 4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1Document1 page4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1rinabiswasNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat BalanceDocument4 pages1 Heat BalanceKiran Veerubhotla100% (1)
- Line III Heat BalanceDocument65 pagesLine III Heat Balancehmaza shakeelNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance CalculationsDocument29 pagesHeat Balance CalculationsGuillermo Càceres100% (1)
- Gas Flow CalculationDocument59 pagesGas Flow CalculationOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Hot AirDocument6 pagesHot AirElancheran RengaNo ratings yet
- 18 Roots Blower I ToDocument31 pages18 Roots Blower I ToBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Is 14164 2008Document45 pagesIs 14164 2008Pukhraj DagaNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling System CalculationDocument4 pagesAsh Handling System CalculationAndi HarsoNo ratings yet
- Verification of Capacity of Secondary Air Fan For Bagasse Fired BoilerDocument2 pagesVerification of Capacity of Secondary Air Fan For Bagasse Fired BoilerAu TagolimotNo ratings yet
- Kiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationDocument4 pagesKiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationVijay Bhan75% (4)
- Result: Economizer Heating Surface and Outlet Flue Gas Temperature CalculationDocument2 pagesResult: Economizer Heating Surface and Outlet Flue Gas Temperature CalculationjagjitNo ratings yet
- Heat Rate Calc in ExcelDocument13 pagesHeat Rate Calc in ExcelMukesh VadaliaNo ratings yet
- Normal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow RateDocument25 pagesNormal To Real Flow Rate and FAD Flow RateChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- ATEC Preheater Data Sheet - Old EnglDocument2 pagesATEC Preheater Data Sheet - Old Englayaskant751001100% (1)
- Cooler BalanceDocument16 pagesCooler BalanceIrfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Dryer EBDocument4 pagesDryer EBOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Steam Cost Calculations 2020Document3 pagesSteam Cost Calculations 2020Malwadkar P.B.0% (1)
- Burner Calculation OCLDocument4 pagesBurner Calculation OCLayaskant751001100% (1)
- Coal CombustionDocument3 pagesCoal CombustionRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- WHR Kcal Per HR Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesWHR Kcal Per HR Calculation SheetirfanNo ratings yet
- 1X 66 Mwkohinoor Power Pvt. Ltd. CNT 5110122 Stack Height SizingDocument4 pages1X 66 Mwkohinoor Power Pvt. Ltd. CNT 5110122 Stack Height SizingPriyanathan ThayalanNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Calc VisaDocument4 pagesStoichiometric Calc Visamkchy12No ratings yet
- Cooler Air Flow Vs Kiln FeedDocument2 pagesCooler Air Flow Vs Kiln FeedBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Cement Kiln Pyro BalanceDocument44 pagesCement Kiln Pyro BalanceirfanNo ratings yet
- Heat Rate Calculation - JITPLDocument8 pagesHeat Rate Calculation - JITPLbnswain1No ratings yet
- Heat & Mass BalanceDocument2 pagesHeat & Mass Balancesneha_21100% (1)
- Coal Drying (Dry Basis)Document9 pagesCoal Drying (Dry Basis)billyNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance Programme0Document18 pagesHeat Balance Programme0Mohamed SelimNo ratings yet
- Boiler CalculationDocument4 pagesBoiler Calculationmohsin husen BargirNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDocument50 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDilip MishraNo ratings yet
- Chimney Height CalculationDocument3 pagesChimney Height CalculationDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine EfficiencyDocument71 pagesSteam Turbine EfficiencyAnonymous LjE1R12CasNo ratings yet
- Application Procedure - Phoscast 60Document2 pagesApplication Procedure - Phoscast 60RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cost Per Hour CalculationDocument1 pageBoiler Cost Per Hour Calculationsreelu100% (2)
- Desalination Plant Feed Water ArrangementsDocument11 pagesDesalination Plant Feed Water ArrangementsSooraj Surendran SugathaNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Chemical Analysis of CementDocument1 pageFormulas of Chemical Analysis of CementFahadullah Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Chimney Draft CalculationsDocument4 pagesChimney Draft CalculationsTushar KhannaNo ratings yet
- Pump Calculation Data Sheet: Wilmar Id Engineering Amd Construction Management Flourmills Greenfield PelintungDocument11 pagesPump Calculation Data Sheet: Wilmar Id Engineering Amd Construction Management Flourmills Greenfield PelintungcitramuaraNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsDocument7 pagesHeat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsmanojNo ratings yet
- Air Receivers Volume CalculationDocument19 pagesAir Receivers Volume CalculationKenny Ruiz100% (4)
- MMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - ProblemDocument13 pagesMMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - Problemyasin kocaboğaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanic and Turbines IDocument45 pagesFluid Mechanic and Turbines IAbdulrazzak AmanNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal CompressorsDocument40 pagesReciprocal CompressorsSathish KasilingamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Part 8Document9 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics Part 8Amanullah RafiNo ratings yet
- SketchsDocument1 pageSketchsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Successful Solution: To The Challenge ofDocument2 pagesSuccessful Solution: To The Challenge ofKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Solar CellsDocument8 pagesElectrical Properties of Solar CellsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC417Document4 pagesMba ZC417Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Book-I Chapter 1: Input DataDocument3 pagesBook-I Chapter 1: Input DataKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Fly AcDocument7 pagesFly AcKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Test Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaDocument6 pagesTest Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Partial Report - RawanDocument23 pagesPartial Report - RawanKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- VB 29 - 10Document5 pagesVB 29 - 10Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Annexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeDocument3 pagesAnnexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- WE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelDocument1 pageWE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- List of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameDocument2 pagesList of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- cdk1 Coal B-EDocument1 pagecdk1 Coal B-EKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Equipment Dossier R0Document50 pagesEquipment Dossier R0Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 139 FPDocument7 pages139 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 142 EaDocument3 pages142 EaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 148 FPDocument2 pages148 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialDocument4 pagesIIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)Document43 pagesChapter - 03 - PPT (Supplementary To ISpace)kjw 2No ratings yet
- McDonald & Dominos Entry in IndiaDocument24 pagesMcDonald & Dominos Entry in IndiaRaj Paroha83% (6)
- Complexometric Titrations by Gunja ChaturvediDocument16 pagesComplexometric Titrations by Gunja ChaturvediGunja Chaturvedi100% (3)
- Eppendorf Centrifuge 5415D and 5415R DatasheetDocument4 pagesEppendorf Centrifuge 5415D and 5415R DatasheetGeorgyNo ratings yet
- Ashridge Business School, UK: Scientist-PractitionerDocument1 pageAshridge Business School, UK: Scientist-PractitionerSharma ShikhaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Document Star Health Insurance Hospital MOUDocument9 pagesHospital Document Star Health Insurance Hospital MOUSanket Sahare100% (1)
- Enviroline 199+ds+eng PDFDocument4 pagesEnviroline 199+ds+eng PDFMohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- Warrenton Horse Show Program 2016Document36 pagesWarrenton Horse Show Program 2016Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz 300sd 1993 Operators ManualDocument10 pagesMercedes Benz 300sd 1993 Operators Manualvirginia100% (55)
- PriceSmart FoodsDocument12 pagesPriceSmart FoodsPraneet BatwarNo ratings yet
- Sample Application For NCH Nomination On Province Reserved Seats 2017Document2 pagesSample Application For NCH Nomination On Province Reserved Seats 2017Tabib Afzaal Ahmad Virk100% (1)
- Vartes Io-A2 Final VersionDocument94 pagesVartes Io-A2 Final VersionAlex CastelNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Purpose of The Unit: 8 Design of Distillation ColumnDocument16 pages8.1 Purpose of The Unit: 8 Design of Distillation Columnsami ullahNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Portfolio: Jhon Carlo Cera CatindoyDocument22 pagesWork Immersion Portfolio: Jhon Carlo Cera CatindoyJoel DufaleNo ratings yet
- English File Intermediate Third Edition-Pages-5-8Document4 pagesEnglish File Intermediate Third Edition-Pages-5-8akbal13No ratings yet
- Fall Arrest SystemDocument16 pagesFall Arrest SystemDragos VerdesNo ratings yet
- Hop Swimming Pool & Fire Water Tank Method of StatementDocument5 pagesHop Swimming Pool & Fire Water Tank Method of StatementRichard DumaogNo ratings yet
- CBT 210Document1 pageCBT 210Carlos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Perspective: The Integrative Human Microbiome ProjectDocument8 pagesPerspective: The Integrative Human Microbiome Projectdainsyah dainNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa - MechanismsDocument22 pagesAntibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa - MechanismsValentina RondonNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Control Circuits MC34063A: DescriptionDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter Control Circuits MC34063A: Descriptionfarhood ranjbarkhanghahNo ratings yet
- Kingspan Bluemaster PRO PDFDocument2 pagesKingspan Bluemaster PRO PDFDiego Felipe Gavilán RetamalesNo ratings yet
- Solubility Equilibria Tutorial Answers OHTDocument4 pagesSolubility Equilibria Tutorial Answers OHTDomNo ratings yet
- CA1 Online Class 2Document13 pagesCA1 Online Class 2kemerutNo ratings yet
- LP No 11 BMPDocument11 pagesLP No 11 BMPVikasNo ratings yet
- 718Document19 pages718shankerahulNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drainage SystemDocument7 pagesArchitectural Drainage SystemReuben ValencinasNo ratings yet
- HIRA of Batching Plant Erection.Document3 pagesHIRA of Batching Plant Erection.Gyanendra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- XC975 EV 英语译文Document2 pagesXC975 EV 英语译文abangNo ratings yet